Linux-进程的管理与调度8(基于6.1内核)---进程的创建过程分析
一、fork,vfork,clone
Linux标准的复制进程的系统调用时fork(即分叉),但是Linux,BSD等操作系统并不止实现这一个,确切的说linux实现了三个,fork,vfork,clone(确切说vfork创造出来的是轻量级进程,也叫线程,是共享资源的进程)
| 系统调用 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| fork | fork创造的子进程是父进程的完整副本,复制了父亲进程的资源,包括内存的内容task_struct内容。 |
| vfork | vfork创建的子进程与父进程共享数据段,而且由vfork()创建的子进程将先于父进程运行。 |
| clone | Linux上创建线程一般使用的是pthread库 实际上linux也给我们提供了创建线程的系统调用,就是clone。 |
fork, vfork和clone的系统调用的入口地址分别是sys_fork, sys_vfork和sys_clone, 而他们的定义是依赖于体系结构的, 因为在用户空间和内核空间之间传递参数的方法因体系结构而异。
系统调用的参数传递
系统调用的实现与C库不同, 普通C函数通过将参数的值压入到进程的栈中进行参数的传递。由于系统调用是通过中断进程从用户态到内核态的一种特殊的函数调用,没有用户态或者内核态的堆栈可以被用来在调用函数和被调函数之间进行参数传递。系统调用通过CPU的寄存器来进行参数传递。在进行系统调用之前,系统调用的参数被写入CPU的寄存器,而在实际调用系统服务例程之前,内核将CPU寄存器的内容拷贝到内核堆栈中,实现参数的传递。
即不同的体系结构可能需要采用不同的方式或者寄存器来存储函数调用的参数, 因此linux在设计系统调用的时候, 将其划分成体系结构相关的层次和体系结构无关的层次, 前者复杂提取出依赖与体系结构的特定的参数, 后者则依据参数的设置执行特定的真正操作。
二、fork, vfork, clone系统调用的实现
2.1、do_fork的改变
在 Linux 6.1 版本中,do_fork() 函数不再直接存在于 kernel/fork.c 文件中。这是因为在 Linux 内核的开发过程中,为了提高代码的可维护性和模块化,很多核心功能被重构或拆分成更小的部分。do_fork() 的功能被分散到了多个相关的函数和文件中。
在 Linux 6.1 中,进程创建的主要逻辑现在通过以下步骤和相关函数来实现:
do_fork()功能的替代:- 虽然
do_fork()函数本身在kernel/fork.c中不存在,但相关的功能被封装在 __ARCH_WANT_SYS_FORK, __ARCH_WANT_SYS_VFORK, __ARCH_WANT_SYS_CLONE等函数中。这些函数是系统调用的后端实现,用于处理不同的进程创建和执行请求。
- 虽然
- 核心函数:
- __ARCH_WANT_SYS_FORK, __ARCH_WANT_SYS_VFORK, __ARCH_WANT_SYS_CLONE等函数最终会调用一个更底层的函数
copy_process(),它负责实际的进程创建和状态复制工作。 copy_process()函数在kernel/fork.c文件中可以找到,它负责为新的进程分配必要的内核数据结构(如任务结构体task_struct),复制父进程的上下文(如寄存器状态、文件描述符表、内存空间等),并设置新的进程状态。
- __ARCH_WANT_SYS_FORK, __ARCH_WANT_SYS_VFORK, __ARCH_WANT_SYS_CLONE等函数最终会调用一个更底层的函数
- 进程调度:
- 在
copy_process()完成后,新创建的进程会被添加到调度器的就绪队列中,等待 CPU 分配时间片运行。 - 调度相关的代码位于
kernel/sched/目录下,其中wake_up_new_task()函数负责将新创建的进程唤醒并加入到调度队列。
- 在
- 系统调用接口:
- 用户空间程序通过调用系统调用(如
fork(),vfork(),clone(),execve())来请求创建新进程。 - 这些系统调用在内核中被映射到相应的处理函数(如
sys_fork(),sys_vfork(),sys_clone(),sys_execve()),这些函数再调用上述的do_sys_*系列函数。
- 用户空间程序通过调用系统调用(如
- 其他相关文件:
kernel/exit.c:处理进程的退出和清理工作。fs/namespace.c:处理文件系统的命名空间,与进程的文件描述符表相关。mm/memory.c和相关文件:处理进程的内存管理。
其中clone_flags如下表所示
/*
* cloning flags:
*/
#define CSIGNAL 0x000000ff /* signal mask to be sent at exit */
#define CLONE_VM 0x00000100 /* set if VM shared between processes */
#define CLONE_FS 0x00000200 /* set if fs info shared between processes */
#define CLONE_FILES 0x00000400 /* set if open files shared between processes */
#define CLONE_SIGHAND 0x00000800 /* set if signal handlers and blocked signals shared */
#define CLONE_PIDFD 0x00001000 /* set if a pidfd should be placed in parent */
