Linux中断子系统2(基于Linux6.6)---IRQ Domain介绍
一、概述
Linux kernel中,使用下面两个ID来标识一个来自外设的中断:
1. IRQ number (中断请求号)
IRQ number(或简称 IRQ)是 Linux 内核和硬件之间的标识符,用于标识每个中断源。这个编号在操作系统的中断处理系统中起着关键作用,它是 Linux 内核用来管理和分配中断处理程序的基本单元。
- 作用:IRQ number 是由操作系统管理的,表示一个特定的中断来源。每个硬件中断(无论是外部设备生成的中断,还是内部事件)都会被分配一个唯一的 IRQ number。
- 分配方式:IRQ number 是由硬件平台和操作系统(如 Linux)共同决定的。在 x86 架构上,IRQ number 范围通常是 0 到 15(用于传统的 PIC 中断控制器),而在更现代的系统中(如 ARM 或基于 IOAPIC 的系统),IRQ number 的范围会更大。
在 Linux 中,IRQ number 通常由系统中的中断控制器(如 APIC、GIC、PIC 等)分配和管理。设备驱动程序根据这个 IRQ number 来注册和处理特定的中断。
2. HW interrupt ID (硬件中断标识符)
HW interrupt ID 是由硬件(或中断控制器)分配的中断标识符,通常由硬件本身生成并用来标识特定的中断源。它是硬件级别的标识符,用于区分不同的中断事件。
- 作用:HW interrupt ID 是与硬件平台和中断控制器相关的,表示硬件中断的源或类型。它通常在硬件设备或中断控制器内部使用,以识别触发中断的具体源。
- 实现方式:HW interrupt ID 由中断控制器提供,用于标识不同的硬件中断请求。例如,在 ARM 系统中,GIC(通用中断控制器)会为每个中断源分配一个硬件中断 ID。
3. IRQ number 和 HW interrupt ID 之间的关系
- IRQ number 是操作系统级别的标识符,它用于在内核中注册和处理中断。
- HW interrupt ID 是硬件级别的标识符,它用于硬件和中断控制器中标识中断源。
在 Linux 内核中,中断请求的处理是通过 IRQ number 来管理的,但 IRQ number 最终与 HW interrupt ID 相对应。内核通过 HW interrupt ID 来识别特定的硬件中断源,并为其分配一个 IRQ number 供内核处理。
例如,在 ARM 系统中,GIC 中断控制器会为每个硬件中断源分配一个 HW interrupt ID,Linux 内核会通过这个 ID 来识别和处理相应的中断。同时,内核会为每个中断请求分配一个 IRQ number,这个编号会用于内核中的中断处理机制。
这样,CPU和interrupt controller在标识中断上就有了一些不同的概念,但是,对于驱动工程师而言,和CPU视角是一样的,只希望得到一个IRQ number,而不关系具体是那个interrupt controller上的那个HW interrupt ID。这样一个好处是在中断相关的硬件发生变化的时候,驱动软件不需要修改。因此,linux kernel中的中断子系统需要提供一个将HW interrupt ID映射到IRQ number上来的机制。
二、接口
2.1、向系统注册irq domain
具体如何进行映射是interrupt controller自己的事情,不过,有软件架构思想的工程师更愿意对形形色色的interrupt controller进行抽象,对如何进行HW interrupt ID到IRQ number映射关系上进行进一步的抽象。因此,通用中断处理模块中有一个irq domain的子模块,该模块将这种映射关系分成了三类:
(1)线性映射。其实就是一个lookup table,HW interrupt ID作为index,通过查表可以获取对应的IRQ number。对于Linear map而言,interrupt controller对其HW interrupt ID进行编码的时候要满足一定的条件:hw ID不能过大,而且ID排列最好是紧密的。对于线性映射,其接口API如下:
include/linux/irqdomain.h
/**
* irq_domain_add_linear() - Allocate and register a linear revmap irq_domain.
* @of_node: pointer to interrupt controller's device tree node.
* @size: Number of interrupts in the domain.
* @ops: map/unmap domain callbacks
* @host_data: Controller private data pointer
*/
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_linear(struct device_node *of_node,
unsigned int size,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), size, size, 0, ops, host_data);
}
(2)Radix Tree map。建立一个Radix Tree来维护HW interrupt ID到IRQ number映射关系。HW interrupt ID作为lookup key,在Radix Tree检索到IRQ number。如果的确不能满足线性映射的条件,可以考虑Radix Tree map。实际上,内核中使用Radix Tree map的只有powerPC和MIPS的硬件平台。对于Radix Tree map,其接口API如下:include/linux/irqdomain.h
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_tree(struct device_node *of_node,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), 0, ~0, 0, ops, host_data);
}
(3)no map。有些中断控制器很强,可以通过寄存器配置HW interrupt ID而不是由物理连接决定的。例如PowerPC 系统使用的MPIC (Multi-Processor Interrupt Controller)。在这种情况下,不需要进行映射,直接把IRQ number写入HW interrupt ID配置寄存器就OK了,这时候,生成的HW interrupt ID就是IRQ number,也就不需要进行mapping了。对于这种类型的映射,其接口API如下:include/linux/irqdomain.h
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_nomap(struct device_node *of_node,
unsigned int max_irq,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), 0, max_irq, max_irq, ops, host_data);
}
这类接口的逻辑很简单,根据自己的映射类型,初始化struct irq_domain中的各个成员,调用__irq_domain_add将该irq domain挂入irq_domain_list的全局列表。
include/linux/irqdomain.h
static inline struct fwnode_handle *of_node_to_fwnode(struct device_node *node)
{
return node ? &node->fwnode : NULL;
}
这里的fwnode 值的是firmware node。kernel/irq/irqdomain.c
struct irq_domain *__irq_domain_add(struct fwnode_handle *fwnode, unsigned int size,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_max, int direct_max,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
struct irq_domain *domain;
domain = __irq_domain_create(fwnode, size, hwirq_max, direct_max,
ops, host_data); //调用
if (domain)
__irq_domain_publish(domain);
return domain;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__irq_domain_add);
static struct irq_domain *__irq_domain_create(struct fwnode_handle *fwnode,
unsigned int size,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_max,
int direct_max,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
struct irqchip_fwid *fwid;
struct irq_domain *domain;
static atomic_t unknown_domains;
if (WARN_ON((size && direct_max) ||
(!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_NOMAP) && direct_max) ||
(direct_max && (direct_max != hwirq_max))))
return NULL;
//申请一个irq_domain , size个中断个数(irq_domain 最后一个变量是可变参的数组)
domain = kzalloc_node(struct_size(domain, revmap, size),
GFP_KERNEL, of_node_to_nid(to_of_node(fwnode)));
if (!domain)
return NULL;
if (is_fwnode_irqchip(fwnode)) {
fwid = container_of(fwnode, struct irqchip_fwid, fwnode);
switch (fwid->type) {
case IRQCHIP_FWNODE_NAMED:
case IRQCHIP_FWNODE_NAMED_ID:
domain->fwnode = fwnode;
domain->name = kstrdup(fwid->name, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!domain->name) {
kfree(domain);
return NULL;
}
domain->flags |= IRQ_DOMAIN_NAME_ALLOCATED;
break;
default:
domain->fwnode = fwnode;
domain->name = fwid->name;
break;
}
} else if (is_of_node(fwnode) || is_acpi_device_node(fwnode) ||
is_software_node(fwnode)) {
char *name;
/*
* fwnode paths contain '/', which debugfs is legitimately
* unhappy about. Replace them with ':', which does
* the trick and is not as offensive as '\'...
*/
/* 把节点中的 / 替换为 : */
name = kasprintf(GFP_KERNEL, "%pfw", fwnode);
if (!name) {
kfree(domain);
return NULL;
}
domain->name = strreplace(name, '/', ':');
domain->fwnode = fwnode;
domain->flags |= IRQ_DOMAIN_NAME_ALLOCATED;
}
if (!domain->name) {
if (fwnode)
pr_err("Invalid fwnode type for irqdomain\n");
domain->name = kasprintf(GFP_KERNEL, "unknown-%d",
atomic_inc_return(&unknown_domains));
if (!domain->name) {
kfree(domain);
return NULL;
}
domain->flags |= IRQ_DOMAIN_NAME_ALLOCATED;
}
fwnode_handle_get(fwnode);
fwnode_dev_initialized(fwnode, true);
/* Fill structure */
INIT_RADIX_TREE(&domain->revmap_tree, GFP_KERNEL);
domain->ops = ops;
domain->host_data = host_data;
domain->hwirq_max = hwirq_max;
if (direct_max)
domain->flags |= IRQ_DOMAIN_FLAG_NO_MAP;
domain->revmap_size = size;
/*
* Hierarchical domains use the domain lock of the root domain
* (innermost domain).
