第一章:上次课回顾
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/zhikanjiani/article/details/95059959
第二章、DataFrame使用
任何一个产品(交由用户使用的)最终都需要落地到SQL;项目可以由自己来维护写代码无所谓。
SparkSession就是Spark的一个入口点,getOrCreate底层调用的也是SparkConf和SparkContext。
2.1 DataFrame简介
A DataFrame is a Dataset organized into named columns. It is conceptually equivalent to a table in a relational database or a dataframe is R/Python,but with richer optimizations under the hood,
DataFrames can be constructed from a wide array of sources such as : structured data files , table in Hive , external databases, of existing RDDs.
翻译:dataframe能够从数组过来,转换为文件;
数据在hdfs上,把数据搞过来,dataframe处理;
hive中的表;
外部数据(用户行为数据、配置信息)
已经存在的RDD
2.2 使用DataFrame读取json文件
我们直接进行测试:
JSON文件转换为DataFrame:
- 首先准备好要读取的json文件:
在/home/hadoop/data目录下准备一份json文件:
Json文件是带Schema信息的。
[hadoop@hadoop002 data]$ cat people.json
{"name":"john","salary":3500}
{"name":"sail","salary":4500}
{"name":"fox","salary":5500}
spark-shell窗口下测试读取JSON文件:
思考:如何使用mapreduce来读取json文件??
json文件中的一行信息中有1个、2个、3个 key、value你怎么进行判断呢?
第一种读取方式:
- spark.read.json(“file:///home/hadoop/data/people.json”).show

第二种读取方式:
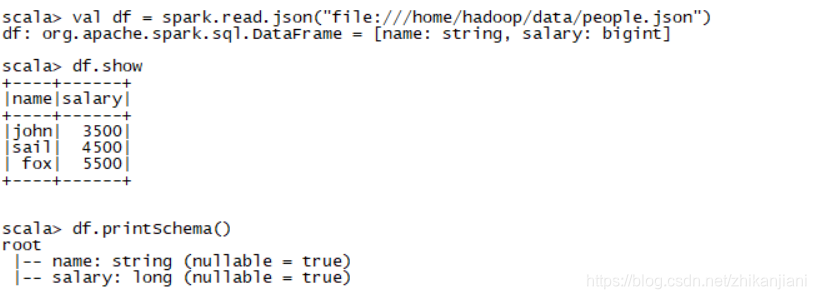
1、 val df = spark.read.json(“file:///home/hadoop/data/people.json”)
2 、df.show
3 、df.printSchema() //打印出它的数据结构
通过这种方式把数据加载进来变成一个DataFrame
小结:
- 这种方式(spark.read.json)读取进来的数据有就有,没有就是null补值,也不需要改代码啥的
- 好处:根本不用考虑数据类型,字段多与少
- 文本类型不支持
2.3 使用DataFrame读取文本
读取文本,结果如下:
- spark.read.text(“file:///home/hadoop/data/ruozeinput.txt”)
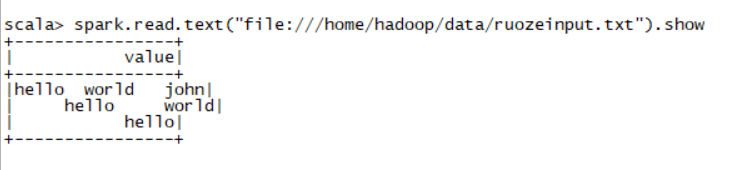
- 我们使用DataFrame读取文本打印出来只有一个字段value,这个value是String类型的。
- 对于文本来讲是没有schema信息的,
- 如何操作使得我们能知道每一行信息代表什么,自定义外部数据源???
创建成为临时视图:
- val df = spark.read.json(“file:///home/hadoop/data/people.json”)
- df.createOrReplaceTempView(“people”)
- spark.sql(“select * from people”).show
- spark.sql(“show tables”).show //people表是我们注册进来的临时表,当前session关闭,临时表就会消失。
2.4 使用DataFrame进行查询、过滤读取json文件字符串
前提:数据准备,自己本地编辑两个employees.json和people.json文件
vi people.json
{"name":"john","salary":3500}
{"name":"sail","salary":4500}
{"name":"fox","salary":5500}
直接在虚拟机上启动spark-shell,输入:spark.read.json(“file:///home/hadoop/data/people.json”)
注意:本地路径要加file://,不加的话会去hdfs路径上去读,""双引号不写会报错。
1、读取people.json文件并打印出来
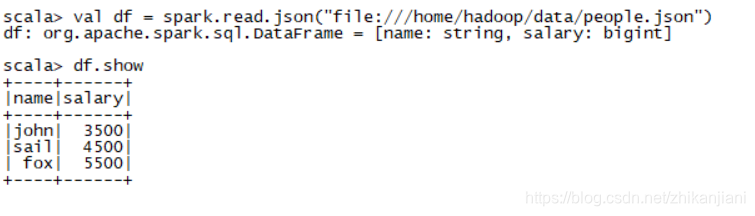
- val df = spark.read.json(“file:///home/hadoop/data/people.json”)
- df.show //打印信息
2、打印出它的数据结构
df.printSchema()

