(20) decltype 类型推断时会保留引用类型么? 首先 typeid ( A ) .name ( ) 在打印时是会去掉引用 && 这些符号的:
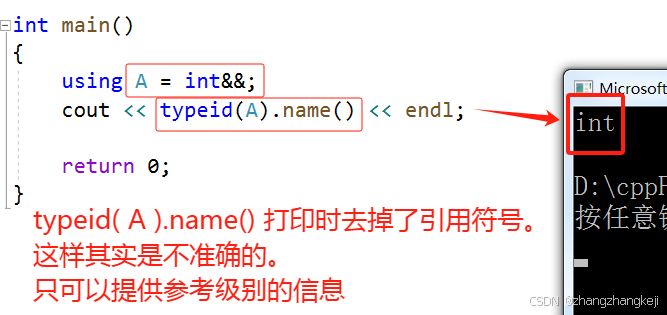
++ 那么 decltype ( ) 可以提供准确的类型信息推断么。答案是可以提供准确的类型推断的,先学习其语法:
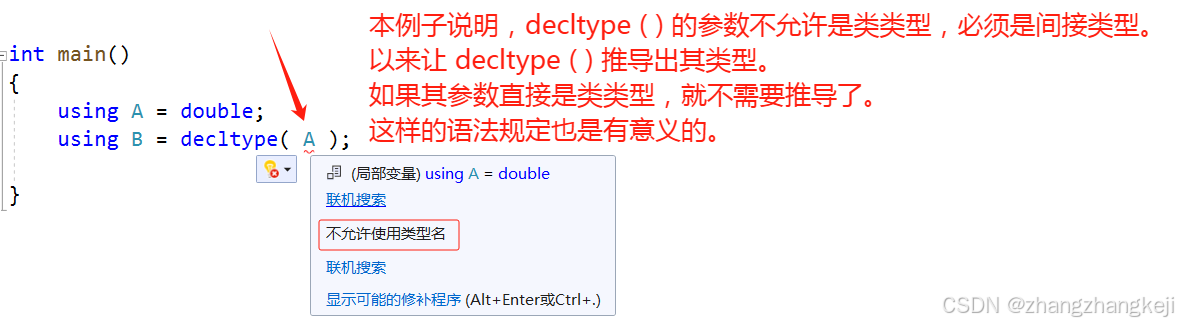
++ 再写测试例:
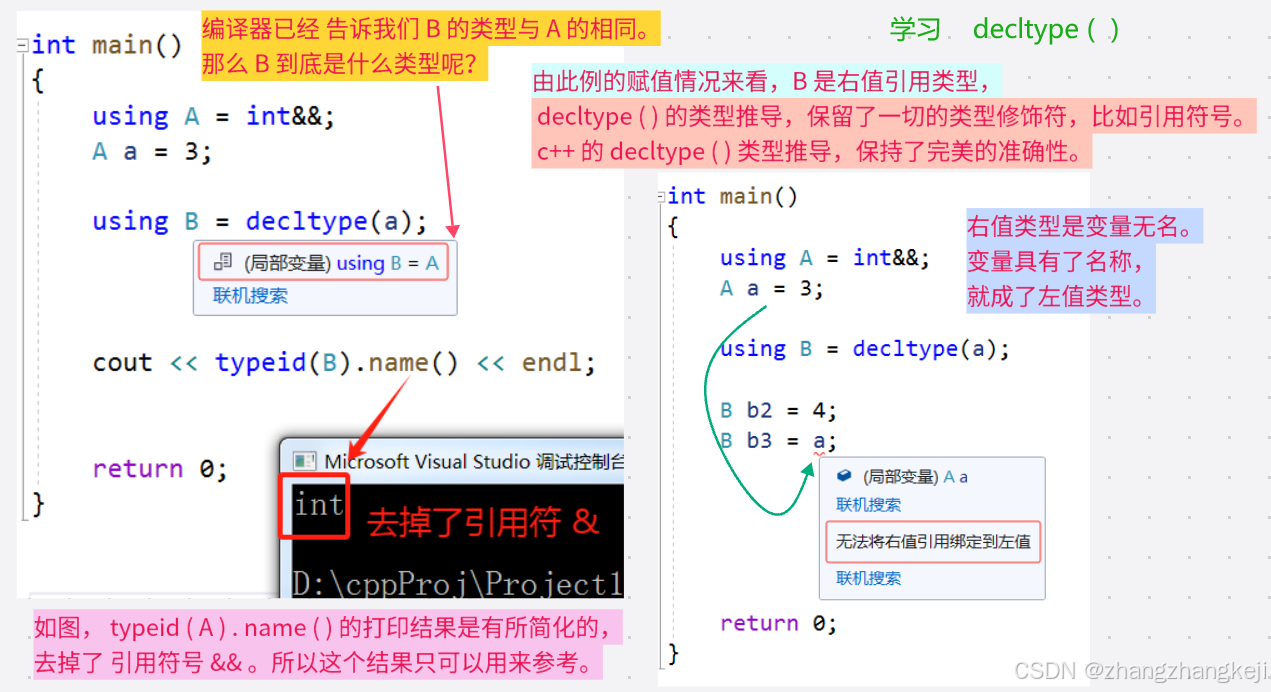
++ 当然,实际的 decltype ( ) 肯定不会这么简单,而是比如用于对函数的返回值的类型的判断与推导。再举例:
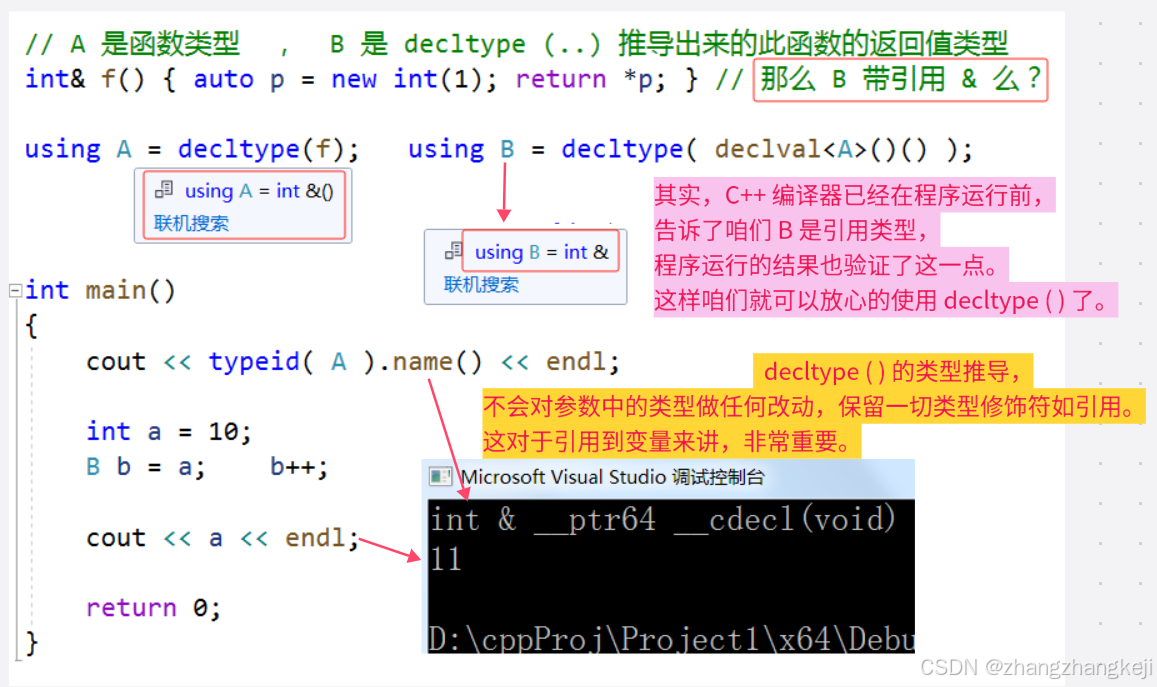
++ 推导函数的返回值类型,在本 < future > 头文件中,也会用到。所以单独整理学习一下其用法。
(21) 全局函 _Get_associated_state (),字面意思,该函数生成一个 _Associated_state 类型的的对象,该对象保存了线程中函数的返回值,但 _Associated_state 类型既有儿子类,又有孙子类,本函数实际是返回一个爷爷类指针,实现爷爷类指针指向孙子类对象。源码如下:
// construct associated asynchronous state object for the launch type 为启动类型构造关联的异步状态对象
// 模板参数 _Fty 就是 _Fake_no_copy_callable_adapter<T...> 类型,该类型的对象是可调用对象;
template <class _Ret, class _Fty> // 模板参数 _Fty 的对象其实是一个包含被调函数及其实参的 tuple 元组
_Associated_state<typename _P_arg_type<_Ret>::type>* // 返回值
_Get_associated_state(launch _Psync, _Fty&& _Fnarg)
{
switch (_Psync) // select launch type
{
case launch::deferred : // 这是爷爷 _Associated_state 的孙类
return new _Deferred_async_state<_Ret>(_STD forward<_Fty>(_Fnarg));
// 这个 _Ret 是函数的返回结果,可以是值,引用或者为 void ,重载般的选择一个父类 _Packaged_state
case launch::async : // TRANSITION, fixed in vMajorNext, should create a new thread here
default: // 注意,默认态下也将创建新线程 //这也是爷爷 _Associated_state的孙类
return new _Task_async_state<_Ret>(_STD forward<_Fty>(_Fnarg));
}
}
(22) 管理函数返回值的状态的基类 _State_manager, 顾名思义, _State_manager 就是为了管理 _Associated_state<_Ty> 的。本序号开始,又开始了一个大的系列,又定义了一组模板类 ( 父类与子类 ),该类的源码如下:
//*******************下面这是一段父类 _State_manager 与子类 future,子类 shared_future*********************
// 爷类 _Associated_state 与子类 _Packaged_state 与孙类 _Deferred_async_state + _Task_async_state
// 顾名思义,现在是要开始管理这些 包含了函数返回值的 state 类。
template <class _Ty>
class _State_manager
{
private:
_Associated_state<_Ty>* _Assoc_state; // 本模板类管理里一个 state 类
bool _Get_only_once; // 当 本模板 作为 future 的父类时,_Get_only_once 为 true ;
// 当 本模板 作为 shared_future 的父类时,_Get_only_once 为 false
public:
// construct with no associated asynchronous state object
_State_manager() : _Assoc_state(nullptr) { _Get_only_once = false; } // 默认构造函数
// construct with _New_state
_State_manager(_Associated_state<_Ty>* _New_state, bool _Get_once) // 有参构造函数
: _Assoc_state(_New_state) { _Get_only_once = _Get_once; }
// template <class _Ty> //用于管理关联同步状态的类
