
1. 从进程到线程
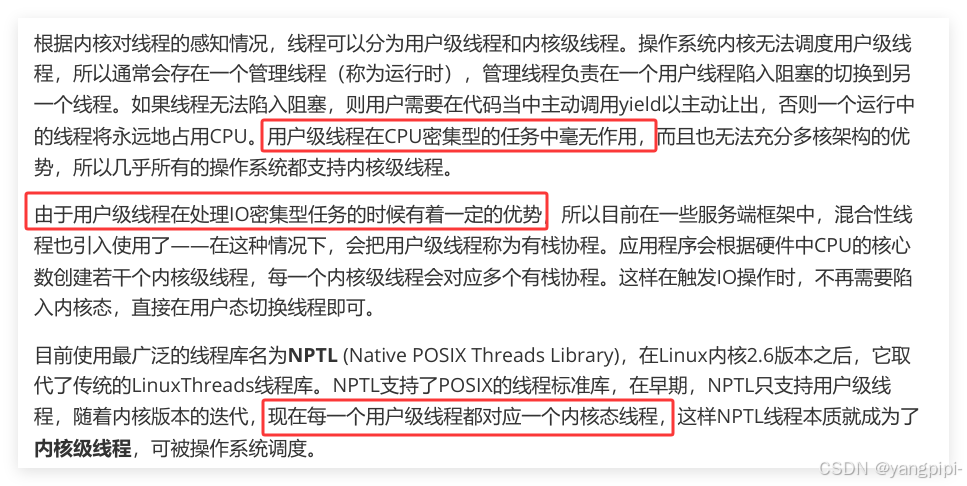
1.1 用户级线程和内核级线程
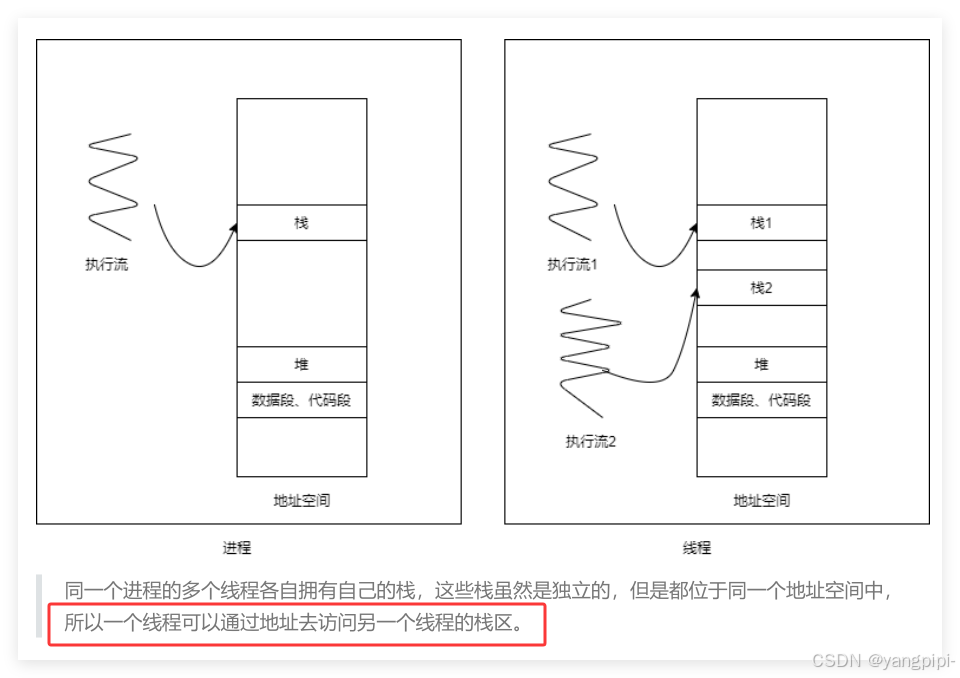