*
* For non-hierarchical domains (as for root domains), the root
* pointer is set to the domain itself so that &domain->root->mutex
* always points to the right lock.
*/
mutex_init(&domain->mutex);
domain->root = domain;
irq_domain_check_hierarchy(domain);
return domain;
}
2.2、为irq domain创建映射
上文的内容主要是向系统注册一个irq domain,具体HW interrupt ID和IRQ number的映射关系都是空的,因此,具体各个irq domain如何管理映射所需要的database还是需要建立的。例如:对于线性映射的irq domain,需要建立线性映射的lookup table,对于Radix Tree map,要把那个反应IRQ number和HW interrupt ID的Radix tree建立起来。创建映射有四个接口函数:
(1)调用irq_create_mapping函数建立HW interrupt ID和IRQ number的映射关系。该接口函数以irq domain和HW interrupt ID为参数,返回IRQ number(这个IRQ number是动态分配的)。该函数的原型定义如下:include/linux/irqdomain.h
extern unsigned int irq_create_mapping_affinity(struct irq_domain *host,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq,
const struct irq_affinity_desc *affinity);
驱动调用该函数的时候必须提供HW interrupt ID,也就是意味着driver知道自己使用的HW interrupt ID,而一般情况下,HW interrupt ID其实对具体的driver应该是不可见的,不过有些场景比较特殊,例如GPIO类型的中断,它的HW interrupt ID和GPIO有着特定的关系,driver知道自己使用那个GPIO,也就是知道使用哪一个HW interrupt ID。
(2)irq_create_of_mapping。看到函数名字中的of(open firmware),我想你也可以猜到了几分,这个接口当然是利用device tree进行映射关系的建立。具体函数的原型定义如下:
include/linux/of_irq.h
extern unsigned int irq_create_of_mapping(struct of_phandle_args *irq_data);
(3)irq_domain。在 Linux 6.x 中,irq_create_strict_mappings 这个接口已经被移除,取而代之的是更灵活和通用的 IRQ 映射机制,尤其是通过 irq_domain API 来处理。
具体来说,Linux 6.x 使用以下方法来处理类似的 IRQ 映射功能:
irq_domain:Linux 通过 irq_domain 来创建和管理 IRQ 映射。irq_domain 允许硬件中断和虚拟 IRQ 号之间的映射,可以实现更复杂的中断管理需求。通过 irq_create_mapping()、irq_domain_add() 等函数,可以为硬件中断分配虚拟 IRQ,并确保映射的准确性。
irq_alloc_descs():这是用来为一组中断号分配描述符的函数,虽然不直接涉及到“严格映射”,但它在创建多个 IRQ 号时仍然发挥着作用。
irq_chip 和 irq_domain 抽象:Linux 6.x 使用 irq_chip 和 irq_domain 进一步抽象硬件中断处理,简化了 IRQ 分配与管理,并通过 irq_set_type()、irq_set_affinity() 等接口提供更多的控制选项。
通常,一个普通设备的device tree node已经描述了足够的中断信息,在这种情况下,该设备的驱动在初始化的时候可以调用irq_of_parse_and_map这个接口函数进行该device node中和中断相关的内容(interrupts和interrupt-parent属性)进行分析,并建立映射关系,具体代码如下:
drivers/of/irq.c
/**
* irq_of_parse_and_map - Parse and map an interrupt into linux virq space
* @dev: Device node of the device whose interrupt is to be mapped
* @index: Index of the interrupt to map
*
* This function is a wrapper that chains of_irq_parse_one() and
* irq_create_of_mapping() to make things easier to callers
*/
unsigned int irq_of_parse_and_map(struct device_node *dev, int index)
{
struct of_phandle_args oirq;
if (of_irq_parse_one(dev, index, &oirq)) /* 分析device node中的interrupt相关属性 */
return 0;
return irq_create_of_mapping(&oirq); /* 创建映射,并返回对应的IRQ number */
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(irq_of_parse_and_map);
对于一个使用设备树的普通驱动程序,基本上初始化需要调用irq_of_parse_and_map获取IRQ number,然后调用request_threaded_irq申请中断handler。
(4)irq_create_direct_mapping。这是给no map那种类型的interrupt controller使用的,这里不再赘述。include/linux/irqdomain.h
extern unsigned int irq_create_direct_mapping(struct irq_domain *host);
三、数据结构描述
3.1、irq domain的callback接口
struct irq_domain_ops抽象了一个irq domain的callback函数,定义如下:include/linux/irqdomain.h
/**
* struct irq_domain_ops - Methods for irq_domain objects
* @match: Match an interrupt controller device node to a host, returns
* 1 on a match
* @map: Create or update a mapping between a virtual irq number and a hw
* irq number. This is called only once for a given mapping.
* @unmap: Dispose of such a mapping
* @xlate: Given a device tree node and interrupt specifier, decode
* the hardware irq number and linux irq type value.
*
* Functions below are provided by the driver and called whenever a new mapping
* is created or an old mapping is disposed. The driver can then proceed to
* whatever internal data structures management is required. It also needs
* to setup the irq_desc when returning from map().
*/
struct irq_domain_ops {
int (*match)(struct irq_domain *d, struct device_node *node,
enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token);
int (*select)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_fwspec *fwspec,
enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token);
int (*map)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq, irq_hw_number_t hw);
void (*unmap)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq);
int (*xlate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct device_node *node,
const u32 *intspec, unsigned int intsize,
unsigned long *out_hwirq, unsigned int *out_type);
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY
/* extended V2 interfaces to support hierarchy irq_domains */
int (*alloc)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq,
unsigned int nr_irqs, void *arg);
void (*free)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq,
unsigned int nr_irqs);
int (*activate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_data *irqd, bool reserve);
void (*deactivate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_data *irq_data);
int (*translate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_fwspec *fwspec,
unsigned long *out_hwirq, unsigned int *out_type);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_DEBUGFS
void (*debug_show)(struct seq_file *m, struct irq_domain *d,
struct irq_data *irqd, int ind);
#endif
};
3.2、irq domain
在内核中,irq domain的概念由struct irq_domain表示:include/linux/irqdomain.h
/**
* struct irq_domain - Hardware interrupt number translation object
* @link: Element in global irq_domain list.
* @name: Name of interrupt domain
* @ops: pointer to irq_domain methods
* @host_data: private data pointer for use by owner. Not touched by irq_domain
* core code.
* @flags: host per irq_domain flags
* @mapcount: The number of mapped interrupts
*
* Optional elements
* @fwnode: Pointer to firmware node associated with the irq_domain. Pretty easy
* to swap it for the of_node via the irq_domain_get_of_node accessor
* @gc: Pointer to a list of generic chips. There is a helper function for
* setting up one or more generic chips for interrupt controllers
* drivers using the generic chip library which uses this pointer.