// class _Associated_state
// { void _Release() { if (_MT_DECR(_Refs) == 0) _Delete_this(); } };
~_State_manager() { if (_Assoc_state) _Assoc_state->_Release(); } // 析构函数
// copy stored associated asynchronous state object from _Other 从“其他”复制存储的关联异步状态对象
void _Copy_from(const _State_manager& _Other) // 感觉核心代码就是增加了一个引用计数
{
if (this != _STD addressof(_Other)) // 本函数服务于 copy 构造函数与 copy 赋值运算符函数
{
if ( _Assoc_state ) _Assoc_state->_Release(); // 释放本类原来管理的函数返回值
if (_Other._Assoc_state) // do the copy
{
_Other._Assoc_state->_Retain();
// class _Associated_state { void _Retain(){ _MT_INCR(_Refs); } }; //增加引用计数
_Assoc_state = _Other._Assoc_state ;
_Get_only_once = _Other._Get_only_once ;
}
else
_Assoc_state = nullptr;
}
}
_State_manager(const _State_manager& _Other, bool _Get_once = false) // copy 构造函数
: _Assoc_state(nullptr) { _Copy_from(_Other); _Get_only_once = _Get_once; }
_State_manager& operator=(const _State_manager& _Other) { _Copy_from(_Other); return *this; }
void _Move_from(_State_manager& _Other) // 服务于 move 构造函数与 move 赋值运算符函数
{
if (this != _STD addressof(_Other))
{
if (_Assoc_state) _Assoc_state->_Release(); // 释放本类原来管理的函数返回值
_Assoc_state = _Other._Assoc_state ;
_Other._Assoc_state = nullptr ;
_Get_only_once = _Other._Get_only_once ;
}
}
_State_manager(_State_manager&& _Other, bool _Get_once = false) // 移动构造函数
: _Assoc_state(nullptr) { _Move_from(_Other); _Get_only_once = _Get_once; }
_State_manager& operator=(_State_manager&& _Other) { _Move_from(_Other); return *this; }
// abandon shared state 这是出错时候的逻辑,本函数用的应该不多。正常情况下线程不会出错。故略
void _Abandon() { if (_Assoc_state) _Assoc_state->_Abandon(); }
// exchange with _Other
void _Swap(_State_manager& _Other) { _STD swap(_Assoc_state, _Other._Assoc_state); }
_Associated_state<_Ty>* _Ptr() const { return _Assoc_state; } // 返回本类保存的裸指针成员
//*********以下是各种成员功能函数*****
bool _Is_ready() const { return _Assoc_state && _Assoc_state->_Is_ready(); }
/*
class _Associated_state // 爷爷类,本注释服务于附近的三个成员函数
{
int _Ready; bool _Ready_at_thread_exit; bool _Retrieved;
bool _Is_ready() const { return _Ready != 0; }
bool _Is_ready_at_thread_exit() const { return _Ready_at_thread_exit; }
bool _Already_retrieved() const { return _Retrieved; }
};
*/
bool _Is_ready_at_thread_exit() const
{
return _Assoc_state && _Assoc_state->_Is_ready_at_thread_exit();
