LeetCode - 684. Redundant Connection (DFS | 并查集)
题目链接
题目
DFS
思路:
- 每次添加一条边,然后判断加上这条边之后会不会构成环;
- 判断一个图有没有环用
dfs,这里需要维护一个pre变量,表示上次访问的节点,然后使用vis数组标记以及访问的节点,如果再次访问到,就表明有环了;
class Solution {
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
if (edges == null || edges.length == 0)
return new int[2];
int n = edges.length;
ArrayList<Integer> G[] = new ArrayList[n+1]; //二维数组中的整数在1到N之间,其中N是输入数组的大小。
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
G[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
int from = edges[i][0];
int to = edges[i][1];
G[from].add(to);
G[to].add(from);
boolean[] vis = new boolean[n+1];
if(!dfs(from, -1, vis, G))// 从当前节点出发查找
return edges[i];
}
return new int[2];
}
// 判断一个图有没有环(维护一个pre变量)
private boolean dfs(int v, int pre, boolean[] vis, ArrayList<Integer>G[]){
if(vis[v])
return false;
vis[v] = true;
for(int next : G[v]){
if(next != pre)
if(!dfs(next, v, vis, G))
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
并查集
并查集模板题。
- 直接判断当前的两个顶点有没有在同一个集合中,如果是,则一定会构成环;
- 否则合并这两个顶点即可;
class Solution {
private class UnionSet{
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank;
public UnionSet(int n){
parent = new int[n+1];
rank = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
public int findRoot(int p){
while(parent[p] != p){
p = parent[parent[p]];
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
public void union(int a, int b){
int aRoot = findRoot(a);
int bRoot = findRoot(b);
if(aRoot == bRoot)
return;
if(rank[aRoot] < rank[bRoot]){
parent[aRoot] = bRoot;
}else if(rank[aRoot] > rank[bRoot]){
parent[bRoot] = aRoot;
}else {
parent[aRoot] = bRoot;
rank[bRoot]++;
}
}
}
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
if (edges == null || edges.length == 0)
return new int[2];
int n = edges.length;
UnionSet uSet = new UnionSet(n);
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
int from = edges[i][0];
int to = edges[i][1];
if(uSet.findRoot(from) == uSet.findRoot(to))
return edges[i];
else
uSet.union(from, to);
}
return new int[2];
}
}
LeetCode - 685. Redundant Connection II
题目链接
题目

解析
这个和上面那个不同的是这里是有向图。
由于必须要求父节点个数为1(除根节点),那么添加额外边后不合法只有两种情况 :
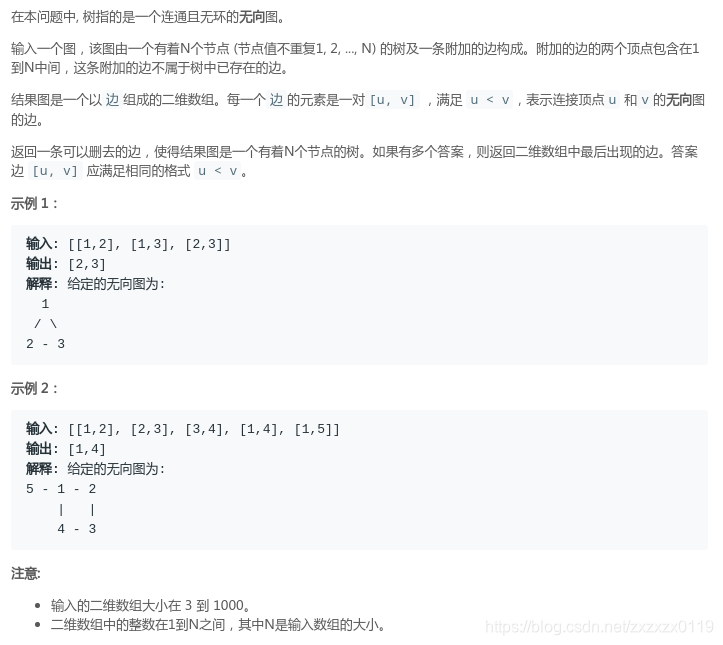
case 1: 没有节点存在两个父节点,但是存在环; (和LeetCode - 684. Redundant Connection一样)
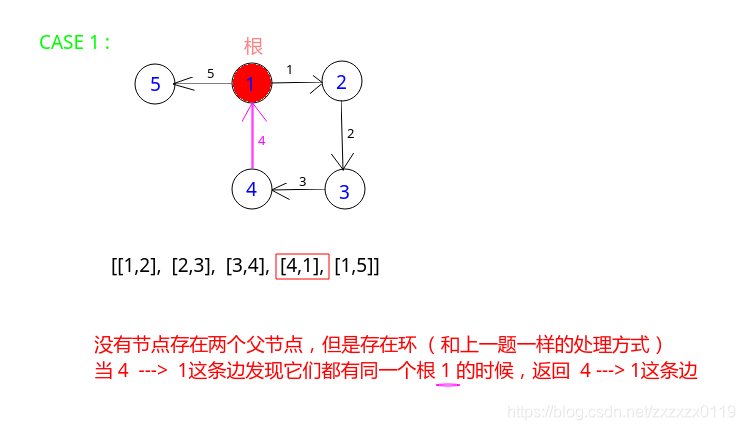
case 2: 又可以分为两种情况:case 2.1: 一个节点存在两个父节点但是不存在环;
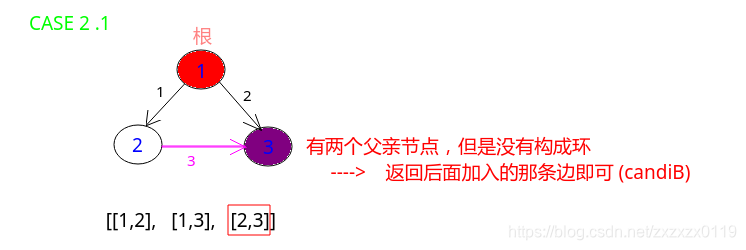
case 2.2: 一个节点存在两个父节点且存在环;

