并发与并行区别
并发:当有多个线程在操作时,如果系统只有一个CPU(单核心),则它根本不可能真正同时进行一个以上的线程,它只能把CPU运行时间划分成若干个时间段,再将时间 段分配给各个线程执行,在一个时间段的线程代码运行时,其它线程处于挂起状。.这种方式我们称之为并发(Concurrent)。
并行:当系统有一个以上CPU(一个CPU具备多核心)时,则线程的操作有可能非并发。当一个CPU执行一个线程时,另一个CPU可以执行另一个线程,两个线程互不抢占CPU资源,可以同时进行,这种方式我们称之为并行(Parallel)。
区别:并发和并行是即相似又有区别的两个概念,并行是指两个或者多个事件在同一时刻发生;而并发是指两个或多个事件在同一时间间隔内发生。在多道程序环境下,并发性是指在一段时间内宏观上有多个程序在同时运行,但在单处理机系统中,每一时刻却仅能有一道程序执行,故微观上这些程序只能是分时地交替执行。倘若在计算机系统中有多个处理机,则这些可以并发执行的程序便可被分配到多个处理机上,实现并行执行,即利用每个处理机来处理一个可并发执行的程序,这样,多个程序便可以同时执行。
实际的数据统计范例
某公司有4个工厂,分布在不同地区,同一时段都生产了P1,P2,P3这3种产品,产量(单位;吨),
| 工厂\产品 | P1 | P2 | P3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 甲 | 5 | 2 | 4 |
| 乙 | 3 | 8 | 2 |
| 丙 | 6 | 0 | 4 |
| 丁 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
可用下面的矩阵描述

