题目:找出字符串中最长连续的无重复字符个数?
样例:
输入'weee',输出2,即最长连续的无重复字符串为'we'
输入'asddfghkh',输出5,最长串为'dfghk'
方法一:暴力破解。双层循环,从下标0开始,每次尽可能的去匹配最长的不重复字符串。每当出现重复的时候,返回开始下标+1的位置。继续匹配。
def GetMaxLongestSubStr0(source_str) :iMaxCount = 0iCurrCount = 0dict_str = {}for i in range(len(source_str)) :for j in range(i, len(source_str)) :if source_str[j] in dict_str.keys() :iMaxCount = iMaxCount if iCurrCount <= iMaxCount else iCurrCountiCurrCount = 0dict_str = {}else :iCurrCount += 1dict_str[source_str[j]] = 1iMaxCount = iMaxCount if iCurrCount <= iMaxCount else iCurrCountiCurrCount = 0return iMaxCountprint(GetMaxLongestSubStr0('werrtgtgh'))
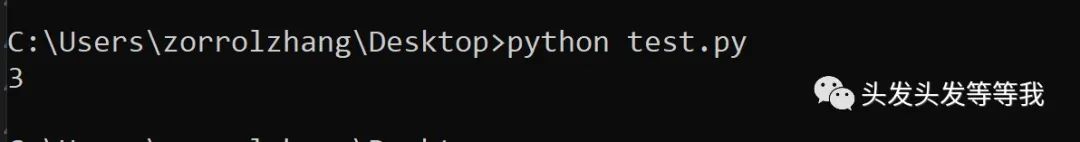
以上算法有一个很明显的弊端。假设我们遇到的字符串为,'qwertttttt'。当我们遇到匹配失败的字符't'的时候,我们返回开始下标+1的位置,必然会再次遇到这个失败的情况
为了避免这种情况,尽量节省空间。我们采用跳跃法,也可以叫滑动窗口法。因为他的原理很类似于滑动窗口。
仍然从0开始,不过我们保存的字典中,value变成了key对应的字符串的下标。因此当我们遭遇到一次失败的时候,将替换调失败字符在字典中对应的下标,与此同时,干掉失败字符以前插入进字典的key-value数值。继续匹配。

如上图,当我们第一次尽可能匹配的时候,会匹配到'qwerty'超长子串,此时字典内容如旁边红色标注。当下次匹配'e'失败后,我们突出前一个字符'e'及以前所有的字符,插入当前匹配到的字符'e'。如此往复。
def GetMaxLongestSubStr1(source_str) :iMaxCount = 0iCurrCount = 0dict_str = {}begin = 0for i in range(len(source_str)) :if source_str[i] in dict_str.keys() :iMaxCount = iMaxCount if iCurrCount <= iMaxCount else iCurrCountend = dict_str[source_str[i]]# 从begin开始移除dict中保存的数据while(begin <= end) :# 是重复字符,更新位置信息。非重复字符,删除对应keyif source_str[i] == source_str[begin] :dict_str[source_str[begin]] = ielse :iCurrCount -= 1del dict_str[source_str[begin]]begin += 1else :iCurrCount += 1dict_str[source_str[i]] = ii += 1iMaxCount = iMaxCount if iCurrCount <= iMaxCount else iCurrCountreturn iMaxCountprint(GetMaxLongestSubStr1('ftfyihefeh'))print(GetMaxLongestSubStr1('werrtgtgh'))print(GetMaxLongestSubStr1('wwwwwwwww'))
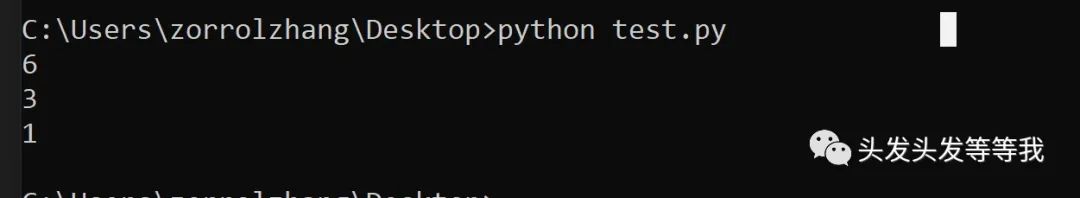
 优化算法:找到字符串中最长无重复字符子串
优化算法:找到字符串中最长无重复字符子串





 该博客介绍了两种方法来解决找出字符串中最长连续无重复字符子串的问题。首先,通过暴力破解的方法,使用双层循环进行匹配,但效率较低。接着,提出了一种改进的滑动窗口算法,利用字典记录字符及其位置,当遇到重复字符时,更新字典并继续匹配,提高了效率。这种方法适用于处理包含大量重复字符的字符串。
该博客介绍了两种方法来解决找出字符串中最长连续无重复字符子串的问题。首先,通过暴力破解的方法,使用双层循环进行匹配,但效率较低。接着,提出了一种改进的滑动窗口算法,利用字典记录字符及其位置,当遇到重复字符时,更新字典并继续匹配,提高了效率。这种方法适用于处理包含大量重复字符的字符串。
















 2194
2194

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








