详细链接
视图
视图是一个把select查询出来的虚拟表,以表结构frm存下来,表数据是和原表一个表数据ibd,方便以后使用
#语法:CREATE VIEW 视图名称 AS SQL语句
mysql> select * from employee;
# 查询出来的虚拟表
mysql> select name,age,post from employee where salary > 10000;
+-----------+-----+-----------+
| name | age | post |
+-----------+-----+-----------+
| alex | 78 | teacher |
| jinxin | 18 | teacher |
| 张野 | 28 | operation |
| 程咬金 | 18 | operation |
| 程咬银 | 18 | operation |
| 程咬铜 | 18 | operation |
| 程咬铁 | 18 | operation |
+-----------+-----+-----------+
#创建视图
# select查询出来的虚拟表不在屏幕中,而是写到视图里面去了
mysql> create view nep as select name,age,post from employee where salary >10000;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show tables;
+---------------+
| Tables_in_db3 |
+---------------+
| employee |
| nep |
| test2 |
+---------------+
# 查看视图
mysql> select * from nep;
+-----------+-----+-----------+
| name | age | post |
+-----------+-----+-----------+
| alex | 78 | teacher |
| jinxin | 18 | teacher |
| 张野 | 28 | operation |
| 程咬金 | 18 | operation |
| 程咬银 | 18 | operation |
| 程咬铜 | 18 | operation |
| 程咬铁 | 18 | operation |
+-----------+-----+-----------+
# 查看之后只有表结构,没有表数据,和原数据用一个ibd数据文件(视图的背后就是运行那条select语句)
[root@db01 db3]# pwd
/data/3307/data/db3
[root@db01 db3]# ls
course.frm employee.frm
course.ibd employee.ibd
db.opt nep.frm
# 修改视图
mysql> alter view nep as select name,age from employee where id < 3;
# 查看视图
mysql> select * from nep;
+------+-----+
| name | age |
+------+-----+
| egon | 18 |
| alex | 78 |
+------+-----+
# 查看创建视图
mysql> show create view nep;
# 删除视图
mysql> drop view nep;
# 视图太依赖与数据库,视图是建立在数据库的虚拟表,用起来麻烦,查询就现场连表查询
触发器
使用触发器可以定制用户对表进行【增、删、改】操作时前后的行为,注意:没有查询
#准备表
CREATE TABLE cmd (
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
USER CHAR (32),
priv CHAR (10),
cmd CHAR (64),
sub_time datetime, #提交时间
success enum ('yes', 'no') #0代表执行失败
);
CREATE TABLE errlog (
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
err_cmd CHAR (64),
err_time datetime
);
#创建触发器
delimiter //
CREATE TRIGGER tri_after_insert_cmd AFTER INSERT ON cmd FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
IF NEW.success = 'no' THEN #等值判断只有一个等号
INSERT INTO errlog(err_cmd, err_time) VALUES(NEW.cmd, NEW.sub_time) ; #必须加分号
END IF ; #必须加分号
END//
delimiter ;
#往表cmd中插入记录,触发触发器,根据IF的条件决定是否插入错误日志
INSERT INTO cmd (
USER,
priv,
cmd,
sub_time,
success
)
VALUES
('egon','0755','ls -l /etc',NOW(),'yes'),
('egon','0755','cat /etc/passwd',NOW(),'no'),
('egon','0755','useradd xxx',NOW(),'no'),
('egon','0755','ps aux',NOW(),'yes');
#查询错误日志,发现有两条
mysql> select * from errlog;
+----+-----------------+---------------------+
| id | err_cmd | err_time |