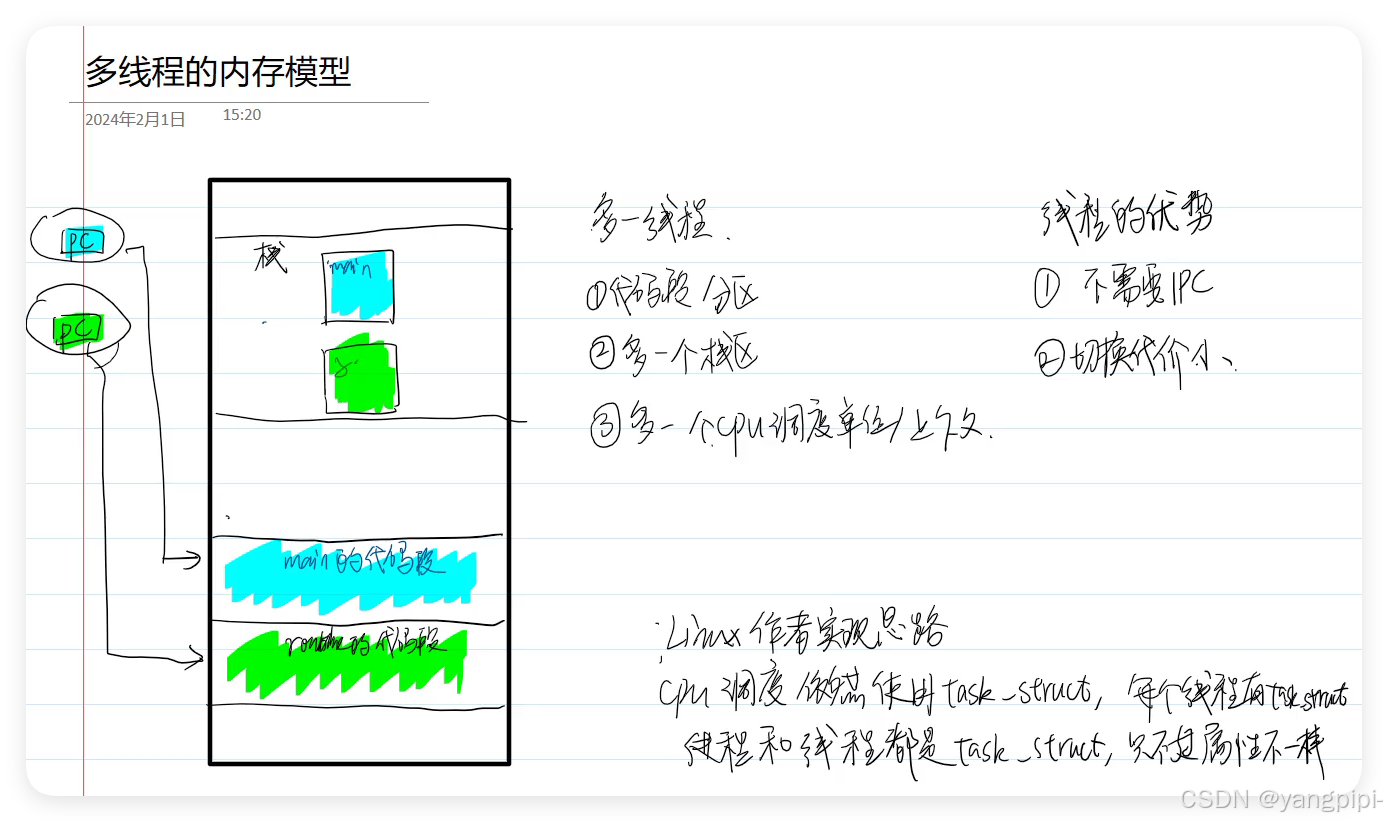
- 内存仍然以进程为单位,cpu以线程为单位


2. 线程的创建和终止
