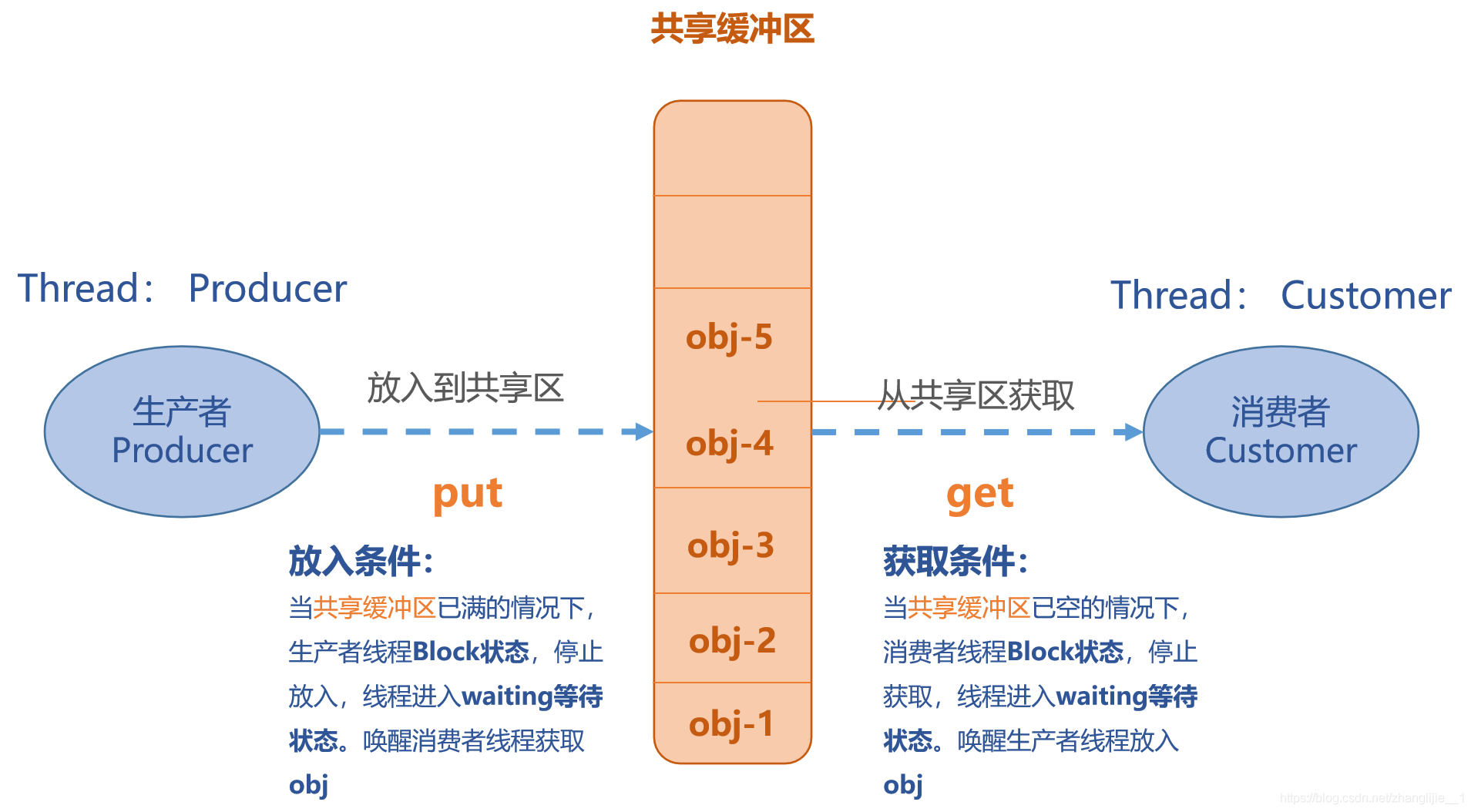
生产者消费者问题(英语:Producer-consumer problem),也称有限缓冲问题(英语:Bounded-buffer problem),是一个多线程同步问题的经典案例。
该问题描述了两个共享固定大小缓冲区的线程——即所谓的“生产者”和“消费者”——在实际运行时会发生的问题。
生产者的主要作用是生成一定量的数据放到缓冲区中,然后重复此过程。 消费者也在缓冲区消耗这些数据。
该问题的关键就是要保证生产者不会在缓冲区满时加入数据,消费者也不会在缓冲区中空时消耗数据。
代码:
#_*_coding:utf-8 _*_
'''
ch04-demo06-customer.py
----------------------
生产者-消费者
@Copyright:Chinasoft International.ETC
@author:Alvin
@data:2018-04-24
'''
#导入多线程模块
import threading
#倒入时间模块
import time
#导入随机模块
import random
#使用共享区模拟变量
count=0
#创建条件对象
condition = threading.Condition()
#生产者线程类
class Producer(threading.Thread):
#重写构造方法
def __init__(self,threadName):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadName=threadName
#重写run()方法
def run(self):
global count #引用全局共享变量count
while True:
#使用条件对象获取锁并锁定
if condition.acquire():
#判断共享变量是否已达上限
if count>=0:
print('共享区已满,生产者producer线程进入阻塞Block状态,停止放入!')
