前言
Webpack 中的核心架构是基于 Tapable 实现的,Tapable 是一个类似于 Node.js 的 EventEmitter 的库,专门用于实现发布-订阅模式。Webpack 中的核心组件 Compiler、Compilation、Module、Chunk、ChunkGroup、Dependency、Template 都是通过 Tapable 实现的。
Tappable 主要负责管理 Hooks,Hooks 是一系列具有特定生命周期的事件。通过 Tappable,Webpack 中的不同部分可以创建和触发 Hooks,而插件可以监听这些 Hooks,在适当的时机执行自定义的逻辑。这种设计模式使得插件开发更加灵活,能够介入 Webpack 构建流程的不同阶段。
Tappable 可以被视为 Webpack 插件系统的基石。它提供了一种机制,使得插件可以注册自己的逻辑,而这些逻辑可以被集中执行,而不需要硬编码到 Webpack 的核心逻辑中。这种松耦合的设计让插件开发者更容易理解和维护自己的代码,也让整个插件系统更容易扩展。
本节对应的 demo 可以在这里找到。
Tapable 中的核心概念
Hook
在 Tappable 中,Hook 是一个核心类,代表一个事件(或者说是一个钩子)。每个 Hook 实例都可以被订阅,订阅者可以在事件触发时执行自己的逻辑。Hook 的主要职责是管理订阅者和触发事件。
const {
Hook } = require("tapable");
const myHook = new Hook(["arg1", "arg2"]);
myHook.tap("Plugin1", (arg1, arg2) => {
console.log("Plugin1:", arg1, arg2);
});
myHook.tap("Plugin2", (arg1, arg2) => {
console.log("Plugin2:", arg1, arg2);
});
myHook.call(42, "hello");
HookCodeFactory
HookCodeFactory 是一个工厂类,用于生成 Hook 的触发函数。每个 Hook 都有一个对应的 HookCodeFactory,HookCodeFactory 会根据 Hook 的类型和订阅者的类型生成不同的触发函数。
const {
Hook, HookCodeFactory } = require("tapable");
class MyHook extends Hook {
constructor(args) {
super(args);
this.compile = this.compileFactory();
}
compileFactory() {
return HookCodeFactory((args) => {
return args.map((arg) => `console.log('${
arg}:', ${
arg});`).join("");
});
}
}
const myHook = new MyHook(["arg1", "arg2"]);
const code = myHook.compile({
tap: (tapInfo) => {
return `console.log('Tapped by ${
tapInfo.name}');`;
},
type: "sync",
});
console.log(code);
在上述示例中,MyHook 继承自 Hook,并通过 HookCodeFactory 生成了用于触发事件的代码。compileFactory 方法返回一个函数,该函数接受一个参数 args,并返回一个字符串,其中包含了触发 Hook 事件时执行的代码。这样的设计使得 Hook 类型可以通过不同的 HookCodeFactory 来实现不同的触发逻辑。
Hook 的类型与用途
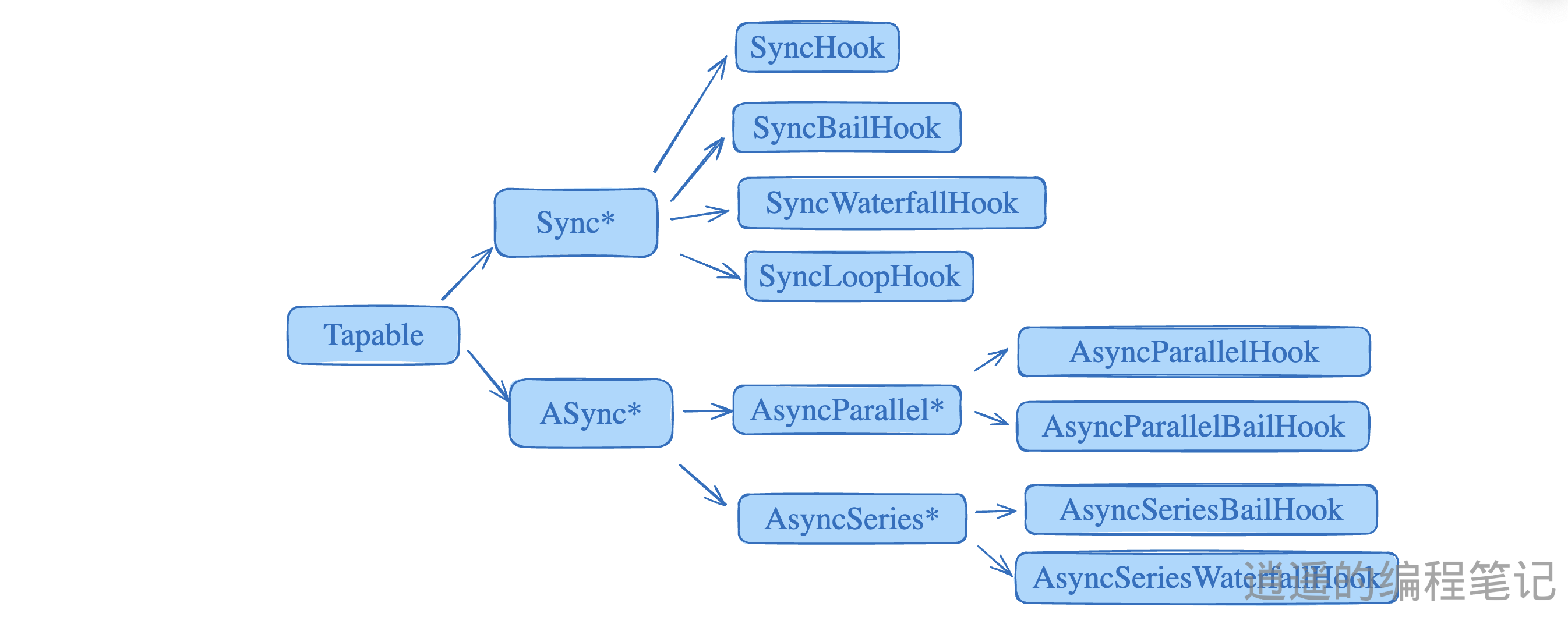
