分发饼干

- 这里应该注意,优先遍历谁
class Solution
{
public:
// 每次都以最大的饼干数来满足胃口最大的孩子
int findContentChildren(vector<int> &g, vector<int> &s)
{ // g表示还在的胃口 s表示饼干 只有s[j] >= g[i] 时才能将饼干给孩子,返回满足孩子的数量
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
sort(g.begin(), g.end());
int count = 0;
int j = s.size() - 1;
for (int i = g.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) // 遍历胃口
{
if (j >= 0 && s[j] >= g[i]) // 遍历饼干:以最大饼干满足大胃口,如果最大的不能满足,此孩子不能吃到
{
count++;
j--; // 目前的最大饼干被分出去
}
}
// 注意,不能先遍历饼干在遍历孩子。因为如果分配出去饼干的话,大饼干一定被分配去除,但是这个大饼干不一定会给大胃口
return count;
}
};
摆动序列

错误的理解
- 可以修改顺序
class Solution
{
/*
按照从小到大排列
结果集合
先取right,再取left,一旦不交叉则退出
*/
public:
int wiggleMaxLength(vector<int> &nums)
{
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
vector<int> result;
result.push_back(nums[right--]);
result.push_back(nums[left++]);
int flag = 1;
// 前面>后面
int top = 1;
while (left <= right)
{
if (flag == 1)
{
flag = 0;
if (result[top] < nums[right]) // 这次要求后面小于前面
{
top++;
result.push_back(nums[right--]);
}
else
break;
}
else
{
flag = 1;
if (result[top] > nums[left]) // 这次要求后面大于前面
{
top++;
result.push_back(nums[left++]);
}
else
break;
}
}
return result.size() - 1;
}
};
正确理解
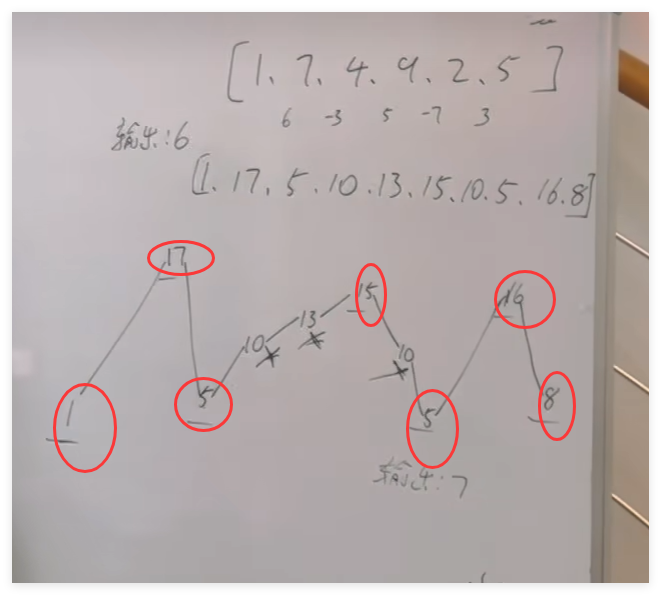
自己的
- 刚开始的检查:只有小于两个数时;最开始的数都是相等的
- 递增和递减时也有可能出现相等的,
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int wiggleMaxLength(vector<int> &nums)
{
int count = 2;
int flag = -1;
if (nums.size() == 1)
return 1;
if (nums.size() == 2)
{
if (nums[0] != nums[1])
return 2;
else
return 1;
}
// 找到最前面不同的两个
int begin;
for (begin = 0; (begin + 1) < nums.size() && nums[begin] == nums[begin + 1]; begin++)
;
if ((begin + 1) < nums.size())
{
if (nums[begin] < nums[begin + 1])
flag = 1; // 先增
else if (nums[begin] > nums[begin + 1])
flag = 0; // 先减
else
return 1;
}
else
{
return 1;
}
for (int i = begin; (i + 1) < nums.size();)
{
if (flag == 1)
{
// 先增再减
while ((i + 1) < nums.size() && nums[i] <= nums[i + 1])
i++;
if ((i + 1) < nums.size())
count++;
else
break;
while ((i + 1) < nums.size() && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1])
i++;
if ((i + 1) < nums.size())
count++;
else
break;
}
else if (flag == 0) // 先减再增
{
while ((i + 1) < nums.size() && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1])
i++;
if ((i + 1) < nums.size())
count++;
else
break;
while ((i + 1) < nums.size() && nums[i] <= nums[i + 1])
i++;
if ((i + 1) < nums.size())
count++;
else
break;
}
}
return count;
}
};
代码随想录
class Solution {
public:
int wiggleMaxLength(vector<int>& nums) {
if (nums.size() <= 1) return nums.size();
int curDiff = 0; // 当前一对差值
int preDiff = 0; // 前一对差值
int result = 1; // 记录峰值个数,序列默认序列最右边有一个峰值
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++) {
curDiff = nums[i + 1] - nums[i];
// 出现峰值
if ((preDiff <= 0 && curDiff > 0) || (preDiff >= 0 && curDiff < 0)) {
result++;
preDiff = curDiff; // 注意这里,只在摆动变化的时候更新prediff
}
}
return result;
}
};
最大子数组求和

class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int result = INT32_MIN;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
count += nums[i];
if (count > result) { // 取区间累计的最大值(相当于不断确定最大子序终止位置)
result = count;
}
if (count <= 0) count = 0;
// 相当于重置最大子序起始位置,因为遇到负数一定是拉低总和
// 注意这里的如何抛弃:丢弃掉原来的成绩,从0开始
}
return result;
}
};
买卖股票最佳时机II

