简介
前文我们通过风险指针的方式实现了无锁栈,但是也提出了一些弊端,比如每次pop都要从风险数组中选择一个空闲的节点作为标记。其次删除节点前要遍历风险数组对比节点是否被风险指针所指涉,如果被风险指针指涉则需放入待删列表。最后pop结束时也要回收待删列表中的节点,还要依次将待删列表中的节点和风险数组对比,如果未被风险指针指涉则需删除,否则跳过。
但是这种方式多次遍历风险数组,会有性能损耗,我们提出一种新的解决方式,利用引用计数实现无锁并发的栈。
引用计数
在C++并发编程一书中提出了两个计数,一个外部计数,一个内部计数,二者加起来就是有效的引用计数,很多读者对此费解,为何不用一个引用计数维护呢?那本文就是带着大家如何一步一步去实现并说明单引用计数的不可行性。
那我们先定义一个栈结构,以及它的内部节点结构
template<typename T>
class single_ref_stack {
public:
single_ref_stack():head(nullptr) {
}
~single_ref_stack() {
//循环出栈
while (pop());
}
private:
struct ref_node {
//1 数据域智能指针
std::shared_ptr<T> _data;
//2 引用计数
std::atomic<int> _ref_count;
//3 下一个节点
ref_node* _next;
ref_node(T const& data_) : _data(std::make_shared<T>(data_)),
_ref_count(1), _next(nullptr) {}
};
//头部节点
std::atomic<ref_node*> head;
};

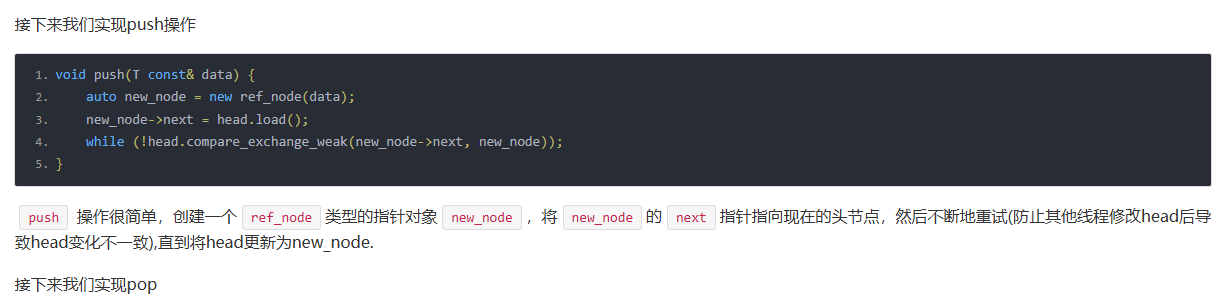
std::shared_ptr<T> pop() {
ref_node* old_head = head.load();
for (;;) {
if (!old_head) {
return std::shared_ptr<T>();
}
//1 只要执行pop就对引用计数+1
++(old_head->_ref_count);
//2 比较head和old_head想等则交换否则说明head已经被其他线程更新
if (head.compare_exchange_strong(old_head, old_head->_next)) {
