要想拿到多线程的返回值,就要用Callable接口,
Runable的run方法是没有返回值的,用Callable去获取你多线程中方法的返回值,配合FutureTask去获取线程中的返回值
1,整一个需要返回值的类实现Callable<V> 接口,重写call接口。
public class Person implements Callable<Person> {
private String name;
public Person(String name){
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public Person call() throws Exception {
this.name= "hello," +this.name;
System.out.println(this.name);
return this;
}
}2,创建FutureTask 实例,
// 创建实例
FutureTask<Person> zhs=new FutureTask<>(new Person("zhs"));
// 调用线程的构造方法,这里可以猜出来FutureTask其实也是实现了Runable接口的,不信的点进去看看就知道了
new Thread(zhs).start();3,获取到线程中的返回值
Person person=zhs.get();完整代码如下
public class ThreadMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask<Person> zhs=new FutureTask<>(new Person("zhs"));
new Thread(zhs).start();
FutureTask<Person> lcc=new FutureTask<>(new Person("lcc"));
new Thread(lcc).start();
Person personzhs=zhs.get();
Person personlcc=lcc.get();
System.out.println(personzhs.toString());
System.out.println(personlcc.toString());
}
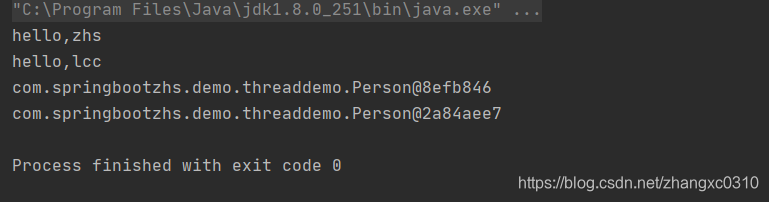
}返回结果如下
Callable 在线程池中的使用
这里就直接用ExecutorService去创建线程池了,自定义创建线程池的请参考《线程池的使用》
public class CallableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService exec=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
ArrayList<Future<Person>> results=new ArrayList<Future<Person>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
results.add(exec.submit(new Person(i+"")));
}
for (Future<Person> future : results) {
try {
System.out.println(future.get());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
exec.shutdown();
}
}
}
}返回结果如下
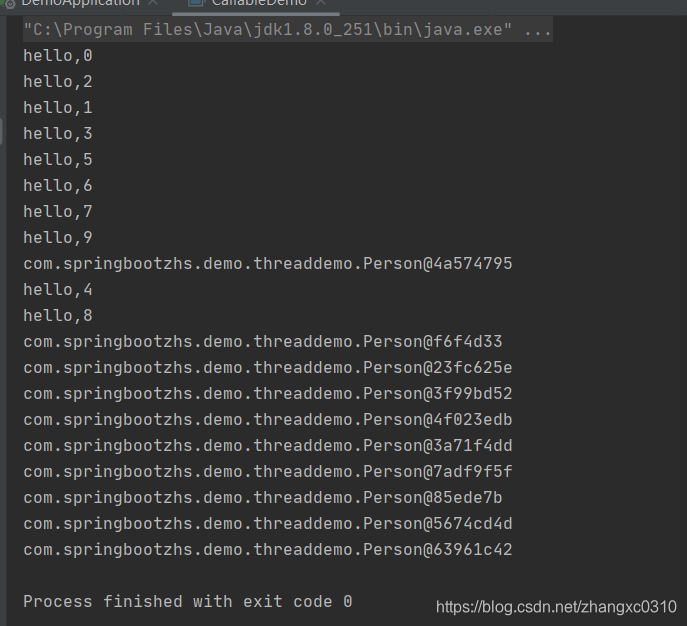
这里就可以看出多个线程是异步执行了,有call方法体打印的语句,还有返回结果打印的对象























 1004
1004

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








