在android中用的最多的就是TextView,如果我们要获取TextView在父布局中的位置来如何处理呢,主要原理还是利用
getLeft(),getRight(),getTop(),getBottom(),getX,getY来计算,这里就是对这几个方法的使用说明
我们做一个实验,画了一个宽为300 高100的矩形框,这时左边有,上边也有一个高有100的矩形框
前提条件
父布局:相距屏幕左边的边距是40
左边:一个宽为100的矩形框
上边:一个高为100的矩形框
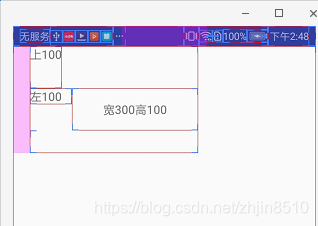
这时我们点击获取这个300*100图片的getLeft(),getRight(),getTop(),getBottom(),getX,getY,获取的结果图片如下
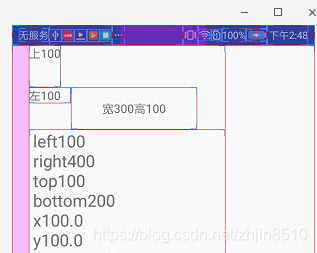
从图中我们可以看出来,getLeft和getx都是相对父布局的,但不包括父布局的marginleft,gettop和gety也是相对父布局的,这里最不同的是getRight和getBottom,getRight是控件最右边相对于父控件左边的距离,getBottom是控件最下面相对父控件顶部的距离。
| getleft | 100 | 左100 |
| getright | 400 | 宽300+左100 |
| gettop | 100 | 上100 |
| getbottom | 200 | 高100+上100 |
| getx | 100 | 左100 |
| gety | 100 | 上100 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/left"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/top"
android:text="左100" />
<com.sinping.arouter.myandroid.component.SimpleTextView
android:id="@+id/simpleTextView_20"
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/left"
android:layout_below="@+id/top"
android:text="宽300高100" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/top"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="上100" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/left_right_top_bottom_20"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/simpleTextView_20"
android:textSize="20sp"/>
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>
simpleTextView_20.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
left_right_top_bottom_20.setText(
" left" + simpleTextView_20.getLeft()
+ "\n right" + simpleTextView_20.getRight()
+ "\n top" + simpleTextView_20.getTop()
+ "\n bottom" + simpleTextView_20.getBottom()
+"\n x" + simpleTextView_20.getX()
+"\n y" + simpleTextView_20.getY()
);
}
});
到这里只是计算了控件的几个属性,还是没有介绍TextView是如何计算文字相对父控件的位置的,下面我们专一来讲解这个,这些内容也是参考了magic的源码,我这里只是做了分解。
这里先要介绍这个方法getTextBound,这个方法是计算文字的宽度的,原理把文字放入一个矩形内来计算文字的宽度,这个方法以后再详细介绍,得到的结果如下图:
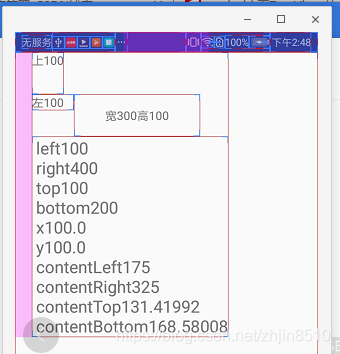
在这里计算宽度用到了getTextBound方法,计算高度用到了getPaint().getFontMetrics()方法,有了这些方法的支撑,我们就可以得到文字的位置了,代码如下
public class SimpleTextView extends AppCompatTextView {
public SimpleTextView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public SimpleTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public SimpleTextView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public int getContentLeft(){
String longestString = "";
Rect rect =new Rect();
longestString=getText().toString();
getPaint().getTextBounds(longestString,0,longestString.length(),rect);
//计算文本的left
return getLeft()+getWidth()/2-rect.width()/2;
}
public int getContentRight(){
String longestString = "";
Rect rect =new Rect();
longestString=getText().toString();
getPaint().getTextBounds(longestString,0,longestString.length(),rect);
//计算文本的right
return getLeft()+getWidth()/2+rect.width()/2;
}
public float getContentTop(){
Paint.FontMetrics metrics = getPaint().getFontMetrics();
float contentHeight = metrics.bottom - metrics.top;
//计算文本的top
return getTop()+ getHeight()/2-contentHeight/2;
}
public float getContentBottom(){
Paint.FontMetrics metrics = getPaint().getFontMetrics();
float contentHeight = metrics.bottom - metrics.top;
//计算文本的bottom
return getTop()+getHeight()/2+contentHeight/2;
}
}





 本文深入解析Android中TextView的定位机制,通过实例演示如何使用getLeft(), getRight(), getTop(), getBottom(), getX(), getY()等方法计算控件及文字在父布局中的精确位置。适合Android开发者理解布局和定位原理。
本文深入解析Android中TextView的定位机制,通过实例演示如何使用getLeft(), getRight(), getTop(), getBottom(), getX(), getY()等方法计算控件及文字在父布局中的精确位置。适合Android开发者理解布局和定位原理。
















 318
318

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