* @parent: Pointer to parent irq_domain to support hierarchy irq_domains
* @debugfs_file: dentry for the domain debugfs file
*
* Revmap data, used internally by irq_domain
* @revmap_direct_max_irq: The largest hwirq that can be set for controllers that
* support direct mapping
* @revmap_size: Size of the linear map table @linear_revmap[]
* @revmap_tree: Radix map tree for hwirqs that don't fit in the linear map
* @linear_revmap: Linear table of hwirq->virq reverse mappings
*/
struct irq_domain {
struct list_head link;
const char *name;
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops; /* callback函数 */
void *host_data;
unsigned int flags;
unsigned int mapcount;
/* Optional data */
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode;
enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token;
struct irq_domain_chip_generic *gc; /* generic irq chip的概念,本文暂不描述 */
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY
struct irq_domain *parent;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_DEBUGFS
struct dentry *debugfs_file;
#endif
/* reverse map data. The linear map gets appended to the irq_domain */
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_max; /* 该domain中最大的那个HW interrupt ID */
unsigned int revmap_direct_max_irq; /* 直接映射的最大值; 使用〜0没有限制; 0表示没有直接映射 */
unsigned int revmap_size; /* 线性映射的size,for Radix Tree map和no map,该值等于0 */
struct radix_tree_root revmap_tree; /* Radix Tree map使用到的radix tree root node */
struct mutex revmap_tree_mutex;
unsigned int linear_revmap[];
};
linux内核中,所有的irq domain被挂入一个全局链表,链表头定义如下:kernel/irq/irqdomain.c
static LIST_HEAD(irq_domain_list);
struct irq_domain中的link成员就是挂入这个队列的节点。通过irq_domain_list这个指针,可以获取整个系统中HW interrupt ID和IRQ number的mapping DB。
host_data定义了底层interrupt controller使用的私有数据,和具体的interrupt controller相关(对于GIC,该指针指向一个struct gic_chip_data数据结构,对于VIC,该指针指向一个struct vic_device数据结构)。
1.对于线性映射:
(1)linear_revmap保存了一个线性的lookup table,index是HW interrupt ID,table中保存了IRQ number值。
(2)revmap_size等于线性的lookup table的size。
(3)hwirq_max保存了最大的HW interrupt ID。
(4)revmap_direct_max_irq没有用,设定为0。revmap_tree没有用。
2.对于Radix Tree map:
(1)linear_revmap没有用,revmap_size等于0。
(2)hwirq_max没有用,设定为一个最大值。
(3)revmap_direct_max_irq没有用,设定为0。
(4)revmap_tree指向Radix tree的root node。
四、中断相关的设备树
想要进行映射,首先要了解interrupt controller的拓扑结构。系统中的interrupt controller的拓扑结构以及其interrupt request line的分配情况(分配给哪一个具体的外设)都在Device Tree Source文件中通过下面的属性给出了描述。这些内容在Device Tree的三份文档中给出了一些描述,这里简单总结一下:
对于那些产生中断的外设,我们需要定义interrupt-parent和interrupts属性:
(1)interrupt-parent。表明该外设的interrupt request line物理的连接到了哪一个中断控制器上
(2)interrupts。这个属性描述了具体该外设产生的interrupt的细节信息(也就是传说中的interrupt specifier)。例如:HW interrupt ID(由该外设的device node中的interrupt-parent指向的interrupt controller解析)、interrupt触发类型等。
对于Interrupt controller,我们需要定义interrupt-controller和#interrupt-cells的属性:
(1)interrupt-controller。表明该device node就是一个中断控制器
(2)#interrupt-cells。该中断控制器用多少个cell(一个cell就是一个32-bit的单元)描述一个外设的interrupt request line。?具体每个cell表示什么样的含义由interrupt controller自己定义。
(3)interrupts和interrupt-parent。对于那些不是root 的interrupt controller,其本身也是作为一个产生中断的外设连接到其他的interrupt controller上,因此也需要定义interrupts和interrupt-parent的属性。
arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3568.dtsi
/dts-v1/;
#include <dt-bindings/gpio/gpio.h>
#include <dt-bindings/pinctrl/rockchip.h>
#include "rk3568.dtsi"
#include "rk3568-evb.dtsi"
/ {
model = "Rockchip RK3568 EVB1 DDR4 V10 Board";
compatible = "rockchip,rk3568-evb1-ddr4-v10", "rockchip,rk3568";
gic: interrupt-controller@fd400000 {
compatible = "arm,gic-v3";
#interrupt-cells = <3>;
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <2>;
ranges;
interrupt-controller;
reg = <0x0 0xfd400000 0 0x10000>, /* GICD */
<0x0 0xfd460000 0 0xc0000>; /* GICR */
interrupts = <GIC_PPI 9 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
its: interrupt-controller@fd440000 {
compatible = "arm,gic-v3-its";
msi-controller;
#msi-cells = <1>;
reg = <0x0 0xfd440000 0x0 0x20000>;
};
};
/* pinctrl子系统,也是一个中断子系统,但不是根中断子系统,它是接在一个根中断子系统上的*/
pinctrl: pinctrl {
compatible = "rockchip,rk3568-pinctrl";
rockchip,grf = <&grf>;
rockchip,pmu = <&pmugrf>;
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <2>;
ranges;
gpio0: gpio0@fdd60000 {
compatible = "rockchip,gpio-bank";
reg = <0x0 0xfdd60000 0x0 0x100>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 33 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&pmucru PCLK_GPIO0>, <&pmucru DBCLK_GPIO0>;
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <2>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <2>;
};
gpio1: gpio1@fe740000 {
compatible = "rockchip,gpio-bank";
reg = <0x0 0xfe740000 0x0 0x100>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 34 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&cru PCLK_GPIO1>, <&cru DBCLK_GPIO1>;
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <2>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <2>;
};
gpio2: gpio2@fe750000 {
compatible = "rockchip,gpio-bank";
reg = <0x0 0xfe750000 0x0 0x100>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 35 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&cru PCLK_GPIO2>, <&cru DBCLK_GPIO2>;
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <2>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <2>;
};
gpio3: gpio3@fe760000 {
compatible = "rockchip,gpio-bank";
reg = <0x0 0xfe760000 0x0 0x100>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 36 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&cru PCLK_GPIO3>, <&cru DBCLK_GPIO3>;
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <2>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <2>;
};
gpio4: gpio4@fe770000 {
compatible = "rockchip,gpio-bank";
reg = <0x0 0xfe770000 0x0 0x100>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 37 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&cru PCLK_GPIO4>, <&cru DBCLK_GPIO4>;
gpio-controller;
#gpio-cells = <2>;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <2>;
};
};
};
在RK3568的数据手册中pinctrl子系统代表的就是一个中断子系统,是gpio0的第33个中断。即数据手册中65-32(PPI不可共享中断)=33。
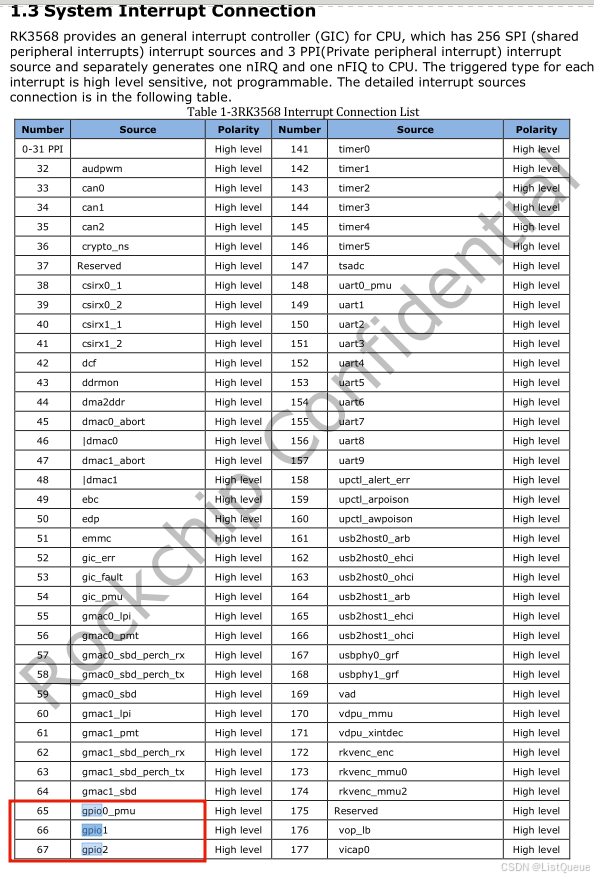
子节点中共享其父节点中的属性的,当然子节点中如果自己定义了的话,就会覆盖掉其父节点的。这里就体现了面向对象中的基类的作用。
五、Mapping DB的建立
5.1、概述
系统中HW interrupt ID和IRQ number的mapping DB是在整个系统初始化的过程中建立起来的,过程如下:
(1)dts文件描述了系统中的interrupt controller以及外设IRQ的拓扑结构,在linux kernel启动的时候,由bootloader传递给kernel(实际传递的是DTB)。
(2)在设备树初始化的时候,形成了系统内所有的device node的树状结构,当然其中包括所有和中断拓扑相关的数据结构(所有的interrupt controller的node和使用中断的外设node)
(3)在machine driver初始化的时候会调用of_irq_init函数,在该函数中会扫描所有interrupt controller的节点,并调用适合的interrupt controller driver进行初始化。、初始化需要注意顺序,首先初始化root,然后first level,second level,最好是leaf node。在初始化的过程中,一般会调用上面的中的接口函数向系统增加irq domain。有些interrupt controller会在其driver初始化的过程中创建映射。
(4)在各个driver初始化的过程中,创建映射。
5.2、 interrupt controller初始化的过程中,注册irq domain
以GIC为例:
下面是gic的一些基本资料:
分配器:执行中断优先级划分并分配到CPU接口。
CPU接口:为系统中连接的处理器执行优先级屏蔽和抢占处理。
中断状态:非活动,待处理,活动,活动和待处理。
中断类型:
1.外设中断:由信号通知GIC的中断。 包括SPI和PPI
2.软件产生的中断(SGI):这是由软件写入GIC中的GICD_SGIR寄存器产生的中断。
中断ID:ID0-ID31用于CPU接口专用的中断。 这些中断存储在分发服务器中。
可以一个GIC看到总共可以支持1020个中断drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c
/* 默认定义了GIC的总个数不能超过CONFIG_ARM_GIC_MAX_NR */
static struct gic_chip_data gic_data[CONFIG_ARM_GIC_MAX_NR] __read_mostly;
/* 每个中断控制器都会调用该函数注册一次 */
int __init
gic_of_init(struct device_node *node, struct device_node *parent)
{
struct gic_chip_data *gic;
int irq, ret;
if (WARN_ON(!node))
return -ENODEV;
if (WARN_ON(gic_cnt >= CONFIG_ARM_GIC_MAX_NR))
return -EINVAL;
gic = &gic_data[gic_cnt]; //获取一个gic数据
ret = gic_of_setup(gic, node); //设备节点和gic绑定,并把设备地址之类映射初始化好
if (ret)
return ret;
/*
* Disable split EOI/Deactivate if either HYP is not available
* or the CPU interface is too small.
