OkHttp网络请求框架源码解析一
基本使用,在app的build.gradle添加依赖
compile 'com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:3.8.1'
在配置文件添加网络访问权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"></uses-permission>
具体使用流程:
//创建client
OkHttpClient client=new OkHttpClient.Builder().readTimeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS).build();
//创建request
final Request request=new Request.Builder().url("http://www.baidu.com").get().build();
//调用
Call call=client.newCall(request);
call.enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
Log.d("fail",e.toString());
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
Log.d("baidu:",response.body().string());
}
});
源码分析:
//第一步:
OkHttpClient client=new OkHttpClient.Builder().readTimeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS).build();
//其中Builder()方法,初始化一些默认参数,包括Dispatcher的创建,连接池的创建等。
public Builder() {
//核心Dispatcher,call.enqueue()方法最终由dispatcher的enqueue()方法来完成请求。
dispatcher = new Dispatcher();
......
//连接池
connectionPool = new ConnectionPool();
......
}
//其中build()方法,最终获取OkHttpClient实例。典型的构建者模式。
public OkHttpClient build() {
return new OkHttpClient(this);
}
call.enqueue()方法
//最终调用RealCall里面的enqueue
@Override public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {
//锁住RealCall对象
synchronized (this) {
//保证只请求一次
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
//忽略非核心代码
......
//调用Dispatcher的enqueue方法 ,其中AsyncCall是Runnable。
client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));
}
//调用Dispatcher的enqueue方法 ,其中AsyncCall是Runnable。
synchronized void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
//分别判断正在执行的异步请求队列大小 和 正在执行的主机请求队列大小
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < 64 && runningCallsForHost(call) < 5) {
//将Runnable添加到正在执行的异步请求队列
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
//线程池来执行此Runnable
executorService().execute(call);
} else {
//否则将Runnable添加到正在等待的异步请求队列
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
}
}
//Dispatcher类里面创建线程池,虽然这里运行的最大线程数为Integer.MAX_VALUE,
//但是记住前面正在运行的异步队列大小限制为64.
public synchronized ExecutorService executorService() {
if (executorService == null) {
executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp Dispatcher", false));
}
return executorService;
}
//作为Runnable的 AsyncCall,最终的execute()方法为RealCall里面的execute()方法。
@Override protected void execute() {
//获取响应回来的数据response
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
//回调onFailure
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
//回调onResponse
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
......
//线程池执行完线程任务后,调用此方法.
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
//作为Runnable的 AsyncCall,最终的execute()方法为RealCall里面的execute()方法。
@Override protected void execute() {
//获取响应回来的数据response
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
//回调onFailure
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
//回调onResponse
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
......
//线程池执行完线程任务后,调用此方法.
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
//client.dispatcher().finished(this)的实现
private <T> void finished(Deque<T> calls, T call, boolean promoteCalls) {
synchronized (this) {
//将任务从队列中移除
if (!calls.remove(call)) throw new AssertionError("Call wasn't in-flight!");
//处理就绪状态的异步请求队列
if (promoteCalls) promoteCalls();
}
}
//处理就绪状态的异步请求队列 promoteCalls() 的实现
private void promoteCalls() {
//遍历就绪状态的异步请求队列readyAsyncCalls
for (Iterator<AsyncCall> i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
AsyncCall call = i.next();
if (runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
//如果满足条件,则将任务从readyAsyncCalls移除,
//并添加至runningAsyncCalls,然后线程池执行该任务
i.remove();
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
executorService().execute(call);
}
}
}
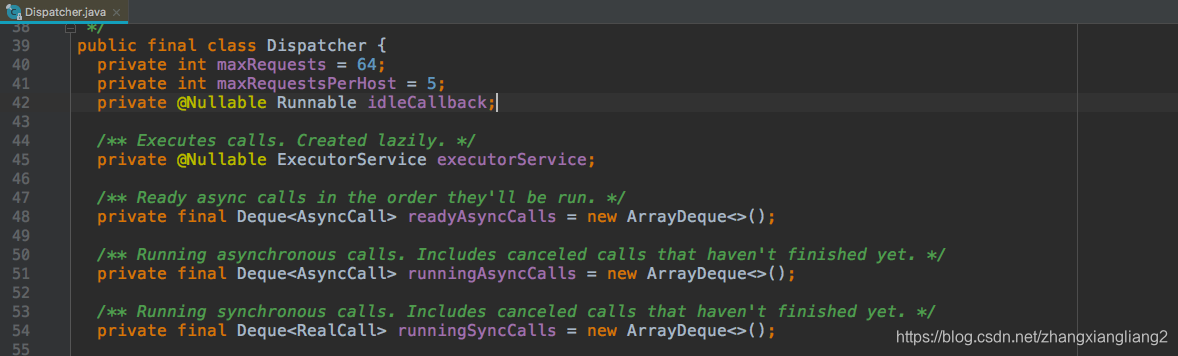
核心Dispatcher类,维护着线程池executorService,和三个队列,分别为就绪状态的异步请求队列readyAsyncCalls,运行状态的异步请求队列runningAsyncCalls, 运行状态的同步请求队列runningSyncCalls。







 本文详细解析了OkHttp网络请求框架的基本使用及源码流程,包括依赖添加、权限配置、请求发送、响应处理及核心Dispatcher工作原理,深入探讨了线程池、请求队列管理及异步请求处理机制。
本文详细解析了OkHttp网络请求框架的基本使用及源码流程,包括依赖添加、权限配置、请求发送、响应处理及核心Dispatcher工作原理,深入探讨了线程池、请求队列管理及异步请求处理机制。
















 670
670

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