画图
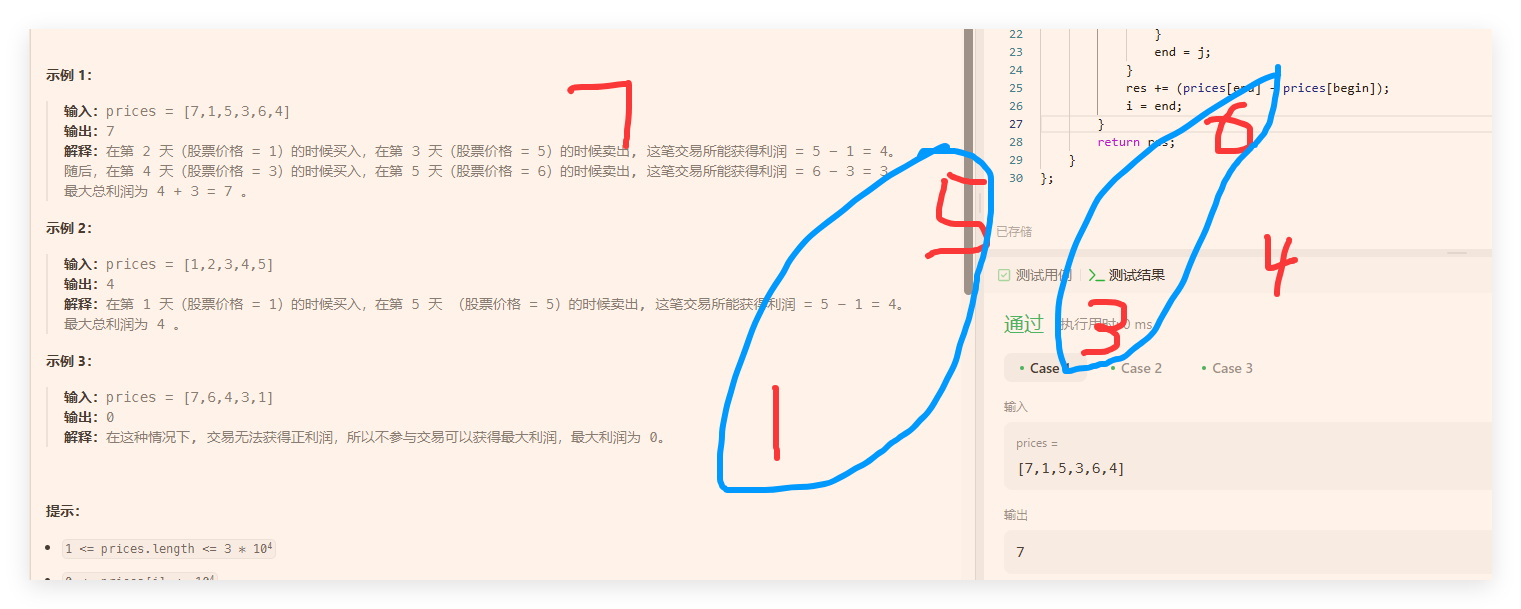
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int> &prices)
{
int res = 0;
int begin = 0;
int end = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.size(); i++)
{
begin = i;
end = i;
for (int j = begin; (j + 1) < prices.size();)
{
if (prices[j] <= prices[j + 1])
{
j++;
}
else
{
break;
}
end = j;
}
res += (prices[end] - prices[begin]);
i = end;
}
return res;
}
};
贪心

// 每天只贪增加的利润
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.size(); i++) {
result += max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1], 0);
}
return result;
}
};
动态规划也可以解决
跳跃游戏


贪的时每次的最大覆盖范围。
注意:下标为i的元素的覆盖范围是:i+cover[i]
class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(vector<int>& nums) {
int cover = 0;
if (nums.size() == 1) return true; // 只有一个元素,就是能达到
for (int i = 0; i <= cover; i++) { // 注意这里是小于等于cover
cover = max(i + nums[i], cover);
if (cover >= nums.size() - 1) return true; // 说明可以覆盖到终点了
}
return false;
}
};
跳跃游戏II


class Solution
{
public:
int jump(vector<int> &nums)
{
int cover = 0, results = 0;
int next = 0; // 下一个步的覆盖范围
if (nums.size() == 1)
return 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= cover; i++)
{
next = max(next, i + nums[i]);
if (i == cover) // i 已经走到当前的覆盖范围的尽头了
if (cover != (nums.size() - 1))
{
results++;
cover = next;
if (cover > (nums.size() - 1))
break;
}
else
break;
}
return results;
}
};
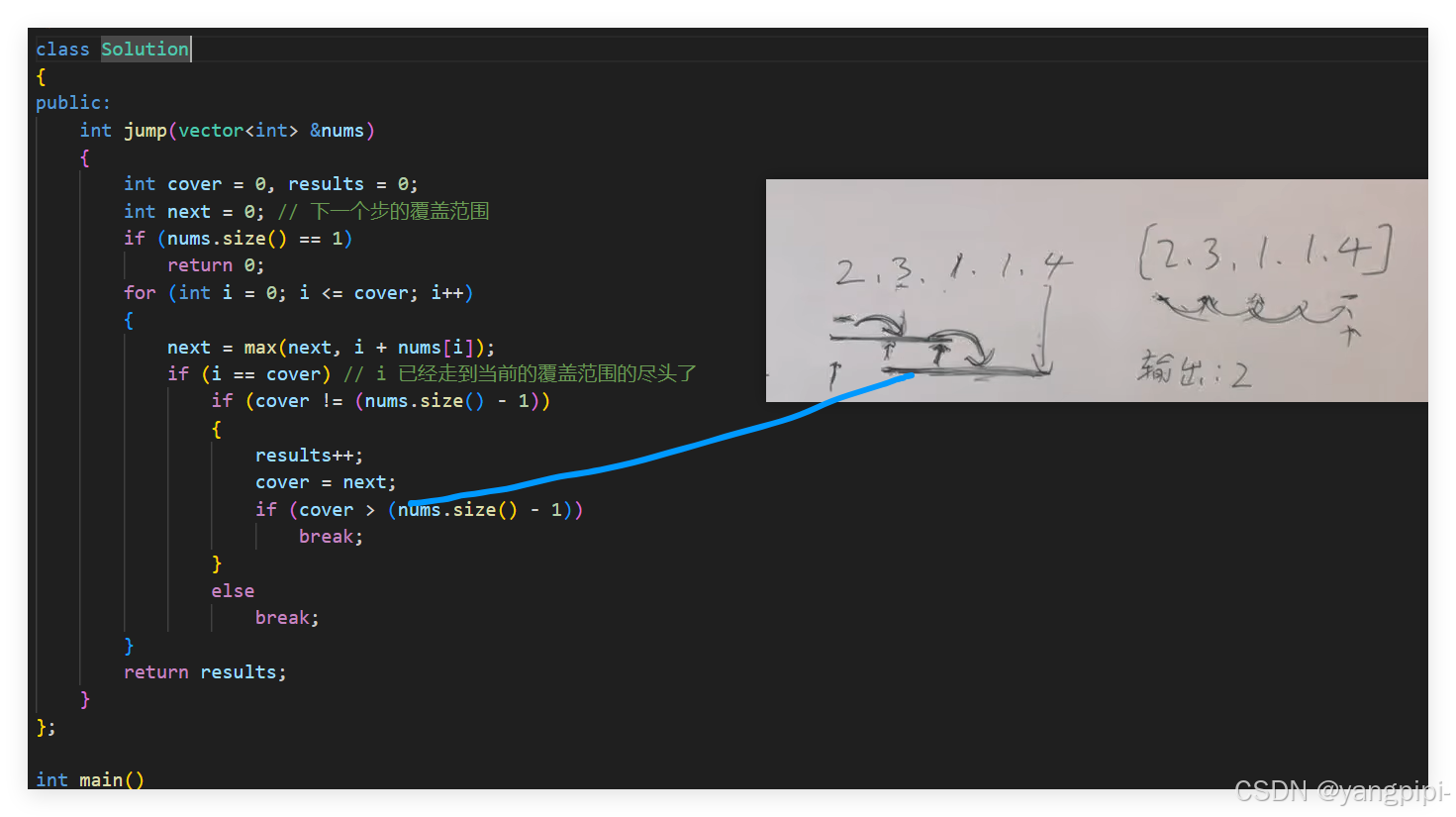
K次取反后最大化的数组和

