1、简介
在开发中会有大量的字符串处理工作,其中经常会涉及到字符串格式的校验。
场景1:如何判断一个字符串是手机号呢?
测试文件
13811011234
1a3hi233rhi3
87156340场景2:在一个文件中,查找出itcast开头的语句
测试文件
itcast hello python
itcast c++
itheima ios
itheima php场景3:在一个文件中,找到含有itcast的语句
测试文件
hello itcast python
www.itcast.cn c++
itheima ios
itheima php场景4:在一个文件中,找到邮箱为163或者126的所有邮件地址
正则表达式(Regular Expression,在代码中常简写为regex、regexp或RE),使用单个字符串来描述、匹配一系列匹配某个句法规则的字符串。在很多文本编辑器里,正则表达式通常被用来检索、替换那些匹配某个模式的文本。
2、re模块操作
在Python中需要通过正则表达式对字符串进行匹配的时候,可以使用一个模块,名字为re
2.1、re模块的使用过程
#coding=utf-8
# 导入re模块
import re
# 使用match方法进行匹配操作
result = re.match(正则表达式,要匹配的字符串)
# 如果上一步匹配到数据的话,可以使用group方法来提取数据
result.group()re.match是用来进行正则匹配检查的方法,若字符串匹配正则表达式,则match方法返回匹配对象(Match Object),否则返回None(注意不是空字符串”“)。
匹配对象Macth Object具有group方法,用来返回字符串的匹配部分。
2.2、re模块示例(匹配以itcast开头的语句)
#coding=utf-8
import re
result = re.match("itcast","itcast.cn")
result.group()运行结果为:
itcast2.3、说明
re.match() 能够匹配出以xxx开头的字符串
3、表示字符
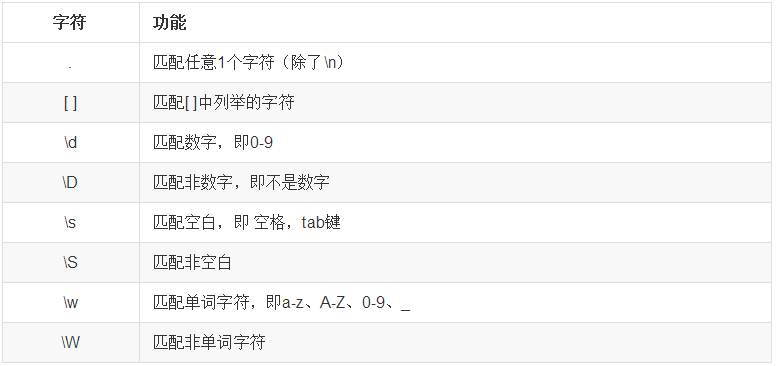
示例1: .