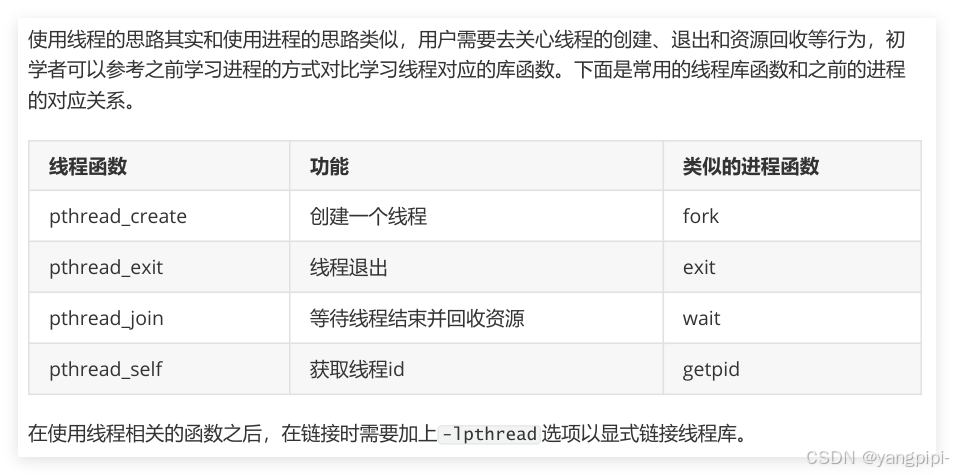
- 注意线程不存在父子关系,main函数启动的是主线程,其他都是子线程
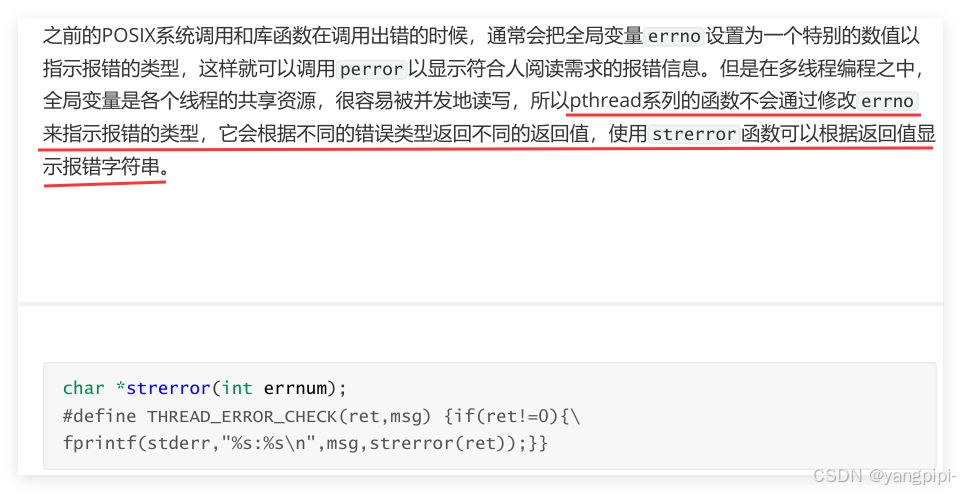