+----+-----------------+---------------------+
| 1 | cat /etc/passwd | 2017-09-14 22:18:48 |
| 2 | useradd xxx | 2017-09-14 22:18:48 |
+----+-----------------+---------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# 删除触发器
drop trigger tri_after_insert_cmd;
函数
# 查看目录
mysql> select database();
# 查看用户
mysql> select user();
# 查看当前时间
mysql> select now();
函数只能在SQL语句中用,不能独立调用
聚合函数(常用于GROUP BY从句的SELECT查询中)
AVG(col)返回指定列的平均值
COUNT(col)返回指定列中非NULL值的个数
MIN(col)返回指定列的最小值
MAX(col)返回指定列的最大值
SUM(col)返回指定列的所有值之和
GROUP_CONCAT(col) 返回由属于一组的列值连接组合而成的结果
#2 准备表和记录
CREATE TABLE blog (
id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
NAME CHAR (32),
sub_time datetime
);
INSERT INTO blog (NAME, sub_time)
VALUES
('第1篇','2015-03-01 11:31:21'),
('第2篇','2015-03-11 16:31:21'),
('第3篇','2016-07-01 10:21:31'),
('第4篇','2016-07-22 09:23:21'),
('第5篇','2016-07-23 10:11:11'),
('第6篇','2016-07-25 11:21:31'),
('第7篇','2017-03-01 15:33:21'),
('第8篇','2017-03-01 17:32:21'),
('第9篇','2017-03-01 18:31:21');
mysql> select * from blog;
# 调用date_format()函数对sub_time字段值(列)格式化,年和月分组 count统计个数
mysql> select date_format(sub_time,"%Y-%m"),count(id) from blog group by date_fformat(sub_time,"%Y-%m");
+-------------------------------+-----------+
| date_format(sub_time,"%Y-%m") | count(id) |
+-------------------------------+-----------+
| 2015-03 | 2 |
| 2016-07 | 4 |
| 2017-03 | 3 |
+-------------------------------+-----------+
# 自定义函数
自己造小工具
https://www.cnblogs.com/linhaifeng/articles/7495918.html
流程控制
# 代码运行流程:if 判断成立会运行子流水线,运行完子代码块再跳到主流水线运行代码 while循环也一样
# 一 条件语句
delimiter //
CREATE PROCEDURE proc_if ()
BEGIN
declare i int default 0;
if i = 1 THEN
SELECT 1;
ELSEIF i = 2 THEN
SELECT 2;
ELSE
SELECT 7;
END IF;
END //
delimiter ;
# 二 循环语句
delimiter //
CREATE PROCEDURE proc_while ()
BEGIN
DECLARE num INT ;
SET num = 0 ;
WHILE num < 10 DO
SELECT
num ;
SET num = num + 1 ;
END WHILE ;
END //
delimiter ;
# 掉存储过程
mysql> call proc_while ();
存储过程
把一堆功能在SQL语句中写好打包好,提交给前端的应用开发者调用
开发人员 DBA
调用存储过程 编写存储过程
编写原生sql 管理好数据库即可
orm框架-》原生sql 管理好数据库即可
# 创建简单存储过程(无参)
delimiter //
create procedure p1()
BEGIN
select * from blog;
INSERT into blog(name,sub_time) values("xxx",now());
END //
delimiter ;
#在mysql中调用
call p1();
######################################################################
# 创建存储过程(有参)
对于存储过程,可以接收参数,其参数有三类:
#in 仅用于传入参数用
#out 仅用于返回值用
#inout 既可以传入又可以当作返回值
delimiter //
create procedure p2(
in n1 int,
in n2 int
)
BEGIN
select * from blog where id > n1;
END //
delimiter ;
# 传参调用(没有返回值)
mysql> call p2(3,5);
################################################################################
delimiter //
create procedure p3(
