Document
A document, then, is a collection of fields that map to particular field types defined in a schema. Each field in a document has its content analyzed according to its field type, and the results of that analysis are saved into a search index in order to later retrieve the document by sending in a related query.
The inverted index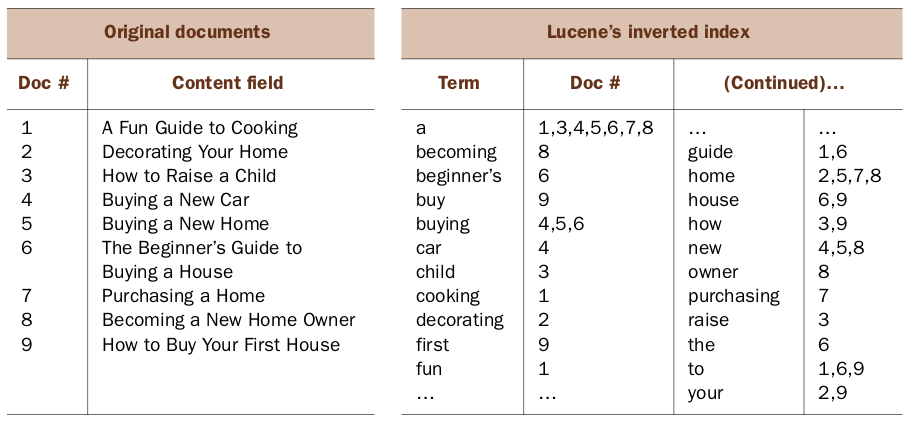
Graphical representation of using common Boolean query operators
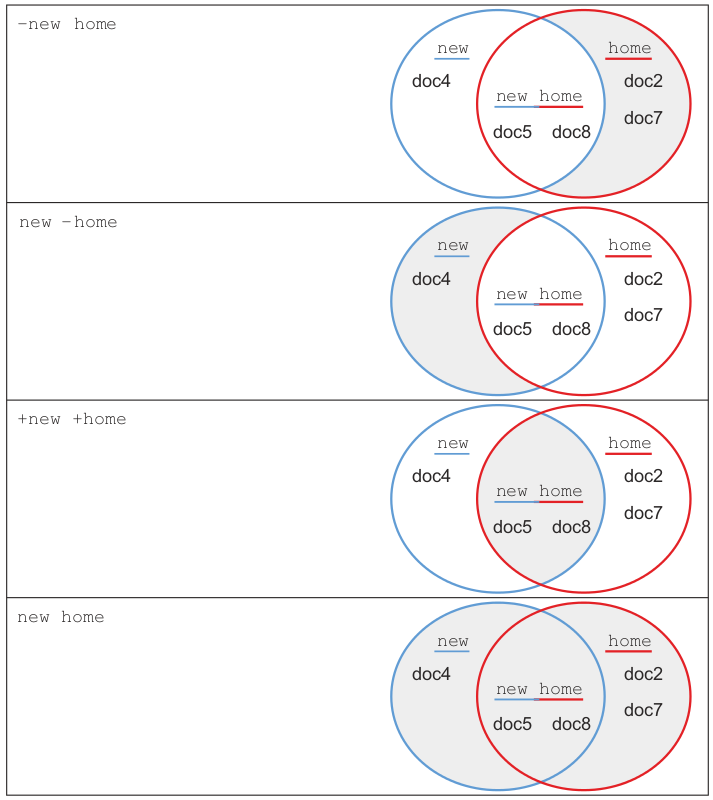
Phrase queries and term positions
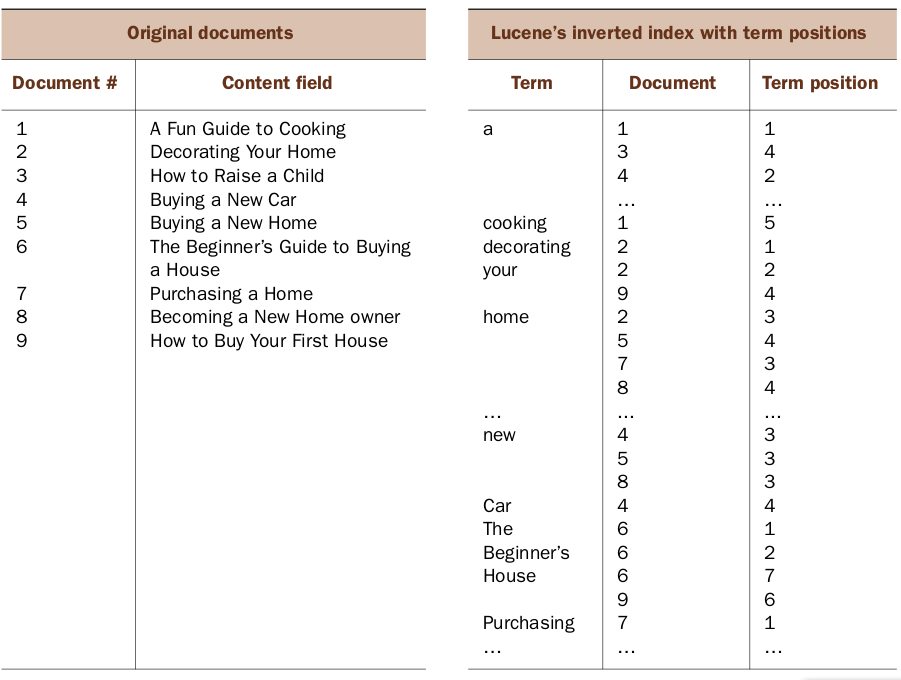
inverted index with term positions
Fuzzy matching
Fuzzy matching is defined as the ability to perform inexact matches on terms in the search index.
- wildcard searching someone may want to search for any words that start with a particular prefix
- fuzzy searching or edit distance searching may want to find spelling variations within one or two characters
- proximity searching may want to match two terms within some maximum distance of each other.
- range searching search for terms that fall between known values.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Default similarity scoring algorithm

Normalization factors
- FIELD NORMS Field norms are calculated at index time and are represented as an additional byte per field in the Solr index. norm(t,d) = d.getBoost() • lengthNorm(f) • f.getBoost()
- QUERY NORMS t uses the sum of the squared weights for each of the query terms to generate this factor, which is multiplied with the rest of the relevancy score to normalize it. The query norm should not affect the relative weighting of each document that matches a given query.
- COORD FACTOR The idea behind the coord factor is that, all things being equal, documents that
contain more of the terms in the query should score higher than documents that only match a few.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Precision and Recall
- Precision The Precision of a search results set (the documents that match a query) is a measurement attempting to answer the question, “Were the documents that came back the ones I was looking for?” #Correct Matches / #Total Results Returned
- Recall Recall is answering the question:“How many of the correct documents were returned?”#Correct Matches / (#Correct Matches + #Missed Matches)
The critical difference between Precision and Recall: Precision is high when the results returned are correct; Recall is high when the correct results are present. Recall does not care that all of the results are correct. Precision does not care that all of the results are present.
The decision on how to best balance Precision and Recall is ultimately dependent upon your use case.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Searching at scale
The denormalized document
Central to Solr is the concept of all documents being denormalized. A denormalized document is one in which all fields are self-contained within the document, even if the values in those fields are duplicated across many documents.