*/
if (gic_cnt == 0 && !gic_check_eoimode(node, &gic->raw_cpu_base))
static_branch_disable(&supports_deactivate_key);
/* 注册一个GIC */
ret = __gic_init_bases(gic, -1, &node->fwnode);
if (ret) {
gic_teardown(gic);
return ret;
}
if (!gic_cnt) {
gic_init_physaddr(node); //初始化gic的资源信息
gic_of_setup_kvm_info(node); //获取资源信息,将中断解析并映射到linux virq空间等
}
if (parent) {
irq = irq_of_parse_and_map(node, 0); //解析和映射irq
gic_cascade_irq(gic_cnt, irq); //获取对应的irq_desc之类
}
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ARM_GIC_V2M))
gicv2m_init(&node->fwnode, gic_data[gic_cnt].domain);
gic_cnt++; //每次注册一个中断控制器,这个gic的数量都会增加
return 0;
}
static int gic_init_bases(struct gic_chip_data *gic, int irq_start,
struct fwnode_handle *handle)
{
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_base;
int gic_irqs, irq_base, ret;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GIC_NON_BANKED) && gic->percpu_offset) {
/* Frankein-GIC without banked registers... */
unsigned int cpu;
gic->dist_base.percpu_base = alloc_percpu(void __iomem *);
gic->cpu_base.percpu_base = alloc_percpu(void __iomem *);
if (WARN_ON(!gic->dist_base.percpu_base ||
!gic->cpu_base.percpu_base)) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto error;
}
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
u32 mpidr = cpu_logical_map(cpu);
u32 core_id = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 0);
unsigned long offset = gic->percpu_offset * core_id;
*per_cpu_ptr(gic->dist_base.percpu_base, cpu) =
gic->raw_dist_base + offset;
*per_cpu_ptr(gic->cpu_base.percpu_base, cpu) =
gic->raw_cpu_base + offset;
}
gic_set_base_accessor(gic, gic_get_percpu_base);
} else {
/* Normal, sane GIC... */
WARN(gic->percpu_offset,
"GIC_NON_BANKED not enabled, ignoring %08x offset!",
gic->percpu_offset);
gic->dist_base.common_base = gic->raw_dist_base;
gic->cpu_base.common_base = gic->raw_cpu_base;
gic_set_base_accessor(gic, gic_get_common_base);
}
/*
* Find out how many interrupts are supported.
* The GIC only supports up to 1020 interrupt sources.
*/
gic_irqs = readl_relaxed(gic_data_dist_base(gic) + GIC_DIST_CTR) & 0x1f;
gic_irqs = (gic_irqs + 1) * 32;
if (gic_irqs > 1020) //gic只支持到1020个中断
gic_irqs = 1020;
gic->gic_irqs = gic_irqs;
if (handle) { /* DT/ACPI */
/* 固件节点的句柄要是存在,则创建线性映射表 */
gic->domain = irq_domain_create_linear(handle, gic_irqs,
&gic_irq_domain_hierarchy_ops, //申请一个domain时,也注册了ops操作函数
gic);
} else { /* Legacy support 支持老的遗留代码, */
/*
* For primary GICs, skip over SGIs. 对于主要GIC,请跳过SGI
* For secondary GICs, skip over PPIs, too. 于二级GIC,也可以跳过PPI
*/
if (gic == &gic_data[0] && (irq_start & 31) > 0) {
hwirq_base = 16; //跳过前16个SIG
if (irq_start != -1)
irq_start = (irq_start & ~31) + 16;
} else {
hwirq_base = 32; //16个SIG和跳过16~31的PPI
}
gic_irqs -= hwirq_base; /* calculate # of irqs to allocate */
/* 申请gic_irqs个IRQ资源,从16号开始搜索IRQ number。由于是root GIC,申请的IRQ基本上会从16号开始 */
irq_base = irq_alloc_descs(irq_start, 16, gic_irqs,
numa_node_id());
if (irq_base < 0) {
WARN(1, "Cannot allocate irq_descs @ IRQ%d, assuming pre-allocated\n",
irq_start);
irq_base = irq_start;
}
/* 向系统注册irq domain并创建映射 */
gic->domain = irq_domain_add_legacy(NULL, gic_irqs, irq_base,
hwirq_base, &gic_irq_domain_ops, gic); //同时给这个domain注册了ops操作集合
}
if (WARN_ON(!gic->domain)) {
ret = -ENODEV;
goto error;
}
gic_dist_init(gic);
ret = gic_cpu_init(gic);
if (ret)
goto error;
ret = gic_pm_init(gic);
if (ret)
goto error;
return 0;
error:
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GIC_NON_BANKED) && gic->percpu_offset) {
free_percpu(gic->dist_base.percpu_base);
free_percpu(gic->cpu_base.percpu_base);
}
return ret;
}
在GIC的代码中是调用标准的注册irq domain的接口函数。irq_domain_create_linear
HW interrupt ID和IRQ number的关系是固定的。一旦关系固定,我们就可以在interupt controller的代码中创建这些映射关系。具体代码如下:kernel/irq/irqdomain.c
/**
* irq_domain_add_legacy() - Allocate and register a legacy revmap irq_domain.
* @of_node: pointer to interrupt controller's device tree node.
* @size: total number of irqs in legacy mapping
* @first_irq: first number of irq block assigned to the domain
* @first_hwirq: first hwirq number to use for the translation. Should normally
* be '0', but a positive integer can be used if the effective
* hwirqs numbering does not begin at zero.
* @ops: map/unmap domain callbacks
* @host_data: Controller private data pointer
*
* Note: the map() callback will be called before this function returns
* for all legacy interrupts except 0 (which is always the invalid irq for
* a legacy controller).
