文章目录
1. 概念
🐯volume 1 - 6.5 INTERRUPTS AND EXCEPTIONS
The processor provides two mechanisms for interrupting program execution, interrupts, and exceptions:
• An interrupt is an asynchronous event that is typically triggered by an I/O device.
• An exception is a synchronous event that is generated when the processor detects one or more predefined conditions while executing an instruction. The IA-32 architecture specifies three classes of exceptions: faults, traps, and aborts.
The processor responds to interrupts and exceptions in essentially the same way. When an interrupt or exception is signaled, the processor halts execution of the current program or task and switches to a handler procedure that has been written specifically to handle the interrupt or exception condition. The processor accesses the handler procedure through an entry in the interrupt descriptor table (IDT). When the handler has completed handling the interrupt or exception, program control is returned to the interrupted program or task.
程序提供2种中断系统执行的机制,中断和异常:
- 中断机制:是一个被IO硬件设备触发的异步事件
- 异常机制:处理器在执行程序时检测一个或多个预定义条件时,发生同步事件,IA-32架构指定了3个异常类:fault,trap,abort
处理器用同样的方式对于中断和异常做出响应。当一个中断/异常被标记,处理器停止当前程序/任务的执行并切换一个处理程序,用来处理预先被卸卸任的中断/异常场景,处理器通过一个
IDT的入口点来处理程序。当处理完成中断/异常时,程序控制会返回被中断的程序/任务。
中断的异步机制:通过硬件自己的8259A阵脚INT来标记1,然后CPU的中断检测周期到了后,会识别CPU上的INTR阵脚,从而进行处理。
异步:硬件相关的自己处理,是一个异步处理,当处理完后,CPU会定期检测
🐯volume 1 - 6.5 INTERRUPTS AND EXCEPTIONS
The operating system, executive, and/or device drivers normally handle interrupts and exceptions independently from application programs or tasks. Application programs can, however, access the interrupt and exception
handlers incorporated in an operating system or executive through assembly-language calls. The remainder of this section gives a brief overview of the processor’s interrupt and exception handling mechanism. See Chapter 7, “Interrupt and Exception Handling,” in the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A, for a description of this mechanism.
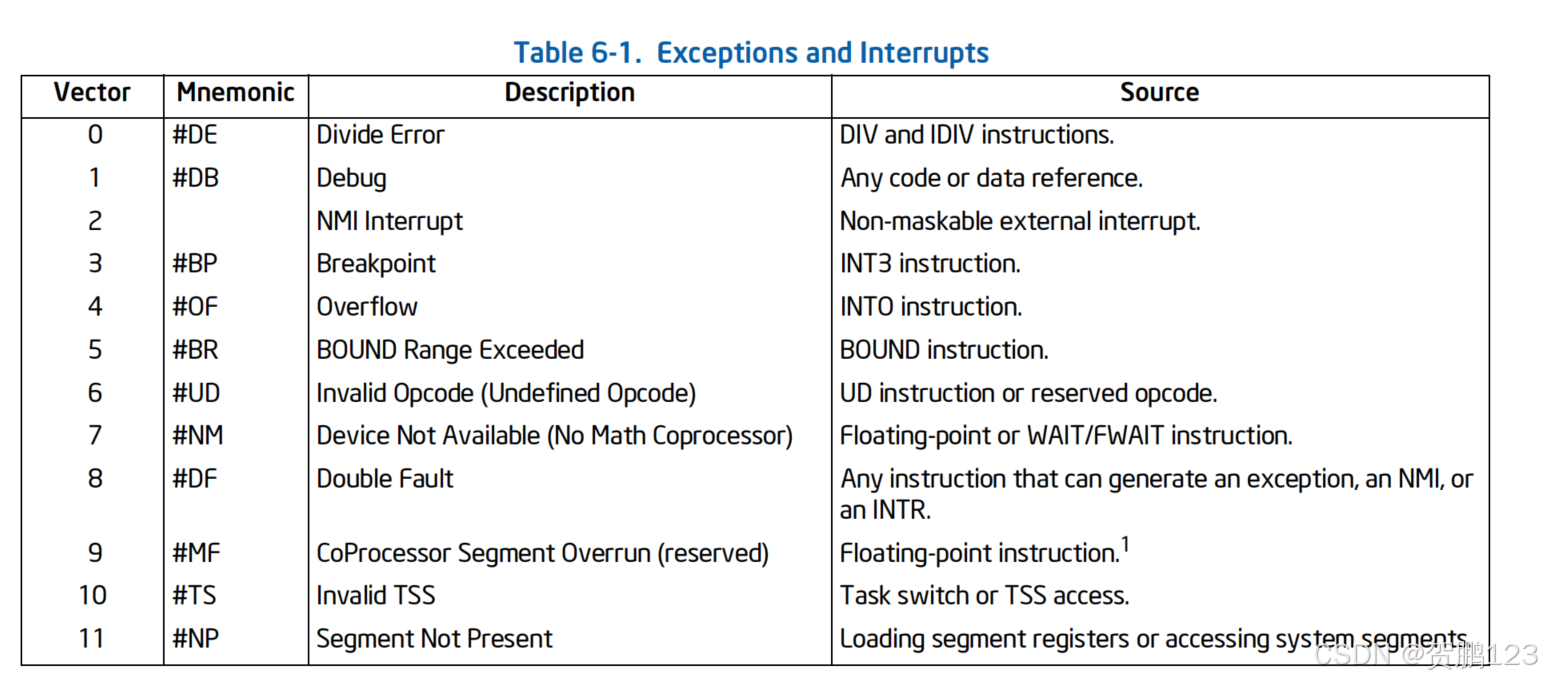
The IA-32 Architecture defines 18 predefined interrupts and exceptions and 224 user defined interrupts, which are associated with entries in the IDT. Each interrupt and exception in the IDT is identified with a number, called a vector. Table 6-1 lists the interrupts and exceptions with entries in the IDT and their respective vectors. Vectors 0 through 8, 10 through 14, and 16 through 19 are the predefined interrupts and exceptions; vectors 32 through 255 are for software-defined interrupts, which are for either software interrupts or maskable hardware interrupts.
