(14) 模板 conditional_t<T…> ,定义于 < xtr1common > , 在本 模板里也会用到:

(15)void_t 用于构成特化模板,只要 T 可以被编译器推断为某种类型,void_t 就有意义。 STL 库大师们写的代码,多结合 decltype 来完成类型推断。 当然 T 为空也可以。但为空与 decltype 推断不出来,是两回事。本头文件也用到了,简化逻辑,举例学习一下:
其定义如下:

++ 举例:

++ 再举例测试,学习 void_ :

(16) 存储函数返回值的爷爷基类 _Associated_state<_Ty> , 使用 thread 类来创建线程,没法获得函数的返回值。所以 STL 库又新增了别的具有存储线程中函数返回值的精巧的类。就是该类及其儿子类,孙子类。其子孙类,又扩展了数据成员,存储了可调用对象。这样堆区中的本系列对象,就既存储了线程中的可执行对象,又可以存储函数的返回值了。以下给出其带注释的源码:
template <class _Ty> // 模板参数 _Ty 与线程中执行的函数的返回值类型有关。本类的对象建立在堆区。
class _Associated_state // class for managing associated synchronous state 用于管理关联同步状态的类
{
public:
using _State_type = _Ty; // 函数返回值则 _Ty是对象类型; 返回左值引用则 _Ty是地址; 返回 void则 _Ty是 int
using _Mydel = _Deleter_base<_Ty>;
_Ty _Result; // 当执行函数没有返回值, 则 _Ty 是 int , result 取值为 1 ,表函数执行成功。
exception_ptr _Exception;
mutex _Mtx; // 线程获得锁以后才可以读写 _Associated_state 指针指向对象的这些数据成员
condition_variable _Cond; // 用于线程同步
bool _Retrieved; // 表函数返回值是否被读取过
int _Ready; // 表示函数返回值是否已计算好,可以等待读取了, 初始化为 0 = false ,未准备好
bool _Ready_at_thread_exit; // 是否要待线程结束才允许函数返回值被读取,但代码里貌似未使用,可以用 !_Ready 替代
bool _Has_stored_result; // 先后将 _Has_stored_result 与 _Ready 都设置后外界才可以读取函数返回值
bool _Running; // 表计算函数返回值的线程是否已启动执行,初始化为 false
private:
_Atomic_counter_t _Refs; // using _Atomic_counter_t = unsigned long;
// future 的父类 _State_manager 的 copy 构造与赋值运算符函数,就是仅仅将 _Refs 加一。堆区仅有此一份结果。
_Mydel* _Deleter; // 初始化为 nullptr ,表程序员未使用自己编写的 删除器 ,用的系统默认版本。
void _Delete_this() // delete this object 销毁本模板类的对象自身(也存在父类指针指向子类对象)
{
if (_Deleter) _Deleter->_Delete(this);
else delete this;
}
// overridden by _Deferred_async_state 这俩虚函数仅由孙类 _Deferred_async_state 进行了重定义
// 字面意思就是线程中的函数是否被延迟执行了,是则返回 true
virtual bool _Has_deferred_function() const noexcept { return false; }
/*
template <class _Rx> // 用于管理从异步延迟执行的关联同步状态的类, 此类改写了这俩虚函数
class _Deferred_async_state : public _Packaged_state<_Rx()> // 本类是 _Associated_state 的孙子类
{
virtual bool _Has_deferred_function() override { return ! this->_Running; }
virtual void _Run_deferred_function(unique_lock<mutex>& _Lock) override // run the deferred function
{
_Lock.unlock();
_Packaged_state<_Rx()>::_Call_immediate();
_Lock.lock();
}
};
template <class _Ty>
class _Associated_state
{
virtual void _Run_deferred_function(unique_lock<mutex>&) {} // do nothing 由子类重写这个函数
void _Maybe_run_deferred_function(unique_lock<mutex>& _Lock) // 运行一个延迟函数(如果还没有完成)
{
if (!_Running) // run the function
{
_Running = true;
_Run_deferred_function(_Lock);
}
}
};
*/
virtual void _Run_deferred_function(unique_lock<mutex>&) {} // do nothing 由子类重写这个函数
protected:
// set ready status at thread exit 未见到哪里调用了此函数。本函就是给 _Ready 成员赋值了
void _Make_ready_at_thread_exit() { if (_Ready_at_thread_exit) _Ready = true; }
// run a deferred function if not already done // 运行一个延迟函数(如果还没有完成)
void _Maybe_run_deferred_function(unique_lock<mutex>& _Lock)
{ // 对于正在运行的线程中的函数,本函什么也不做
if (!_Running) { _Running = true; _Run_deferred_function(_Lock); }
}
public:
// non-atomic initialization 构造函数。本类默认模板参数 _Ty 是可构造的,对 _Ty 采用默认构造。
_Associated_state(_Mydel* _Dp = nullptr) : _Refs(1), _Exception(), _Retrieved(false), _Ready(false),