3、打印出name列或salary列或者两列一起打印出来。
df.select(“name”).show
df.select(“name”,“age”).show //select中需要几个就写几个
另外一种写的方式:
df.select(
"
n
a
m
e
"
)
/
/
选
择
名
字
这
一
列
d
f
.
s
e
l
e
c
t
(
"name") //选择名字这一列 df.select(
"name")//选择名字这一列df.select(“name”,$“salary”).show //多几列也没事情
扩充写法:
回字的8种写法:
1、 df.select(df(“name”)).show
2、 df.select(df(“name”),df(“salary”)+1000).show
3、 df.select(df(“name”),df(“salary”),df(“salary”)+1000).show
注意:
df.select($“name”) 在idea中使用时,要加入隐式转换;而在控制台上时默认导入的。

4、在薪水的基础上+1000,筛选出薪水>5000的。
5、过滤出薪水大于4000的人员。(这一步是在临时表中完成的)
scala> df.filter(df(“salary”)>4000).show

6、同一薪水下统计人数
df.groupBy(“salary”).count().show()

第三章:DataFrame实际应用
3.1 通过反射将文本转换为DataFrame
新建一份数据,名字列中需要缺失两个名字,名字中带null或NULL(模拟真实生产数据)
vi student.data
。。。。
此时需要使用Interoperating with RDDs
1、spark SQL supports two different methods for converting existing RDDs into Datasets.
SparkSQL支持两种不同的方式把已经存在的RDD转换到Datasets
2、The first method uses reflection to infer the schema of an RDD that contains specific types of objects
第一种方式使用反射来推断出RDD中的schema信息
3、This reflection-based leads to more concise code and works well when you already know the schema while writing your Spark Application.
这个基于反射的方式使得代码精简,工作高效当你知道schema的时候,当你正在写Spark应用程序的时候。
How to use
4、The Scala interface for Spark SQL supports automatically converting an RDD containing case classes to a DataFrame,
Scala中的接口对于Spark SQl支持自动转从RDD转换为DataFrame,使用case classes
5、The case class defines the schema of the table. The names of the argument to the case are read using reflection and become the names of the columns. Case classes can also be nested or contain complex types such as Seqs or Arrays. This RDD can be inplicitly converted to a DataFrame and the be registered as a table, Tables can be used in a subsequent SQL statements.
注意:以下操作在Spark-shell中测试完成:
第一步操作:
case class Student(id:String,name:String,email:String,phone:String) //定义这张表:字段和类型
第二步操作:
val student = spark.sparkContext.textFile(“file:///home/hadoop/data/student.data”) //RDD[String]
.map(_.split("|")) //根据竖线|分割
.map(x => Student(x,0),x(1),x(2),x(3)) //里面每一个元素这样转换
.toDF() //
注意:在2中的以竖线|分割需要转义,修改为.map(_.split"\|"),不然会报错。
第三步操作:
student.show() //不写false会只显示前20个字符
修改:student.show(false) //展示全部数据,默认显示20个字符
student.show(50,false) //放50条数据进来。
student.printSchema //查看学生结构,通过反射把数据取进来
结果:id name phone email 通过反射都会推导出来。
第四步操作:
我们在RDD中取前三条数据可以采用take(3),进到源码中去查看take方法,发现其返回的是一个数组,不能show,需要修改为如下:
student.take(3).foreach(println)
如下互相调用的几个操作:
first、head用法(发现first调用的是head,head调用的是head(1))
1)student.first
2)student.head
3)student.head(3)
3.1.1 转换好后的数据进行统计分析:
需求一:
打印出学生id>10的
student.filter(“id>10”).show
需求二:
过滤出 “null” 、"NULL"和 " " 的学生名字字符
student.filter("name=’ ’ or name = ‘null’ or name = ‘NULL’ ").show
