2.组件状态共享
1. 状态共享-父子单向
State是当前组件的状态,用State修饰的数据变化会驱动UI的更新(只有一层)
父传子的时候,子组件定义变量的时候,如果没有任何的修饰符,那么该值只会在第一次渲染时生效
State是当前组件的状态,他的数据变化可以驱动UI,但是子组件接收的数据没办法更新
父子单向:
@Prop:子组件可以接收父组件的值,父组件不能接收子组件的值(单向)
@Entry
@Component
struct ComponentQuestionCase {
@State money: number = 999999;
build() {
Column() {
Text('father:' + this.money)
Button('存100块')
.onClick(()=>{
this.money+=100
})
CompQsChild({money:this.money})
}
.padding(20)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
@Component
struct CompQsChild {
@Prop money: number = 0
build() {
Column() {
Text('child:' + this.money)
Button('花100块')
.onClick(()=>{
this.money-=100
})
}
.padding(20)
.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
}
2. 状态共享-父子双向
父子双向:
@Link:子组件用Link修饰了传递过来的数据,就是双向同步了
注意:Link修饰符不允许给初始值
@Entry
@Component
struct ComponentQuestionCase {
@State
money: number = 999999;
build() {
Column() {
Text('father:' + this.money)
Button('存100块')
.onClick(()=>{
this.money+=100
})
CompQsChild({money:this.money})
}
.padding(20)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
@Component
struct CompQsChild {
// 各玩各的
// @State money: number = 0
// 听爸爸的话
// @Prop money: number
// 团结一心
@Link money: number
build() {
Column() {
Text('child:' + this.money)
Button('花100块')
.onClick(()=>{
this.money-=100
})
}
.padding(20)
.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
}
3. 状态共享-后代组件
后代组件:
祖组件:@Provide来传值 @Provie data : one={ num:1 }
后代组件:@Consume接收数据 @Consume data : one
注意:@Consume 不允许有默认值
注意:Provide 和 Consume 必须同名,书写时没有校验
建议:在提供数据和访问数据时,使用全局别名。
如果组件已有该命名变量,可以起全局别名进行提供/接收
1.提供起别名
@Provide(全局别名) 组件内名字:类型 = 初始值
2.接收起别名
@Consume(全局别名)组件内名字:类型 组件内名字可以起个不冲突的
@Entry
@Component
struct ComponentQuestionCase1 {
@Provide
dataInfo: MoneyInfo1 = {
money: 99999,
bank: '中国银行'
}
build() {
Column() {
Text('father:' + this.dataInfo.money)
Button('存100块')
.onClick(() => {
this.dataInfo.money += 100
})
CompQsChild1()
}
.padding(20)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
}
}
@Component
struct CompQsChild1 {
// 各玩各的
// @State money: number = 0
// 听爸爸的话
// @Prop money: number
// 团结一心
@Consume
dataInfo: MoneyInfo1
build() {
Column() {
Text('child:' + this.dataInfo.money)
Button('花100块')
.onClick(() => {
this.dataInfo.money -= 100
})
ChildChild1()
}
.padding(20)
.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
}
}
@Component
struct ChildChild1 {
// 各玩各的
// @State money: number = 0
// 听爸爸的话
// @Prop money: number
// 团结一心
@Consume
dataInfo: MoneyInfo1
// @Link dataInfo: MoneyInfo
build() {
Column() {
Text('ChildChild:' + this.dataInfo.money)
Button('花100块')
.onClick(() => {
this.dataInfo.money -= 100
})
}
.padding(20)
.backgroundColor(Color.Red)
}
}
interface MoneyInfo1 {
money: number
bank: string
}
4.状态监听
如果开发者需要关注某个状态变量的值是否改变,可以使用 @Watch 为状态变量设置回调函数。
Watch(“回调函数名”)中的回调必须在组件中声明,该函数接收一个参数,参数为修改的属性名
注意:Watch修饰符要写 State Prop Link Provide的修饰符下面,否则会有问题
在第一次初始化的时候,@Watch装饰器的方法不会被调用
@Entry
@Component
struct PlayControlComp {