in n1 int,
out res int
)
BEGIN
select * from blog where id > n1;
set res = 1;
END //
delimiter ;
#在mysql中调用(控制返回值)
set @res=0; #0代表假(执行失败),1代表真(执行成功)
call p3(3,@res);
select @res;
####################################################################################
delimiter //
create procedure p4(
inout n1 int
)
BEGIN
select * from blog where id > n1;
set n1 = 1;
END //
delimiter ;
#在mysql中调用
set @x=3;
call p4(@x);
select @x;
# 删除存储过程
## drop procedure proc_name;
SQL注入问题
mysql服务端是socket套接字,python是socket套接字客户端,在Python里面有个模块叫pymysql
program ===file======settings========project======python interpreter(解释器)=====点+号搜pymysql=======点击下方install 就可以使用套接字程序了
mysql> grant all on *.* to "yang"@"%" identified by "123";
mysql> flush privileges;
mysql> create database db2;
mysql> create table user(id int,name varchar(16),password varchar(10));
mysql> insert user values(1,"yang","123");
mysql> insert user values(1,"tom","456");
mysql> select * from user;
+------+------+----------+
| id | name | password |
+------+------+----------+
| 1 | yang | 123 |
| 1 | tom | 456 |
+------+------+----------+
# pymysql
import pymysql 导入模块
conn = pymysql.connect(host='192.168.13.36', user='egon', password='123', database='db2', charset='utf8')
cursor = conn.cursor()
inp_user = input("请输入您的账号名>>>: ") # inp_user = ""
inp_pwd = input("请输入您的密码>>>: ") # inp_pwd = ""
# sql = "select * from user where name='%s' and password = '%s';" % (inp_user,inp_pwd )
sql = "select * from user where name='asdasdf' or 1=1 -- asfdsadf' and password = '%s';" % (inp_user,inp_pwd )
print(sql)
rows = cursor.execute(sql)
# print(rows)
if rows != 0:
print("登录成功")
else:
print("登录失败")
cursor.close()
conn.close()
# 通过一些特殊符号改变了SQL语句的运行逻辑就叫sql注入,这样可以通过非法字符破坏sql语句。
#可以限制登录 字母数字下划线,不允许有特殊符号
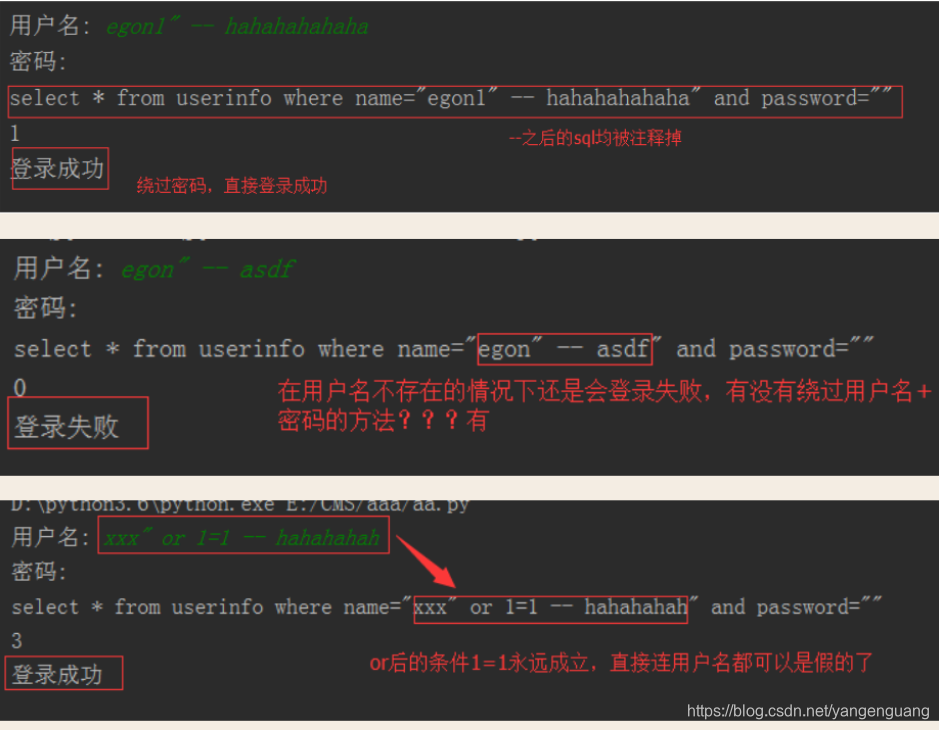
解决方法
# 原来是我们对sql进行字符串拼接
# sql="select * from userinfo where name='%s' and password='%s'" %(user,pwd)
# print(sql)
# res=cursor.execute(sql)
#改写为(execute帮我们做字符串拼接,我们无需且一定不能再为%s加引号了)
sql="select * from userinfo where name=%s and password=%s" #!!!注意%s需要去掉引号,因为pymysql会自动为我们加上
res=cursor.execute(sql,[user,pwd]) #pymysql模块自动帮我们解决sql注入的问题,只要我们按照pymysql的规矩来。





 本文详细介绍了数据库中的视图创建与使用,包括其作为虚拟表的特性及修改、删除操作。接着讨论了触发器的概念,展示了如何在MySQL中创建和删除触发器,以及它们在数据操作中的作用。接着讲解了函数的使用,特别是聚合函数在数据统计中的应用。此外,还涉及到了存储过程的创建和调用,以及如何防止SQL注入问题。最后,通过一个Python示例演示了SQL注入攻击及防范措施。
本文详细介绍了数据库中的视图创建与使用,包括其作为虚拟表的特性及修改、删除操作。接着讨论了触发器的概念,展示了如何在MySQL中创建和删除触发器,以及它们在数据操作中的作用。接着讲解了函数的使用,特别是聚合函数在数据统计中的应用。此外,还涉及到了存储过程的创建和调用,以及如何防止SQL注入问题。最后,通过一个Python示例演示了SQL注入攻击及防范措施。

















 1810
1810

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