需求三:
按名字排序:在IDEA中操作(因为有提示):
student.sort(“name”).desc //不加美金符号,我们发现没有desc这个方法。
所以建议大家排序的时候使用Column,也就是DF的方式,在name前加上"美金符号",才会出现.desc这个方法。
- student.sort($“name”.desc).show
//可以根据一列名字来排,加上美金符号,美金符号在此编辑器上不显示,故做此说明 - student.sort($“name”.desc,“id”.desc).show.
//也可以根据两列来排序,名字相同还会根据id的降序排列
需求四:
修改列名:
student.select($“phone”.as(“mobile”)).show()
需求五:
join操作,自己join自己:
val stu1 = spark.textFile(“file:///home/hadoop/data/student.data”)
val stu2 = spark.textFile(“file:///home/hadoop/data/student.data”)
stu1.join(stu2).show //这样写会导致笛卡尔积,因为没有条件。
stu1.join(stu2,stu1(“id”) === stu2(“id”)).show(false) // “=”号是赋值,“”是等于,但是这边要三等号“=”
注意点:
在开发语言中,“=”号是赋值,“”是等于,但是这边要三等号“=”
需求六:
a表和b表join多个?
语法支持
大数据面试题:左连接?右连接? 以链接的表为基准,没有的值补none
3.2 转换的另一种方式:
场景二:
第一种方式的前提是已经知道源头数据
- The second method for creating Datasets is through a programmatic interface that allows you to construct a schema and then apply it to an existing RDD, while this method is more verbose, it allows you to construct Datasets when the columns and their types are not known until runtime.
- 第二种方式是创建一个Dataset通过一个可编程的接口,那允许你创建一个schema,并且作用在一个已经存在的RDD.
- when case class cannot be defined ahead of time(for example, the structure of records is encoded in a string, or a text dataset will be parsed and fields will be projected differently for different users), a DataFrame can be created programmatically with three steps
- 当case class不能被提前定义,(记录的结构,或者一个文本dataset将被解析,fields将被…),一个DataFrame可以被编程通过如下三步走。
当我们事先不明确case class 怎么定义的时候,
使用下面三部曲:
1、create an RDD of rows from the original RDD.
- 创建一个row类型的RDD从原始的RDD中过来
2、create the schema represented by a StructType matching the structure of Rows in the RDD created in step 1.
- 定义上schema,名字叫StructType去匹配结构
3、Apply the schema to the RDD of rows via createDataFrame method provided by a SparkSession.
- 要把schema和row RDD综合起来使用通过SparkSession提供的的createDataFrame方法
IDEA开搞:
第一步:
package sparksql02
import org.apache.spark.sql.types.{StringType, StructField, StructType}
import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession}
object DataFrameApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = new SparkSession()
//Create an RDD of Rows from the original RDD
val rdd = spark.sparkContext.textFile("file:///home/hadoop/data/student.data")
.map(_.split("\\|"))
.map( x => Row(x(0),x(1),x(2),x(3)))
//structType = N个 StructFields
//StructFields =
//Create the schema represented by a StructType matching the structureof Rows
val structType = StructType(Array(StructField("id",StringType,true),
StructField("name",StringType,true),
StructField("phone",StringType,true),
StructField("email",StringType,true)))
val df = spark.createDataFrame(rdd,structType)
