sqlalchemy基本使用
创建一个表以及一个数据:
import sqlalchemy
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import Column,Integer,String
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:hcl3533036@localhost/test',encoding = 'utf-8')#,echo = True
Base = declarative_base()#生成orm基类
class User(Base):
__tablename__ = 'user'#表名
id = Column(Integer,primary_key = True)
name = Column(String(32))
password = Column(String(64))
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)#创建表结构
#创建于数据库的绘画session class,注意,这里返回给session的是个class,不是实例
Session_class = sessionmaker(bind = engine)
#生成session实例
Session = Session_class()
#生成你要创建的数据对象
user_obj = User(name='hcl',password='123456')
#此时还没创建对象,打印出来id为none
print(user_obj.name,user_obj.id)
#把要创建的数据对象添加到这个session里,一会统一创建
Session.add(user_obj)
#此时也依然还没创建
print(user_obj.name,user_obj.id)
#此时才统一提交,创建数据
Session.commit()
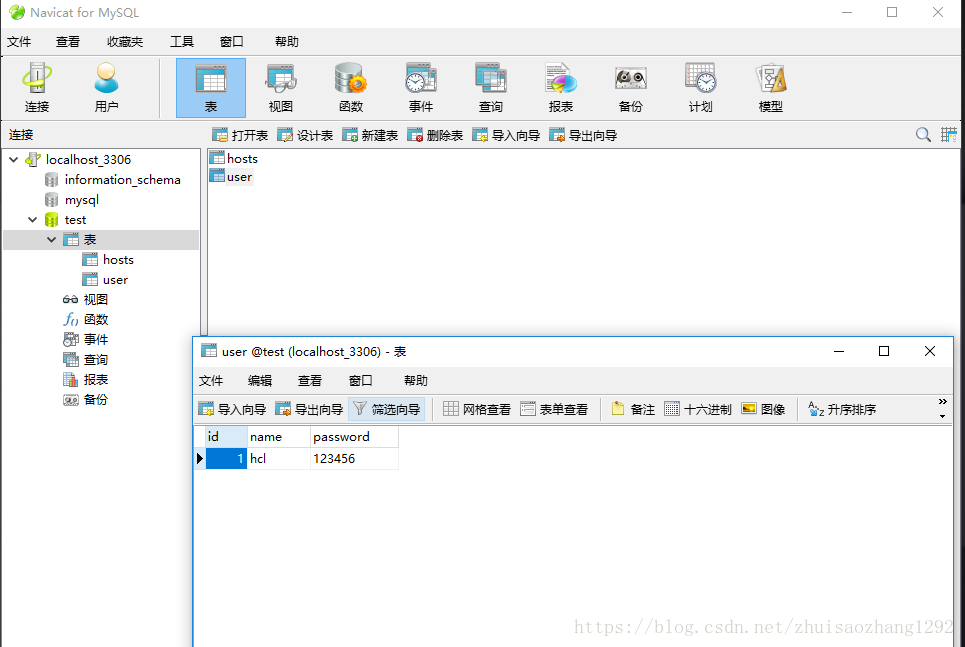
print(user_obj.name,user_obj.id)输出:
hcl None
hcl None
hcl 1效果:
查询:
'''
Created on 2018年7月9日
@author: hcl
'''
import sqlalchemy
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import Column,Integer,String
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:hcl3533036@localhost/test',encoding = 'utf-8')#,echo = True
Base = declarative_base()#生成orm基类
class User(Base):
__tablename__ = 'user'#表名
id = Column(Integer,primary_key = True)
name = Column(String(32))
password = Column(String(64))
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)#创建表结构
#创建于数据库的绘画session class,注意,这里返回给session的是个class,不是实例
Session_class = sessionmaker(bind = engine)
#生成session实例
Session = Session_class()
my_user = Session.query(User).filter_by(name="hcl").first()
print(my_Usr)
print(my_user.id,my_user.name,my_user.password)输出:
<__main__.User object at 0x0000021DD1EE8F28>
1 hcl 123456不过刚才上面的显示的内存对象对址你是没办法分清返回的是什么数据的,除非打印具体字段看一下,如果想让它变的可读,只需在定义表的类下面加上这样的代码
def __repr__(self):#定义一个类的特定返回形式
return "<User(name='%s', password='%s')>" % (
self.name, self.password)<User(name='hcl', password='123456')>
1 hcl 123456修改:
my_user = Session.query(User).filter_by(name="hcl").first()
my_user.name = "hcllllllll"
Session.commit()
print(my_user)<User(name='hcllllllll', password='123456')>回滚:
my_user = Session.query(User).filter_by(id=1).first()
my_user.name = "Jack"
fake_user = User(name='Rain', password='12345')
Session.add(fake_user)
print(Session.query(User).filter(User.name.in_(['Jack','rain'])).all() ) #这时看session里有你刚添加和修改的数据
print(Session.query(User.name,User.id).all() )#获取所有数据
Session.rollback() #此时你rollback一下
print(Session.query(User).filter(User.name.in_(['Jack','rain'])).all() ) #再查就发现刚才添加的数据没有了。
#Session.commit()[<User(name='Jack', password='123')>, <User(name='Rain', password='12345')>]
[('Jack', 1), ('Rain', 7)]
[]objs = Session.query(User).filter(User.id>0).filter(User.id<7).all()统计:
Session.query(User).filter(User.name.like("Ra%")).count()分组:
from sqlalchemy import func
print(Session.query(func.count(User.name),User.name).group_by(User.name).all() )多外键关联
One of the most common situations to deal with is when there are more than one foreign key path between two tables.