*/
struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_legacy(struct device_node *of_node,
unsigned int size,
unsigned int first_irq,
irq_hw_number_t first_hwirq,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return irq_domain_create_legacy(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), size,
first_irq, first_hwirq, ops, host_data);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(irq_domain_add_legacy);
struct irq_domain *irq_domain_create_legacy(struct fwnode_handle *fwnode,
unsigned int size,
unsigned int first_irq,
irq_hw_number_t first_hwirq,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
struct irq_domain *domain;
/* 注册irq domain */
domain = __irq_domain_add(fwnode, first_hwirq + size, first_hwirq + size, 0, ops, host_data);
if (domain) //创建映射
irq_domain_associate_many(domain, first_irq, first_hwirq, size);
return domain;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(irq_domain_create_legacy);
这时候,对于这个版本的GIC driver而言,初始化之后,HW interrupt ID和IRQ number的映射关系已经建立,保存在线性lookup table中,size等于GIC支持的中断数目,具体如下:
index 0~15对应的IRQ无效
16号IRQ <------------------>16号HW interrupt ID
17号IRQ <------------------>17号HW interrupt ID
5.3、创建映射
在各个硬件外设的驱动初始化过程中,创建HW interrupt ID和IRQ number的映射关系。
设备的驱动在初始化的时候可以调用irq_of_parse_and_map这个接口函数进行该device node中和中断相关的内容(interrupts和interrupt-parent属性)进行分析,并建立映射关系,具体代码如下:
unsigned int irq_of_parse_and_map(struct device_node *node, int index)
{
struct platform_device *op = of_find_device_by_node(node);
if (!op || index >= op->archdata.num_irqs)
return 0;
return op->archdata.irqs[index];
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(irq_of_parse_and_map);
再来看看irq_create_of_mapping函数如何创建映射:drivers/of/irq.c
/**
* irq_of_parse_and_map - Parse and map an interrupt into linux virq space
* @dev: Device node of the device whose interrupt is to be mapped
* @index: Index of the interrupt to map
*
* This function is a wrapper that chains of_irq_parse_one() and
* irq_create_of_mapping() to make things easier to callers
*/
unsigned int irq_of_parse_and_map(struct device_node *dev, int index)
{
struct of_phandle_args oirq;
if (of_irq_parse_one(dev, index, &oirq))
return 0;
return irq_create_of_mapping(&oirq);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(irq_of_parse_and_map);
看之前,先了解一下这个函数用到的参数
include/linux/of.h
#define MAX_PHANDLE_ARGS 16
include/linux/of.h
struct of_phandle_args {
struct device_node *np; //指向外设对应的interrupt controller的device node
int args_count; //该外设定义的interrupt相关属性的个数
uint32_t args[MAX_PHANDLE_ARGS]; //具体的interrupt相关属性的定义
};
include/linux/irqdomain.h
#define IRQ_DOMAIN_IRQ_SPEC_PARAMS 16
/**
* struct irq_fwspec - generic IRQ specifier structure
*
* @fwnode: Pointer to a firmware-specific descriptor
* @param_count: Number of device-specific parameters
* @param: Device-specific parameters
*
* This structure, directly modeled after of_phandle_args, is used to
* pass a device-specific description of an interrupt.
*/
struct irq_fwspec {
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode; //指向特殊固件的描述
int param_count; //参数个数
u32 param[IRQ_DOMAIN_IRQ_SPEC_PARAMS]; //存放具体参数
};
kernel/irq/irqdomain.c
unsigned int irq_create_of_mapping(struct of_phandle_args *irq_data)
{
struct irq_fwspec fwspec;
of_phandle_args_to_fwspec(irq_data->np, irq_data->args,
irq_data->args_count, &fwspec);
return irq_create_fwspec_mapping(&fwspec);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(irq_create_of_mapping);
kernel/irq/irqdomain.c
static void of_phandle_args_to_fwspec(struct of_phandle_args *irq_data,
struct irq_fwspec *fwspec)
{
int i;
//确定中断应的设备节点存在,取出对应的固件节点
fwspec->fwnode = irq_data->np ? &irq_data->np->fwnode : NULL;
fwspec->param_count = irq_data->args_count; //获得属性个数
/* 这里把所有的在设备节点属性参数放在irq_fwspec 的参数列表中 */
for (i = 0; i < irq_data->args_count; i++)
fwspec->param[i] = irq_data->args[i];
}
unsigned int irq_create_fwspec_mapping(struct irq_fwspec *fwspec)
{
struct irq_domain *domain;
struct irq_data *irq_data;
irq_hw_number_t hwirq;
unsigned int type = IRQ_TYPE_NONE; //普通类型的中断
int virq;
/* 查找一个合适的domain ,看下面AAAAA位置分析 */
if (fwspec->fwnode) { /* 固件节点存在 */
domain = irq_find_matching_fwspec(fwspec, DOMAIN_BUS_WIRED);
if (!domain)
domain = irq_find_matching_fwspec(fwspec, DOMAIN_BUS_ANY);
} else {
domain = irq_default_domain;
}
if (!domain) { //没找到对应的domain,则不再继续映射下去
pr_warn("no irq domain found for %s !\n",
of_node_full_name(to_of_node(fwspec->fwnode)));
return 0;
}
/* 解析物理中断号和中断类型,看下面BBBBB位置分析 */
if (irq_domain_translate(domain, fwspec, &hwirq, &type))
return 0;
/*
* WARN if the irqchip returns a type with bits
* outside the sense mask set and clear these bits.
*/
if (WARN_ON(type & ~IRQ_TYPE_SENSE_MASK)) //只保留有效的低四位
type &= IRQ_TYPE_SENSE_MASK;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
/*
* If we've already configured this interrupt,
* don't do it again, or hell will break loose.
*/
//创建hwirq和virq的映射-查看CCCCC分析,返回一个空desc的虚拟中断号
virq = irq_find_mapping(domain, hwirq);
if (virq) {
/*
* If the trigger type is not specified or matches the
* current trigger type then we are done so return the
* interrupt number.
*/
/* 如果是一个没指定中断类型,或者是刚好和指定的匹配,直接返回 */
if (type == IRQ_TYPE_NONE || type == irq_get_trigger_type(virq))
return virq;
/*
* If the trigger type has not been set yet, then set
* it now and return the interrupt number.
*/
/* 设置触发类型 */
if (irq_get_trigger_type(virq) == IRQ_TYPE_NONE) {
irq_data = irq_get_irq_data(virq);
if (!irq_data)
return 0;
/* 设置其中断触发状态类型 */
irqd_set_trigger_type(irq_data, type);
return virq;
}
pr_warn("type mismatch, failed to map hwirq-%lu for %s!\n",
hwirq, of_node_full_name(to_of_node(fwspec->fwnode)));
return 0;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------
/* 如果是一个级联的domain */
if (irq_domain_is_hierarchy(domain)) {
/* 层次结构的,里面重新创建映射,等等 */
virq = irq_domain_alloc_irqs(domain, 1, NUMA_NO_NODE, fwspec);
if (virq <= 0) //virq <= 表示出错
return 0;
} else {
/* Create mapping */
virq = irq_create_mapping(domain, hwirq); //创建完映射表 DDDDD分析
if (!virq)
return virq;
}
/* 继续处理级联方式的domain */
irq_data = irq_get_irq_data(virq);
if (!irq_data) {
if (irq_domain_is_hierarchy(domain))
irq_domain_free_irqs(virq, 1);
else
irq_dispose_mapping(virq);
return 0;
}
/* Store trigger type */
irqd_set_trigger_type(irq_data, type);
return virq;
}
继续分析:
include/linux/irqdomain_defs.h
/*
* Should several domains have the same device node, but serve
* different purposes (for example one domain is for PCI/MSI, and the
* other for wired IRQs), they can be distinguished using a
* bus-specific token. Most domains are expected to only carry
* DOMAIN_BUS_ANY.
*/
enum irq_domain_bus_token {
DOMAIN_BUS_ANY = 0,
DOMAIN_BUS_WIRED,
DOMAIN_BUS_PCI_MSI,
DOMAIN_BUS_PLATFORM_MSI,
DOMAIN_BUS_NEXUS,
DOMAIN_BUS_IPI,
DOMAIN_BUS_FSL_MC_MSI,
};
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c
/* 这种是在注册一个中断控制器获取domain时,是通过设备树分析得到的,则handle存在的情况下,是下面这个操作函数 */
static const struct irq_domain_ops gic_irq_domain_hierarchy_ops = {
.translate = gic_irq_domain_translate,
.alloc = gic_irq_domain_alloc,
.free = irq_domain_free_irqs_top,
};
/* 如果是不是设备树传参注册,是通过代码注册,则是这个 */
static const struct irq_domain_ops gic_irq_domain_ops = {
.map = gic_irq_domain_map,
.unmap = gic_irq_domain_unmap,
};
/**
* irq_find_matching_fwspec() - Locates a domain for a given fwspec
* @fwspec: FW specifier for an interrupt
* @bus_token: domain-specific data
*/
struct irq_domain *irq_find_matching_fwspec(struct irq_fwspec *fwspec,
enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token)
{
struct irq_domain *h, *found = NULL;
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode = fwspec->fwnode;
int rc;
/* We might want to match the legacy controller last since
* it might potentially be set to match all interrupts in
* the absence of a device node. This isn't a problem so far
* yet though...