示例2:[ ]
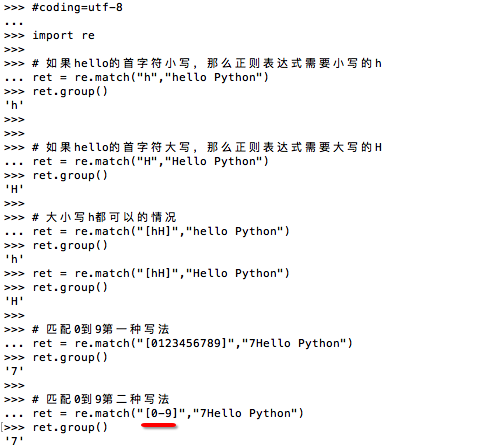
示例3:\d

4、原始字符串
>>> mm = "c:\\a\\b\\c"
>>> mm
'c:\\a\\b\\c'
>>> print(mm)
c:\a\b\c
>>> print(mm)
c:\a\b\c
>>> re.match("c:\\\\",mm).group()
'c:\\'
>>> ret = re.match("c:\\\\",mm).group()
>>> print(ret)
c:\
>>> ret = re.match("c:\\\\a",mm).group()
>>> print(ret)
c:\a
>>> ret = re.match(r"c:\\a",mm).group()
>>> print(ret)
c:\a
>>> ret = re.match(r"c:\a",mm).group()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'group'说明:
Python中字符串前面加上 r 表示原生字符串,
与大多数编程语言相同,正则表达式里使用”\”作为转义字符,这就可能造成反斜杠困扰。假如你需要匹配文本中的字符”\”,那么使用编程语言表示的正则表达式里将需要4个反斜杠”\”:前两个和后两个分别用于在编程语言里转义成反斜杠,转换成两个反斜杠后再在正则表达式里转义成一个反斜杠。
Python里的原生字符串很好地解决了这个问题,有了原始字符串,你再也不用担心是不是漏写了反斜杠,写出来的表达式也更直观。
>>> ret = re.match(r"c:\\a",mm).group()
>>> print(ret)
c:\a5、表示数量
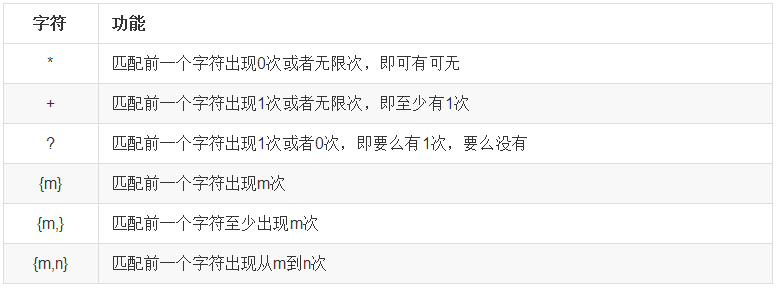
示例1:*
需求:匹配出,一个字符串第一个字母为大小字符,后面都是小写字母并且这些小写字母可有可无