逻辑推理
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <limits>
#include <cmath>
#include <functional>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
// 先排序,
class Solution
{
public:
int largestSumAfterKNegations(vector<int> &nums, int k)
{
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // 从小到达
int less_zero = count_if(nums.begin(), nums.end(), [](int value)
{ return value < 0; });
bool isExitZero = find(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0) == nums.end() ? false : true;
if (less_zero > 0) // 存在负数
{
if (less_zero >= k) // 负数的个数大于k
{
for (int i = 0; k > 0; k--)
{
nums[i] = -nums[i];
i++;
}
}
else // 负数的个数小于k
{
if (isExitZero) // 存在0
{
for (int i = 0; less_zero > 0; less_zero--)
{
nums[i] = -nums[i];
i++;
}
}
else // 不存在0
{
int k2 = k - less_zero; // 大于0的个数
// 将所有数变成正数
for (int i = 0; less_zero > 0; less_zero--)
{
nums[i] = -nums[i];
i++;
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // 从小到达
bool even = k2 % 2 == 0 ? true : false;
if (even) // 偶数
;
else
nums[0] = -nums[0];
}
}
}
else // 不存在负数
{
if (isExitZero) // 存在0
{
;
}
else // 不存在0
{ // 奇数 odd 偶数:even
bool even = k % 2 == 0 ? true : false;
if (even) // 偶数
;
else
nums[0] = -nums[0];
}
}
return accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);
}
};
贪心方法
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <limits>
#include <cmath>
#include <functional>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
// 先排序,
class Solution
{
public:
int largestSumAfterKNegations(vector<int> &nums, int k)
{ // 贪心2次:1. 贪负数最小的 2. 贪整数最小的
