题目地址:Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List - LeetCode
Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right pointers as synonymous to the previous and next pointers in a doubly-linked list.
Let’s take the following BST as an example, it may help you understand the problem better:
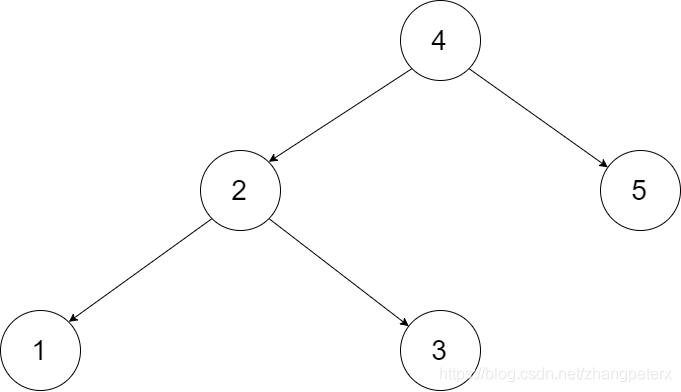
We want to transform this BST into a circular doubly linked list. Each node in a doubly linked list has a predecessor and successor. For a circular doubly linked list, the predecessor of the first element is the last element, and the successor of the last element is the first element.
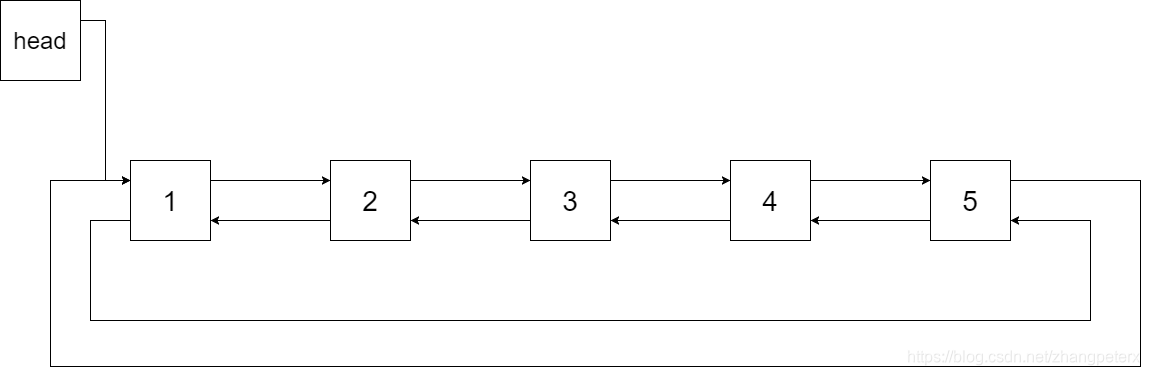
The figure below shows the circular doubly linked list for the BST above. The “head” symbol means the node it points to is the smallest element of the linked list.
Specifically, we want to do the transformation in place. After the transformation, the left pointer of the tree node should point to its predecessor, and the right pointer should point to its successor. We should return the pointer to the first element of the linked list.
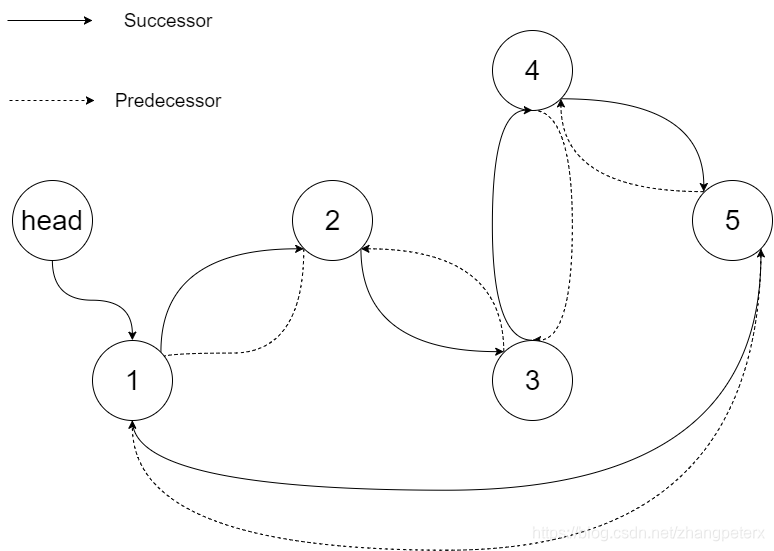
The figure below shows the transformed BST. The solid line indicates the successor relationship, while the dashed line means the predecessor relationship.
java官方解法如下:
class Solution {
// the smallest (first) and the largest (last) nodes
Node first = null;
Node last = null;
public void helper(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
// left
helper(node.left);
// node
if (last != null) {
// link the previous node (last)
// with the current one (node)
last.right = node;
node.left = last;
}
else {
// keep the smallest node
// to close DLL later on
first = node;
}
last = node;
// right
helper(node.right);
}
}
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if (root == null) return null;
helper(root);
// close DLL
last.right = first;
first.left = last;
return first;
}
}
Python官方解法如下:
class Solution:
def treeToDoublyList(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
def helper(node):
"""
Performs standard inorder traversal:
left -> node -> right
and links all nodes into DLL
"""
nonlocal last, first
if node:
# left
helper(node.left)
# node
if last:
# link the previous node (last)
# with the current one (node)
last.right = node
node.left = last
else:
# keep the smallest node
# to close DLL later on
first = node
last = node
# right
helper(node.right)
if not root:
return None
# the smallest (first) and the largest (last) nodes
first, last = None, None
helper(root)
# close DLL
last.right = first
first.left = last
return first
C++官方解法如下:
class Solution {
public:
// the smallest (first) and the largest (last) nodes
Node* first = NULL;
Node* last = NULL;
void helper(Node* node) {
if (node) {
// left
helper(node->left);
// node
if (last) {
// link the previous node (last)
// with the current one (node)
last->right = node;
node->left = last;
}
else {
// keep the smallest node
// to close DLL later on
first = node;
}
last = node;
// right
helper(node->right);
}
}
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if (!root) return NULL;
helper(root);
// close DLL
last->right = first;
first->left = last;
return first;
}
};
最优的做法是中序遍历:
def treeToDoublyList(self, root):
if not root: return
dummy = Node(0, None, None)
prev = dummy
stack, node = [], root
while stack or node:
while node:
stack.append(node)
node = node.left
node = stack.pop()
node.left, prev.right, prev = prev, node, node
node = node.right
dummy.right.left, prev.right = prev, dummy.right
return dummy.right








 将二叉搜索树(BST)原地转换为有序的循环双链表。官方提供了Java、Python和C++的解法。转换后,每个节点的左指针指向其前驱,右指针指向其后继,形成闭合环状链表。
将二叉搜索树(BST)原地转换为有序的循环双链表。官方提供了Java、Python和C++的解法。转换后,每个节点的左指针指向其前驱,右指针指向其后继,形成闭合环状链表。
















 541
541

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