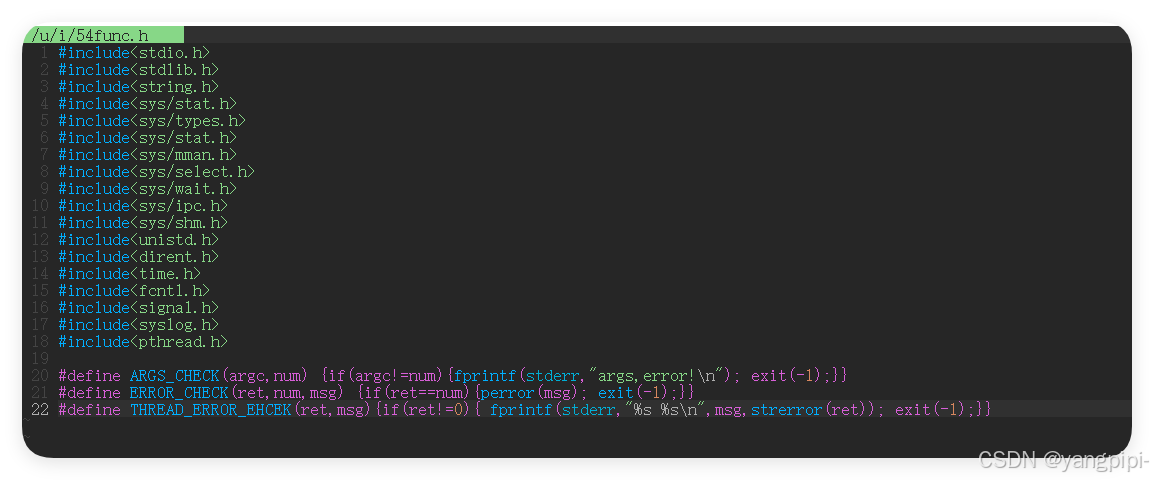
2.1 线程函数的错误处理
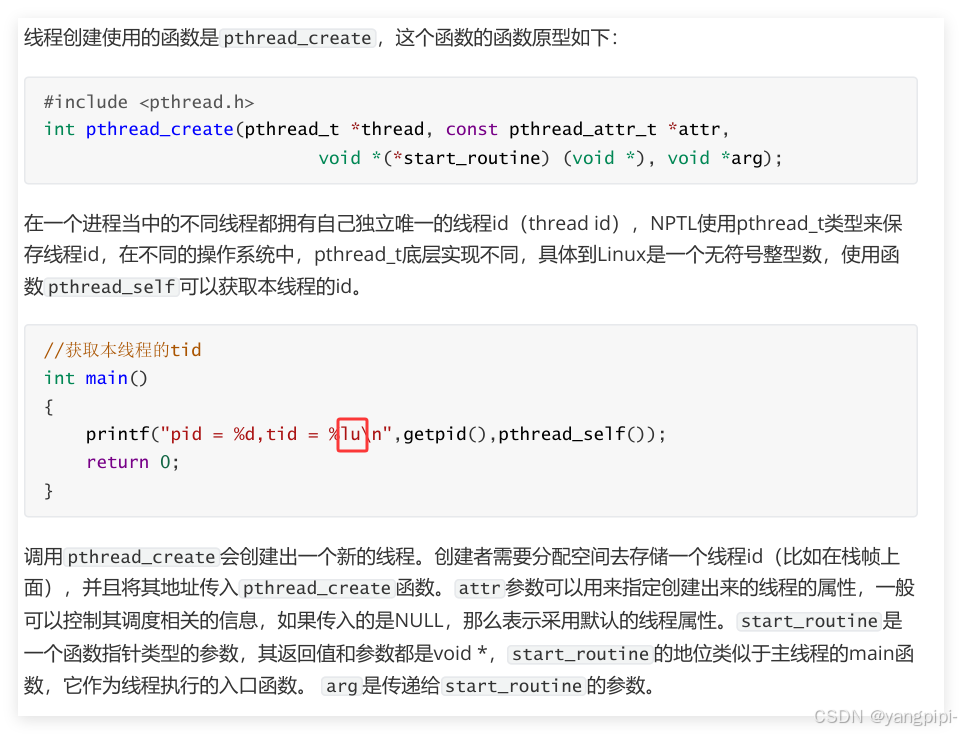
