springboot启动分为2部分:
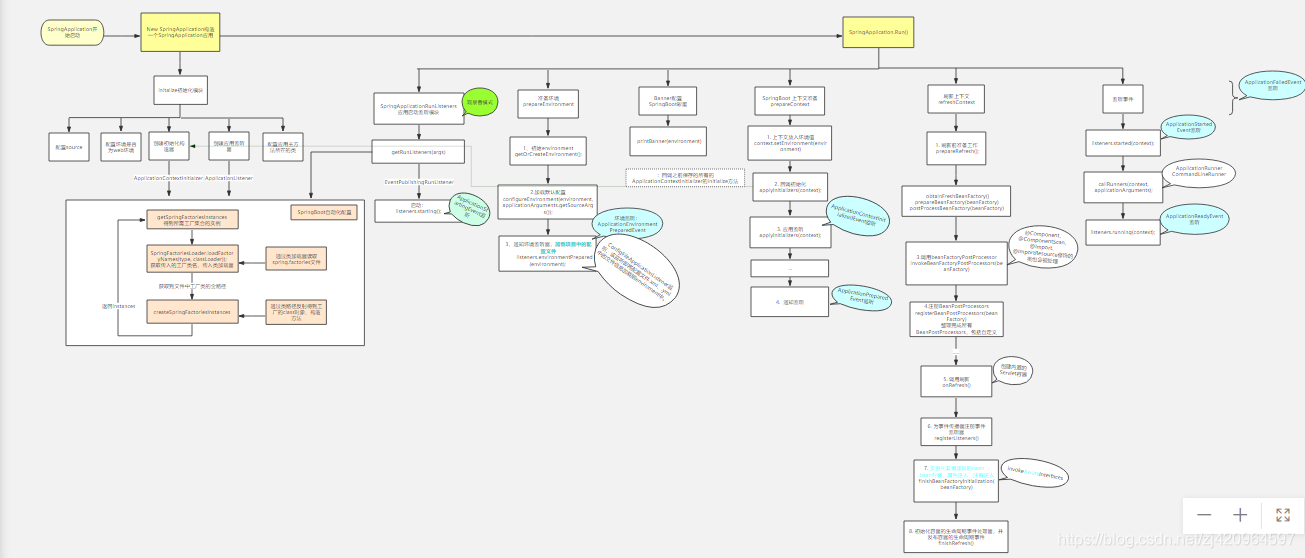
大图查看:https://www.processon.com/view/link/5cb0562ee4b0bb527acc9be9
Springboot 启动原理简单梳理:
1. 初始化构造器、初始化监听器
2. applicationStaringEvent监听
3. prepareEnvironment->ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent监听中的ConfigFileApplicationListener监听器,将配置文件xml、yml中配置信息加载到environment
4. banner->打印springboot彩蛋
5. prepareContext->ApplicationContextInitializedEvent监听->ApplicationPreparedEvent监听
6. refreshContext->处理@Component@ComponentScan@Import注解修饰的类->实例化非懒加载的bean,bean封装、属性注入、注解注入
7. ApplicationStartedEvent监听->AppliactionReadyEvent监听一、New SpringApplication()
二、Run()
第一部分New SpringApplication分析
直接从SpringApplication构造函数开始:
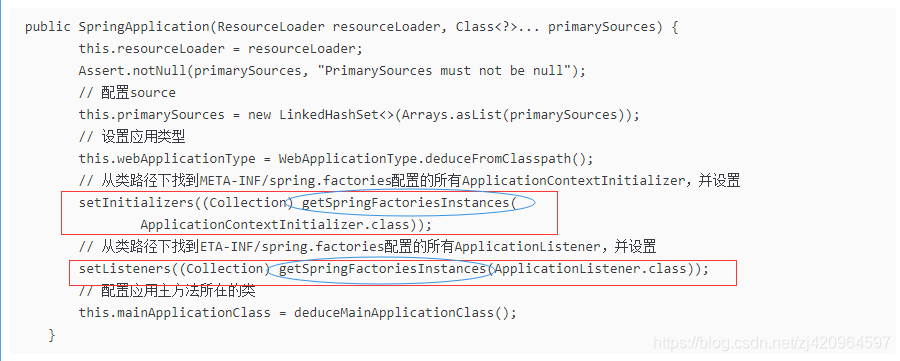
getSpringFactoriesInstances分析:
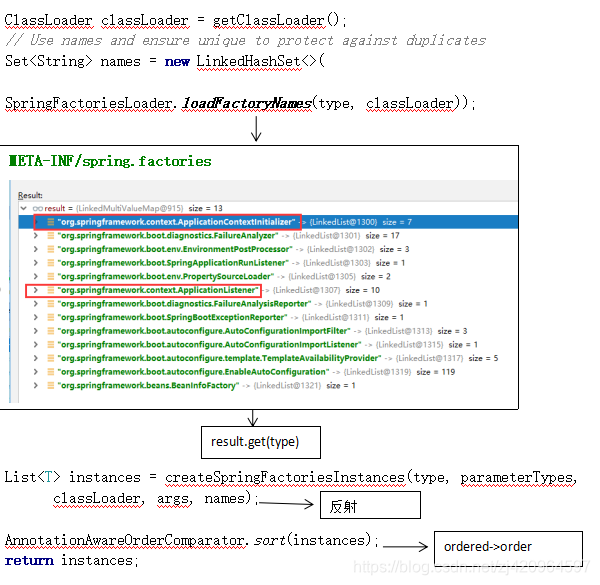
loadFactoryNames分析:
第一次启用时将META-INF/spring.factories的配置信息添加到result,并缓存起来
通过type(即META-INF/spring.factories的key)从result取出Set<String>
createSpringFactoriesInstances分析:
通过取出来的Set<String> names 进行反射,获取实例List<T>
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort分析:
通过实现org.springframework.core.Ordered接口,重新getOrder方法,通过order值可进行排序,使得调用顺序不同
deduceMainApplicationClass()分析:
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}通过堆栈中获取方法名为main的信息,找到当前类并返回
第二部分Run()分析
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 开始起止的监听
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 声明IOC容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// awt 相关,省略
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 得到一个org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//回调所有的获取SpringApplicationRunListener.starting()方法
// 启动ApplicationStartingEvent监听
listeners.starting();
try {
// 封装命令行参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
// 准备环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 控制台打印Spring banner图标
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建ApplicationContext;决定创建web的ioc还是普通的ioc