*
* bus_token == DOMAIN_BUS_ANY matches any domain, any other
* values must generate an exact match for the domain to be
* selected.
*/
mutex_lock(&irq_domain_mutex);
/* 这里是分析所有的在irq_domain_list链表上的domain,通过domain中ops的select或match
* 函数来获得最佳匹配,如果找不到,那找到和自己fwnode一样的fwnode所在domain,且确定这个domain
* 是可以任意匹配的,实际无论是哪种,GIC控制器都是没定义的
*/
list_for_each_entry(h, &irq_domain_list, link) {
if (h->ops->select && fwspec->param_count)
rc = h->ops->select(h, fwspec, bus_token);
else if (h->ops->match)
rc = h->ops->match(h, to_of_node(fwnode), bus_token);
else
/* 最后找不到的情况下,在确定自己是不是可以匹配任何DOMAIN_BUS */
rc = ((fwnode != NULL) && (h->fwnode == fwnode) &&
((bus_token == DOMAIN_BUS_ANY) ||
(h->bus_token == bus_token)));
if (rc) {
found = h; //确定这个固件节点可以匹配,任何domain_bus,那这个
break;
}
}
mutex_unlock(&irq_domain_mutex);
return found;
}
kernel/irq/irqdomain.c
static int irq_domain_translate(struct irq_domain *d,
struct irq_fwspec *fwspec,
irq_hw_number_t *hwirq, unsigned int *type)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY
if (d->ops->translate)
return d->ops->translate(d, fwspec, hwirq, type);
#endif
if (d->ops->xlate) //这种gic里没定义
return d->ops->xlate(d, to_of_node(fwspec->fwnode),
fwspec->param, fwspec->param_count,
hwirq, type);
/* If domain has no translation, then we assume interrupt line */
*hwirq = fwspec->param[0]; //实在没定义,就假设第一个就是中断号
return 0;
}
以RK3568为例:dts配置:
gic: interrupt-controller@fd400000 {
compatible = "arm,gic-v3";
#interrupt-cells = <3>;
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <2>;
ranges;
interrupt-controller;
reg = <0x0 0xfd400000 0 0x10000>, /* GICD */
<0x0 0xfd460000 0 0xc0000>; /* GICR */
interrupts = <GIC_PPI 9 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
its: interrupt-controller@fd440000 {
compatible = "arm,gic-v3-its";
msi-controller;
#msi-cells = <1>;
reg = <0x0 0xfd440000 0x0 0x20000>;
};
};
sdhci: sdhci@fe310000 {
compatible = "rockchip,rk3568-dwcmshc", "rockchip,dwcmshc-sdhci";
reg = <0x0 0xfe310000 0x0 0x10000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 19 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
assigned-clocks = <&cru BCLK_EMMC>, <&cru TCLK_EMMC>,
<&cru CCLK_EMMC>;
assigned-clock-rates = <200000000>, <24000000>, <200000000>;
clocks = <&cru CCLK_EMMC>, <&cru HCLK_EMMC>,
<&cru ACLK_EMMC>, <&cru BCLK_EMMC>,
<&cru TCLK_EMMC>;
clock-names = "core", "bus", "axi", "block", "timer";
resets = <&cru SRST_C_EMMC>, <&cru SRST_H_EMMC>,
<&cru SRST_A_EMMC>, <&cru SRST_B_EMMC>,
<&cru SRST_T_EMMC>;
reset-names = "core", "bus", "axi", "block", "timer";
status = "disabled";
};
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c
#define GIC_SPI 0
#define GIC_PPI 1
static int gic_irq_domain_translate(struct irq_domain *d,
struct irq_fwspec *fwspec,
unsigned long *hwirq,
unsigned int *type)
{
if (is_of_node(fwspec->fwnode)) { //确认是通过设备树方式创建的固件节点
if (fwspec->param_count < 3) //且属性大于3个
return -EINVAL;
/* Get the interrupt number and add 16 to skip over SGIs */
*hwirq = fwspec->param[1] + 16; //硬件中断号,默认是要加上SGI的0~15
/*
* For SPIs, we need to add 16 more to get the GIC irq
* ID number
*/
if (!fwspec->param[0]) //第一个属性如果是SPI,还要加上PPI的16~31
*hwirq += 16;
*type = fwspec->param[2] & IRQ_TYPE_SENSE_MASK; //解析中断类型(上升,下降,双边沿这些)
/* Make it clear that broken DTs are... broken */
WARN_ON(*type == IRQ_TYPE_NONE);
return 0;
}
if (is_fwnode_irqchip(fwspec->fwnode)) { /* 检查是不是通过代码中默认初始化的(非设备树) */
if(fwspec->param_count != 2)
return -EINVAL;
/* 代码中,不需要指定gic的属性 */
*hwirq = fwspec->param[0]; //那个中断
*type = fwspec->param[1]; //中断类型
WARN_ON(*type == IRQ_TYPE_NONE);
return 0;
}
return -EINVAL;
}
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c
include/linux/irqdomain.h
/**
* irq_find_mapping() - Find a linux irq from a hw irq number.
* @domain: domain owning this hardware interrupt
* @hwirq: hardware irq number in that domain space
*/
static inline unsigned int irq_find_mapping(struct irq_domain *domain,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq)
{
unsigned int irq;
if (__irq_resolve_mapping(domain, hwirq, &irq))
return irq;
return 0;
}
kernel/irq/irqdomain.c
/**
* __irq_resolve_mapping() - Find a linux irq from a hw irq number.
* @domain: domain owning this hardware interrupt
* @hwirq: hardware irq number in that domain space
* @irq: optional pointer to return the Linux irq if required
*
* Returns the interrupt descriptor.
*/
struct irq_desc *__irq_resolve_mapping(struct irq_domain *domain,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq,
unsigned int *irq)
{
struct irq_desc *desc = NULL;
struct irq_data *data;
/* Look for default domain if nececssary */
if (domain == NULL)
domain = irq_default_domain;
if (domain == NULL) //
return 0;
/* hwirq是小于该domain中的直接映射的最大中断的 */
if (hwirq < domain->revmap_direct_max_irq) { //线性映射这个值为非 0
data = irq_domain_get_irq_data(domain, hwirq);
if (data && data->hwirq == hwirq)
return hwirq;
}
/* 检查硬件中断号,是不是在这个域范内内 */
/* Check if the hwirq is in the linear revmap. */
if (hwirq < domain->revmap_size)
return domain->linear_revmap[hwirq]; //返回这个中断芯片在上一层的中断号(或者这个设备在,上一层中断芯片的中断好)
//到这里说是非线性映射,使用基数树进行映射
rcu_read_lock();
/* Check if the hwirq is in the linear revmap. */
if (hwirq < domain->revmap_size)
data = rcu_dereference(domain->revmap[hwirq]);
else
data = radix_tree_lookup(&domain->revmap_tree, hwirq);
if (likely(data)) {
desc = irq_data_to_desc(data);
if (irq)
*irq = data->irq;
}
rcu_read_unlock();
return desc;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__irq_resolve_mapping);
//对于采用级联映domain采用下面这种方式,一层一层的找到一个合适的desc
/**
* irq_domain_get_irq_data - Get irq_data associated with @virq and @domain
* @domain: domain to match
* @virq: IRQ number to get irq_data
*/
struct irq_data *irq_domain_get_irq_data(struct irq_domain *domain,
unsigned int virq)
{
struct irq_data *irq_data;
/* 从对于设备从其所接的中断控制器的d获取一个irq_desc
* 对于一个子中断控制器,要从其父中断控制器获取一个irq_desc
*/
for (irq_data = irq_get_irq_data(virq); irq_data;
irq_data = irq_data->parent_data)
if (irq_data->domain == domain) //域到匹配,即只能从设备所属的中断控制器所获取
return irq_data;
return NULL;
}
//对于采用水平的domain,直接获取一个desc,可以用就行
/**
* irq_domain_get_irq_data - Get irq_data associated with @virq and @domain
* @domain: domain to match
* @virq: IRQ number to get irq_data
*/
struct irq_data *irq_domain_get_irq_data(struct irq_domain *domain,
unsigned int virq)
{
struct irq_data *irq_data = irq_get_irq_data(virq);
return (irq_data && irq_data->domain == domain) ? irq_data : NULL;
}
struct irq_data *irq_get_irq_data(unsigned int irq)
{
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(irq); //获取一个空的irq_desc
return desc ? &desc->irq_data : NULL; //把这个空的irq_desc 的irq_data返回
}
继续分析:
include/linux/irqdomain.h
static inline unsigned int irq_create_mapping(struct irq_domain *host,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq)
{
return irq_create_mapping_affinity(host, hwirq, NULL);
}
kernel/irq/irqdomain.c
/**
* irq_create_mapping_affinity() - Map a hardware interrupt into linux irq space
* @domain: domain owning this hardware interrupt or NULL for default domain
* @hwirq: hardware irq number in that domain space
* @affinity: irq affinity
*
* Only one mapping per hardware interrupt is permitted. Returns a linux
* irq number.