#define CLONE_PTRACE 0x00002000 /* set if we want to let tracing continue on the child too */
#define CLONE_VFORK 0x00004000 /* set if the parent wants the child to wake it up on mm_release */
#define CLONE_PARENT 0x00008000 /* set if we want to have the same parent as the cloner */
#define CLONE_THREAD 0x00010000 /* Same thread group? */
#define CLONE_NEWNS 0x00020000 /* New mount namespace group */
#define CLONE_SYSVSEM 0x00040000 /* share system V SEM_UNDO semantics */
#define CLONE_SETTLS 0x00080000 /* create a new TLS for the child */
#define CLONE_PARENT_SETTID 0x00100000 /* set the TID in the parent */
#define CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID 0x00200000 /* clear the TID in the child */
#define CLONE_DETACHED 0x00400000 /* Unused, ignored */
#define CLONE_UNTRACED 0x00800000 /* set if the tracing process can't force CLONE_PTRACE on this clone */
#define CLONE_CHILD_SETTID 0x01000000 /* set the TID in the child */
#define CLONE_NEWCGROUP 0x02000000 /* New cgroup namespace */
#define CLONE_NEWUTS 0x04000000 /* New utsname namespace */
#define CLONE_NEWIPC 0x08000000 /* New ipc namespace */
#define CLONE_NEWUSER 0x10000000 /* New user namespace */
#define CLONE_NEWPID 0x20000000 /* New pid namespace */
#define CLONE_NEWNET 0x40000000 /* New network namespace */
#define CLONE_IO 0x80000000 /* Clone io context */
2.2、sys_fork的实现
#ifdef __ARCH_WANT_SYS_FORK
SYSCALL_DEFINE0(fork)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_MMU
struct kernel_clone_args args = {
.exit_signal = SIGCHLD,
};
return kernel_clone(&args);
#else
/* can not support in nommu mode */
return -EINVAL;
#endif
}
#endif可以看到唯一使用的标志是SIGCHLD。这意味着在子进程终止后将发送信号SIGCHLD信号通知父进程,
由于写时复制(COW)技术, 最初父子进程的栈地址相同, 但是如果操作栈地址闭并写入数据, 则COW机制会为每个进程分别创建一个新的栈副本
如果do_fork成功, 则新建进程的pid作为系统调用的结果返回, 否则返回错误码
2.3、sys_vfork的实现
#ifdef __ARCH_WANT_SYS_VFORK
SYSCALL_DEFINE0(vfork)
{
struct kernel_clone_args args = {
.flags = CLONE_VFORK | CLONE_VM,
.exit_signal = SIGCHLD,
};
return kernel_clone(&args);
}
#endif可以看到sys_vfork的实现与sys_fork只是略微不同, 前者使用了额外的标志CLONE_VFORK | CLONE_VM
2.4、sys_clone的实现
#ifdef __ARCH_WANT_SYS_CLONE
#ifdef CONFIG_CLONE_BACKWARDS
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(clone, unsigned long, clone_flags, unsigned long, newsp,
int __user *, parent_tidptr,
unsigned long, tls,
int __user *, child_tidptr)
#elif defined(CONFIG_CLONE_BACKWARDS2)
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(clone, unsigned long, newsp, unsigned long, clone_flags,
int __user *, parent_tidptr,