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// 准备上下文环境;将environment保存到ioc中;
// applyInitializers():回调之前保存的所有的ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize方法
// 回调所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的contextPrepared()
// prepareContext运行完成以后回调所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded()
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
// 刷新容器;ioc容器初始化(如果是web应用还会创建嵌入式的Tomcat);Spring注解版
// 扫描,创建,加载所有组件的地方;(配置类,组件,自动配置)
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}getRunListeners分析:
从result中读取key为:SpringApplicationRunListener的监听器,此次返回EventPublishingRunListener
listeners.starting()分析:
EventPublishingRunListener:启动事件发布监听器
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent( new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
//获取线程池,如果为空则同步处理。这里线程池为空,还未没初始化。
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
//异步发送事件
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
//同步发送事件
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
prepareEnvironment分析:
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
//1、初始化environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//2、加载默认配置
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//3、通知环境监听器,加载项目中的配置文件
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}listeners.environmentPrepared(environment)分析:1. 通知环境监听器进行监听
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
this.application, this.args, environment));2.加载项目中的配置文件
如进行加载:application.yml application.properties application-mybatis.yml 等
加载 application-mybatis.yml时,需要在application.yml中进行如下配置
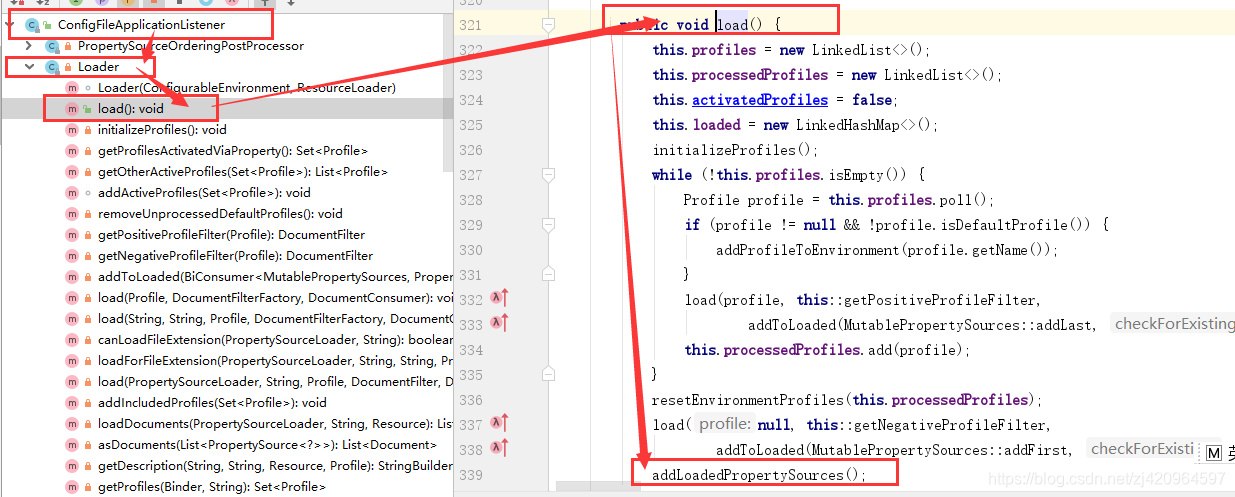
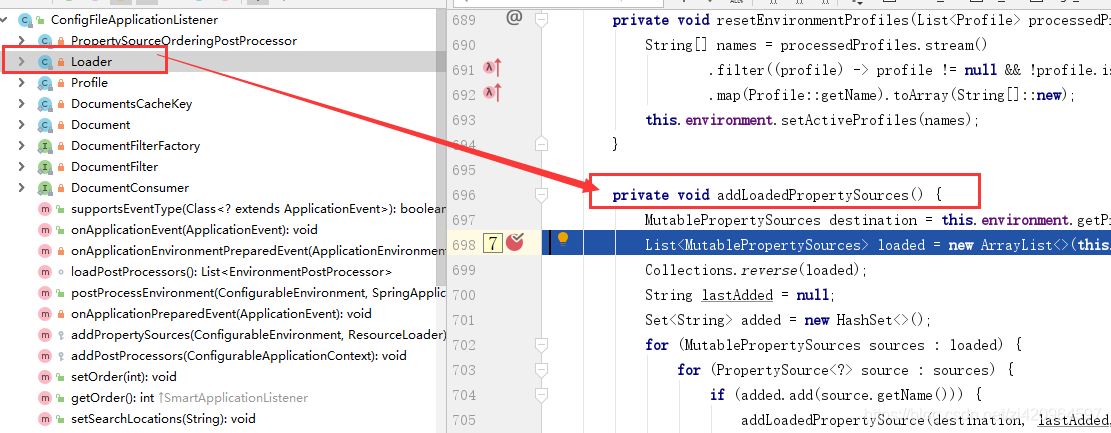
spring.profiles.active = mybatisctrl+左键点击spring.profiles.active 进入到 ConfigFileApplicationListener监听,该监听即将配置文件.xml、.yml中的文件信息加载到enviroment中。
调用链为:
ConfigFileApplicationListener的Loader下load()方法,然后进入addLoadedPropertySources()进行将配置信息绑定到environment的propertysources中
printBanner分析:
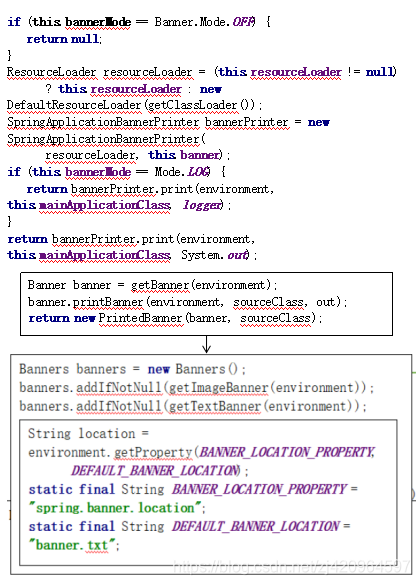
可resource/banner.txt自定义banner信息,或者配置文件中配置spring.banner.location中配置路径
prepareContext分析:

refreshContext(context)分析:class AbstractApplicationContext
......
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {//refresh过程只能一个线程处理,不允许并发执行
// 刷新前准备工作
prepareRefresh();
// 调用子类refreshBeanFactory()方法,获取bean factory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 创建bean Factory的通用设置,添加ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,
// ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisher、ApplicationContext这3个接口对应的bean都设置为当前的Spring容器,注册环境bean
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 子类特殊的bean factory设置
// GenericWebApplicationContext容器会在BeanFactory中添加ServletContextAwareProcessor用于处理ServletContextAware类型的bean初始化的时候调用setServletContext或者setServletConfig方法
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 实例化beanFactoryPostProcessor
// 调用beanFactoryPostProcessor 这里会调用ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,解析@Configuration的类为BeanDefinition,为后面实例化作准备
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册 beanPostProcessors 包括自定义的BeanPostProcessor
// 在实例化Bean后处理 比如AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理被@Autowired注解修饰的bean并注入)、RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(处理被@Required注解修饰的方法)
// 这些都是在创建Context时的reader的构造器中的AnnotationConfigUtils的registerAnnotationConfigProcessors方法中注册的
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 初始化信息源,和国际化相关
initMessageSource();
// 初始化容器事件传播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 调用子类特殊的刷新逻辑
// web程序的容器AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext中会调用createEmbeddedServletContainer方法
//去创建内置的Servlet容器,目前只支持三种 tomcat,jetty,undertow
onRefresh();
// 为事件传播器注册事件监听器
registerListeners();
//实例化非懒加载的bean、bean封装、属性注入、注解注入(主要使用BeanPostProcessor或子类实现)等
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布容器的生命周期事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// ...