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() && k>0; i++) //k>0
{
if (nums[i] >= 0)
break;
nums[i] = -nums[i];
k--;
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
bool even = (k == 0 || k % 2 == 0) ? true : false; // 偶数 //k == 0
if (!even)
nums[0] = -nums[0]; // 最小的位于0
return accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);
}
};
加油站
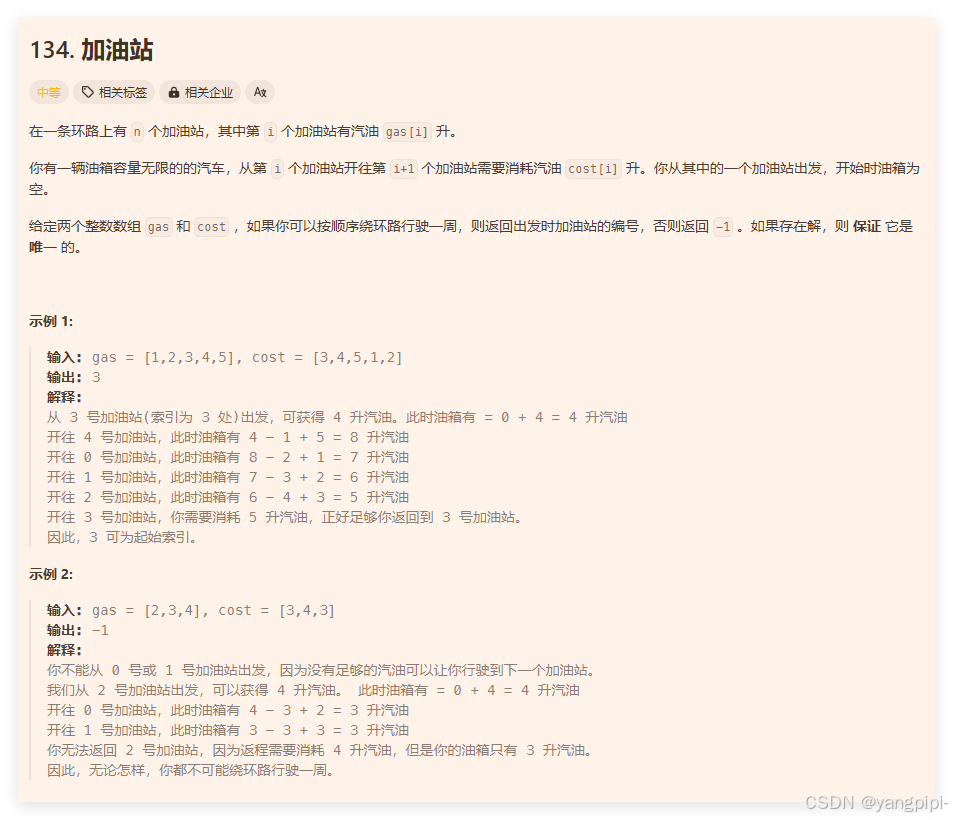
暴力法
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int canCompleteCircuit(vector<int> &gas, vector<int> &cost)
{
int n = gas.size();
for (int begin = 0; begin < n; ++begin)
{
int gasLeft = 0;
int pass = 0; // 改为从0开始计数
for (int now = begin; pass < n;)
{ // 更新循环条件,确保遍历n个站点
gasLeft += gas[now]; // 得到本站的油
if (gasLeft < cost[now]) // 检查是否足够到达下一站
break;
gasLeft -= cost[now]; // 减去到达下一站所需的油量
now = (now + 1) % n; // 正确地得到下一站的坐标
pass++;
if (pass == n)
return begin; // 如果已经通过了所有加油站,则返回起始点
}
}
return -1; // 如果没有找到合适的起始站
}
};
// 注意:实际使用时应添加main函数以及测试用例。
贪心解法
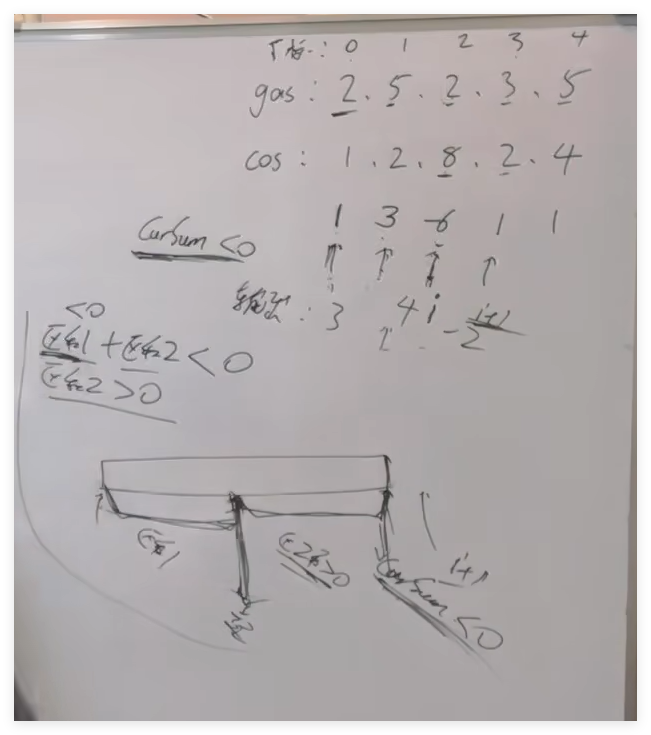
贪心,计算每个站点剩余的,当累加小于0时,以下一站点为起始点开始计算
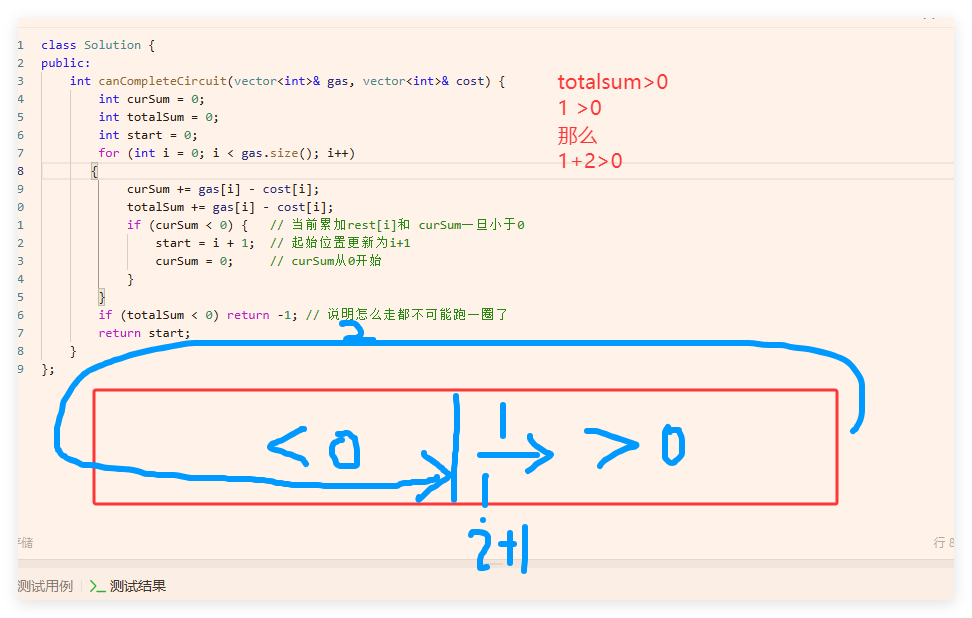
class Solution {
public:
int canCompleteCircuit(vector<int>& gas, vector<int>& cost) {
int curSum = 0;
int totalSum = 0;
int start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < gas.size(); i++)
{
curSum += gas[i] - cost[i];
totalSum += gas[i] - cost[i];
if (curSum < 0) { // 当前累加rest[i]和 curSum一旦小于0
start = i + 1; // 起始位置更新为i+1
curSum = 0; // curSum从0开始
}
}
if (totalSum < 0) return -1; // 说明怎么走都不可能跑一圈了
return start;
}
};
分发糖果