condition.wait()#当前线程进入阻塞状态
else:
count +=1 #共享变量自增1
msg = time.ctime()+""+self.threadName+'生产了1件商品放入共享区,共享区总计商品个数:'+str(count)
print(msg)
condition.notify()#唤醒其他阻塞状态的线程(如,消费者线程)
condition.release()#解除锁定
time.sleep(random.randrange(10)/5)#随机休眠N秒
#消费者线程
class Customer(threading.Thread):
#重写构造方法
def __init__(self,threadName):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadName =threadName
#重写run()方法
def run(self):
global count #引用全局共享变量count
while True:
#使用条件对象获取锁并锁定
if condition.acquire():
#判断共享变量是否已为0
if count<1:
print('共享区已空,消费者Customer线程进入阻塞Block状态,停止获取!')
condition.wait() #当前线程进入阻塞状态
else:
count -=1#共享变量自减1
msg = time.ctime()+''+self.threadName+'消费了1件商品,共享区总计商品个数:'+str(count)
print(msg)
condition.notify() # 唤醒其他阻塞状态的线程(如,消费者线程)
condition.release() # 解除锁定
time.sleep(random.randrange(10)) # 随机休眠N秒
#脚本程序入口
if __name__ == '__main__':
for i in range(2):
p=Producer('[生产者-'+str(i+1)+']')
p.start()
for i in range(5):
c = Producer('[消费者-' + str(i + 1) + ']')
c.start()
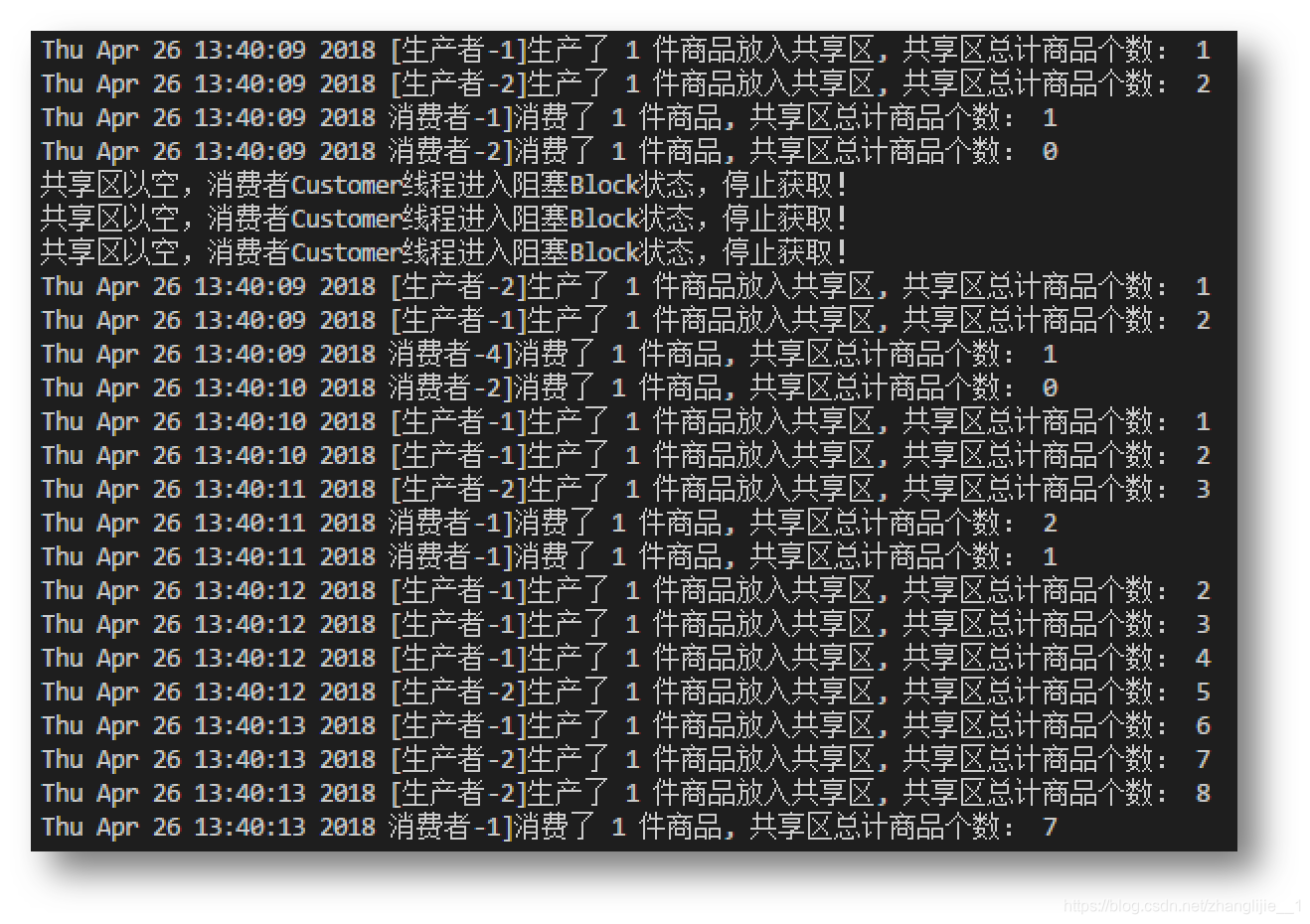
结果如下图:





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