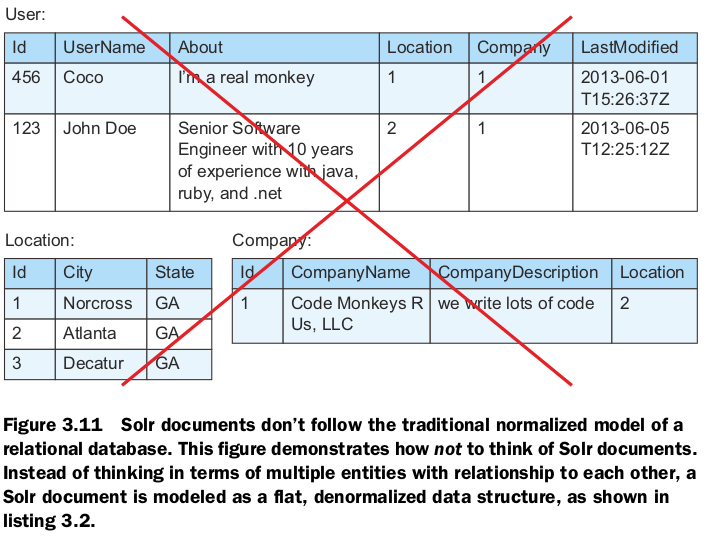
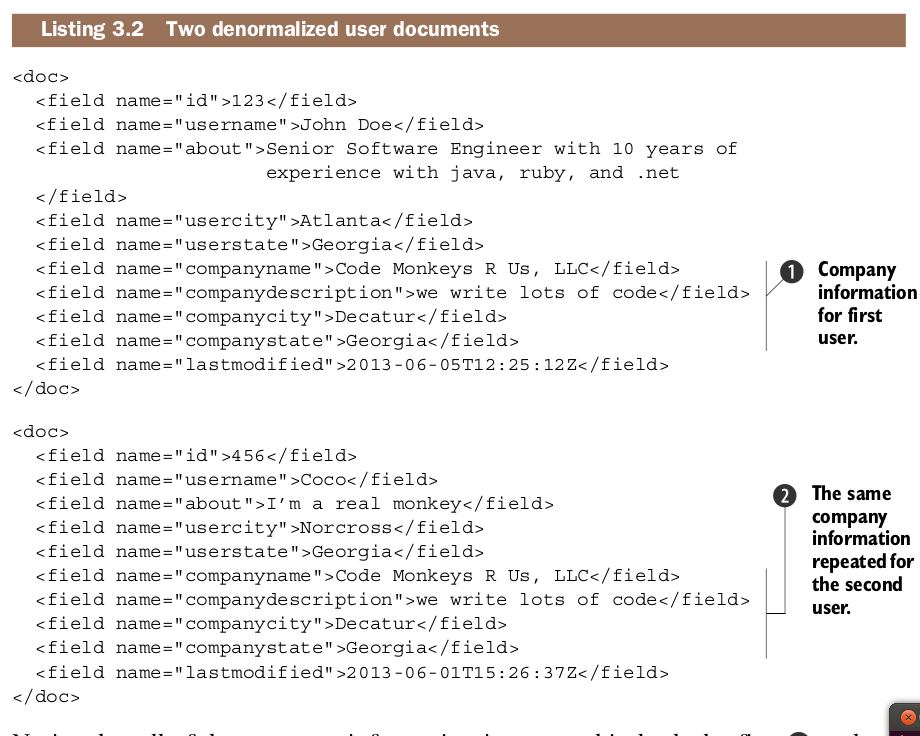
While this denormalized document data model may sound limiting, it also provides a sizable advantage: extreme scalability. Because we can make the assumption that each document is self-contained, this means that we can also partition documents across multiple servers without having to keep related documents on the same server (because documents are independent of one another). This fundamental assumption of document independence allows queries to be parallelized across multiple partitions
of documents and multiple servers to improve query performance, and this ultimately allows Solr to scale horizontally to handle querying billions of documents. This ability to scale across multiple partitions and servers is called distributed searching.
http://box1:8983/solr/core1/select?q=*:*&shards=box1:8983/solr/core1,box2:8983/solr/core2,box2:8983/solr/core3
(Query Speed on N+1 indexes) = Aggregation Overhead + (Query Speed on N indexes)/(N+1)





 本文详细介绍了搜索引擎的工作原理,包括倒排索引、模糊匹配等关键技术,并探讨了如何通过精度和召回率来评估搜索效果。
本文详细介绍了搜索引擎的工作原理,包括倒排索引、模糊匹配等关键技术,并探讨了如何通过精度和召回率来评估搜索效果。
















 121
121

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