int __user *, child_tidptr,
unsigned long, tls)
#elif defined(CONFIG_CLONE_BACKWARDS3)
SYSCALL_DEFINE6(clone, unsigned long, clone_flags, unsigned long, newsp,
int, stack_size,
int __user *, parent_tidptr,
int __user *, child_tidptr,
unsigned long, tls)
#else
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(clone, unsigned long, clone_flags, unsigned long, newsp,
int __user *, parent_tidptr,
int __user *, child_tidptr,
unsigned long, tls)
#endif
{
struct kernel_clone_args args = {
.flags = (lower_32_bits(clone_flags) & ~CSIGNAL),
.pidfd = parent_tidptr,
.child_tid = child_tidptr,
.parent_tid = parent_tidptr,
.exit_signal = (lower_32_bits(clone_flags) & CSIGNAL),
.stack = newsp,
.tls = tls,
};
return kernel_clone(&args);
}
#endif可以看到sys_clone的标识不再是硬编码的, 而是通过各个寄存器参数传递到系统调用, 需要提取这些参数。
另外,clone也不再复制进程的栈, 而是可以指定新的栈地址, 在生成线程时, 可能需要这样做, 线程可能与父进程共享地址空间, 但是线程自身的栈可能在另外一个地址空间
另外还指令了用户空间的两个指针(parent_tidptr和child_tidptr), 用于与线程库通信。
三、创建子进程的流程
3.1、do_fork的流程
在 Linux 6.1 中,进程创建的实现已经做了调整,do_fork 并不再直接作为一个单独的函数存在。相反,do_fork 被其他更具功能性和灵活性的函数所取代。进程创建的流程现在是通过 kernel/fork.c 中的多个函数__ARCH_WANT_SYS_FORK、__ARCH_WANT_SYS_VFORK、__ARCH_WANT_SYS_CLONE来实现的。
具体而言,进程创建的过程会通过以下函数和机制来完成:
sys_clone以调用copy_process开始, 后者执行生成新的进程的实际工作, 并根据指定的标志复制父进程的数据。在子进程生成后, 内核必须执行下列收尾操作:
-
调用 copy_process 为子进程复制出一份进程信息
-
如果是 vfork(设置了CLONE_VFORK和ptrace标志)初始化完成处理信息
-
调用 wake_up_new_task 将子进程加入调度器,为之分配 CPU
-
如果是 vfork,父进程等待子进程完成 exec 替换自己的地址空间
sys_clone 是 Linux 中的系统调用入口,它会根据传入的参数(例如 clone_flags)来决定如何创建一个新进程。sys_clone 是内核提供的系统调用接口,用户空间的进程可以通过它来请求内核创建新进程。它的定义通常在 kernel/sys.c 文件中。
pid_t kernel_clone(struct kernel_clone_args *args)
{
u64 clone_flags = args->flags;
struct completion vfork;
struct pid *pid;
struct task_struct *p;
int trace = 0;
pid_t nr;
/*
* For legacy clone() calls, CLONE_PIDFD uses the parent_tid argument
* to return the pidfd. Hence, CLONE_PIDFD and CLONE_PARENT_SETTID are
* mutually exclusive. With clone3() CLONE_PIDFD has grown a separate
* field in struct clone_args and it still doesn't make sense to have
* them both point at the same memory location. Performing this check
* here has the advantage that we don't need to have a separate helper
* to check for legacy clone().
*/
if ((args->flags & CLONE_PIDFD) &&
(args->flags & CLONE_PARENT_SETTID) &&
(args->pidfd == args->parent_tid))
return -EINVAL;
/*
* Determine whether and which event to report to ptracer. When
* called from kernel_thread or CLONE_UNTRACED is explicitly
* requested, no event is reported; otherwise, report if the event
* for the type of forking is enabled.