错误的思路


#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int candy(vector<int> &ratings)
{ // 从前往后,大了给
vector<int> child(ratings.size(), 0);
child[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; (i + 1) < ratings.size(); i++)
{
if (ratings[i] < ratings[i + 1]) // 将要分配的分数大
child[i + 1] = child[i] + 1;
else // // 将要分配的分数小
{
if (child[i] <= 1)
child[i + 1] = child[i] - 1;
else
child[i + 1] = 1;
}
}
while (1)
{
vector<int>::iterator res = find_if(child.begin(), child.end(), [](int elem)
{ return elem <= 0; });
if (res != child.end()) // 容器中含有小于0的元素
{
for_each(child.begin(), child.end(), [](int &val) // 注意这里必须是引用传参
{ cout<<val<<ends;val += 1; });
cout << endl;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return accumulate(child.begin(), child.end(), 0);
}
};
贪心(两边都要贪心)

// 涉及两边的比较:应该先关照一遍再关照另外一遍为好
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int candy(vector<int> &ratings)
{ // 从左往右:只贪从左往右满足条件
vector<int> child(ratings.size(), 0);
child[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; (i + 1) < ratings.size(); i++)
{
if (ratings[i] < ratings[i + 1]) // 将要分配的分数大
child[i + 1] = child[i] + 1;
else if (ratings[i] >= ratings[i + 1])
{
child[i + 1] = 1;
}
}
// 从右往左:只贪从右往左满足条件
for (int i = ratings.size() - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
if (ratings[i] < ratings[i - 1]) // 左边大
{
if (child[i - 1] != (child[i] + 1))
child[i - 1] = max(child[i - 1], child[i] + 1); // ***********
}
}
return accumulate(child.begin(), child.end(), 0);
}
};
柠檬水找零

贪心
每次贪最大的钱
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
bool lemonadeChange(vector<int> &bills)
{
/* 每次来钱了,先存入moneys中,不是5的,从bills中找
*/
vector<int> moneys;
for (int i = 0; i < bills.size(); i++)
{
if (bills[i] == 5)
{
moneys.push_back(5);
sort(moneys.begin(), moneys.end(), greater<int>());
}
else // 需要找零
{
moneys.push_back(bills[i]);
bills[i] -= 5; // 要找的钱数
sort(moneys.begin(), moneys.end(), greater<int>());
for (int j = 0; j < moneys.size(); j++)
{
if (moneys[j] <= bills[i])
{
cout << moneys[j] << endl;
bills[i] -= moneys[j];
moneys[j] = 0;
if (bills[i] <= 0)
break;
}
}
if (bills[i] < 0 || bills[i] > 0)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool lemonadeChange(vector<int>& bills) {
int five = 0, ten = 0, twenty = 0;
for (int bill : bills) {
// 情况一
if (bill == 5) five++;
// 情况二
if (bill == 10) {
if (five <= 0) return false;
ten++;
five--;
}
// 情况三
if (bill == 20) {
// 优先消耗10美元,因为5美元的找零用处更大,能多留着就多留着
if (five > 0 && ten > 0) {
five--;
ten--;
twenty++; // 其实这行代码可以删了,因为记录20已经没有意义了,不会用20来找零
} else if (five >= 3) {
five -= 3;
twenty++; // 同理,这行代码也可以删了
} else return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
买卖股票的最佳时机i

暴力搜索
超出时机限制
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
// 1。 暴力法
int maxProfit(vector<int> &prices)
{
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < prices.size(); j++)
{
if (max < (prices[j] - prices[i]))
max = prices[j] - prices[i];
}
}
return max;
}
};
贪心算法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
/*连续贪
每次先贪最小值,然后根据最小值来贪最大差值
*/
int maxProfit(vector<int> &prices)
{
if (prices.empty())
return 0;
int minPrice = INT_MAX; // 初始化最低价格为最大值
int maxProfit = 0; // 初始化最大利润为0
for (int price : prices)
{
// 更新最低价格
minPrice = min(minPrice, price);
// 更新最大利润
maxProfit = max(maxProfit, price - minPrice);
}
return maxProfit;
}
};
买卖股票的最佳时机II
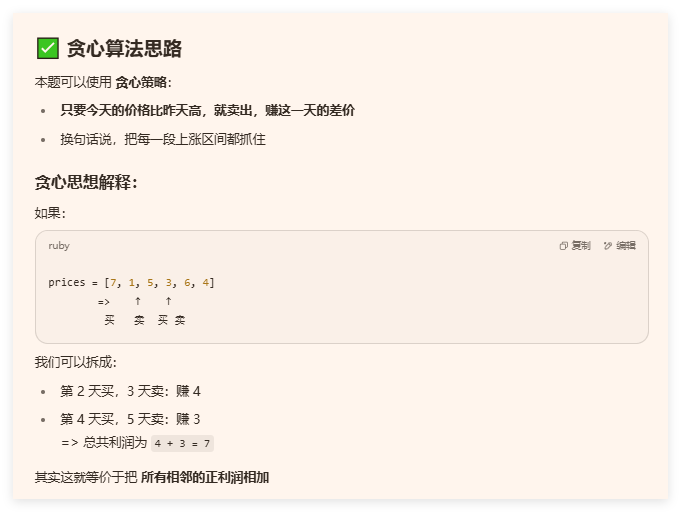
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int profit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.size(); ++i) {
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) {
profit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1]; // 贪心地加上每一次上涨的差值
}
}
return profit;
}
根据身高重建队列


#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
// 版本一
class Solution
{
// 两个条件限制时,要两次贪心
/*首先按照h进行排序,从大到小 h相等,k小的在前面
再根据k进行调整
*/
public:
static bool cmp(const vector<int> &a, const vector<int> &b)
{
if (a[0] == b[0])
return a[1] < b[1];
return a[0] > b[0];
}
vector<vector<int>> reconstructQueue(vector<vector<int>> &people)
{
sort(people.begin(), people.end(), cmp);
vector<vector<int>> que;
for (int i = 0; i < people.size(); i++)
{
int position = people[i][1]; // why 可以直接根据[2]的数值进行插入,因为经过第一次贪心,前面的一定大于后面的
que.insert(que.begin() + position, people[i]);
}
return que;
}
};
用最少数量的箭引爆气球