auto cur_count = old_head->_ref_count.load();
auto new_count;
//3 循环重试保证引用计数安全更新
do {
//4 减去本线程增加的1次和初始的1次
new_count = cur_count - 2;
} while (!old_head->_ref_count.compare_exchange_weak(cur_count, new_count));
//返回头部数据
std::shared_ptr<T> res;
//5 交换数据
res.swap(old_head->_data);
//6
if (old_head->_ref_count == 0) {
delete old_head;
}
return res;
}
else {
//7
if (old_head->_ref_count.fetch_sub(1) == 1) { // 这里为什么和1比较,因为fetch_sub返回的是之前的值
delete old_head;
}
}
}
}

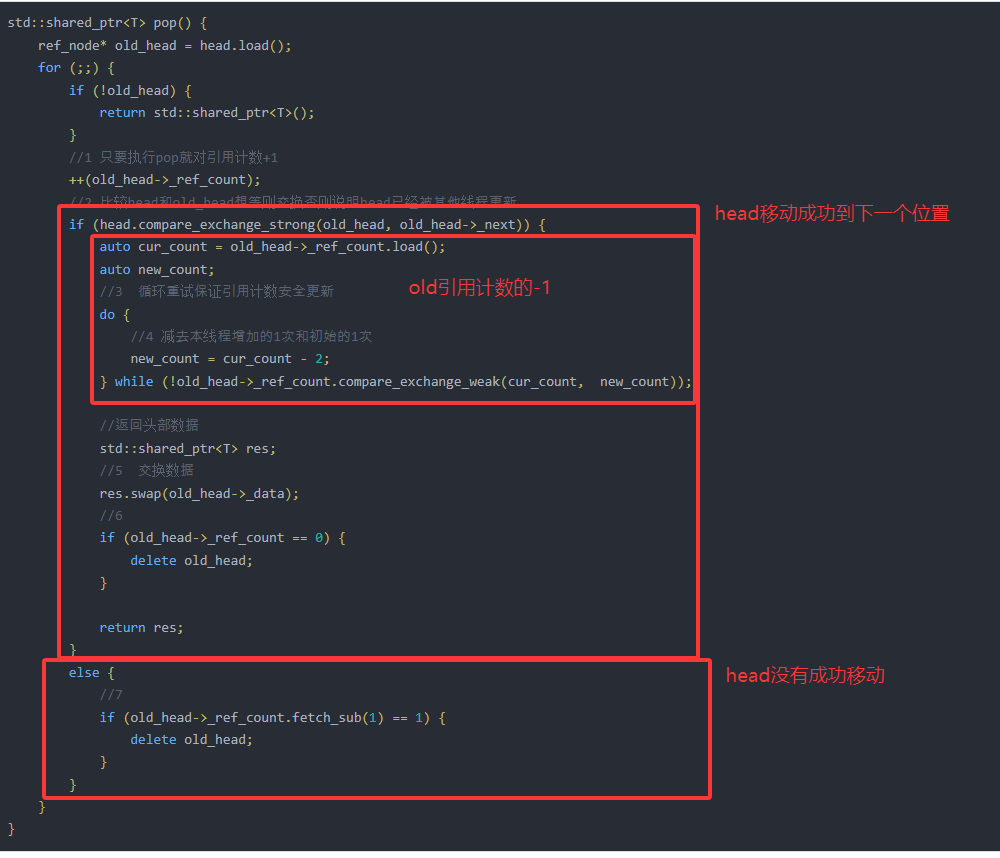
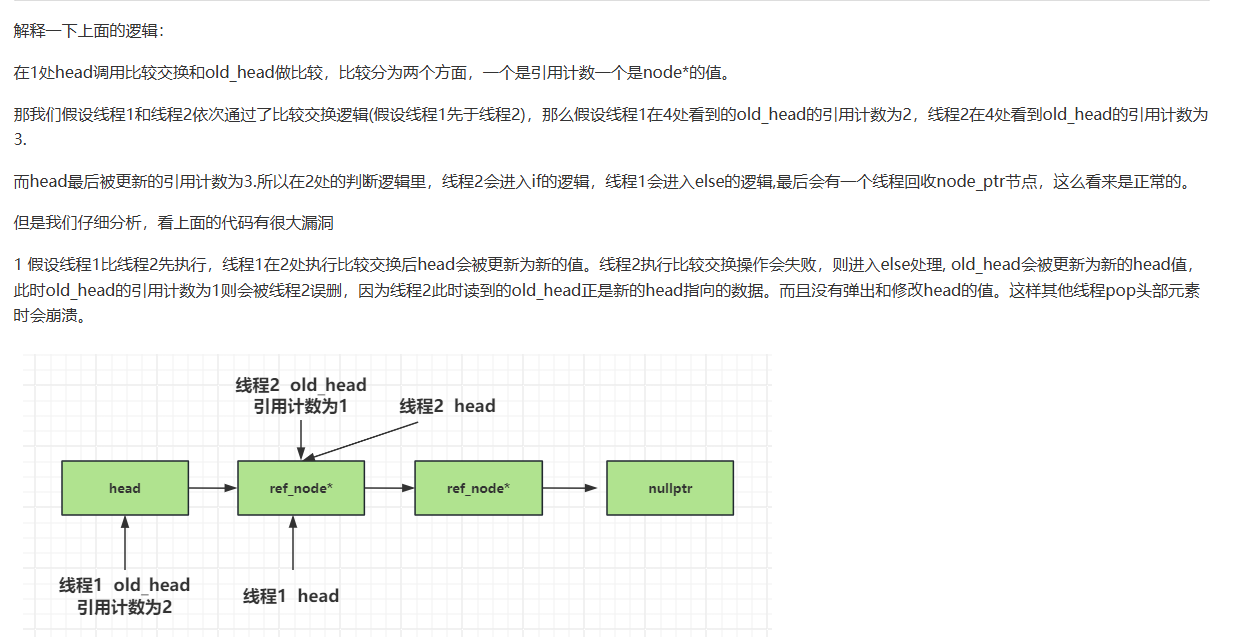
std::shared_ptr<T> pop() {
//0 处
ref_node* old_head = head.load();
for (;;) {
//1 只要执行pop就对引用计数+1并更新到head中
ref_node* new_head;
do {
new_head = old_head;
//7 处
new_head->_ref_count += 1;
} while (!head.compare_exchange_weak(old_head, new_head));
//4
old_head = new_head;
auto* node_ptr = old_head->_node_ptr;
if (node_ptr == nullptr) {
return std::shared_ptr<T>();
}
//2 比较head和old_head想等则交换否则说明head已经被其他线程更新
if (head.compare_exchange_strong(old_head, node_ptr->_next)) {
//要返回的值
std::shared_ptr<T> res;
//交换智能指针
//5 处