代码实现:
-
一开始先处理有两个父亲的节点,分别将有两个父亲的节点相连的边记为
candiA(更早的)、candiB(更晚的); -
然后有一个很重要的处理,将更晚的的父亲对应的那条边(
candiB)标记为-1,这条边在后续并查集中不考虑;(如果后面并查集没有找到环,就会返回candiB); -
并查集过程: ①若存在回路且没有节点有两个父节点,那么返回最后遇到的一条边即可(
case1);②若存在回路且有节点是有2个parent,则返回candiA(更早标记的那条在环中的边); -
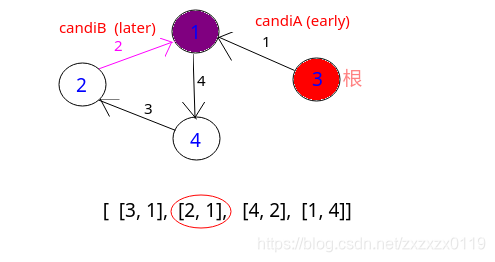
注意最后返回的
candiB有两种情况: ①case 2.1;②case 2.2的变式,看下面,如果给定数组的顺序改变如下:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank;
public int findRoot(int p){
while(parent[p] != p){
p = parent[parent[p]];
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
public void union(int a, int b){
int aRoot = findRoot(a);
int bRoot = findRoot(b);
if(aRoot == bRoot)
return;
if(rank[aRoot] < rank[bRoot]){
parent[aRoot] = bRoot;
}else if(rank[aRoot] > rank[bRoot]){
parent[bRoot] = aRoot;
}else {
parent[aRoot] = bRoot;
rank[bRoot]++;
}
}
public int[] findRedundantDirectedConnection(int[][] edges) {
if(edges == null || edges.length == 0 || edges[0].length == 0)
return new int[2];
int n = edges.length;
parent = new int[n + 1];
rank = new int[n + 1];
int[] candiA = new int[]{-1, -1};
int[] candiB = new int[]{-1, -1};
// 第一遍循环,若节点存在有两个父节点,那么将这两条边分别作为候选A, B
for(int[] edge : edges){
int from = edge[0];
int to = edge[1];
if(parent[to] == 0){ // now, 'to' don't have parent
parent[to] = from; // now, 'to' only have one parent, is 'from'
}else { // 'to' already have a parent
candiA[0] = parent[to]; // pre parent
candiA[1] = to;
candiB[0] = from;
candiB[1] = to;
edge[0] = edge[1] = -1; // mark this, unionSet will don't consider this
}
}
// init unionSet
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1; // height
}
for(int[] edge : edges){
int from = edge[0];
int to = edge[1];
if(from == -1 || to == -1) // the later(second) edge, don't consider
continue;
if(findRoot(from) == findRoot(to)){ // 添加这条边之后存在回路
if(candiA[0] == -1 && candiA[1] == -1) // no 2 parent
return edge;
else // have 2 parent, can't return edge, return previous candinate
return candiA;
}else
union(from, to);
}
return candiB; // case2.1 && case2.2 egde[0] = edge[1] = -1
}
public static void main(String[] args){
PrintStream out = System.out;
int[][] edges = {
{1, 2},
{2, 3},
{3, 4},
{4, 1},
{1, 5}
};
out.println(Arrays.toString(new Solution().
findRedundantDirectedConnection(edges))
);
}
}






 本文详细介绍了如何使用深度优先搜索(DFS)和并查集解决LeetCode上的684和685题,即检测和处理冗余连接。对于684题,通过DFS检测环;对于685题,处理有向图中的冗余连接,包括环和双父节点的情况。并提供了详细的代码实现。
本文详细介绍了如何使用深度优先搜索(DFS)和并查集解决LeetCode上的684和685题,即检测和处理冗余连接。对于684题,通过DFS检测环;对于685题,处理有向图中的冗余连接,包括环和双父节点的情况。并提供了详细的代码实现。
















 440
440

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