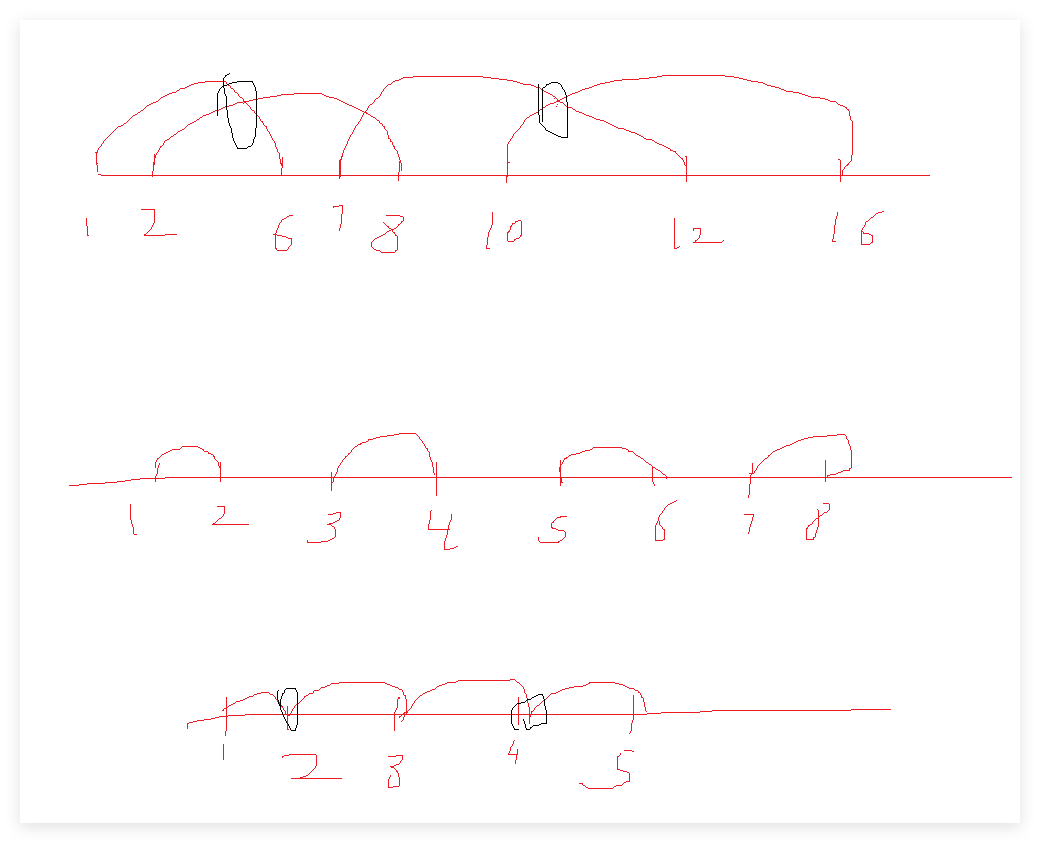
贪心1
代码巧妙
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int findMinArrowShots(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
if (points.empty()) return 0;
// 按照结束点从小到大排序
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) {
return a[1] < b[1];
});
int arrows = 1; // 至少需要一支箭
int end = points[0][1]; // 第一个气球的结束点
for (size_t i = 1; i < points.size(); ++i) {
if (points[i][0] > end) {
// 当前气球的起始点大于上一支箭的结束点,需要新的箭
arrows++;
end = points[i][1]; // 更新结束点
}
}
return arrows;
}
};
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> points = {{10, 16}, {2, 8}, {1, 6}, {7, 12}};
Solution solution;
cout << "Minimum arrows needed: " << solution.findMinArrowShots(points) << endl;
return 0;
}
贪心2(推荐)
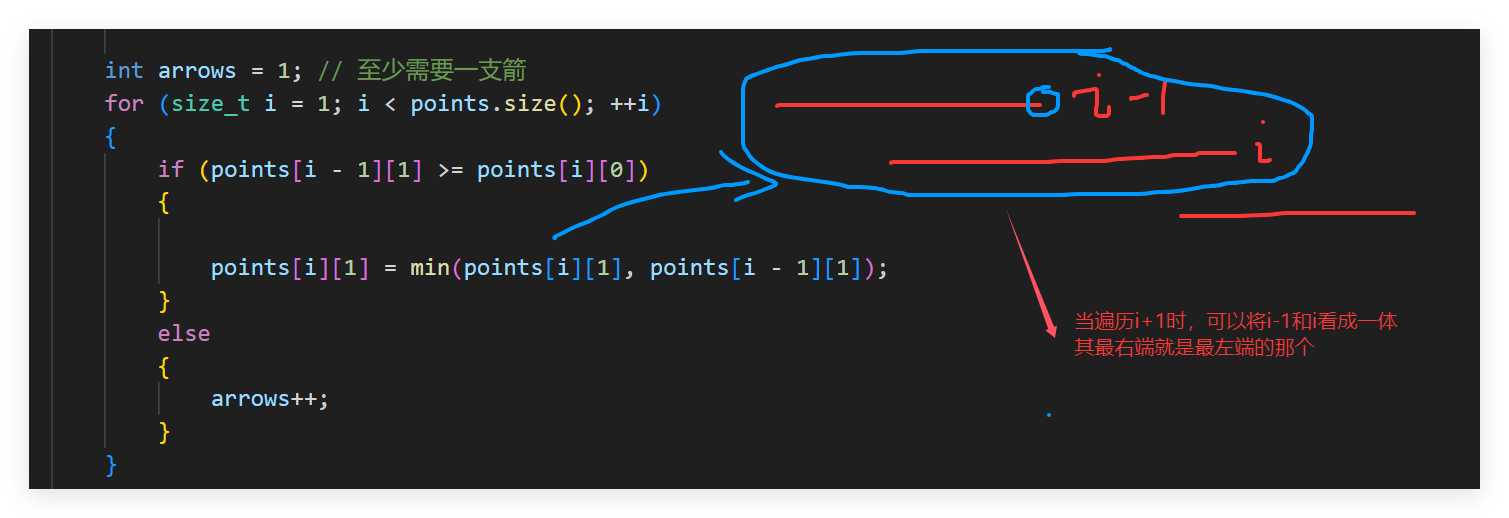
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int findMinArrowShots(vector<vector<int>> &points)
{
if (points.empty())
return 0;
// 按照结束点从小到大排序
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), [](const vector<int> &a, const vector<int> &b)
{ return a[1] < b[1]; });
int arrows = 1; // 至少需要一支箭
for (size_t i = 1; i < points.size(); ++i)
{
if (points[i - 1][1] >= points[i][0])
{
points[i][1] = min(points[i][1], points[i - 1][1]);
}
else
{
arrows++;
}
}
return arrows;
}
};
无重叠区间