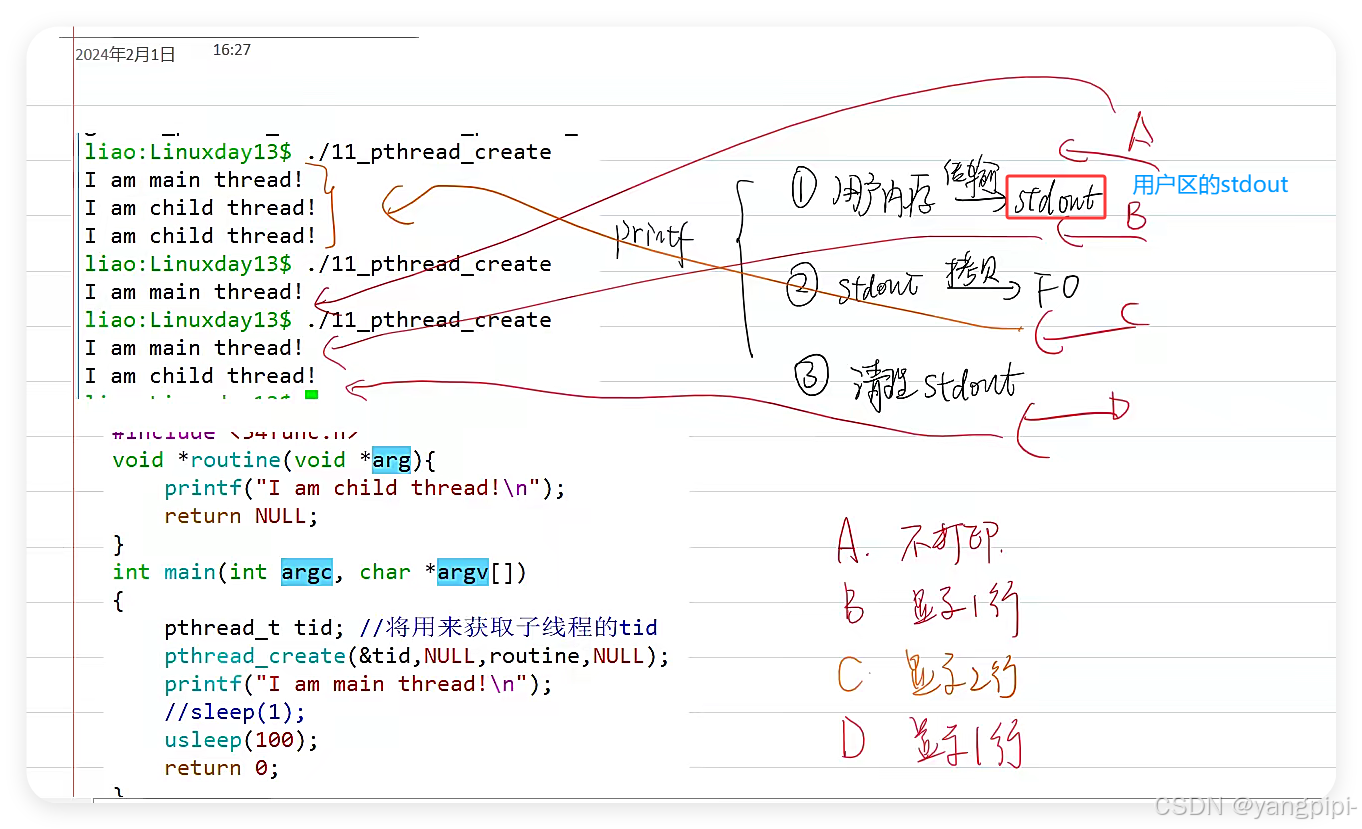
2.2 创建线程


2.3 线程和数据共享
- 全局变量,堆上变量,栈上变量均可共享


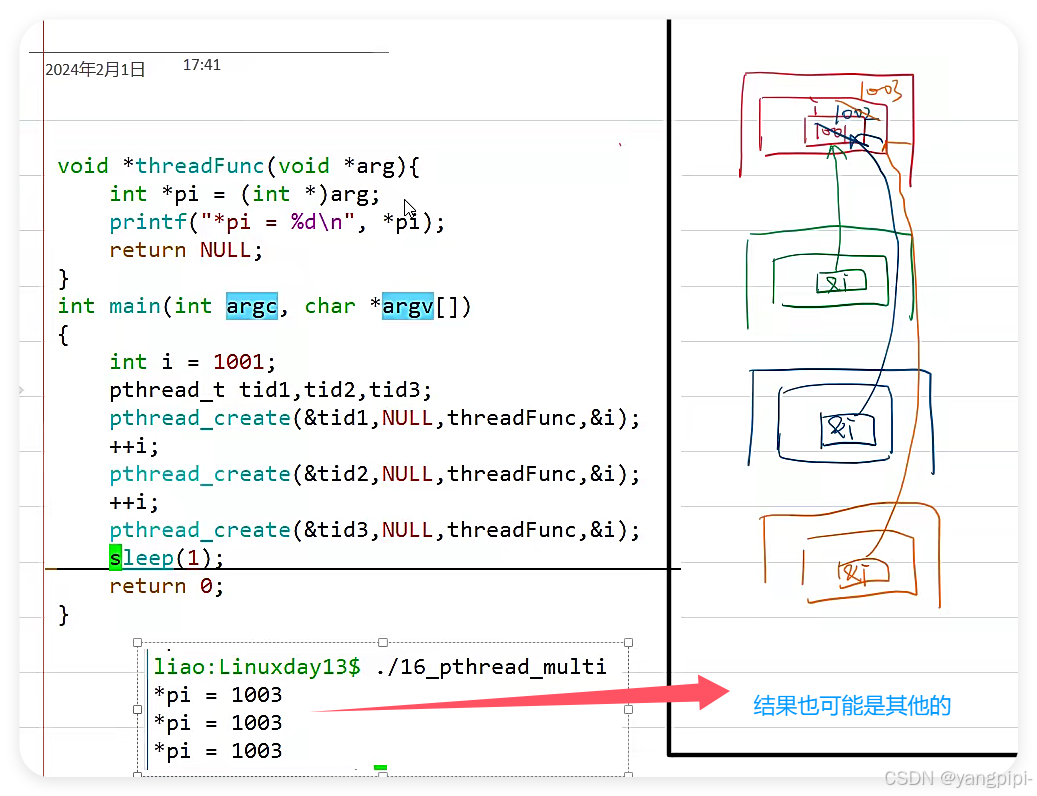