}
// 如经 future 读取,_Get_only_once 为 true ,只要读过一次,就不让读了
// 如经 shared_future 读取,_Get_only_once 为 false ,则本 valid() 始终返 true,表可多次读取
bool valid() const noexcept // 表本类管理的函数的返回值是否有效可读,是则返回 true
{
return _Assoc_state && !(_Get_only_once && _Assoc_state->_Already_retrieved());
}
_Ty& _Get_value() const // 获得对 _Associated_state<_Ty> 中保存的函数返回值的左值引用
{
if ( !valid() )
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::no_state));
return _Assoc_state->_Get_value(_Get_only_once);
}
void _Set_value(const _Ty& _Val, bool _Defer) // copy 函数的返回值
{
if ( !valid() )
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::no_state));
/*
template <class _Ty>
class _Associated_state //用于管理关联同步状态的类
{
// store a result while inside a locked block
void _Set_value_raw(const _Ty& _Val, unique_lock<mutex>* _Lock, bool _At_thread_exit)
{
if (_Has_stored_result)
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::promise_already_satisfied));
_Result = _Val;
_Do_notify(_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
void _Set_value(const _Ty& _Val, bool _At_thread_exit) // store a result
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
_Set_value_raw(_Val, &_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
};
*/
_Assoc_state->_Set_value(_Val, _Defer);
}
// 从这里可以看出:_Packaged_state<T> 内封装的函数执行完后,可以设置函数的返回值;
// 但 future<T> 除了可以读取函数的返回值,也有此 set_value(..) 成员函数可以直接设置一个函数返回值
void _Set_value(_Ty&& _Val, bool _Defer) // 移动函数的返回值
{
if (!valid())
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::no_state));
/*
template <class _Ty>
class _Associated_state //用于管理关联同步状态的类
{
// store a result while inside a locked block
void _Set_value_raw(_Ty&& _Val, unique_lock<mutex>* _Lock, bool _At_thread_exit)
{
if (_Has_stored_result)
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::promise_already_satisfied));
_Result = _STD forward<_Ty>(_Val);
_Do_notify(_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
void _Set_value(_Ty&& _Val, bool _At_thread_exit) // store a result
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
_Set_value_raw(_STD forward<_Ty>(_Val), &_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
};
*/
_Assoc_state->_Set_value(_STD forward<_Ty>(_Val), _Defer);
}
void _Set_exception(exception_ptr _Exc, bool _Defer) //异常处理用的不多
{
if (!valid())