*/
if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_UNTRACED)) {
if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK)
trace = PTRACE_EVENT_VFORK;
else if (args->exit_signal != SIGCHLD)
trace = PTRACE_EVENT_CLONE;
else
trace = PTRACE_EVENT_FORK;
if (likely(!ptrace_event_enabled(current, trace)))
trace = 0;
}
p = copy_process(NULL, trace, NUMA_NO_NODE, args);
add_latent_entropy();
if (IS_ERR(p))
return PTR_ERR(p);
...
}3.2、copy_process流程
copy_process的流程:
-
调用 dup_task_struct 复制当前的 task_struct
-
检查进程数是否超过限制
-
初始化自旋锁、挂起信号、CPU 定时器等
-
调用 sched_fork 初始化进程数据结构,并把进程状态设置为 TASK_RUNNING
-
复制所有进程信息,包括文件系统、信号处理函数、信号、内存管理等
-
调用 copy_thread_tls 初始化子进程内核栈
-
为新进程分配并设置新的 pid
kernel/fork.c
__latent_entropy struct task_struct *copy_process(
struct pid *pid,
int trace,
int node,
struct kernel_clone_args *args)
{
int pidfd = -1, retval;
struct task_struct *p;
struct multiprocess_signals delayed;
struct file *pidfile = NULL;
const u64 clone_flags = args->flags;
struct nsproxy *nsp = current->nsproxy;
/*
* Don't allow sharing the root directory with processes in a different
* namespace
*/
if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS)) == (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_NEWUSER|CLONE_FS)) == (CLONE_NEWUSER|CLONE_FS))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
if ((clone_flags & CLONE_NEWUSER) && !unprivileged_userns_clone)
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
return ERR_PTR(-EPERM);
/*
* Thread groups must share signals as well, and detached threads
* can only be started up within the thread group.
*/
if ((clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) && !(clone_flags & CLONE_SIGHAND))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
/*
* Shared signal handlers imply shared VM. By way of the above,
* thread groups also imply shared VM. Blocking this case allows
* for various simplifications in other code.
*/
if ((clone_flags & CLONE_SIGHAND) && !(clone_flags & CLONE_VM))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
/*
* Siblings of global init remain as zombies on exit since they are
* not reaped by their parent (swapper). To solve this and to avoid
* multi-rooted process trees, prevent global and container-inits
* from creating siblings.
*/
if ((clone_flags & CLONE_PARENT) &&
current->signal->flags & SIGNAL_UNKILLABLE)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
/*
* If the new process will be in a different pid or user namespace
* do not allow it to share a thread group with the forking task.
*/
if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) {
if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_NEWUSER | CLONE_NEWPID)) ||
(task_active_pid_ns(current) != nsp->pid_ns_for_children))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
if (clone_flags & CLONE_PIDFD) {
/*
* - CLONE_DETACHED is blocked so that we can potentially
* reuse it later for CLONE_PIDFD.
* - CLONE_THREAD is blocked until someone really needs it.
*/
if (clone_flags & (CLONE_DETACHED | CLONE_THREAD))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
/*
* Force any signals received before this point to be delivered
* before the fork happens. Collect up signals sent to multiple
* processes that happen during the fork and delay them so that
* they appear to happen after the fork.