res.swap(node_ptr->_data);
//6 增加的数量
int increase_count = old_head->_ref_count.fetch_sub(2);
//3 处判断仅有当前线程持有指针则删除
if (increase_count == 2) {
delete node_ptr;
}
return res;
}else {
if (old_head->_ref_count.fetch_sub(1) == 1) {
delete node_ptr;
}
}
}
}
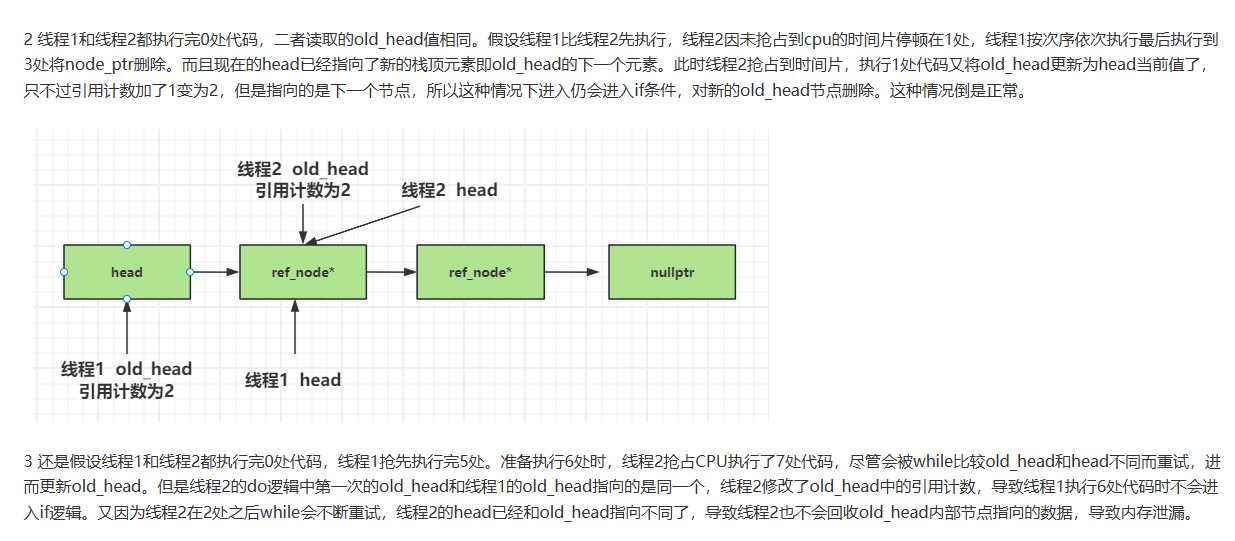
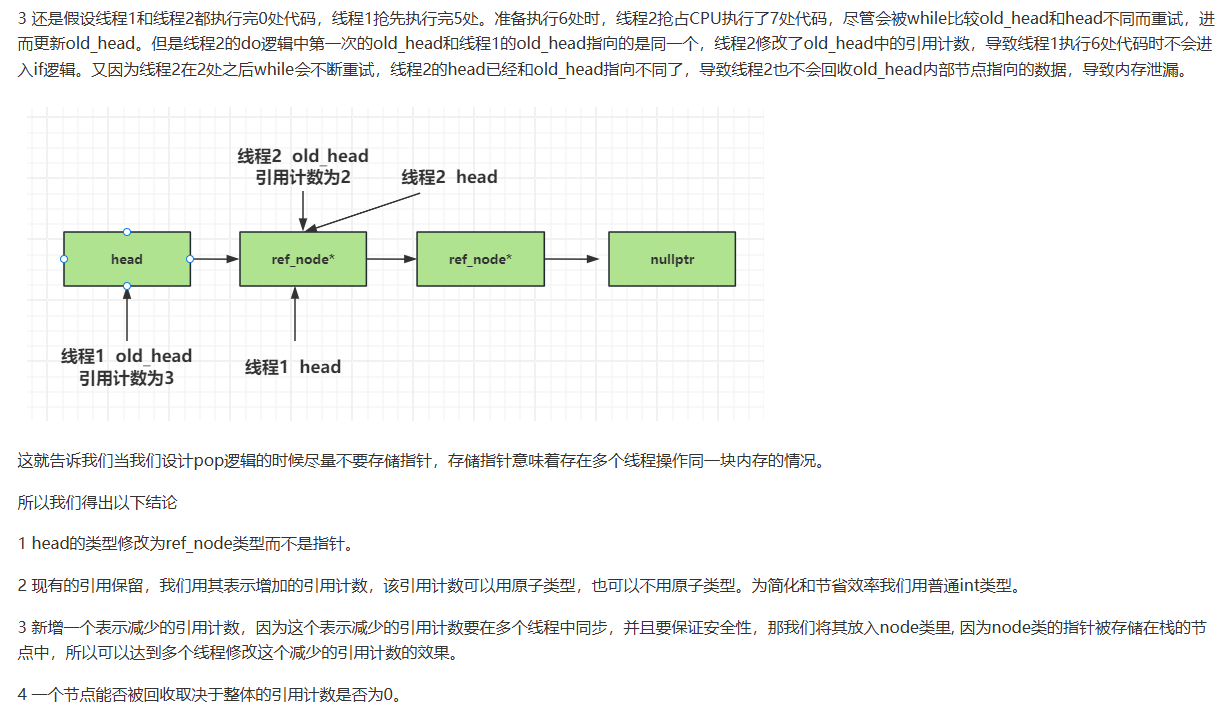
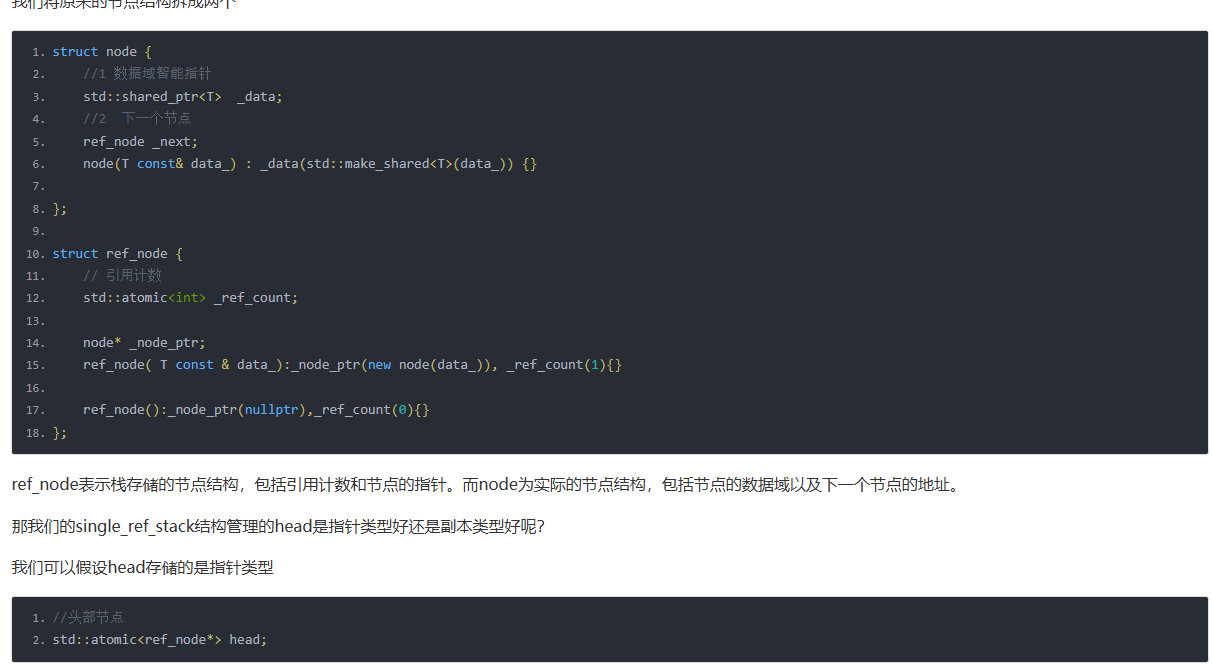
改进引用节点
按照上面的推论,我们新增_dec_count表示减少的引用计数,放在node结构里。
struct ref_node;
struct node {
//1 数据域智能指针
std::shared_ptr<T> _data;
//2 下一个节点
ref_node _next;
node(T const& data_) : _data(std::make_shared<T>(data_)) {}
//减少的数量
std::atomic<int> _dec_count;
};
struct ref_node {
// 引用计数
int _ref_count;
node* _node_ptr;
ref_node( T const & data_):_node_ptr(new node(data_)), _ref_count(1){}
ref_node():_node_ptr(nullptr),_ref_count(0){}
};
然后将栈中的head结构变为ref_node类型的原子变量。
//头部节点
std::atomic<ref_node> head;
我们重新实现push
void push(T const& data) {
auto new_node = ref_node(data);
new_node._node_ptr->_next = head.load();
while (!head.compare_exchange_weak(new_node._node_ptr->_next, new_node));
}
我们重新实现pop