_Ready_at_thread_exit(false), _Has_stored_result(false), _Running(false), _Deleter(_Dp) { }
_Associated_state(const _Associated_state&) = delete; // 禁止 copy 构造函数
_Associated_state& operator=(const _Associated_state&) = delete; // 禁止 copy 赋值运算符
virtual ~_Associated_state() noexcept // registered for release at thread exit 析构函数
{ // 本类存储了线程中函数的返回值。若本类析构时函数返回值没 ready,则不再执行条件变量的唤醒操作
if (_Has_stored_result && !_Ready) { _Cond._Unregister(_Mtx); }
}
void _Retain() { _MT_INCR(_Refs); } // increment reference count 原子性的递增对本对象的引用计数
// decrement reference count and destroy when zero 原子性的递减变量的值
void _Release() { if (_MT_DECR(_Refs) == 0) _Delete_this(); }
// 当没有别处继续引用本对象时,销毁、析构本储存函数返回值的堆区对象。
public:
bool _Is_ready() const { return _Ready != 0; } // 也可直接返回 _Ready,进行默认的类型转换
bool _Is_ready_at_thread_exit() const { return _Ready_at_thread_exit; }
bool _Already_has_stored_result() const { return _Has_stored_result; }
bool _Already_retrieved() const { return _Retrieved; }
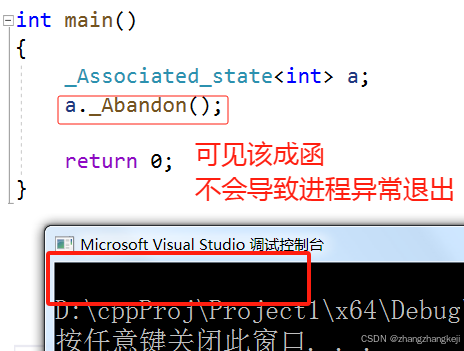
void _Abandon() // 本函的语义可能是当没计算出函数返回值时,本对象就被析构释放,
{ // 则设置 _Associated_state<T>._Exception 成员,以记录此异常情况。
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
// 经测试本函代码的完整执行,仍是正常情况,不会导致进程出错退出。
if (!_Has_stored_result) {
future_error _Fut(make_error_code(future_errc::broken_promise));
_Set_exception_raw(_STD make_exception_ptr(_Fut), &_Lock, false);
}
}
//********以下函数是一组,等待与限时等待********
// 调用本函数的线程会睡眠等待,等待函数返回值的生成。future.wait() 的调用会传递到本函数
virtual void _Wait() // wait for signal 本函会促使函数执行, 以求返回值
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
_Maybe_run_deferred_function(_Lock); // 执行线程中的函数,以得到返回值
while (!_Ready) _Cond.wait(_Lock); // 循环,直到函数的返回值被准备好
}
struct _Test_ready // wraps _Associated_state 类中类,下面的函数会用到
{
const _Associated_state* _State;
_Test_ready(const _Associated_state* _St) : _State(_St) {} // 有参构造函数
bool operator()() const { return _State->_Ready != 0; } // 已 ready 则返回 true
};
// enum class future_status { ready , timeout , deferred };
template <class _Rep, class _Per> // wait for duration
future_status _Wait_for(const chrono::duration<_Rep, _Per>& _Rel_time)
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
if (_Has_deferred_function()) return future_status::deferred; // 延时执行的函数
if (_Cond.wait_for(_Lock, _Rel_time, _Test_ready(this)))
return future_status::ready; // 函数已经执行完毕,返回值已经准备好了
return future_status::timeout; // 正在执行的函数,还没有返回值
}
template <class _Clock, class _Dur> // wait until time point
future_status _Wait_until(const chrono::time_point<_Clock, _Dur>& _Abs_time)
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
if (_Has_deferred_function()) return future_status::deferred;
if ( _Cond.wait_until(_Lock, _Abs_time, _Test_ready(this)) )
return future_status::ready;
return future_status::timeout;
}
//***************************************
// 本函数可以被子类修改,但目前并没有被三个子类修改,所以本代码有效
virtual _Ty& _Get_value( bool _Get_only_once )
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
if (_Get_only_once && _Retrieved)
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::future_already_retrieved));
if (_Exception) _Rethrow_future_exception(_Exception);
