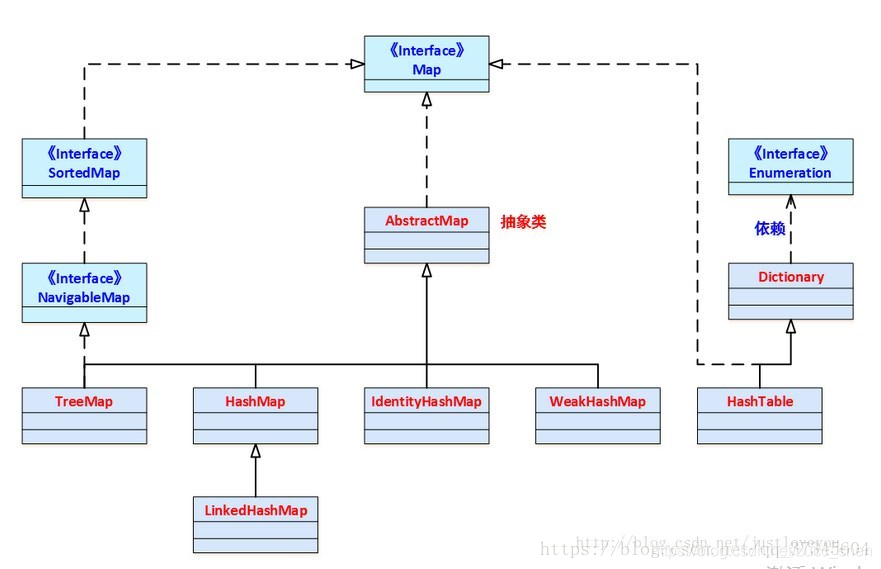
Map 映射
Map是一个以键值对存储的接口
图来自作者 Snow、杨
Map特点
- 数据结构里面包含键值对
- 一个键对应一个值
- 键是唯一的,一个键对应的值也是唯一的
java中的Map
- Hashtable (同步,慢,数据量小)
- HashMap(不支持同步,快,数据量大)
- Properties(同步,文件形式,数据量小)
Hashtable
- K-V 对,K和V都不允许为null。
- 同步,多线程安全
- 无序的
- 适合小数据量
主要方法
-
void clear()
将此哈希表清空,使其不包含任何键。 -
Object clone()
创建此哈希表的浅表副本。 -
boolean contains(Object value)
测试此映射表中是否存在与指定值关联的键。 -
boolean containsKey(Object key)
测试指定对象是否为此哈希表中的键。 -
boolean containsValue(Object value)
如果此 Hashtable 将一个或多个键映射到此值,则返回 true。 -
Enumeration elements()
返回此哈希表中的值的枚举。 -
boolean equals(Object o)
按照 Map 接口的定义,比较指定 Object 与此 Map 是否相等。 -
V get(Object key)
返回指定键所映射到的值,如果此映射不包含此键的映射,则返回 null. 更确切地讲,如果此映射包含满足 (key.equals(k)) 的从键 k 到值 v 的映射,则此方法返回 v;否则,返回 null。 -
int hashCode()
按照 Map 接口的定义,返回此 Map 的哈希码值。 -
boolean isEmpty()
测试此哈希表是否没有键映射到值。 -
Enumeration keys()
返回此哈希表中的键的枚举。 -
Set keySet()
返回此映射中包含的键的 Set 视图。 -
V put(K key, V value)
将指定 key 映射到此哈希表中的指定 value。 -
void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> t)
将指定映射的所有映射关系复制到此哈希表中,这些映射关系将替换此哈希表拥有的、针对当前指定映射中所有键的所有映射关系。 -
protected void rehash()
增加此哈希表的容量并在内部对其进行重组,以便更有效地容纳和访问其元素。 -
V remove(Object key)
从哈希表中移除该键及其相应的值。 -
int size()
返回此哈希表中的键的数量。 -
String toString()
返回此 Hashtable 对象的字符串表示形式,其形式为 ASCII 字符 ", " (逗号加空格)分隔开的、括在括号中的一组条目。 -
Collection values()
返回此映射中包含的键的 Collection 视图。
public class HashtableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable<Integer,String> ht =new Hashtable<Integer,String>();
//ht.put(1, null); 编译不报错 运行报错
//ht.put(null,1); 编译报错
ht.put(1000, "aaa");
ht.put(2, "bbb");
ht.put(30000, "ccc");
System.out.println(ht.contains("aaa")); //与containsValue 一样
System.out.println(ht.containsValue("aaa"));
System.out.println(ht.containsKey(30000));
System.out.println(ht.get(30000));
ht.put(30000, "ddd"); //更新覆盖ccc
System.out.println(ht.get(30000));
ht.remove(2);
System.out.println("size: " + ht.size());
ht.clear();
System.out.println("size: " + ht.size());
Hashtable<Integer,String> ht2 =new Hashtable<Integer,String>();
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++)
{
ht2.put(i, "aaa");
}
traverseByEntry(ht2);
traverseByKeySet(ht2);
traverseByKeyEnumeration(ht2);
}
public static void traverseByEntry(Hashtable<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============Entry迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = ht.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeySet(Hashtable<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============KeySet迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = ht.keySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeyEnumeration(Hashtable<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============KeyEnumeration迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Enumeration<Integer> keys = ht.keys();
while(keys.hasMoreElements()) {
key = keys.nextElement();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
}
结果
true
true
true
ccc
ddd
size: 2
size: 0
============Entry迭代器遍历==============
9916800纳秒
============KeySet迭代器遍历==============
8998100纳秒
============KeyEnumeration迭代器遍历==============
7309100纳秒
HashMap
- K-V对,K和V都允许为null。
- 不同步,多线程不安全
- 无序的
- key是唯一的,判断key是否重复需要重写hashCode方法和equals方法 和set一样
主要方法
-
void clear()
从此映射中移除所有映射关系。 -
boolean containsKey(Object key)
如果此映射包含对于指定键的映射关系,则返回 true。 -
boolean containsValue(Object value)
如果此映射将一个或多个键映射到指定值,则返回 true。 -
V get(Object key)
返回指定键所映射的值;如果对于该键来说,此映射不包含任何映射关系,则返回 null。 -
boolean isEmpty()
如果此映射不包含键-值映射关系,则返回 true。 -
V put(K key, V value)
在此映射中关联指定值与指定键。 -
V remove(Object key)
从此映射中移除指定键的映射关系(如果存在)。 -
int size()
返回此映射中的键-值映射关系数。 -
Collection values()
返回此映射所包含的值的 Collection 视图。
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer,String> hm =new HashMap<Integer,String>();
hm.put(1, null);
hm.put(null, "abc");
hm.put(1000, "aaa");
hm.put(2, "bbb");
hm.put(30000, "ccc");
System.out.println(hm.containsValue("aaa"));
System.out.println(hm.containsKey(30000));
