基本介绍
- prctl()原型为int prctl (int __option, …);用于控制主进程或者子进程的属性;
- 本文主要介绍使用PR_SET_NAME 这个flag设定线程的名字,这个在平常调试中很有帮助,比如想知道哪个线程的CPU占用高;
- 需要包含的头文件为 sys/prctl.h;
- 用法:prctl(PR_SET_NAME , (char*)name);
- 其中设定的名字字符串长度不能超过15bytes;
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/prctl.h>
#define DBG_PRINT(fmt, args...) {printf("%s %d ", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);printf(fmt,##args);}
/**
* [msSleep 用nanosleep实现的毫秒级线程休眠]
* @param msTime [description]
*/
void msSleep(unsigned msTime)
{
struct timespec reqTime;
struct timespec remTime;
int ret = 0;
if(msTime == 0)
{
DBG_PRINT("invalid argument!\n");
return;
}
else if(msTime>=1000)
{
reqTime.tv_sec = msTime/1000;
reqTime.tv_nsec = (unsigned long)((msTime%1000)*1000000UL);
}
else
{
reqTime.tv_sec = 0;
reqTime.tv_nsec = (unsigned long)(msTime*1000000UL);
}
do
{
/**
* 由于nanosleep在休眠线程过程中,线程可能会被中断唤醒,并且唤醒后,剩余的休眠时间会保存在
* remTime中,所以使用remTime中的时间继续休眠线程;
*/
ret = nanosleep(&reqTime, &remTime);
if(-1 == ret)
{
switch(errno)
{
case EINTR:
reqTime.tv_sec = remTime.tv_sec;
reqTime.tv_nsec = remTime.tv_nsec;
continue;
default:
break;
}
}
break;
}while(1);
}
void *testThead1(void* arg)
{
//设定线程名为zoobiTask1
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, "zoobiTask1");
while(1)
{
DBG_PRINT("Start\n");
msSleep(1);
DBG_PRINT("End\n");
}
}
void *testThead2(void* arg)
{
//设定线程名为zoobiTask2
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, "zoobiTask2");
while(1)
{
DBG_PRINT("Start\n");
msSleep(1);
DBG_PRINT("End\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
//设定主线程名为zoobiMainTask
prctl(PR_SET_NAME, "zoobiMainTask");
pthread_t thread1ID, thread2ID;
int ret = 0;
ret = pthread_create(&thread1ID, NULL, testThead1, NULL);
if(ret != 0)
{
DBG_PRINT("pthread_create failed! errno:%s\n", strerror(ret));
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(thread1ID);
ret = pthread_create(&thread2ID, NULL, testThead2, NULL);
if(ret != 0)
{
DBG_PRINT("pthread_create failed! errno:%s\n", strerror(ret));
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(thread2ID);
while(1)
{
msSleep(1);
}
return 0;
}编译运行上面的测试程序:
[zoobi@localhost linux_env]$ g++ thread_stack.cpp -o thread_stack -lpthread
[zoobi@localhost linux_env]$ ./thread_stack然后在另一个终端上输入top命令查看进程,并且敲 “shift”+“h”,从进程显示切换到线程显示状态,可以看见下图类似结果:
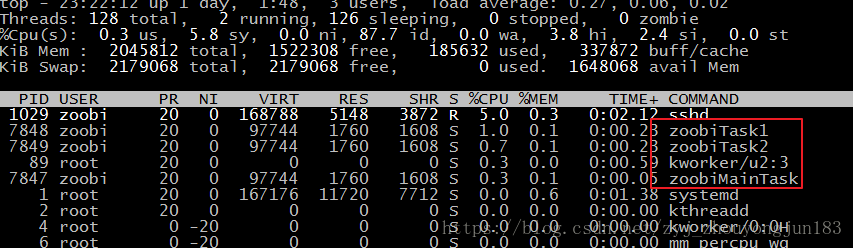
说明主线程和创建的两个子线程的线程名都已经被更改为预期名字;





 这篇博客介绍了如何利用prctl()函数的PR_SET_NAME标志来为线程设置名称,便于调试时识别高CPU占用的线程。内容包括prctl()函数的基本用法和示例,展示了如何在C程序中应用该函数,并通过top命令观察线程名的效果。
这篇博客介绍了如何利用prctl()函数的PR_SET_NAME标志来为线程设置名称,便于调试时识别高CPU占用的线程。内容包括prctl()函数的基本用法和示例,展示了如何在C程序中应用该函数,并通过top命令观察线程名的效果。
















 747
747

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