* If the sense/trigger is to be specified, set_irq_type() should be called
* on the number returned from that call.
*/
unsigned int irq_create_mapping_affinity(struct irq_domain *domain,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq,
const struct irq_affinity_desc *affinity)
{
int virq;
/* Look for default domain if necessary */
if (domain == NULL)
domain = irq_default_domain;
if (domain == NULL) {
WARN(1, "%s(, %lx) called with NULL domain\n", __func__, hwirq);
return 0;
}
mutex_lock(&domain->root->mutex);
/* Check if mapping already exists */
virq = irq_find_mapping(domain, hwirq);
if (virq) {
pr_debug("existing mapping on virq %d\n", virq);
goto out;
}
virq = irq_create_mapping_affinity_locked(domain, hwirq, affinity);
out:
mutex_unlock(&domain->root->mutex);
return virq;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(irq_create_mapping_affinity);
static unsigned int irq_create_mapping_affinity_locked(struct irq_domain *domain,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq,
const struct irq_affinity_desc *affinity)
{
struct device_node *of_node = irq_domain_get_of_node(domain);
int virq;
pr_debug("irq_create_mapping(0x%p, 0x%lx)\n", domain, hwirq);
/* Allocate a virtual interrupt number */
virq = irq_domain_alloc_descs(-1, 1, hwirq, of_node_to_nid(of_node),
affinity);
if (virq <= 0) {
pr_debug("-> virq allocation failed\n");
return 0;
}
if (irq_domain_associate_locked(domain, virq, hwirq)) {
irq_free_desc(virq);
return 0;
}
pr_debug("irq %lu on domain %s mapped to virtual irq %u\n",
hwirq, of_node_full_name(of_node), virq);
return virq;
}
int irq_domain_alloc_descs(int virq, unsigned int cnt, irq_hw_number_t hwirq,
int node, const struct cpumask *affinity)
{
unsigned int hint;
/* 分配一个IRQ 描述符以及对应的irq number,后面章节会详细的解释如何分配desc,这里跳过 */
if (virq >= 0) {
virq = __irq_alloc_descs(virq, virq, cnt, node, THIS_MODULE,
affinity);
} else {
hint = hwirq % nr_irqs;
if (hint == 0)
hint++;
virq = __irq_alloc_descs(-1, hint, cnt, node, THIS_MODULE,
affinity);
if (virq <= 0 && hint > 1) {
virq = __irq_alloc_descs(-1, 1, cnt, node, THIS_MODULE,
affinity);
}
}
return virq;
}
int irq_domain_associate(struct irq_domain *domain, unsigned int virq,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq)
{
int ret;
mutex_lock(&domain->root->mutex);
ret = irq_domain_associate_locked(domain, virq, hwirq);
mutex_unlock(&domain->root->mutex);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(irq_domain_associate);
static int irq_domain_associate_locked(struct irq_domain *domain, unsigned int virq,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq)
{
struct irq_data *irq_data = irq_get_irq_data(virq);
int ret;
if (WARN(hwirq >= domain->hwirq_max,
"error: hwirq 0x%x is too large for %s\n", (int)hwirq, domain->name))
return -EINVAL;
if (WARN(!irq_data, "error: virq%i is not allocated", virq))
return -EINVAL;
if (WARN(irq_data->domain, "error: virq%i is already associated", virq))
return -EINVAL;
mutex_lock(&irq_domain_mutex);
irq_data->hwirq = hwirq;
irq_data->domain = domain;
if (domain->ops->map) {
ret = domain->ops->map(domain, virq, hwirq); /* 调用irq domain的map callback函数 */
if (ret != 0) {
/*
* If map() returns -EPERM, this interrupt is protected
* by the firmware or some other service and shall not
* be mapped. Don't bother telling the user about it.
*/
if (ret != -EPERM) {
pr_info("%s didn't like hwirq-0x%lx to VIRQ%i mapping (rc=%d)\n",
domain->name, hwirq, virq, ret);
}
irq_data->domain = NULL;
irq_data->hwirq = 0;
mutex_unlock(&irq_domain_mutex);
return ret;
}
/* If not already assigned, give the domain the chip's name */
if (!domain->name && irq_data->chip)
domain->name = irq_data->chip->name;
}
domain->mapcount++;
irq_domain_set_mapping(domain, hwirq, irq_data); /* 填写线性映射lookup table的数据 */
mutex_unlock(&irq_domain_mutex);
irq_clear_status_flags(virq, IRQ_NOREQUEST); /* 该IRQ已经可以申请了,因此clear相关flag */
return 0;
}
static void irq_domain_set_mapping(struct irq_domain *domain,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq,
struct irq_data *irq_data)
{
/*
* This also makes sure that all domains point to the same root when
* called from irq_domain_insert_irq() for each domain in a hierarchy.
*/
lockdep_assert_held(&domain->root->mutex);
if (irq_domain_is_nomap(domain))
return;
if (hwirq < domain->revmap_size)
rcu_assign_pointer(domain->revmap[hwirq], irq_data);
else
radix_tree_insert(&domain->revmap_tree, hwirq, irq_data); /* 向radix tree插入一个node */
}
六、将HW interrupt ID转成IRQ number
创建了庞大的HW interrupt ID到IRQ number的mapping DB,最终还是要使用。具体的使用场景是在CPU相关的处理函数中,程序会读取硬件interrupt ID,并转成IRQ number,调用对应的irq event handler。在本章中,我们以一个级联的GIC系统为例,描述转换过程
6.1、GIC driver初始化
上面已经描述了root GIC的的初始化,second GIC的初始化。具体代码在gic_of_init->gic_init_bases中,如下:drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c
static int gic_init_bases(struct gic_chip_data *gic, int irq_start,
struct fwnode_handle *handle)
{
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_base;
int gic_irqs, irq_base, ret;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GIC_NON_BANKED) && gic->percpu_offset) {
/* Frankein-GIC without banked registers... */
unsigned int cpu;
gic->dist_base.percpu_base = alloc_percpu(void __iomem *);
gic->cpu_base.percpu_base = alloc_percpu(void __iomem *);
if (WARN_ON(!gic->dist_base.percpu_base ||
!gic->cpu_base.percpu_base)) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto error;
}
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
u32 mpidr = cpu_logical_map(cpu);
u32 core_id = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 0);
unsigned long offset = gic->percpu_offset * core_id;
*per_cpu_ptr(gic->dist_base.percpu_base, cpu) =
gic->raw_dist_base + offset;
*per_cpu_ptr(gic->cpu_base.percpu_base, cpu) =
gic->raw_cpu_base + offset;
}
gic_set_base_accessor(gic, gic_get_percpu_base);
} else {
/* Normal, sane GIC... */
WARN(gic->percpu_offset,
"GIC_NON_BANKED not enabled, ignoring %08x offset!",
gic->percpu_offset);
gic->dist_base.common_base = gic->raw_dist_base;
gic->cpu_base.common_base = gic->raw_cpu_base;
gic_set_base_accessor(gic, gic_get_common_base);
}
/*
* Find out how many interrupts are supported.
* The GIC only supports up to 1020 interrupt sources.
*/
gic_irqs = readl_relaxed(gic_data_dist_base(gic) + GIC_DIST_CTR) & 0x1f;
gic_irqs = (gic_irqs + 1) * 32;
if (gic_irqs > 1020)
gic_irqs = 1020;
gic->gic_irqs = gic_irqs;
if (handle) { /* DT/ACPI */
gic->domain = irq_domain_create_linear(handle, gic_irqs,
&gic_irq_domain_hierarchy_ops,
gic);
} else { /* Legacy support */
/*
* For primary GICs, skip over SGIs.