*/
sigemptyset(&delayed.signal);
INIT_HLIST_NODE(&delayed.node);
spin_lock_irq(¤t->sighand->siglock);
if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD))
hlist_add_head(&delayed.node, ¤t->signal->multiprocess);
recalc_sigpending();
spin_unlock_irq(¤t->sighand->siglock);
retval = -ERESTARTNOINTR;
if (task_sigpending(current))
goto fork_out;
retval = -ENOMEM;
p = dup_task_struct(current, node);
if (!p)
goto fork_out;
p->flags &= ~PF_KTHREAD;
if (args->kthread)
p->flags |= PF_KTHREAD;
if (args->user_worker) {
/*
* Mark us a user worker, and block any signal that isn't
* fatal or STOP
*/
p->flags |= PF_USER_WORKER;
siginitsetinv(&p->blocked, sigmask(SIGKILL)|sigmask(SIGSTOP));
}
if (args->io_thread)
p->flags |= PF_IO_WORKER;
if (args->name)
strscpy_pad(p->comm, args->name, sizeof(p->comm));
p->set_child_tid = (clone_flags & CLONE_CHILD_SETTID) ? args->child_tid : NULL;
/*
* Clear TID on mm_release()?
*/
p->clear_child_tid = (clone_flags & CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID) ? args->child_tid : NULL;
ftrace_graph_init_task(p);
rt_mutex_init_task(p);
lockdep_assert_irqs_enabled();
#ifdef CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKING
DEBUG_LOCKS_WARN_ON(!p->softirqs_enabled);
#endif
retval = copy_creds(p, clone_flags);
if (retval < 0)
goto bad_fork_free;
retval = -EAGAIN;
if (is_rlimit_overlimit(task_ucounts(p), UCOUNT_RLIMIT_NPROC, rlimit(RLIMIT_NPROC))) {
if (p->real_cred->user != INIT_USER &&
!capable(CAP_SYS_RESOURCE) && !capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
goto bad_fork_cleanup_count;
}
current->flags &= ~PF_NPROC_EXCEEDED;
/*
* If multiple threads are within copy_process(), then this check
* triggers too late. This doesn't hurt, the check is only there
* to stop root fork bombs.
*/
retval = -EAGAIN;
if (data_race(nr_threads >= max_threads))
goto bad_fork_cleanup_count;
delayacct_tsk_init(p); /* Must remain after dup_task_struct() */
p->flags &= ~(PF_SUPERPRIV | PF_WQ_WORKER | PF_IDLE | PF_NO_SETAFFINITY);
p->flags |= PF_FORKNOEXEC;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->children);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->sibling);
rcu_copy_process(p);
p->vfork_done = NULL;
spin_lock_init(&p->alloc_lock);
init_sigpending(&p->pending);
p->utime = p->stime = p->gtime = 0;
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SCALED_CPUTIME
p->utimescaled = p->stimescaled = 0;
#endif
prev_cputime_init(&p->prev_cputime);
#ifdef CONFIG_VIRT_CPU_ACCOUNTING_GEN
seqcount_init(&p->vtime.seqcount);
p->vtime.starttime = 0;
p->vtime.state = VTIME_INACTIVE;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_IO_URING
p->io_uring = NULL;
#endif
#if defined(SPLIT_RSS_COUNTING)
memset(&p->rss_stat, 0, sizeof(p->rss_stat));
#endif
p->default_timer_slack_ns = current->timer_slack_ns;
#ifdef CONFIG_PSI
p->psi_flags = 0;
#endif
task_io_accounting_init(&p->ioac);
acct_clear_integrals(p);
posix_cputimers_init(&p->posix_cputimers);
p->io_context = NULL;
audit_set_context(p, NULL);
cgroup_fork(p);
if (args->kthread) {
if (!set_kthread_struct(p))
goto bad_fork_cleanup_delayacct;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
p->mempolicy = mpol_dup(p->mempolicy);
if (IS_ERR(p->mempolicy)) {
retval = PTR_ERR(p->mempolicy);
p->mempolicy = NULL;
goto bad_fork_cleanup_delayacct;
}
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CPUSETS
p->cpuset_mem_spread_rotor = NUMA_NO_NODE;
p->cpuset_slab_spread_rotor = NUMA_NO_NODE;
seqcount_spinlock_init(&p->mems_allowed_seq, &p->alloc_lock);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGS
memset(&p->irqtrace, 0, sizeof(p->irqtrace));
p->irqtrace.hardirq_disable_ip = _THIS_IP_;
p->irqtrace.softirq_enable_ip = _THIS_IP_;
p->softirqs_enabled = 1;
p->softirq_context = 0;
#endif
p->pagefault_disabled = 0;
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
lockdep_init_task(p);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_MUTEXES