}
finally {
// ...
}
}
}
1. preparePefresh()分析:
刷新前的准备:设置spring容器的启动时间,撤销关闭状态、开启活跃状态、在上下文环境中初始化任何占位符属性源、environment的all properties验证所有标记为“必需”的属性是否可解析
2. obtainFreshBeanFactory()分析:
3. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)分析:
4. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory)分析:
5. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)分析:
AutoConfigurationImportSelector类的process()将装载完成的自动配置类存入autoConfigurationEntries属性,然后调用Iterable<Entry> selectImports()方法,确定需要导入的自动配置类并进行排序
ConfigurationClassParser类进行解析,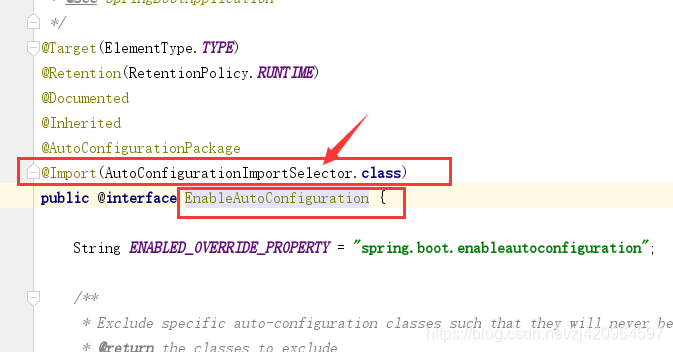
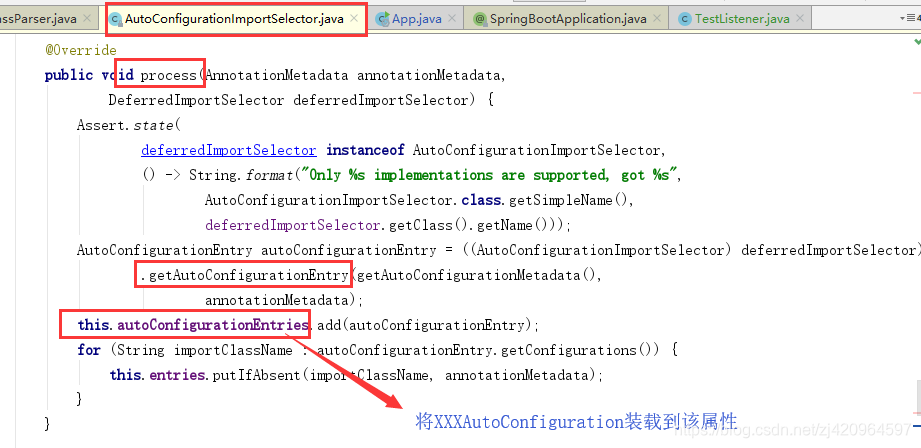

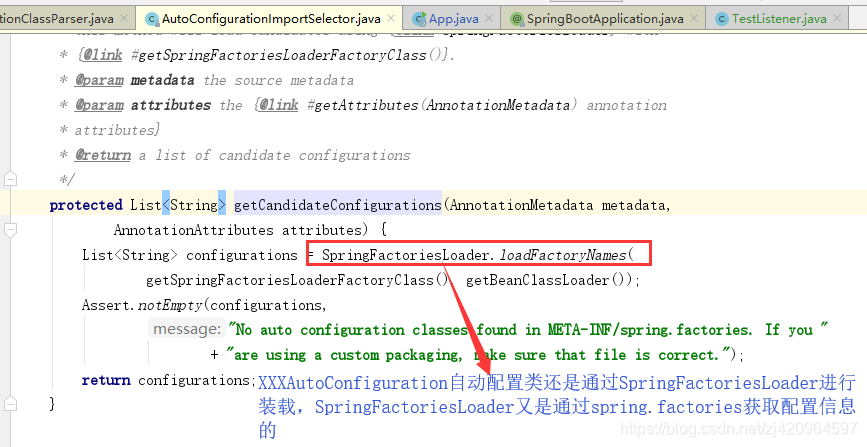
继而进入AutoConfigurationImportSelector类的Iterable<Entry> selectImports()方法,springboot 2.1后不再进入
String[] selectImports
总结:
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法总结来说就是从Spring容器中找出BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的实现类并按照一定的规则顺序进行执行。 其中ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor优先级最高,它会对项目中的@Configuration注解修饰的类(@Component、@ComponentScan、@Import、@ImportResource修饰的类也会被处理)进行解析,解析完成之后把这些bean注册到BeanFactory中。需要注意的是这个时候注册进来的bean还没有实例化。
6. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)分析:
7. onRefresh()分析:
一个模板方法,不同的Spring容器做不同的事情。
比如web程序的容器AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext中会调用createEmbeddedServletContainer方法去创建内置的Servlet容器。