* For secondary GICs, skip over PPIs, too.
*/
if (gic == &gic_data[0] && (irq_start & 31) > 0) {
hwirq_base = 16;
if (irq_start != -1)
irq_start = (irq_start & ~31) + 16;
} else {
hwirq_base = 32; //对于second GIC
}
gic_irqs -= hwirq_base; /* calculate # of irqs to allocate */
irq_base = irq_alloc_descs(irq_start, 16, gic_irqs,
numa_node_id());
if (irq_base < 0) {
WARN(1, "Cannot allocate irq_descs @ IRQ%d, assuming pre-allocated\n",
irq_start);
irq_base = irq_start;
}
gic->domain = irq_domain_add_legacy(NULL, gic_irqs, irq_base,
hwirq_base, &gic_irq_domain_ops, gic);
}
if (WARN_ON(!gic->domain)) {
ret = -ENODEV;
goto error;
}
gic_dist_init(gic);
ret = gic_cpu_init(gic);
if (ret)
goto error;
ret = gic_pm_init(gic);
if (ret)
goto error;
return 0;
error:
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GIC_NON_BANKED) && gic->percpu_offset) {
free_percpu(gic->dist_base.percpu_base);
free_percpu(gic->cpu_base.percpu_base);
}
return ret;
}
second GIC初始化之后,该irq domain的HW interrupt ID和IRQ number的映射关系已经建立,保存在线性lookup table中,size等于GIC支持的中断数目,具体如下:
index 0~32对应的IRQ无效
root GIC申请的最后一个IRQ号+1 <------------------>32号HW interrupt ID
root GIC申请的最后一个IRQ号+2 <------------------>33号HW interrupt ID
回到gic的初始化函数,对于second GIC,还有其他部分的初始化内容:drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c
int __init
gic_of_init(struct device_node *node, struct device_node *parent)
{
struct gic_chip_data *gic;
int irq, ret;
if (WARN_ON(!node))
return -ENODEV;
if (WARN_ON(gic_cnt >= CONFIG_ARM_GIC_MAX_NR))
return -EINVAL;
gic = &gic_data[gic_cnt];
ret = gic_of_setup(gic, node);
if (ret)
return ret;
/*
* Disable split EOI/Deactivate if either HYP is not available
* or the CPU interface is too small.
*/
if (gic_cnt == 0 && !gic_check_eoimode(node, &gic->raw_cpu_base))
static_branch_disable(&supports_deactivate_key);
ret = __gic_init_bases(gic, -1, &node->fwnode);
if (ret) {
gic_teardown(gic);
return ret;
}
if (!gic_cnt) {
gic_init_physaddr(node);
gic_of_setup_kvm_info(node);
}
if (parent) {
irq = irq_of_parse_and_map(node, 0); /* 解析second GIC的interrupts属性,并进行mapping,返回IRQ number */
gic_cascade_irq(gic_cnt, irq); /* 设置handler */
}
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ARM_GIC_V2M))
gicv2m_init(&node->fwnode, gic_data[gic_cnt].domain);
gic_cnt++;
return 0;
}
对于root GIC,其传入的parent是NULL,因此不会执行级联部分的代码。对于second GIC,它是作为其parent(root GIC)的一个普通的irq source,因此,也需要注册该IRQ的handler。由此可见,非root的GIC的初始化分成了两个部分:一部分是作为一个interrupt controller,执行和root GIC一样的初始化代码。另外一方面,GIC又作为一个普通的interrupt generating device,需要象一个普通的设备驱动一样,注册其中断handler。
irq_of_parse_and_map函数相信大家已经熟悉了,这里不再描述。gic_cascade_irq函数如下:
drivers/of/irq.c
/**
* irq_of_parse_and_map - Parse and map an interrupt into linux virq space
* @dev: Device node of the device whose interrupt is to be mapped
* @index: Index of the interrupt to map
*
* This function is a wrapper that chains of_irq_parse_one() and
* irq_create_of_mapping() to make things easier to callers
*/
unsigned int irq_of_parse_and_map(struct device_node *dev, int index)
{
struct of_phandle_args oirq;
if (of_irq_parse_one(dev, index, &oirq))
return 0;
return irq_create_of_mapping(&oirq);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(irq_of_parse_and_map);
drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c
void __init gic_cascade_irq(unsigned int gic_nr, unsigned int irq)
{
BUG_ON(gic_nr >= CONFIG_ARM_GIC_MAX_NR);
irq_set_chained_handler_and_data(irq, gic_handle_cascade_irq,
&gic_data[gic_nr]);
}
kernel/irq/chip.c
void
irq_set_chained_handler_and_data(unsigned int irq, irq_flow_handler_t handle,
void *data)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_get_desc_buslock(irq, &flags, 0);
if (!desc)
return;
desc->irq_common_data.handler_data = data; /* 设置handler data */
__irq_do_set_handler(desc, handle, 1, NULL); /* 设置handler */
irq_put_desc_busunlock(desc, flags);
}
6.2、具体如何在中断处理过程中,将HW interrupt ID转成IRQ number
在系统的启动过程中,经过了各个interrupt controller以及各个外设驱动的努力,整个interrupt系统的database(将HW interrupt ID转成IRQ number的数据库,这里的数据库不是指SQL lite或者oracle这样通用数据库软件)已经建立。一旦发生硬件中断,经过CPU architecture相关的中断代码之后,会调用irq handler,该函数的一般过程如下:
(1)首先找到root interrupt controller对应的irq domain。
(2)根据HW 寄存器信息和irq domain信息获取HW interrupt ID。
(3)调用irq_find_mapping找到HW interrupt ID对应的irq number。
(4)调用handle_IRQ(对于ARM平台)来处理该irq number。
对于级联的情况,过程类似上面的描述,但是需要注意的是在步骤4中不是直接调用该IRQ的hander来处理该irq number因为,这个irq需要各个interrupt controller level上的解析。举一个简单的二阶级联情况:假设系统中有两个interrupt controller,A和B,A是root interrupt controller,B连接到A的13号HW interrupt ID上。在B interrupt controller初始化的时候,除了初始化它作为interrupt controller的那部分内容,还有初始化它作为root interrupt controller A上的一个普通外设这部分的内容。最重要的是调用irq_set_chained_handler设定handler。这样,在上面的步骤4的时候,就会调用13号HW interrupt ID对应的handler(也就是B的handler),在该handler中,会重复上面的(1)~(4)。
其过程如下代码:drivers/irqchip/irq-gic.c
static void gic_handle_cascade_irq(struct irq_desc *desc)
{
struct gic_chip_data *chip_data = irq_desc_get_handler_data(desc); //获取到该gic数据
struct irq_chip *chip = irq_desc_get_chip(desc); //低级中断的访问
unsigned int cascade_irq, gic_irq;
unsigned long status;
chained_irq_enter(chip, desc);
/* 获取中断状态(也是中断号) */
status = readl_relaxed(gic_data_cpu_base(chip_data) + GIC_CPU_INTACK);
gic_irq = (status & GICC_IAR_INT_ID_MASK);
if (gic_irq == GICC_INT_SPURIOUS) //确认不是假中断
goto out;
/* 获取级联号或者实际中断号 */
cascade_irq = irq_find_mapping(chip_data->domain, gic_irq);
if (unlikely(gic_irq < 32 || gic_irq > 1020)) {
handle_bad_irq(desc); //一个普通gic只能执行 32 ~ 1019之间的中断
} else {
isb();
generic_handle_irq(cascade_irq); //执行中断处理
}
out:
chained_irq_exit(chip, desc);
}
/**
* generic_handle_irq - Invoke the handler for a particular irq
* @irq: The irq number to handle
*
*/
int generic_handle_irq(unsigned int irq)
{
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(irq);
if (!desc)
return -EINVAL;
generic_handle_irq_desc(desc); //通用中断函数
return 0;
}
/*
* Architectures call this to let the generic IRQ layer
* handle an interrupt.
*/
static inline void generic_handle_irq_desc(struct irq_desc *desc)
{
//如果这是一个普通设备,那就执行这个设备驱动具体绑定的中断函数了,
//如果是级联的一个中断控制器设备,那么还会在找到对应中断控制器绑定的处理函数,继续这样递归下去知道知道真正的中断设备,执行对应的中断函数
desc->handle_irq(desc);
}





















 742
742

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