df.show()
spark.stop()
}
第四章:Shuffle
不用过脑子写一个wordCount
- spark.sparkContext.textFile(“file:///home/hadoop/data/student.data”).flatMap(.split("\t")).map((,1)).reduceByKey(+).collect
查看DAG图:
发现此时是2个stage,各为2个tasks;第一个stage的来源是textFile底层调用默认的totalCore = local[2],是2个stage。
TextFile底层调用的是这个方法:
override def defaultParallelism(): Int =
scheduler.conf.getInt(“spark.default.parallelism”,totalCores)
修改:
- spark.sparkContext.textFile(“file:///home/hadoop/data/student.data”,1)
reduceByKey可不可以调整呢??
- reduceByKey(+,5) //5就是一个并行度
最后一个stage还有一个学名,叫做ResultStage/FinalStage ShuffleStage
源码中去查看:
collect是一个action,
map端,几个block块,设置几个task
HDFS读数据,partition = task,split
对于reduceByKey端,出:以map端最后一个rdd的partition数作为ResultStage的partition
reduceByKey(func,X) X就是ResultStage的partition
搞一个稍微复杂的:
-
spark.sparkContext.textFile(“file:///home/hadoop/data/student.data”).coalesce(1).flatMap(.split("\t")).map((,1)).reduceByKey(+).collect
-
spark.sparkContext.textFile(“file:///home/hadoop/data/student.data”).repartition(3).flatMap(.split("\t")).map((,1)).reduceByKey(+).collect
查看它的DAG图,为什么它是3个stage,repartition是一个shuffle,reduceByKey也是一个shuffle
4.1 ShuffleManager
在pom.xml中修改spark.version为1.6.0
搜索SparkEnv.scala源码:
在1.6.0版本中:
搜索SparkEnv.scala源码:
- val shortShuffleMgrNames = Map(
“hash” -> “org.apache.spark.shuffle.hash.HashShuffleManager”,
“sort” -> classOf[org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager].getName,
“tungsten-sort” -> classOf[org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager].getName)
然而在spark2.4.0版本中,SparkEnv.scala源吗中去除了hash
- val shortShuffleMgrNames = Map(
“sort” -> classOf[org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager].getName,
“tungsten-sort” -> classOf[org.apache.spark.shuffle.sort.SortShuffleManager].getName)
HashShuffleManager:每一个maptask都会生成N个reducetask的文件。
直接去到官网上找配置参数:
优化点1:
spark.shuffle.file.buffer 32K 给没以恶搞shuffle文件输出使用,目的是为了减少访问磁盘的
会产生的文件个数:map * reduce
Bucket:开了多少个桶?Core的数量 * R
问题:
假设我们现在有8Core,1000个task,会占用多少内存:8 * 1000 * 32k ~~ 256M
假设我们有100个executor,2Core, 1000maptask,1000reducetask
==> …很多
存在致命的问题:
操作文件是使用线程操作,中间文件占用东西比较多,bucket太小,主要是文件个数,文件写磁盘
参数:
spark.local.dir
这个参数没有配置,全写在/tmp目录下,建议你以逗号分割,会刚不住,一会儿就会写挂掉。

弊端:map输出太多,缓冲区太小了。
Shuffle Behavior参数都需要调整,尤其是spark.shuffle.file.buffer,这个参数设置的越小,它写的越频繁,文件数越多,减少和磁盘交互次数。




 本文围绕DataFrame展开,介绍其基础使用,包括读取json文件、文本文件,以及查询、过滤操作。还阐述了DataFrame的实际应用,如通过反射将文本转换为DataFrame并进行统计分析。此外,对Shuffle进行了探讨,涉及ShuffleManager及相关参数配置和优化。
本文围绕DataFrame展开,介绍其基础使用,包括读取json文件、文本文件,以及查询、过滤操作。还阐述了DataFrame的实际应用,如通过反射将文本转换为DataFrame并进行统计分析。此外,对Shuffle进行了探讨,涉及ShuffleManager及相关参数配置和优化。
















 1275
1275

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








