概念
- 粘包:TCP层将应用层多个小的数据包封装成一个大的数据包发送出去;
- 拆包:TCP层将应用层一个大的数据包拆分成多个小的数据包发送出去;
原因
TCP层并不感知应用层数据包的具体含义,它会根据TCP缓冲区实际情况进行包的划分,所以对于应用层来说,一个完整的数据包可能会被TCP拆分成多个包进行发送,也可能被合并装成一个大的数据包发送。
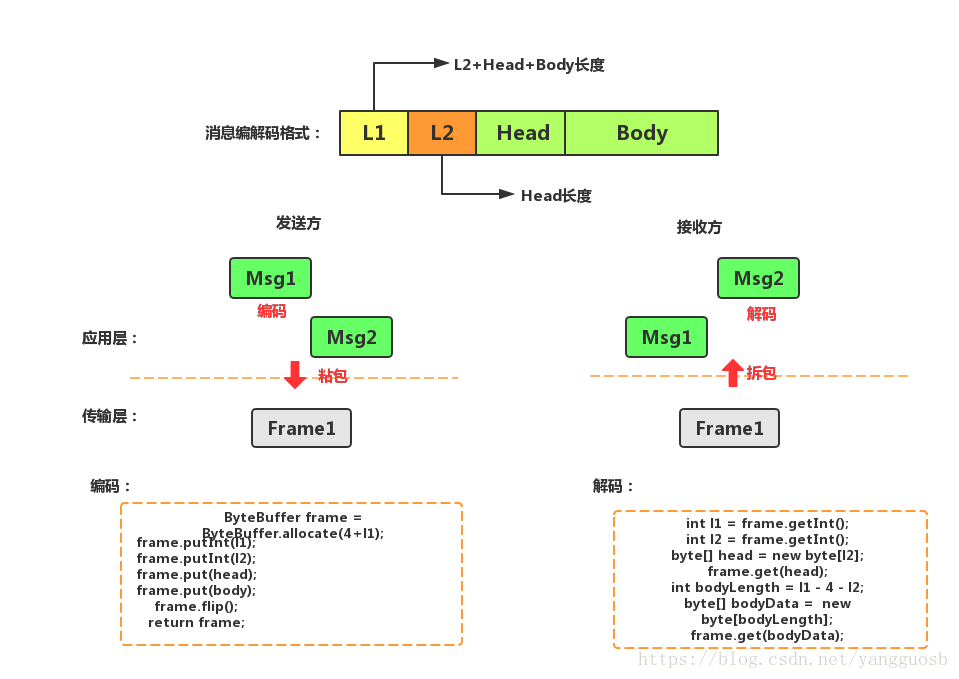
解决方案
由于TCP不感知应用层的数据,所以必须由应用层对数据进行拆分和重组,解决方案方案大体分为两种:基于分隔符的解码和基于长度的解码。整体思路是:每次产生OP_READ事件,数据被读到ByteBuf后,检查ByteBuf中是否包含指定分隔符或者达到指定长度,如果满足则解码,否则继续缓存在ByteBuf中,直至满足条件或者超过最大长度上限抛出TooLongFrameException异常。
基于分隔符
- 基于换行符拆分消息LineBasedFrameDecoder;
- 基于自定义分隔符拆分消息DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder;
基于长度
- 基于固定长度拆分消息FixedLengthFrameDecoder;
- 基于消息头中的长度字段拆分消息LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
代码示例
只有ByteBuf中包含指定分隔符或者达到指定长度时,才会进行解码,以FixedLengthFrameDecoder示例:
@Override
protected final void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
Object decoded = decode(ctx, in);
if (decoded != null) {
out.add(decoded);
}
}
/**
* Create a frame out of the {@link ByteBuf} and return it.
*
* @param ctx the {@link ChannelHandlerContext} which this {@link ByteToMessageDecoder} belongs to
* @param in the {@link ByteBuf} from which to read data
* @return frame the {@link ByteBuf} which represent the frame or {@code null} if no frame could
* be created.
*/
protected Object decode(
@SuppressWarnings("UnusedParameters") ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
if (in.readableBytes() < frameLength) {
return null;
} else {
return in.readSlice(frameLength).retain();
}
}参考:























 983
983

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