_Retrieved = true;
_Maybe_run_deferred_function(_Lock); // 可见,本函也会驱使函数的执行,以获取函数返回值
while (!_Ready) _Cond.wait(_Lock); // 直到函数的返回值准备好了,才返回,才会醒来
if (_Exception) _Rethrow_future_exception(_Exception);
return _Result;
}
//******把函数的返回值存入本结构体*********
private:
// notify waiting threads, This is virtual, but never overridden. 此是虚函数,但从没被改写过
virtual void _Do_notify(unique_lock<mutex>* _Lock, bool _At_thread_exit)
{
_Has_stored_result = true; // 此数据成员显示已计算出函数返回值 , 而 _Ready 表示其它线程可以读取此返回值,分的很细。
if (_At_thread_exit) // notify at thread exit 要求在计算函数返回值的线程退出时,才对外显示 ready 可以读取返回值了
_Cond._Register(*_Lock, &_Ready); // 线程退出时还会检查 _Ready 的值,为 true 才进行唤醒操作么??
else // notify immediately
{
_Ready = true; // 反之,则是在函数返回值计算出来后立马填写 _Associated_state 的数据成员 _Ready
_Cond.notify_all();
}
}
public:
// store a (void) result while inside a locked block 对应于函数的返回值是 void 的情形
void _Set_value_raw(unique_lock<mutex>* _Lock, bool _At_thread_exit)
{
if (_Has_stored_result) // 形参2 _At_thread_exit 只是为了传递给另一成函 _Do_notify(...)
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::promise_already_satisfied));
_Do_notify(_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
void _Set_value_raw(const _Ty& _Val, unique_lock<mutex>* _Lock, bool _At_thread_exit)
{
if (_Has_stored_result)
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::promise_already_satisfied));
_Result = _Val; // 函数的返回值的 copy 赋值运算符函数
_Do_notify(_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
void _Set_value_raw(_Ty&& _Val, unique_lock<mutex>* _Lock, bool _At_thread_exit)
{
if (_Has_stored_result)
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::promise_already_satisfied));
_Result = _STD forward<_Ty>(_Val); // 函数的返回值的 移动 赋值运算符函数
_Do_notify(_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
void _Set_value(const _Ty& _Val, bool _At_thread_exit) // copy 得到的函数返回值
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
_Set_value_raw(_Val, &_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
void _Set_value( _Ty&& _Val , bool _At_thread_exit) // 移动 得到的函数返回值
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
_Set_value_raw(_STD forward<_Ty>(_Val), &_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
void _Set_value(bool _At_thread_exit) // store a (void) result
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx); // 函数的返回值是 void
_Set_value_raw(&_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
//******以下貌似是处理异常情况,用的不多*******
// store a result while inside a locked block
void _Set_exception_raw(exception_ptr _Exc, unique_lock<mutex>* _Lock, bool _At_thread_exit)
{
if (_Has_stored_result)
_Throw_future_error(make_error_code(future_errc::promise_already_satisfied));
_Exception = _Exc; // 给本类的 _Exception 成员赋值,而不是给 _Result 成员赋值
_Do_notify(_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
void _Set_exception(exception_ptr _Exc, bool _At_thread_exit) // store a result
{
unique_lock<mutex> _Lock(_Mtx);
_Set_exception_raw(_Exc, &_Lock, _At_thread_exit);
}
};
++ 接着给出对其成员函数 _Abandon ( ) 的测试:
(17)
谢谢























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