@State shakenX: number = 0
@State shakenY: number = 0
timer: number = -1
@State @Watch('update') isPlay: boolean = false
update() {
if (this.isPlay) {
this.timer = setInterval(() => {
this.shakenX = 2 - Math.random() * 4
this.shakenY = 2 - Math.random() * 4
}, 100)
} else {
clearInterval(this.timer)
this.shakenX = 0
this.shakenY = 0
}
}
build() {
Column() {
Stack() {
Text('抖音')
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor('#ff2d83b3')
.translate({
x: this.shakenX,
y: this.shakenY
})
.zIndex(1)
Text('抖音')
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor('#ffe31fa9')
.translate({
x: this.shakenY,
y: this.shakenX
})
.zIndex(2)
Text('抖音')
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor('#ff030000')
.translate({
x: 0,
y: 0
})
.zIndex(3)
}
Row({ space: 20 }) {
Image($r('sys.media.ohos_ic_public_play_last'))
.width(20)
.aspectRatio(1)
Image(this.isPlay ? $r('sys.media.ohos_ic_public_pause') : $r('sys.media.ohos_ic_public_play'))
.width(20)
.aspectRatio(1)
.onClick(() => {
this.isPlay = !this.isPlay
})
Image($r('sys.media.ohos_ic_public_play_next'))
.width(20)
.aspectRatio(1)
}
.width('100%')
.padding(20)
.backgroundColor(Color.Pink)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
}
5、@Observed与@ObjectLink
Link只有@State或者@Link修饰的数据才能用
如果用ForEatch循环一个数组有多个对象,将对象传给子组件,子组件接收一个个对象就没办法用Link
解决办法:子组件用@ObjectLink来接收,再在Class(i2c生成的)类名前面+@Observed,就可以和对象互相关联了
@Entry
@Component
struct ObservedObjectLinkCase {
@State goodsList: GoodsTypeModel[] = [
new GoodsTypeModel({
name: '瓜子',
price: 3,
count: 0
}),
new GoodsTypeModel({
name: '花生',
price: 3,
count: 0
}),
new GoodsTypeModel({
name: '矿泉水',
price: 3,
count: 0
})
]
build() {
Column() { //ForEach循环数组,传子元素对象
ForEach(this.goodsList, (item: GoodsTypeModel) => {
// 2.确保传递的对象是new过observed修饰的
GoodItemLink({ goodItem: item })
})
}
}
}
@Component
struct GoodItemLink {
// 3.用ObjectLink修饰 子元素接收每一个对象
@ObjectLink goodItem: GoodsTypeModel
build() {
Row({ space: 20 }) {
Text(this.goodItem.name)
Text('¥' + this.goodItem.price)
Image($r('sys.media.ohos_ic_public_remove_filled'))
.width(20)
.aspectRatio(1)
.onClick(() => {
this.goodItem.count--
})
Text(this.goodItem.count.toString())
Image($r('sys.media.ohos_ic_public_add_norm_filled'))
.width(20)
.aspectRatio(1)
.onClick(() => {
this.goodItem.count++
})
}
.width('100%')
.padding(20)
}
}
interface GoodsType {
name: string
price: number
count: number
}
// 1.使用 observed 修饰一个类
@Observed
export class GoodsTypeModel implements GoodsType {
name: string = ''
price: number = 0
count: number = 0
constructor(model: GoodsType) {
this.name = model.name
this.price = model.price
this.count = model.count
}
}
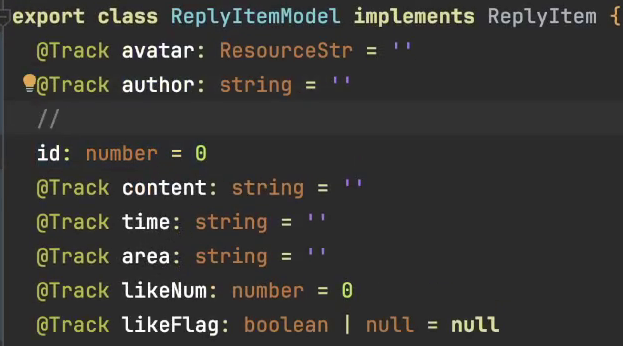
6、@Require 和 @Track
@Require 必传参数装饰器
子组件数据前面+@Require父组件必须传
@Track 节省性能
每个class里面前面默认有一个@Track对象,当我们不跟踪一个对象时不屑@Track ,但是其他的跟踪的需要都写上




















 1121
1121

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