示例2:+
需求:匹配出,变量名是否有效

示例3:?
需求:匹配出,0到99之间的数字

示例4:{m}
需求:匹配出,8到20位的密码,可以是大小写英文字母、数字、下划线

6、表示边界
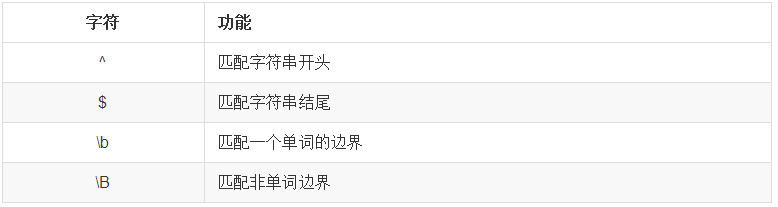
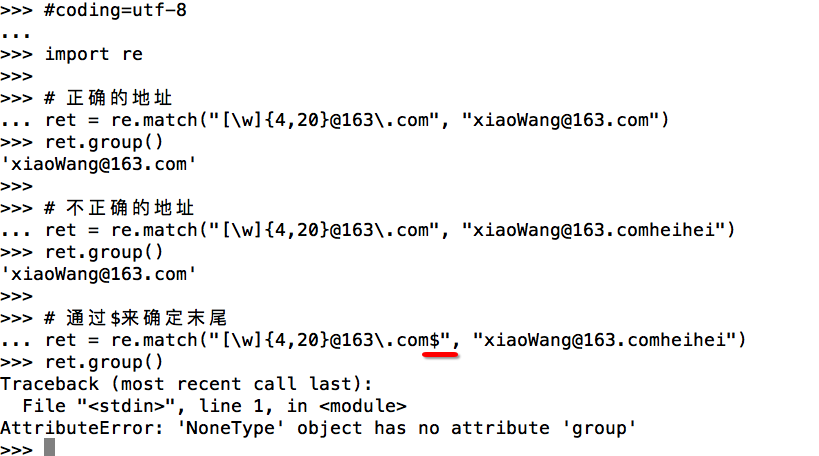
示例1:$
需求:匹配163.com的邮箱地址
示例2: \b
>>> re.match(r".*\bver\b", "ho ver abc").group()
'ho ver'
>>> re.match(r".*\bver\b", "ho verabc").group()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'group'
>>> re.match(r".*\bver\b", "hover abc").group()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'group'示例3:\B
>>> re.match(r".*\Bver\B", "hoverabc").group()
'hover'
>>> re.match(r".*\Bver\B", "ho verabc").group()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'group'
>>> re.match(r".*\Bver\B", "hover abc").group()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'group'
>>> re.match(r".*\Bver\B", "ho ver abc").group()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'group'7、匹配分组
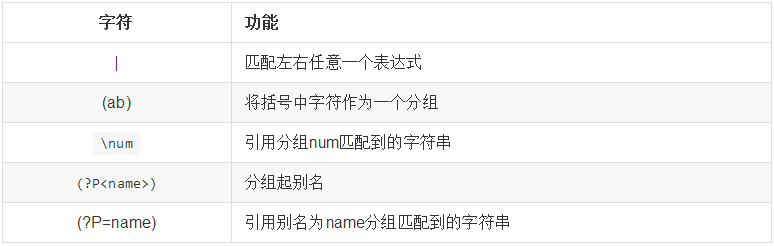
示例1:|
需求:匹配出0-100之间的数字
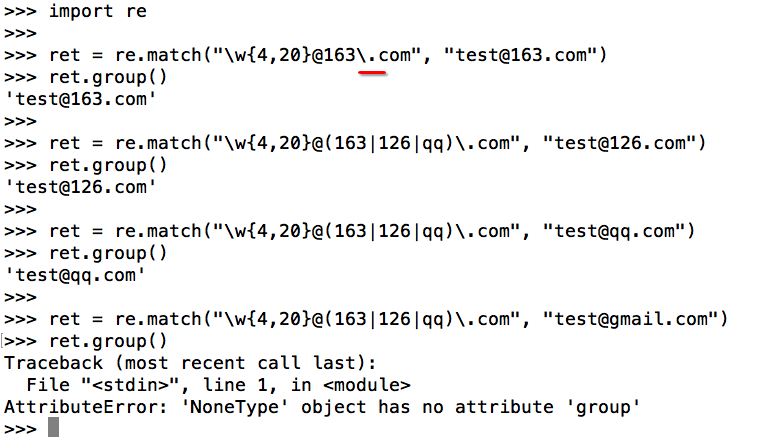
示例2:( )
需求:匹配出163、126、qq邮箱之间的数字
示例3:\
需求:匹配出
<html>hh</html>
<
h
t
m
l
>
h
h
<
/
h
t
m
l
>