System.out.println(hm.get(30000));
hm.put(30000, "ddd"); //更新覆盖ccc
System.out.println(hm.get(30000));
hm.remove(2);
System.out.println("size: " + hm.size());
hm.clear();
System.out.println("size: " + hm.size());
HashMap<Integer,String> hm2 =new HashMap<Integer,String>();
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++)
{
hm2.put(i, "aaa");
}
traverseByEntry(hm2);
traverseByKeySet(hm2);
}
public static void traverseByEntry(HashMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============Entry迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = ht.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeySet(HashMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============KeySet迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = ht.keySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
}
结果
true
true
ccc
ddd
size: 4
size: 0
============Entry迭代器遍历==============
15231300纳秒
============KeySet迭代器遍历==============
10662800纳秒
LinkedHashMap
- Map 接口的哈希表和链接列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序。此实现与 HashMap 的不同之处在于,后者维护着一个运行于所有条目的双重链接列表。此链接列表定义了迭代顺序,该迭代顺序通常就是将键插入到映射中的顺序(插入顺序)。注意,如果在映射中重新插入 键,则插入顺序不受影响。(如果在调用 m.put(k, v) 前 m.containsKey(k) 返回了 true,则调用时会将键 k 重新插入到映射 m 中。)
- 基于双向链表的维持插入顺序的HashMap
- 输出key的顺序和插入key的顺序一样
主要方法
- void clear()
从该映射中移除所有映射关系。 - boolean containsValue(Object value)
如果此映射将一个或多个键映射到指定值,则返回 true。 - V get(Object key)
返回此映射到指定键的值。 - protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest)
如果此映射移除其最旧的条目,则返回 true。
public class LinkedHashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> hm =new LinkedHashMap<Integer,String>();
hm.put(1, null);
hm.put(null, "abc");
hm.put(1000, "aaa");
hm.put(2, "bbb");
hm.put(30000, "ccc");
System.out.println(hm.containsValue("aaa"));
System.out.println(hm.containsKey(30000));
System.out.println(hm.get(30000));
hm.put(30000, "ddd"); //更新覆盖ccc
System.out.println(hm.get(30000));
hm.remove(2);
System.out.println("size: " + hm.size());
//hm.clear();
//System.out.println("size: " + hm.size());
System.out.println("遍历开始==================");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = hm.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
System.out.println("遍历结束==================");
LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> hm2 =new LinkedHashMap<Integer,String>();
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++)
{
hm2.put(i, "aaa");
}
traverseByEntry(hm2);
traverseByKeySet(hm2);
}
public static void traverseByEntry(LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============Entry迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = ht.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeySet(LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============KeySet迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = ht.keySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
}
结果
true
true
ccc
ddd
size: 4
遍历开始==================
Key:1, Value:null
Key:null, Value:abc
Key:1000, Value:aaa
Key:30000, Value:ddd
遍历结束==================
============Entry迭代器遍历==============
6996501纳秒
============KeySet迭代器遍历==============
8241700纳秒
TreeMap
- 基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)的 NavigableMap 实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
- 无序,不允许重复(无序指元素顺序与添加顺序不一致)
- TreeMap集合默认会对键进行排序,所以键必须实现自然排序和定制排序中的一种
- 底层使用的数据结构是二叉树
- key不能为null
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer,String> hm =new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
hm.put(1, null);
//hm.put(null, "abc"); 编译没错,运行报空指针异常
hm.put(1000, "aaa");
hm.put(2, "bbb");
hm.put(30000, "ccc");
System.out.println(hm.containsValue("aaa"));
System.out.println(hm.containsKey(30000));
System.out.println(hm.get(30000));
hm.put(30000, "ddd"); //更新覆盖ccc
System.out.println(hm.get(30000));
//hm.remove(2);
System.out.println("size: " + hm.size());
//hm.clear();
//System.out.println("size: " + hm.size());
