在Winsock中提供了几个关于网络字节顺序与主机字节顺序之间的转换函数:
// h: Host
// n: Network
// s: short
// l(不是1,是小写的L): long
//端口号, 从主机顺序转换为网络顺序
u_short htons(u_short hostshort);
//ip, 从主机顺序转换为网络顺序
u_long htonl(u_long hostlong);
//端口号, 从网络顺序转换为主机顺序
u_short ntohs(u_short netshort);
//ip, 从网络顺序转换为主机顺序
u_long ntohl(u_long netlong);
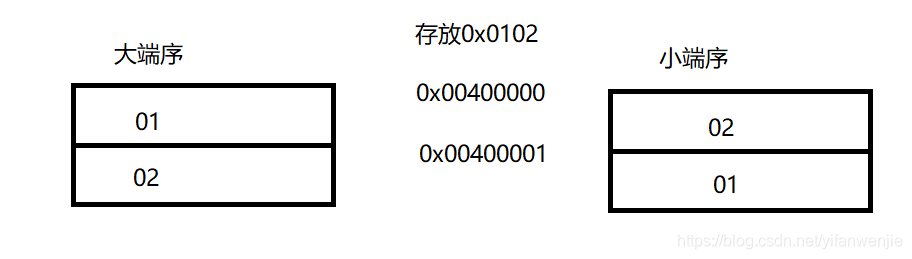
// 大端序: 数字高位存放在起始地址/低地址
// 大端序: 按照人类写数字的顺序保存在计算机中
// 小端序: 数字低位存放在起始地址/低地址
// 数字: 0x010203040506070809 高位<-------------------低位
// 网络通信协议使用的是大端序
// 主机使用的可能是大端序也可能是小端序
// 看一份htons的实现
// 摘自 https://code.woboq.org/userspace/glibc/inet/htons.c.html
uint16_t
htons (uint16_t x)
{
// 如果主机字节序是大端序则直接返回
#if BYTE_ORDER == BIG_ENDIAN
return x;
// 如果主机字节序是小端序则swap(low_byte, high_byte)
#elif BYTE_ORDER == LITTLE_ENDIAN
return __bswap_16 (x);
#else
# error "What kind of system is this?"
#endif
}
// 摘自 https://code.woboq.org/userspace/glibc/bits/byteswap.h.html#__bswap_16
/* Swap bytes in 16-bit value. */
// 通过移位来实现swap
#define __bswap_constant_16(x) \
((__uint16_t) ((((x) >> 8) & 0xff) | (((x) & 0xff) << 8)))
static __inline __uint16_t
__bswap_16 (__uint16_t __bsx)
{
#if __GNUC_PREREQ (4, 8)
return __builtin_bswap16 (__bsx);
#else
// 看这个
return __bswap_constant_16 (__bsx);
#endif
}
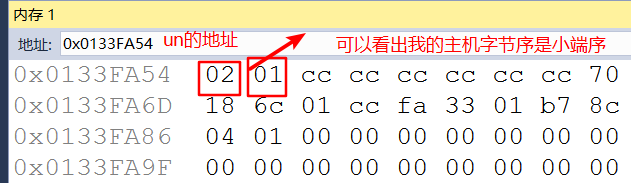
// 摘自 UNIX网络编程卷1 3.4字节排序函数 P63
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// 判断主机字节序是大端序还是小端序
union
{
short s;
char c[sizeof(short)];
} un;
un.s = 0x0102;
if (sizeof(short) == 2)
{
if (un.c[0] == 1 && un.c[1] == 2)
{
// big-endian
}
else if (un.c[0] == 2 && un.c[1] == 1)
{
// little-endian
}
else {
// unknown
}
}
return 0;
}




 本文介绍Winsock中网络字节序与主机字节序之间的转换函数,如htons、htonl、ntohs、ntohl,并展示了这些函数如何在不同字节序的系统上工作,特别解释了htons函数的实现细节。
本文介绍Winsock中网络字节序与主机字节序之间的转换函数,如htons、htonl、ntohs、ntohl,并展示了这些函数如何在不同字节序的系统上工作,特别解释了htons函数的实现细节。
















 9054
9054

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