// 本质上是统计重叠区间的个数
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int eraseOverlapIntervals(vector<vector<int>> &points)
{
if (points.empty())
return 0;
// 按照结束点从小到大排序
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), [](const vector<int> &a, const vector<int> &b)
{ return a[1] < b[1]; });
int count = 0; // 重叠区间的个数
for (size_t i = 1; i < points.size(); ++i)
{
if (points[i - 1][1] > points[i][0]) // 重叠了
{
count++;
points[i][1] = min(points[i][1], points[i - 1][1]);
}
}
cout << count << endl;
return count;
}
};
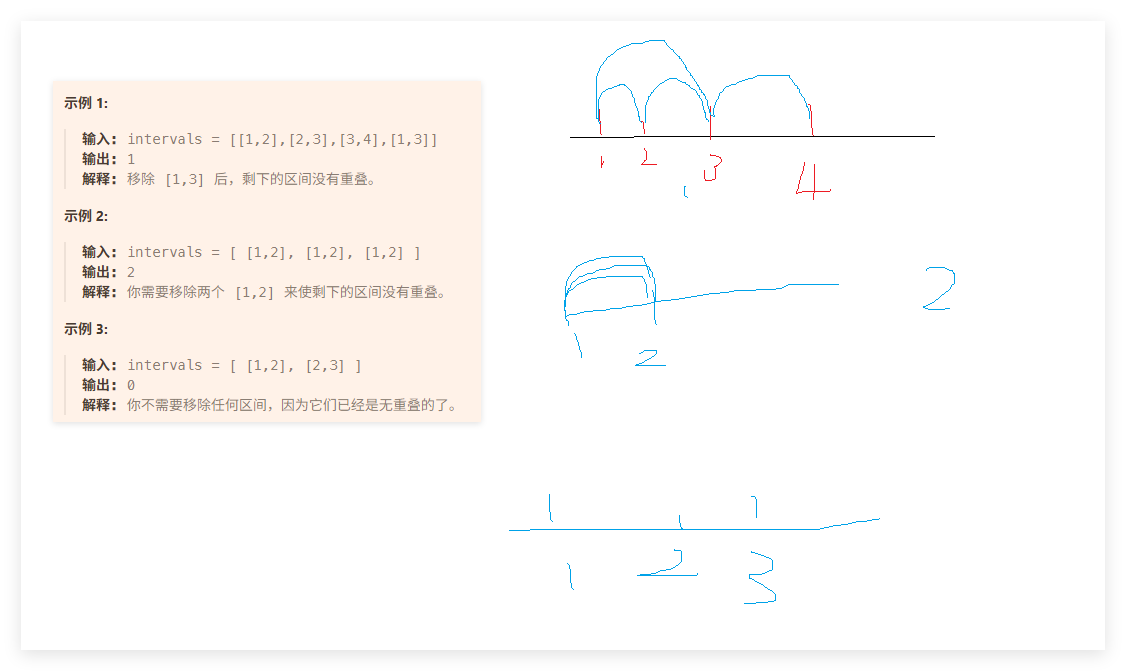
划分字母区间
贪心
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> partitionLabels(string s)
{
int last[26]; // 用于存储每个字符最后出现的索引 26个字母
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i)
last[s[i] - 'a'] = i;
// s[i]-'a' : 'a'的所以位置是0,所以从前向后0位置存储最后出现的`a`的下标
vector<int> res;
int left = 0, right = 0; // right 是当前分区的起点
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i)
{
right = max(right, last[s[i] - 'a']); // 更新当前区间能到达的最远点
if (i == right)
{ // 如果当前位置是当前区间的终点
res.push_back(right - left + 1);
left = i + 1; // 更新下一个区间的起点
}
}
return res;
}
};
合并区间