Note that the processor defines several additional interrupts that do not point to entries in the IDT; the most notable of these interrupts is the SMI interrupt. See Chapter 7, “Interrupt and Exception Handling,” in the Intel®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A, for more information about the interrupts and exceptions.When the processor detects an interrupt or exception, it does one of the following things:
- Executes an implicit call to a handler procedure.
- Executes an implicit call to a handler task.
操作系统,执行,设备驱动来处理中断和异常,不依赖于应用程序/任务。然而,应用程序通过汇编语言调用在操作系统或执行程序中的处理程序,可以访问中断和异常。
IA-32架构图定义了18个预定义的中断和异常,224用户定义的中断,这些预定义的程序的入口在
IDT表里里。在IDT里的每个中断和异常被一个向量数字所标识。注意:程序定义的几个额外的中断,但没有在
IDT里有入口点。这些定义看Vol 3 Chapter7。当程序检测出一个中断/异常,会做如下事情中的一个:
- 执行隐式调用一个处理过程
- 执行隐式调用一个处理任务
🐯volume 1 - 6.5 INTERRUPTS AND EXCEPTIONS
If the code segment for the handler procedure has the same privilege level as the currently executing program or task, the handler procedure uses the current stack; if the handler executes at a more privileged level, the processor switches to the stack for the handler’s privilege level.
如果处理程序的代码段在当前执行程序/任务里,有相同的特权级,处理程序会使用当前栈。
如果处理执行在更高的特权级级别,则处理器切换到处理程序特权级别的堆栈。
🚪这个地方,就涉及到了用户态和内核态之间转换的原理。
上面的话的意思相当于
代码段的特权级权限
- 相同:不切换栈,使用当前栈,可以访问里面的信息
- 不相同:使用调用者的栈,不可以访问处理器程序里的栈信息
处理器栈程序的code segment权限是R0,所以是OS级别的。
如果用户态程序能访问这个级别的栈,就可以操作CPU了,所以用不同的栈来表示,也可以理解为不同特权级都有各自的栈。
🚀每个进程都有自己的内核栈
🐯volume 3 - 7.1 INTERRUPT AND EXCEPTION OVERVIEW
Interrupts and exceptions are events that indicate that a condition exists somewhere in the system, the processor, or within the currently executing program or task that requires the attention of a processor. They typically result in a forced transfer of execution from the currently running program or task to a special software routine or task called an interrupt handler or an exception handler. The action taken by a processor in response to an interrupt or exception is referred to as servicing or handling the interrupt or exception.
Interrupts occur at random times during the execution of a program, in response to signals from hardware. System hardware uses interrupts to handle events external to the processor, such as requests to service peripheral devices. Software can also generate interrupts by executing the INT n instruction.
Exceptions occur when the processor detects an error condition while executing an instruction, such as division by zero. The processor detects a variety of error conditions including protection violations, page faults, and internal machine faults
When an interrupt is received or an exception is detected, the currently running procedure or task is suspended while the processor executes an interrupt or exception handler. When execution of the handler is complete, the processo





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1136
1136

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