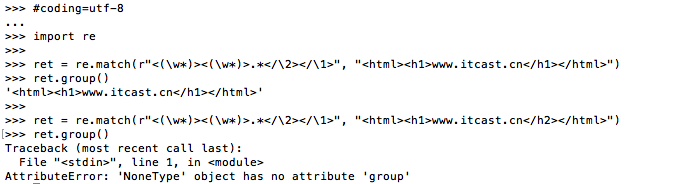
示例4:\number
需求:匹配出
<html><h1>www.itcast.cn</h1></html>
<
h
t
m
l
><
h
1
>
w
w
w
.
i
t
c
a
s
t
.
c
n
<
/
h
1
><
/
h
t
m
l
>
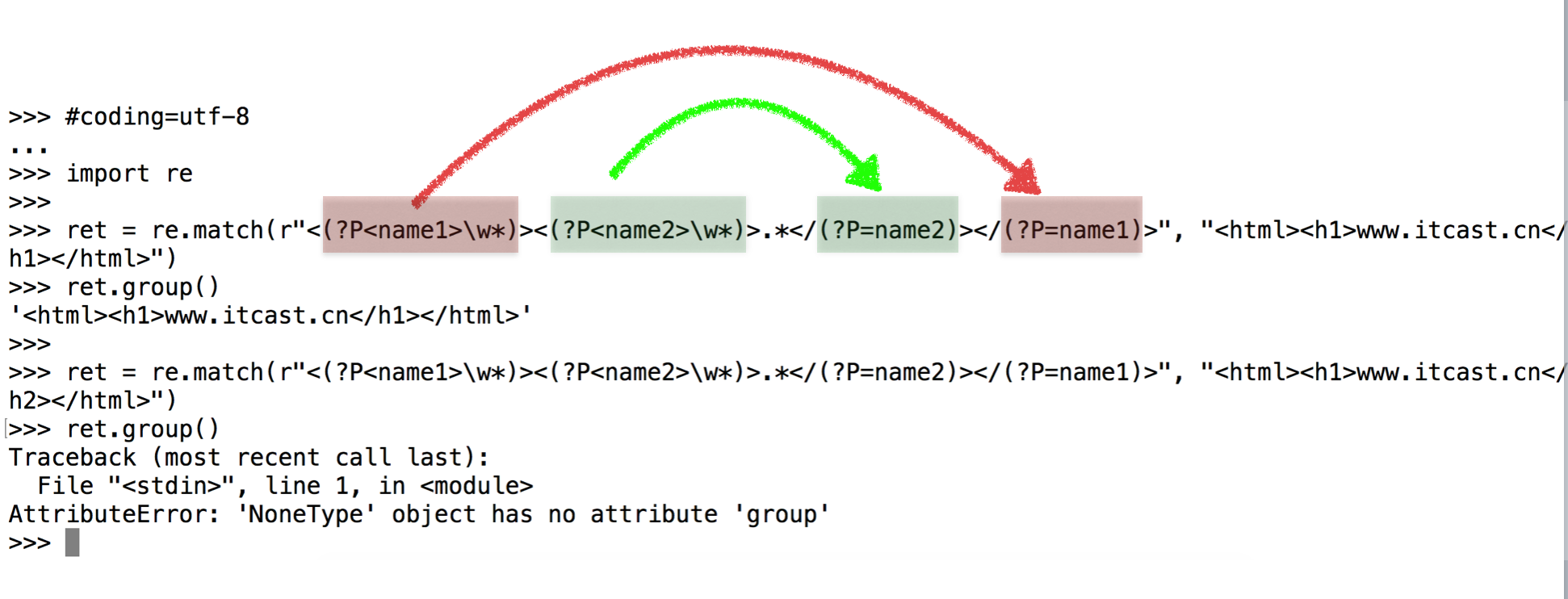
示例5:(?P) (?P=name)
需求:匹配出
<html><h1>www.itcast.cn</h1></html>
<
h
t
m
l
><
h
1
>
w
w
w
.
i
t
c
a
s
t
.
c
n
<
/
h
1
><
/
h
t
m
l
>
8、re模块的高级用法
8.1、search
需求:匹配出文章阅读的次数

8.2、findall
需求:统计出python、c、c++相应文章阅读的次数

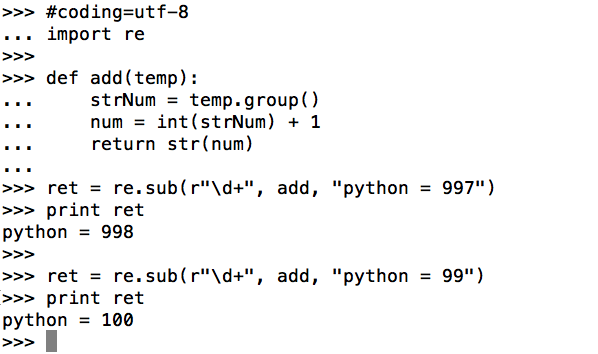
8.3、sub 将匹配到的数据进行替换
需求:将匹配到的阅读次数加1
方法1:

方法2:
8.4、split 根据匹配进行切割字符串,并返回一个列表
需求:切割字符串“info:xiaoZhang 33 shandong”

9、python贪婪和非贪婪
没怎么理解,在以后的使用中在加深
参考文献:
1. python就业班
2. Python 正则表达式 | 菜鸟教程
3. 一篇搞定Python正则表达式
4. Python正则表达式详解
























 1026
1026

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








