策略模式(Strategy)
基本介绍
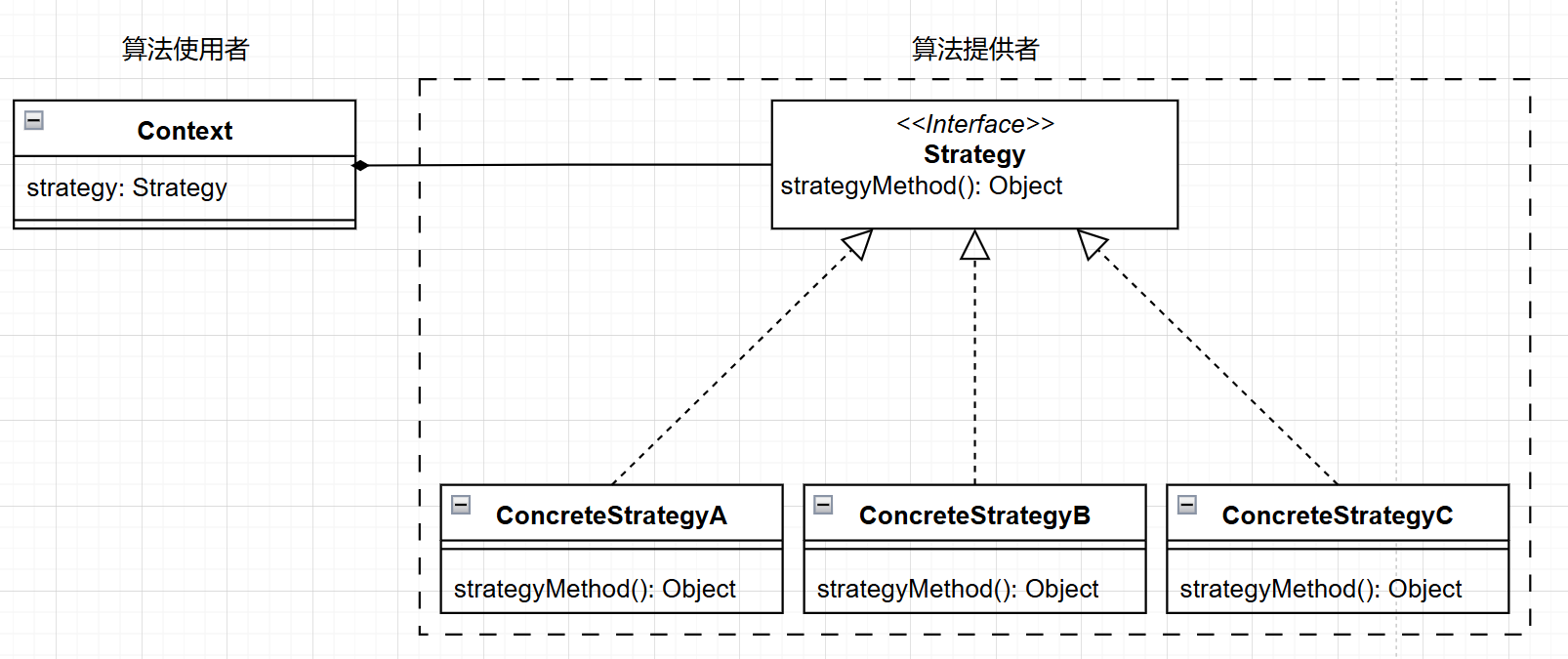
策略模式(Strategy Pattern)是一种行为设计模式,它定义了一系列算法,将每个算法封装起来,并使它们可以互换。策略模式让算法的变化独立于使用算法的客户。它的核心思想是将算法和使用算法的上下文****分离,从而提高代码的灵活性和可维护性。
关键组成部分:
- 策略接口(Strategy):
- 这是一个公共接口,定义了所有支持的算法或策略的方法。
- 具体策略(Concrete Strategy):
- 实现策略接口的具体算法或行为。每个具体策略类实现了接口中定义的方法。
- 上下文(Context):
- 持有对策略接口的引用,客户端通过上下文调用策略的方法。上下文可以在运行时选择具体的策略。
使用场景:
策略模式适用于以下场景:
- 当你有多个算法可以选择,且这些算法可以在运行时互换。
- 当你希望将算法的实现细节封装起来,并使其独立于使用算法的客户。
- 当你希望避免使用大量的条件语句(如
if-else或switch语句)来选择算法。
优点:
- 开放-关闭原则:可以通过添加新的策略类来扩展算法,而无需修改现有代码。
- 提高可读性:将不同的算法封装到独立的策略类中,减少了条件语句的复杂性。
- 灵活性:可以在运行时选择或切换策略。
缺点
- 增加类的数量:每个策略都需要一个具体的类,可能导致类的数量增加。
- 客户端需要了解策略:客户端需要了解所有的策略类,以便选择合适的策略。
策略模式在许多场景中都非常有用,尤其是在需要根据不同条件选择算法时,可以显著提高代码的可维护性和灵活性。
实例演示
:::tips
假设小明去买了一个冰淇凌,现在他需要付款,请使用策略模式设计一个支付的功能,使得小明能够在不同的支付方式间来回的切换
tips:支付方式(支付宝、微信支付、PayPal、现金支付等等)
:::
- 首先设计一种支付策略接口
PaymentStrategy
package com.strategy.paymentStrategy;
/**
* @program: JavaDesignPatterns
* @description: 支付策略
* @author: LyttonYang
* @create: 2024-10-30 15:00
*/
public interface PaymentStrategy {
void pay(double amount);
}
- 设计具体的支付策略
ConcreteStrategy
/**
* @program: JavaDesignPatterns
* @description: 支付宝支付
* @author: LyttonYang
* @create: 2024-10-30 15:02
*/
public class AliPayment implements PaymentStrategy{
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("使用支付宝支付"+amount+"元");
}
}
/**
* @program: JavaDesignPatterns
* @description: PayPal支付
* @author: LyttonYang
* @create: 2024-10-30 15:02
*/
public class PayPalPayment implements PaymentStrategy{
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("使用PayPal支付" + amount + "元");
}
}
/**
* @program: JavaDesignPatterns
* @description: 微信支付
* @author: LyttonYang
* @create: 2024-10-30 15:01
*/
public class WeChatPayment implements PaymentStrategy{
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("使用微信支付支付了"+amount+"元");
}
}
- 让支付者持有这个 支付策略(接口)
package com.strategy.paymentStrategy;
/**
* @program: JavaDesignPatterns
* @description: 支付者
* @author: LyttonYang
* @create: 2024-10-30 15:04
*/
public class PaymentContext {
private PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy;
public PaymentContext(PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy) {
this.paymentStrategy = paymentStrategy;
}