p->blocked_on = NULL; /* not blocked yet */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BCACHE
p->sequential_io = 0;
p->sequential_io_avg = 0;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BPF_SYSCALL
RCU_INIT_POINTER(p->bpf_storage, NULL);
p->bpf_ctx = NULL;
#endif
/* Perform scheduler related setup. Assign this task to a CPU. */
retval = sched_fork(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_policy;
retval = perf_event_init_task(p, clone_flags);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_policy;
retval = audit_alloc(p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_perf;
/* copy all the process information */
shm_init_task(p);
retval = security_task_alloc(p, clone_flags);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_audit;
retval = copy_semundo(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_security;
retval = copy_files(clone_flags, p, args->no_files);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_semundo;
retval = copy_fs(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_files;
retval = copy_sighand(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_fs;
retval = copy_signal(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_sighand;
retval = copy_mm(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_signal;
retval = copy_namespaces(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_mm;
retval = copy_io(clone_flags, p);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_namespaces;
retval = copy_thread(p, args);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_cleanup_io;
stackleak_task_init(p);
if (pid != &init_struct_pid) {
pid = alloc_pid(p->nsproxy->pid_ns_for_children, args->set_tid,
args->set_tid_size);
if (IS_ERR(pid)) {
retval = PTR_ERR(pid);
goto bad_fork_cleanup_thread;
}
}
/*
* This has to happen after we've potentially unshared the file
* descriptor table (so that the pidfd doesn't leak into the child
* if the fd table isn't shared).
*/
if (clone_flags & CLONE_PIDFD) {
/* Note that no task has been attached to @pid yet. */
retval = __pidfd_prepare(pid, O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC, &pidfile);
if (retval < 0)
goto bad_fork_free_pid;
pidfd = retval;
retval = put_user(pidfd, args->pidfd);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_put_pidfd;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_BLOCK
p->plug = NULL;
#endif
futex_init_task(p);
/*
* sigaltstack should be cleared when sharing the same VM
*/
if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_VM|CLONE_VFORK)) == CLONE_VM)
sas_ss_reset(p);
/*
* Syscall tracing and stepping should be turned off in the
* child regardless of CLONE_PTRACE.
*/
user_disable_single_step(p);
clear_task_syscall_work(p, SYSCALL_TRACE);
#if defined(CONFIG_GENERIC_ENTRY) || defined(TIF_SYSCALL_EMU)
clear_task_syscall_work(p, SYSCALL_EMU);
#endif
clear_tsk_latency_tracing(p);
/* ok, now we should be set up.. */
p->pid = pid_nr(pid);
if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) {
p->group_leader = current->group_leader;
p->tgid = current->tgid;
} else {
p->group_leader = p;
p->tgid = p->pid;
}
p->nr_dirtied = 0;
p->nr_dirtied_pause = 128 >> (PAGE_SHIFT - 10);
p->dirty_paused_when = 0;
p->pdeath_signal = 0;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->thread_group);
p->task_works = NULL;
clear_posix_cputimers_work(p);
#ifdef CONFIG_KRETPROBES
p->kretprobe_instances.first = NULL;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_RETHOOK
p->rethooks.first = NULL;
#endif
/*
* Ensure that the cgroup subsystem policies allow the new process to be
* forked. It should be noted that the new process's css_set can be changed
* between here and cgroup_post_fork() if an organisation operation is in
* progress.
*/
retval = cgroup_can_fork(p, args);
if (retval)
goto bad_fork_put_pidfd;
/*
* Now that the cgroups are pinned, re-clone the parent cgroup and put
* the new task on the correct runqueue. All this *before* the task
* becomes visible.