System.out.println("遍历开始==================");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = hm.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
System.out.println("遍历结束==================");
TreeMap<Integer,String> hm2 =new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++)
{
hm2.put(i, "aaa");
}
traverseByEntry(hm2);
traverseByKeySet(hm2);
}
public static void traverseByEntry(TreeMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============Entry迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iter = ht.entrySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = iter.next();
// 获取key
key = entry.getKey();
// 获取value
value = entry.getValue();
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
public static void traverseByKeySet(TreeMap<Integer,String> ht)
{
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("============KeySet迭代器遍历==============");
Integer key;
String value;
Iterator<Integer> iter = ht.keySet().iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
key = iter.next();
// 获取value
value = ht.get(key);
//System.out.println("Key:" + key + ", Value:" + value);
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println(duration + "纳秒");
}
}
结果
true
true
ccc
ddd
size: 4
遍历开始==================
Key:1, Value:null
Key:2, Value:bbb
Key:1000, Value:aaa
Key:30000, Value:ddd
遍历结束==================
============Entry迭代器遍历==============
8653800纳秒
============KeySet迭代器遍历==============
21590599纳秒
Properties
- 继承与Hashtable
- 可以将K-V对保持在文件中
- 适用于数据量小的配置文件
- 从文件加载load方法,写入到文件中store方法
- 获取属性getProperty方法,设置属性setProperty
//关于Properties类常用的操作
public class PropertiesTest {
//根据Key读取Value
public static String GetValueByKey(String filePath, String key) {
Properties pps = new Properties();
try {
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream (new FileInputStream(filePath));
pps.load(in); //所有的K-V对都加载了
String value = pps.getProperty(key);
//System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
return value;
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
//读取Properties的全部信息
public static void GetAllProperties(String filePath) throws IOException {
Properties pps = new Properties();
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
pps.load(in); //所有的K-V对都加载了
Enumeration en = pps.propertyNames(); //得到配置文件的名字
while(en.hasMoreElements()) {
String strKey = (String) en.nextElement();
String strValue = pps.getProperty(strKey);
//System.out.println(strKey + "=" + strValue);
}
}
//写入Properties信息
public static void WriteProperties (String filePath, String pKey, String pValue) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if(!file.exists())
{
file.createNewFile();
}
Properties pps = new Properties();
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从输入流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)
pps.load(in);
//调用 Hashtable 的方法 put。使用 getProperty 方法提供并行性。
//强制要求为属性的键和值使用字符串。返回值是 Hashtable 调用 put 的结果。
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
pps.setProperty(pKey, pValue);
//以适合使用 load 方法加载到 Properties 表中的格式,
//将此 Properties 表中的属性列表(键和元素对)写入输出流
pps.store(out, "Update " + pKey + " name");
out.close();
}
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException{
System.out.println("写入Test.properties================");
WriteProperties("Test.properties","name", "12345");
System.out.println("加载Test.properties================");
GetAllProperties("Test.properties");
System.out.println("从Test.properties加载================");
String value = GetValueByKey("Test.properties", "name");
System.out.println("name is " + value);
}
}
结果
写入Test.properties================
加载Test.properties================
从Test.properties加载================
name is 12345







 本文介绍了Java中的Map接口及其常见实现类:Hashtable、HashMap、LinkedHashMap和TreeMap。详细讲解了各实现类的特点、适用场景及主要方法,包括同步性、数据结构和排序特性等。
本文介绍了Java中的Map接口及其常见实现类:Hashtable、HashMap、LinkedHashMap和TreeMap。详细讲解了各实现类的特点、适用场景及主要方法,包括同步性、数据结构和排序特性等。
















 1867
1867

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








