I am a new Linux and Unix shell user. How do I Remove or delete jobs from current bash / ksh or POSIX based shell?
Job control is nothing but the ability to stop/suspend the execution of processes (command) and continue/resume their execution as per your requirements. This is done using your operating system and shell such as bash/ksh or POSIX shell.
| disown command details | |
|---|---|
| Description | Remove jobs from current shell |
| Category | Processes Management |
| Difficulty | Easy |
| Root privileges | No |
| Estimated completion time | 5m |
|
| |
Purpose
Remove jobs from the table of active job.
Syntax
The basic syntax is as follows:
disown jobID
OR
disown jobID1 jobID2 ... jobIDN
OR
disown [options] jobID1 jobID2 ... jobIDN
A note about BASH and KSH93 disown command
=> The disown command on ksh shell causes the shell not to send a HUP signal to each given job, or all active jobs if job is omitted, when a login shell terminates.
=>The disown command on bash shell can either remove jobs or causes the shell not to send a HUP signal to each given job or all jobs.
=> All examples, on this page are executed on bash shell either on OS X Unix or Ubuntu Linux.
disown command examples
Before you start using fg command, you need to start couple of jobs on your system for demonstration purpose. Type the following commands to start jobs:
xeyes & gnome-calculator & gedit fetch-stock-prices.py &
Finally, run ping command in foreground:
ping cyberciti.biz
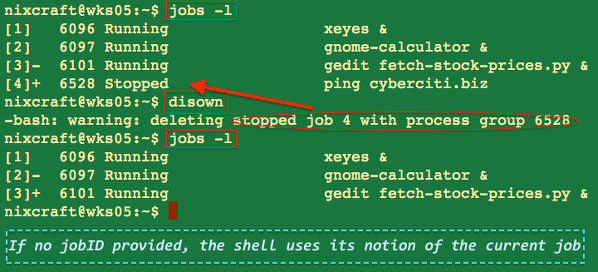
To suspend ping command job hit the Ctrl-Z key sequence. Use the jobs -l command to list current jobs:
$ jobs -l
Without any options, each jobID is removed from the table of active jobs i.e. the bash shell uses its notion of the current job which is displayed by + symbol in jobs -l command:
$ disown
Sample outputs:
How do I remove all jobs?
Pass the -a option to disown command, type:
$ disown -a
## You should not see any jobs running on screen ##
$ jobs -l
How do I remove only running jobs?
Pass the -r option to disown command, type:
$ disown -r
$ jobs -l
How do I keep running job after I exit from a shell prompt in background?
The SIGHUP (Hangup) signal is used by your system on controlling terminal or death of controlling process. You can use SIGHUP to reload configuration files and open/close log files too. In other words if you logout from your terminal all running jobs will be terminated. To avoid this you can pass the -h option to disown command. This option mark each jobID so that SIGHUP is not sent to the job if the shell receives a SIGHUP. The syntax is:
$ disown -h jobID
disown -h %2
In this example, update the Debian or Ubuntu Linux based server using apt-get command in background:
## Step 1: update system ## apt-get upgrade &> /root/system.update.log & ## Step 2: Mark apt-get so that SIGHUP is not sent when you exit and go for tea ## disown -h ## Step 3: exit from root shell ## exit
Please note that you can also use nohup command to set the signal SIGHUP to be ignored for any command on Linux or Unix for same purpose.
disown command options
From the bash(1) command man page:
| Option | Description |
| -a | Delete all jobs if jobID is not supplied. |
| -h | Mark each jobID so that SIGHUP is not sent to the job if the shell receives a SIGHUP. |
| -r | Delete only running jobs. |
Related media
This tutorial is also available in a quick video format:
http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/unix-linux-disown-command-examples-usage-syntax/








 本文详细介绍了如何在Linux Shell环境中使用disown命令删除当前bash/ksh或POSIX shell中的作业,包括删除所有作业、仅删除运行中的作业以及保留运行中作业在退出终端时不被终止的方法。
本文详细介绍了如何在Linux Shell环境中使用disown命令删除当前bash/ksh或POSIX shell中的作业,包括删除所有作业、仅删除运行中的作业以及保留运行中作业在退出终端时不被终止的方法。
















 1697
1697

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