*
* This isn't part of ->can_fork() because while the re-cloning is
* cgroup specific, it unconditionally needs to place the task on a
* runqueue.
*/
sched_cgroup_fork(p, args);
/*
* From this point on we must avoid any synchronous user-space
* communication until we take the tasklist-lock. In particular, we do
* not want user-space to be able to predict the process start-time by
* stalling fork(2) after we recorded the start_time but before it is
* visible to the system.
*/
p->start_time = ktime_get_ns();
p->start_boottime = ktime_get_boottime_ns();
/*
* Make it visible to the rest of the system, but dont wake it up yet.
* Need tasklist lock for parent etc handling!
*/
write_lock_irq(&tasklist_lock);
/* CLONE_PARENT re-uses the old parent */
if (clone_flags & (CLONE_PARENT|CLONE_THREAD)) {
p->real_parent = current->real_parent;
p->parent_exec_id = current->parent_exec_id;
if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD)
p->exit_signal = -1;
else
p->exit_signal = current->group_leader->exit_signal;
} else {
p->real_parent = current;
p->parent_exec_id = current->self_exec_id;
p->exit_signal = args->exit_signal;
}
klp_copy_process(p);
sched_core_fork(p);
spin_lock(¤t->sighand->siglock);
// ......
return p;
}3.3、dup_task_struct 流程
http://lxr.free-electrons.com/source/kernel/fork.c?v=4.5#L334
static struct task_struct *dup_task_struct(struct task_struct *orig, int node)
{
struct task_struct *tsk;
int err;
if (node == NUMA_NO_NODE)
node = tsk_fork_get_node(orig);
tsk = alloc_task_struct_node(node);
if (!tsk)
return NULL;
err = arch_dup_task_struct(tsk, orig);
if (err)
goto free_tsk;
err = alloc_thread_stack_node(tsk, node);
if (err)
goto free_tsk;
#ifdef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
refcount_set(&tsk->stack_refcount, 1);
#endif
account_kernel_stack(tsk, 1);
err = scs_prepare(tsk, node);
if (err)
goto free_stack;
...
return tsk;
}-
调用alloc_task_struct_node分配一个 task_struct 节点
-
调用alloc_thread_info_node分配一个 thread_info 节点,其实是分配了一个thread_union联合体,将栈底返回给 ti
union thread_union {
struct thread_info thread_info;
unsigned long stack[THREAD_SIZE/sizeof(long)];
};-
最后将栈底的值 ti 赋值给新节点的栈
-
最终执行完dup_task_struct之后,子进程除了tsk->stack指针不同之外,全部都一样!
3.4、sched_fork 流程
/*
* fork()/clone()-time setup:
*/
int sched_fork(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct *p)
{
__sched_fork(clone_flags, p);
/*
* We mark the process as NEW here. This guarantees that
* nobody will actually run it, and a signal or other external
* event cannot wake it up and insert it on the runqueue either.
*/
p->__state = TASK_NEW;
/*
* Make sure we do not leak PI boosting priority to the child.
*/
p->prio = current->normal_prio;
uclamp_fork(p);
/*
* Revert to default priority/policy on fork if requested.
