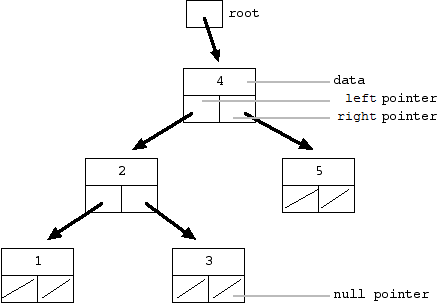
Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right pointers as synonymous to the previous and next pointers in a doubly-linked list.
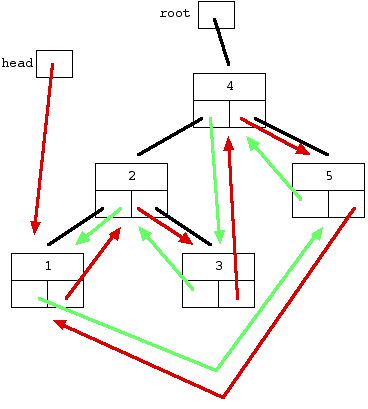
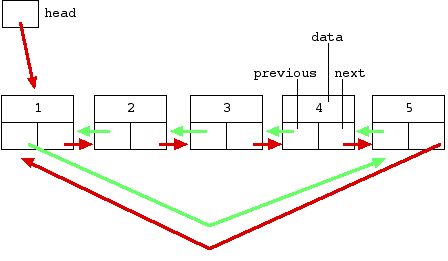
If the problem statement is still not clear to you, below is a pictorial representation of what you need to do:
I originally read this interesting problem here: The Great Tree-List Recursion Problem.
Hint:
Think of in-order traversal. How do you ensure that the last element’s right pointer points back to the first element?
Solution:
When I first see this problem, my first thought was in-order traversal. Couldn’t we modify the nodes’ left and right pointers as we do an in-order traversal of the tree? However, we have to beware not to modify the pointers and accessing it at a later time.
As we traverse the tree in-order, we could safely modify a node’s left pointer to point to the previously traversed node as we never use it once we reach a node. We would also need to modify the previously traversed node’s right pointer to point to the current node. Note: The previously traversed node meant here is not its parent node. It is the node’s previous smaller element.
Easy approach, right? But wait, we are still missing two more steps. First, we did not assign the list’s head pointer. Second, the last element’s right pointer does not point to the first element (similar to the first element’s left pointer).
How do we solve this? My approach is pretty easy: Just update the current node’s right pointer to point back to the head and the head’s left pointer to point to current node in each recursive call. As the recursion ends, the list’s head and tail would be automagically updated with the correct pointers. Don’t forget to check for this special case: A list with only one element should have its left and right pointers both pointing back to itself.
Do you think this approach works? I bet it did! The run time complexity for this solution is O(N) since we are essentially doing a modified in-order traversal. It does have some extra assignments in each recursive call though. But overall I am quite satisfied with this approach because it is intuitive and easy to follow. Besides, we are adapting an existing algorithm (in-order traversal) to solve this problem, isn’t this just neat?
private TreeNode prev;
private TreeNode head;
public TreeNode bstToSortedDLL(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null) return null;
bstToSortedDLL(node.left);
node.left = prev;
if(prev != null) {
prev.right = node;
} else {
head = node;
}
prev = node;
TreeNode right = node.right;
head.left = node;
node.right = head;
bstToSortedDLL(right);
return head;
}
Reference:
http://articles.leetcode.com/2010/11/convert-binary-search-tree-bst-to.html








 本文介绍了一种将二叉搜索树(BST)转换为排序循环双向链表的方法。通过中序遍历调整节点的左右指针,实现链表的构建,并确保最后一个元素的右指针指向第一个元素。
本文介绍了一种将二叉搜索树(BST)转换为排序循环双向链表的方法。通过中序遍历调整节点的左右指针,实现链表的构建,并确保最后一个元素的右指针指向第一个元素。
















 4397
4397

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