,其中4行分别表示甲乙丙丁4个工厂的生产情况,3列分布表示3种产品P1,P2,P3的产量。
产品P1的单件利润为2(单位:元)占用存储空间为4(单位:立方米),
产品P2的单件利润为1(单位:元)占用存储空间为3单位:立方米),
产品P3的单件利润为3(单位:元)占用存储空间为4单位:立方米),
试用矩阵的计算方式来统计这些数据。
| 产品 | 单件利润/单件体积 |
| P1 | 2/4 |
| P2 | 1/3 |
| P3 | 3/2 |
可用下面的矩阵描述
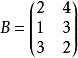
,其中第1列表示3种产品的单件利润,第2列表示3种产品的单件体积。
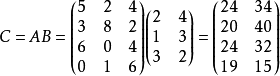
矩阵C的第1列数据分别表示4个工厂的利润,第2列分别表示4个工厂产品需要的存储空间。
我们将使用Java代码来实现数据的统计
定义存储矩阵数据的对象:
package com.contoso;
public class Matrix {
private final int[][] matrix;
public Matrix(int rows, int cols) {
matrix = new int[rows][cols];
}
public int getCols() {
return matrix[0].length;
}
public int getRows() {
return matrix.length;
}
public int getCellValue(int row, int col) {
return matrix[row][col];
}
public void setCellValue(int row, int col, int value) {
matrix[row][col] = value;
}
}
接下来我们将使用两种不同的实现方式来统计数据:
第1种方式:单线程统计方式
package com.contoso;
/**
* 单线程矩阵乘法
*
*/
public class MatrixMultiply {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
A矩阵:4行3列
5 2 4
3 8 2
6 0 4
0 1 6
*/
long start = System.nanoTime();
Matrix a = new Matrix(4, 3);
a.setCellValue(0, 0, 5);
a.setCellValue(0, 1, 2);
a.setCellValue(0, 2, 4);
a.setCellValue(1, 0, 3);
a.setCellValue(1, 1, 8);
a.setCellValue(1, 2, 2);
a.setCellValue(2, 0, 6);
a.setCellValue(2, 1, 0);
a.setCellValue(2, 2, 4);
a.setCellValue(3, 0, 0);
a.setCellValue(3, 1, 1);
a.setCellValue(3, 2, 6);
print(a);
/*
B矩阵:3行2列
2 4
1 3
3 2
*/
Matrix b = new Matrix(3, 2);
b.setCellValue(0, 0, 2);
b.setCellValue(1, 0, 1);
b.setCellValue(2, 0, 3);
b.setCellValue(0, 1, 4);
b.setCellValue(1, 1, 3);
b.setCellValue(2, 1, 2);
print(b);
/*
C矩阵:4行2列 C = A * B
*/
print(multiply(a, b));
long end = System.nanoTime();
double timeTaken = (end - start) / 1e9;
System.out.println("Matrix Multiply Time Taken in seconds:" + timeTaken);
}
public static void print(Matrix mat) {
for (int i = 0; i < mat.getRows(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mat.getCols(); j++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", mat.getCellValue(i, j));
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
public static Matrix multiply(Matrix a, Matrix b) {
if (a.getCols() != b.getRows()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("rows/columns mismatch");
}
Matrix result = new Matrix(a.getRows(), b.getCols());
for (int i = 0; i < a.getRows(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b.getCols(); j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < a.getCols(); k++) {
result.setCellValue(i, j, result.getCellValue(i, j) + a.getCellValue(i, k) * b.getCellValue(k, j));
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
请注意以下单线程统计需要的时间:
run:
5 2 4
3 8 2
6 0 4
0 1 6
2 4
1 3
3 2
24 34
20 40
24 32
19 15
Matrix Multiply Time Taken in seconds:0.036336188
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
第2中方式:超快并行执行的多核心CPU矩阵乘法在数据统计方面的应用
package com.contoso;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveAction;
/**
* 超快并行执行的多核心CPU矩阵乘法在数据统计方面的应用
*
*/
public class RecursiveMatrixMultiply extends RecursiveAction {
private final Matrix a, b, c;
private final int row;
public RecursiveMatrixMultiply(Matrix a, Matrix b, Matrix c) {
this(a, b, c, -1);
}
public RecursiveMatrixMultiply(Matrix a, Matrix b, Matrix c, int row) {
if (a.getCols() != b.getRows()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("rows/columns mismatch");
}
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
this.row = row;
}
@Override
public void compute() {
if (row == -1) {
List<RecursiveMatrixMultiply> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
for (int row = 0; row < a.getRows(); row++) {
tasks.add(new RecursiveMatrixMultiply(a, b, c, row));
}
invokeAll(tasks);
} else {
multiplyRowByColumn(a, b, c, row);
}
}
public static void multiplyRowByColumn(Matrix a, Matrix b, Matrix c, int row) {
for (int j = 0; j < b.getCols(); j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < a.getCols(); k++) {
c.setCellValue(row, j, c.getCellValue(row, j) + a.getCellValue(row, k) * b.getCellValue(k, j));
}
}
}
public static void print(Matrix mat) {
for (int i = 0; i < mat.getRows(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < mat.getCols(); j++) {
System.out.print(mat.getCellValue(i, j) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.nanoTime();
/*
A矩阵:4行3列
5 2 4
3 8 2
6 0 4
0 1 6
*/
Matrix a = new Matrix(4, 3);
a.setCellValue(0, 0, 5);
a.setCellValue(0, 1, 2);
a.setCellValue(0, 2, 4);
a.setCellValue(1, 0, 3);
a.setCellValue(1, 1, 8);
a.setCellValue(1, 2, 2);
a.setCellValue(2, 0, 6);
a.setCellValue(2, 1, 0);
a.setCellValue(2, 2, 4);
a.setCellValue(3, 0, 0);
a.setCellValue(3, 1, 1);
a.setCellValue(3, 2, 6);
print(a);
/*
B矩阵:3行2列
2 4
1 3
3 2
*/
Matrix b = new Matrix(3, 2);
b.setCellValue(0, 0, 2);
b.setCellValue(1, 0, 1);
b.setCellValue(2, 0, 3);
b.setCellValue(0, 1, 4);
b.setCellValue(1, 1, 3);
b.setCellValue(2, 1, 2);
print(b);
/*
C矩阵:4行2列 C = A * B
*/
Matrix c = new Matrix(4, 2);
ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();
pool.invoke(new RecursiveMatrixMultiply(a, b, c));
print(c);
long end = System.nanoTime();
double timeTaken = (end - start) / 1e9;
System.out.println("Recursive Matrix Multiply Time Taken in seconds:" + timeTaken);
System.err.println("单颗CPU内核数 = " + Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
}
}
请注意并行计算的多核心CPU矩阵乘法统计需要的时间:
run:
5 2 4
3 8 2
6 0 4
0 1 6
2 4
1 3
3 2
24 34
20 40
24 32
19 15
单颗CPU内核数 = 4
Recursive Matrix Multiply Time Taken in seconds:0.003261084
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)





 本文详细解析了并发与并行的概念,阐述了两者在多线程和多CPU环境下的工作原理。通过实例对比了单线程与多核心CPU并行计算在矩阵乘法中的效率,展示了并行计算的优势。
本文详细解析了并发与并行的概念,阐述了两者在多线程和多CPU环境下的工作原理。通过实例对比了单线程与多核心CPU并行计算在矩阵乘法中的效率,展示了并行计算的优势。
















 4279
4279

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