public void setPaymentStrategy(PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy) {
this.paymentStrategy = paymentStrategy;
}
public void checkout(double money){
if (paymentStrategy != null) {
paymentStrategy.pay(money);
} else {
System.out.println("请选择支付方式");
}
}
}
- 在使用时可以灵活选择不同的支付策略进行支付
package com.strategy.paymentStrategy;
/**
* @program: JavaDesignPatterns
* @description: 算法使用者
* @author: LyttonYang
* @create: 2024-10-30 15:03
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用支付宝支付
PaymentContext paymentContext = new PaymentContext(new AliPayment());
paymentContext.checkout(1000);
// 使用微信支付
paymentContext.setPaymentStrategy(new WeChatPayment());
paymentContext.checkout(1000);
// 使用银行卡支付
paymentContext.setPaymentStrategy(new PayPalPayment());
paymentContext.checkout(1000);
}
}
项目实战分析
JDK 源码分析-Array 中的策略模式
package com.strategy.ArrayStrategy;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* @program: JavaDesignPatterns
* @description:
* @author: LyttonYang
* @create: 2024-10-30 15:27
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] array = {11, 22, 13, 44, 25, 96, 57, 28, 19, 10};
//比较策略接口
Comparator<Integer> comparator1 = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
//具体的比较策略(升序)
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;
}
};
//比较策略接口
Comparator<Integer> comparator2 = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
//具体的比较策略(降序)
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
};
//使用比较策略接口(升序)
Arrays.sort(array, comparator1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
//使用比较策略接口(降序)
Arrays.sort(array, comparator2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
在 Arrays.sort() 方法中就用到了策略模式
:::info
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c)
:::
其中 Comparator<? super T> c就是一个 比较策略接口
具体使用哪种比较策略完全由用户自己决定, 在上面的代码中我们使用了两种具体的比较策略, 分别是升序和降序的策略:
- 具体策略 1:
//比较策略接口
Comparator<Integer> comparator1 = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
//具体的比较策略(升序)
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;
}
};
- 具体策略 2:
//比较策略接口
Comparator<Integer> comparator2 = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
//具体的比较策略(降序)
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
};
还可以自定义其他各种具体的比较策略…

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