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::no_state));
_Assoc_state->_Set_exception(_Exc, _Defer);
}
//********以下是关于等待*******
void wait() const // wait for signal
{
if (!valid()) // valid() 定义就在上面
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::no_state));
/*
template <class _Ty>
class _Associated_state //用于管理关联同步状态的类
{
virtual void _Wait() // wait for signal
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
// 传递锁进来,是为了解锁,只有写返回值时候才需要加锁。其余时候不必要一直持有锁
_Maybe_run_deferred_function(_Lock);
while (!_Ready) _Cond.wait(_Lock);
}
};
*/
_Assoc_state->_Wait();
}
template <class _Rep, class _Per> // wait for duration
future_status wait_for(const chrono::duration<_Rep, _Per>& _Rel_time) const
{
if (!valid())
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::no_state));
/*
// names for timed wait function returns
enum class future_status { ready, timeout, deferred };
template <class _Ty>
class _Associated_state //用于管理关联同步状态的类
{
template <class _Rep, class _Per> // wait for duration
future_status _Wait_for(const chrono::duration<_Rep, _Per>& _Rel_time)
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
if (_Has_deferred_function())
return future_status::deferred;
if (_Cond.wait_for(_Lock, _Rel_time, _Test_ready(this)))
return future_status::ready;
return future_status::timeout;
}
};*/
return _Assoc_state->_Wait_for(_Rel_time);
}
template <class _Clock, class _Dur> // wait until time point
future_status wait_until(const chrono::time_point<_Clock, _Dur>& _Abs_time) const
{
#if _HAS_CXX20
static_assert(chrono::is_clock_v<_Clock>, "Clock type required");
#endif // _HAS_CXX20
if (!valid())
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::no_state));
/*
template <class _Ty>
class _Associated_state //用于管理关联同步状态的类
{
template <class _Clock, class _Dur> // wait until time point
future_status _Wait_until(const chrono::time_point<_Clock, _Dur>& _Abs_time)
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
if (_Has_deferred_function()) // 注释在上面的函数里
return future_status::deferred;
if (_Cond.wait_until(_Lock, _Abs_time, _Test_ready(this)))
return future_status::ready;
return future_status::timeout;
}
};
*/
return _Assoc_state->_Wait_until(_Abs_time);
}
};
(23)
谢谢






















 2128
2128

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