Consider a Customer class that contains two foreign keys to an Address class:
下表中,Customer表有2个字段都关联了Address表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | from sqlalchemy import Integer, ForeignKey, String, Columnfrom sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_basefrom sqlalchemy.orm import relationshipBase = declarative_base()class Customer(Base): __tablename__ = 'customer' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) name = Column(String) billing_address_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("address.id")) shipping_address_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("address.id")) billing_address = relationship("Address") shipping_address = relationship("Address")class Address(Base): __tablename__ = 'address' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) street = Column(String) city = Column(String) state = Column(String) |
创建表结构是没有问题的,但你Address表中插入数据时会报下面的错
1 2 3 4 5 6 | sqlalchemy.exc.AmbiguousForeignKeysError: Could not determine joincondition between parent/child tables on relationshipCustomer.billing_address - there are multiple foreign keypaths linking the tables. Specify the 'foreign_keys' argument,providing a list of those columns which should becounted as containing a foreign key reference to the parent table. |
解决办法如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | class Customer(Base): __tablename__ = 'customer' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) name = Column(String) billing_address_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("address.id")) shipping_address_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey("address.id")) billing_address = relationship("Address", foreign_keys=[billing_address_id]) shipping_address = relationship("Address", foreign_keys=[shipping_address_id]) |
这样sqlachemy就能分清哪个外键是对应哪个字段了
多对多关系
现在来设计一个能描述“图书”与“作者”的关系的表结构,需求是
- 一本书可以有好几个作者一起出版
- 一个作者可以写好几本书
输入:
from sqlalchemy import Table,Column,Integer,String,DATE,ForeignKey
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:hcl3533036@localhost/test',encoding = 'utf-8')#,echo = True
Base = declarative_base()
book_m2m_author = Table('book_m2m_author',Base.metadata,
Column('book_id',Integer,ForeignKey('books.id')),
Column('author_id',Integer,ForeignKey('authors.id')),
)
class Book(Base):
__tablename__ = 'books'
id = Column(Integer,primary_key = True)
name = Column(String(64))
pub_date = Column(DATE)
authors = relationship('Author',secondary = book_m2m_author,backref = 'books')
def __repr__(self):
return self.name
class Author(Base):
__tablename__ = 'authors'
id = Column(Integer,primary_key = True)