AsyncParallelBailHook
/**
* 类似于 AsyncParallelHook,但如果任何插件的回调函数返回除 undefined 之外的值,执行将停止,并在返回该值的情况下调用最终回调。
* 当插件的结果可以决定是否应执行后续插件时很有用。
* 支持异步插件注册和执行,包括回调函数和返回 Promise 的函数。
*/
class AsyncParallelBailHook {
constructor(args) {
this.args = args;
this.taps = [];
}
tap(name, callback) {
this.taps.push({
type: "sync", callback, pluginName: name });
}
tapPromise(pluginName, callback) {
this.taps.push({
type: "promise", callback, pluginName });
}
tapAsync(pluginName, callback) {
this.taps.push({
type: "async", callback, pluginName });
}
callAsync(...args) {
const finalCallback = args.pop();
let count = 0;
const done = (err, result) => {
count++;
if (err || result || count === this.taps.length) {
finalCallback(err, result);
}
};
for (const tap of this.taps) {
const callback = tap.callback;
if (tap.type === "sync") {
done(null, callback(...args));
} else if (tap.type === "promise") {
Promise.resolve(callback(...args)).then(
(result) => done(null, result),
done
);
} else if (tap.type === "async") {
callback(...args, done);
}
}
}
promise(...args) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this.callAsync(...args, (err, result) => {
if (err) {
reject(err);
} else {
resolve(result);
}
});
});
}
}
// Demo
const asyncParallelBailHook = new AsyncParallelBailHook(["arg1", "arg2"]);
asyncParallelBailHook.tap("Plugin1", (arg1, arg2) => {
console.log("Plugin1:", arg1, arg2);
return "Result from Plugin1";
});
asyncParallelBailHook.tapAsync("Plugin2", (arg1, arg2, callback) => {
console.log("Plugin2:", arg1, arg2);
setTimeout(() => callback("Result from Plugi




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1791
1791

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