std::shared_ptr<T> pop() {
ref_node old_head = head.load();
for (;;) {
//1 只要执行pop就对引用计数+1并更新到head中
ref_node new_head;
//2
do {
new_head = old_head;
new_head._ref_count += 1;
} while (!head.compare_exchange_weak(old_head, new_head));
old_head = new_head;
//3
auto* node_ptr = old_head._node_ptr;
if (node_ptr == nullptr) {
return std::shared_ptr<T>();
}
//4 比较head和old_head相等则交换否则说明head已经被其他线程更新
if (head.compare_exchange_strong(old_head, node_ptr->_next)) {
//要返回的值
std::shared_ptr<T> res;
//交换智能指针
res.swap(node_ptr->_data);
//5 增加的数量
int increase_count = old_head._ref_count - 2;
//6
if (node_ptr->_dec_count.fetch_add(increase_count) == -increase_count) {
delete node_ptr;
}
return res;
}else {
//7
if (node_ptr->_dec_count.fetch_sub(1) == 1) {
delete node_ptr;
}
}
}
}

测试与验证
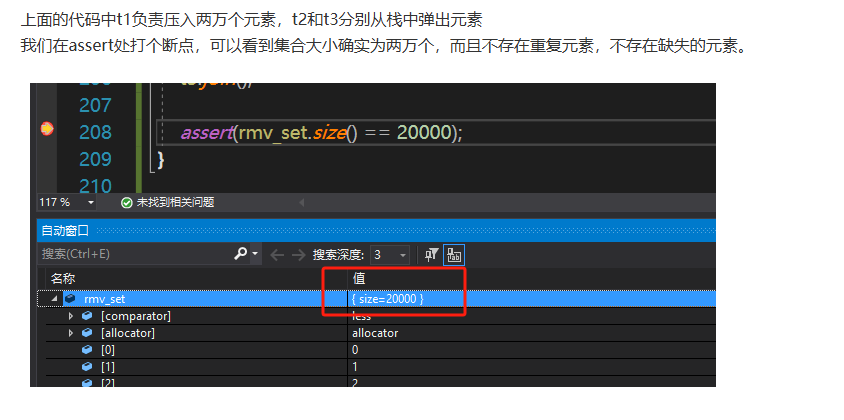
为了测试安全性,效率就不测了,这个无锁的栈后期还要完善,目前我们只要测试安全性即可。
我们启动三个线程t1,t2,t3,t1用来向栈中压入元素,t2和t3用来从栈中弹出元素。
void TestSingleRefStack() {
single_ref_stack<int> single_ref_stack;
std::set<int> rmv_set;
std::mutex set_mtx;
std::thread t1([&]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {
single_ref_stack.push(i);
std::cout << "push data " << i << " success!" << std::endl;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(5));
}
});
std::thread t2([&]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000;) {
auto head = single_ref_stack.pop();
if (!head) {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(10));
continue;
}
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(set_mtx);
rmv_set.insert(*head);
std::cout << "pop data " << *head << " success!" << std::endl;
i++;
}
});
std::thread t3([&]() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000;) {
auto head = single_ref_stack.pop();
if (!head) {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(10));
continue;
}
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(set_mtx);
rmv_set.insert(*head);
std::cout << "pop data " << *head << " success!" << std::endl;
i++;
}
});
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
assert(rmv_set.size() == 20000);
}
总结




















 2450
2450

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