目前SpringBoot只支持3种内置的Servlet容器:
- Tomcat
- Jetty
- Undertow
8. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)分析:
1. 实例化非懒加载的bean、bean封装、属性注入、注解注入(主要使用BeanPostProcessor或子类实现)等
DefaultListableBeanFactory--->preInstantiateSingletons()----->for (String beanName : beanNames):实例化bean2. invokeAwareInterfaces
bean实例化完成后会调用ApplicationContextAwareProcessor类的invokeAwareInterfaces方法
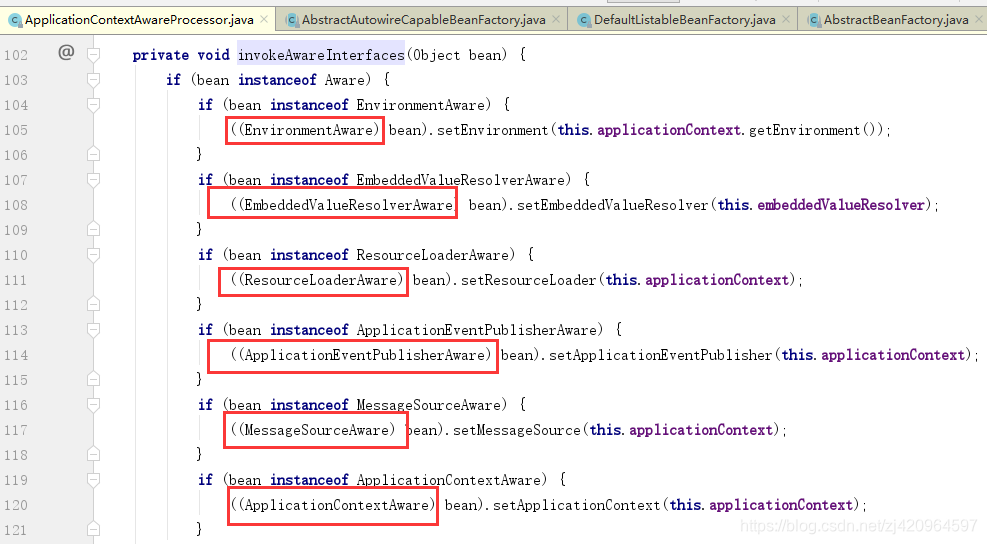
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/leileibest_437147623/article/details/80898878
9. finishRefresh()分析:
可参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/trgl/p/7353782.html
Spring Boot配置
1.配置文件
application.properties(常用)
application.yml(常用)
application.yaml
application.xml
2.加载顺序
优先级从低到高:
classpath:/
classpath:/config/
file:./
file:./config/
优先级由高到低,对于相同的属性配置,高优先级的配置会覆盖优先级低的配置;对于其他不同的属性配置,则会进行互补。
优先级相同的情况下,同时有application.properties和application.yml,那么application.properties里面的属性就会覆盖application.yml里的属性,因为properties比yml优先加载
我们也可以通过配置spring.config.location来改变默认配置





 本文详细剖析了SpringBoot启动过程,从SpringApplication构造函数到Run()方法,涵盖环境准备、事件监听、上下文准备及刷新容器等关键步骤,揭示了SpringBoot如何加载配置文件和初始化bean。
本文详细剖析了SpringBoot启动过程,从SpringApplication构造函数到Run()方法,涵盖环境准备、事件监听、上下文准备及刷新容器等关键步骤,揭示了SpringBoot如何加载配置文件和初始化bean。
















 640
640

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