name = Column(String(32))
def __repr__(self):
return self.name
Base.metadata.create_all(engine) #创建表结构
Session_class = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
s = Session_class()
b1 = Book(name = 'Machine learning')
b2 = Book(name = 'Deep learning')
b3 = Book(name = 'Image Process')
b4 = Book(name = 'DSP')
a1 = Author(name = 'hcl')
a2 = Author(name = 'ln')
a3 = Author(name = 'huainancao')
b1.authors = [a1,a2]
b2.authors = [a1,a2,a3]
s.add_all([b1,b2,b3,b4,a1,a2,a3])
s.commit()
输出:
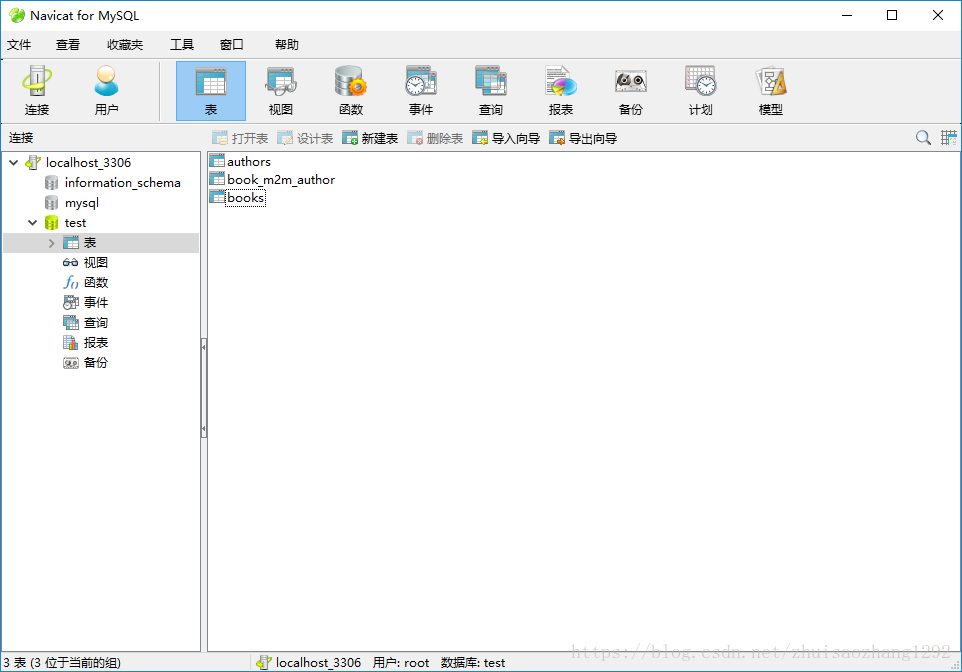
查看多对多:
from sqlalchemy import Table,Column,Integer,String,DATE,ForeignKey
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:hcl3533036@localhost/test',encoding = 'utf-8')#,echo = True
Base = declarative_base()
book_m2m_author = Table('book_m2m_author',Base.metadata,
Column('book_id',Integer,ForeignKey('books.id')),
Column('author_id',Integer,ForeignKey('authors.id')),
)
class Book(Base):
__tablename__ = 'books'
id = Column(Integer,primary_key = True)
name = Column(String(64))
pub_date = Column(DATE)
authors = relationship('Author',secondary = book_m2m_author,backref = 'books')
def __repr__(self):
return self.name
class Author(Base):
__tablename__ = 'authors'
id = Column(Integer,primary_key = True)
name = Column(String(32))
def __repr__(self):
return self.name
Session_class = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
s = Session_class()
print('-----------查看书表查关联的作者------------')
book_obj = s.query(Book).filter_by(name = 'Machine learning').first()
print(book_obj.name,book_obj.authors)
print('-----------通过作者表查关联的书------------')
author_obj = s.query(Author).filter_by(name='hcl').first()
print(author_obj.name,author_obj.books)
s.commit()-----------查看书表查关联的作者------------
Machine learning [hcl, ln]
-----------通过作者表查关联的书------------
hcl [Machine learning, Deep learning]
多对多删除
删除数据时不用管boo_m2m_authors , sqlalchemy会自动帮你把对应的数据删除
通过书删除作者
author_obj = s.query(Author).filter_by(name = 'hcl').first()
book_obj = s.query(Book).filter_by(name = 'Machine learning').first()
book_obj.authors.remove(author_obj)
s.commit()
直接删除作者
删除作者时,会把这个作者跟所有书的关联关系数据也自动删除
author_obj = s.query(Author).filter_by(name = 'hcl').first()
print(author_obj.name,author_obj.books)
s.delete(author_obj)
s.commit()输出:
hcl [Deep learning]
处理中文
sqlalchemy设置编码字符集一定要在数据库访问的URL上增加charset=utf8,否则数据库的连接就不是utf8的编码格式
eng = create_engine('mysql://root:root@localhost:3306/test2?charset=utf8',echo=True)





 本文介绍如何使用Python的SQLAlchemy ORM进行数据库操作,包括创建表、增删改查、多对多关系处理等核心功能。
本文介绍如何使用Python的SQLAlchemy ORM进行数据库操作,包括创建表、增删改查、多对多关系处理等核心功能。
















 304
304

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