*/
if (unlikely(p->sched_reset_on_fork)) {
if (task_has_dl_policy(p) || task_has_rt_policy(p)) {
p->policy = SCHED_NORMAL;
p->static_prio = NICE_TO_PRIO(0);
p->rt_priority = 0;
} else if (PRIO_TO_NICE(p->static_prio) < 0)
p->static_prio = NICE_TO_PRIO(0);
p->prio = p->normal_prio = p->static_prio;
set_load_weight(p, false);
/*
* We don't need the reset flag anymore after the fork. It has
* fulfilled its duty:
*/
p->sched_reset_on_fork = 0;
}
if (dl_prio(p->prio))
return -EAGAIN;
else if (rt_prio(p->prio))
p->sched_class = &rt_sched_class;
else
p->sched_class = &fair_sched_class;
init_entity_runnable_average(&p->se);
#ifdef CONFIG_SCHED_INFO
if (likely(sched_info_on()))
memset(&p->sched_info, 0, sizeof(p->sched_info));
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_SMP)
p->on_cpu = 0;
#endif
init_task_preempt_count(p);
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
plist_node_init(&p->pushable_tasks, MAX_PRIO);
RB_CLEAR_NODE(&p->pushable_dl_tasks);
#endif
return 0;
}我们可以看到sched_fork大致完成了两项重要工作,
-
一是将子进程状态设置为 TASK_RUNNING,
-
二是为其分配 CPU
3.5、copy_thread流程
int copy_thread(struct task_struct *p, const struct kernel_clone_args *args)
{
unsigned long clone_flags = args->flags;
unsigned long stack_start = args->stack;
unsigned long tls = args->tls;
struct thread_info *thread = task_thread_info(p);
struct pt_regs *childregs = task_pt_regs(p);
memset(&thread->cpu_context, 0, sizeof(struct cpu_context_save));
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_USE_DOMAINS
/*
* Copy the initial value of the domain access control register
* from the current thread: thread->addr_limit will have been
* copied from the current thread via setup_thread_stack() in
* kernel/fork.c
*/
thread->cpu_domain = get_domain();
#endif
if (likely(!args->fn)) {
*childregs = *current_pt_regs();
childregs->ARM_r0 = 0;
if (stack_start)
childregs->ARM_sp = stack_start;
} else {
memset(childregs, 0, sizeof(struct pt_regs));
thread->cpu_context.r4 = (unsigned long)args->fn_arg;
thread->cpu_context.r5 = (unsigned long)args->fn;
childregs->ARM_cpsr = SVC_MODE;
}
thread->cpu_context.pc = (unsigned long)ret_from_fork;
thread->cpu_context.sp = (unsigned long)childregs;
clear_ptrace_hw_breakpoint(p);
if (clone_flags & CLONE_SETTLS)
thread->tp_value[0] = tls;
thread->tp_value[1] = get_tpuser();
thread_notify(THREAD_NOTIFY_COPY, thread);
return 0;
}
copy_thread 这段代码为我们解释了两个相当重要的问题:
第一是,为什么 fork 在子进程中返回0,原因是childregs->ax = 0;这段代码将子进程的 eax 赋值为0。
第二是,p->thread.ip = (unsigned long) ret_from_fork;将子进程的 ip 设置为 ret_form_fork 的首地址,因此子进程是从 ret_from_fork 开始执行的。
进程的创建到执行过程如下图所示:
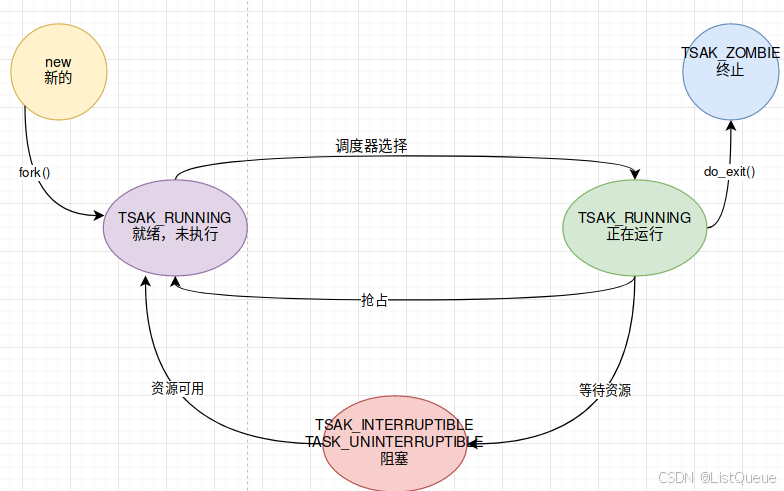





















 1040
1040

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