我的贪心
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>> &intervals)
{
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](vector<int> x, vector<int> y)
{ return x[0] < y[0]; });
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> tmp;
int i = 0;
for (; i < intervals.size(); i++)
{
if (tmp.size() == 0)
{
tmp.push_back(intervals[i][0]);
tmp.push_back(intervals[i][1]);
continue;
}
if (tmp.back() >= intervals[i][0] )
{
if (tmp.back() >= intervals[i][1]) // 防止 [[1,4],[2,3]]
continue;
tmp.pop_back();
tmp.push_back(intervals[i][1]);
}
else if(tmp.back() != intervals[i][1] )
{
if (tmp.back() >= intervals[i][1]) // 防止 [[1,4],[2,3]]
continue;
res.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
i--;
}
}
if (tmp.size() != 0)
{
res.push_back(tmp);
}
return res;
}
};
- 简化版
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>> &intervals)
{
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](vector<int> x, vector<int> y)
{ return x[0] < y[0]; });
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> tmp;
int i = 0;
for (; i < intervals.size(); i++)
{
if (tmp.size() == 0)
{
tmp.push_back(intervals[i][0]);
tmp.push_back(intervals[i][1]);
continue;
}
if (tmp.back() >= intervals[i][1]) // 防止 [[1,4],[2,3]]
continue;
if (tmp.back() >= intervals[i][0])
{
tmp.pop_back();
tmp.push_back(intervals[i][1]);
}
else if (tmp.back() != intervals[i][1])
{
res.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
i--;
}
}
if (tmp.size() != 0)
{
res.push_back(tmp);
}
return res;
}
};
贪心
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>> &intervals)
{
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](vector<int> x, vector<int> y)
{ return x[0] < y[0]; });
vector<vector<int>> res;
res.push_back(intervals[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); i++)
{
if (res.back()[1] >= intervals[i][0])
{
// 更新右区间:max
res.back()[1] = max(intervals[i][1], res.back()[1]);
}
else
{
res.push_back(intervals[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
};
单调递增的数字
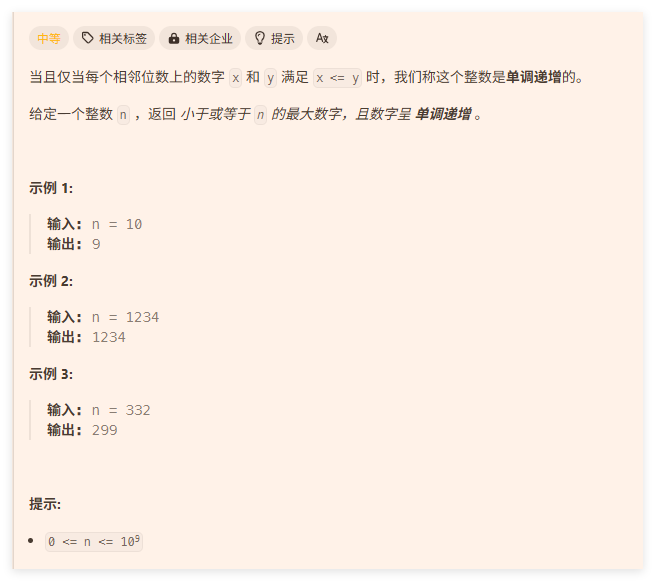
暴力法(超出时间)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
bool isIncreasingDigits(int n)
{
if (n <= 9 && n >= 0)
return true;
int right = n % 10; // 从后往前去取
n = n / 10;
while (n > 0)
{
int left = n % 10;
n = n / 10;
if (left <= right)
{
right = left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int monotoneIncreasingDigits(int n)
{
do
{
if (isIncreasingDigits(n))
return n;
n--;
} while (n > 0);
return n;
}
};
贪心
从后往前两个数字两个数字变量遍历
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int monotoneIncreasingDigits(int n)
{
string str = to_string(n);
int flag = str.size();
for (int i = str.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) // 从后往前遍历
{
if (str[i - 1] > str[i])
{
str[i - 1]--;
flag = i; //记录最后一次变为9的位置
}
}
for (int i = flag; i < str.size(); i++)
{
str[i] = '9';
}
return stoi(str);
}
};
监控二叉树

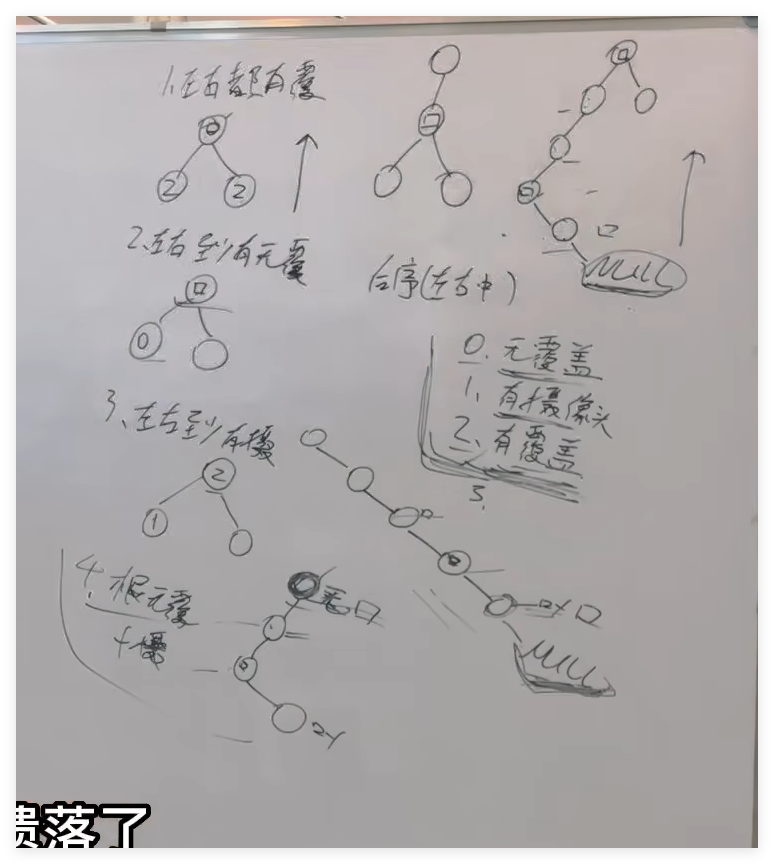
class Solution
{
public:
int result;
int traversal(TreeNode *root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return 2; // 空节点,该节点有覆盖
}
int left = traversal(root->left); // 左子树的状态
int right = traversal(root->right); // 右子树的状态
// 情况1:左右子树都有覆盖
if (left == 2 && right == 2)
{
return 0; // 本节点无覆盖
}
// 情况2:左右子树至少有一个无覆盖
else if (left == 0 || right == 0)
{
result++; // 本节点需要放置摄像头
return 1; // 本节点需要放置摄像头
}
// 情况4:左右子树都有覆盖
else if (left == 1 || right == 1)
{
// 本节点不需要放置摄像头
return 2; // 本节点有覆盖
}
return -1; // 其他情况,返回-1,这是为了防止代码逻辑错误
}
int minCameraCover(TreeNode *root)
{
result = 0; // 初始化摄像头数量
if (traversal(root) == 0)
{
result++; // 根节点无覆盖,需要放置摄像头
}
return result;
}
};





















 343
343

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