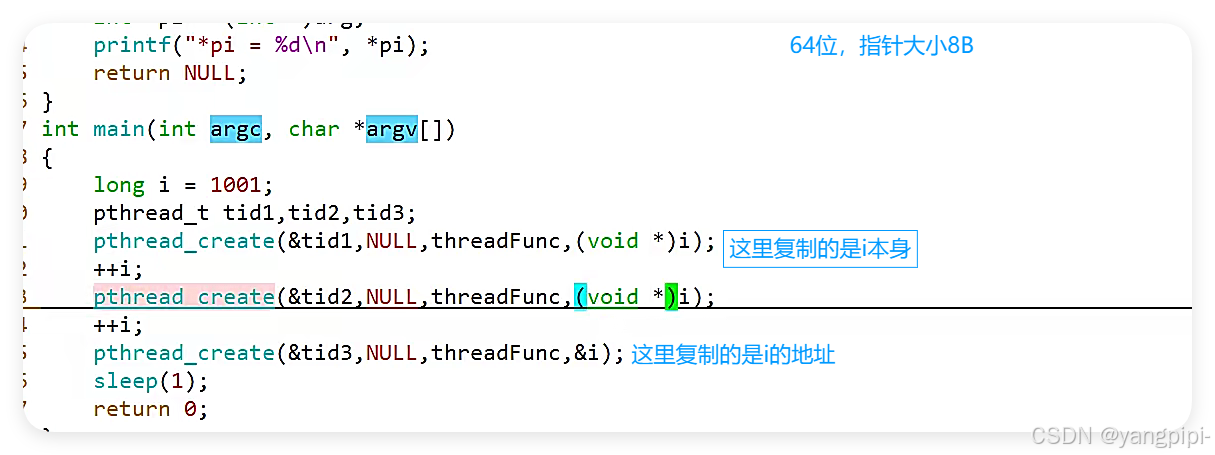
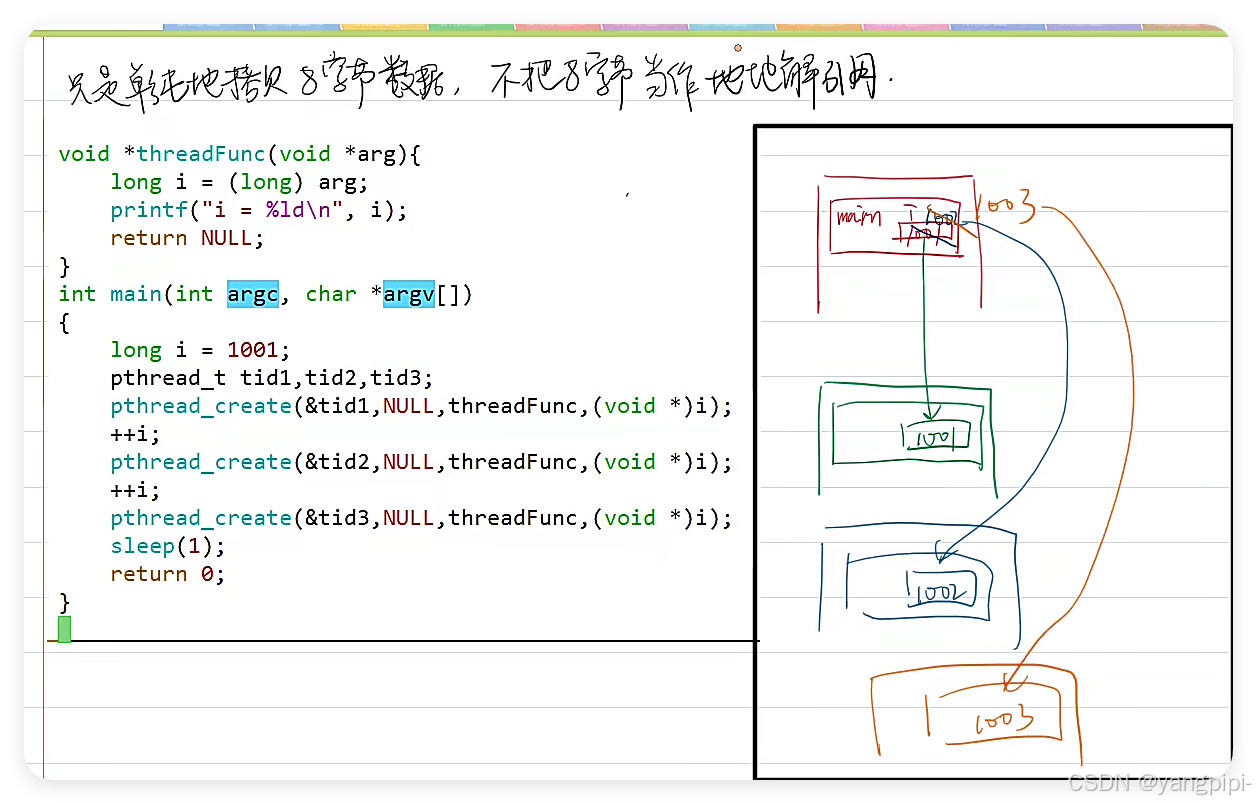
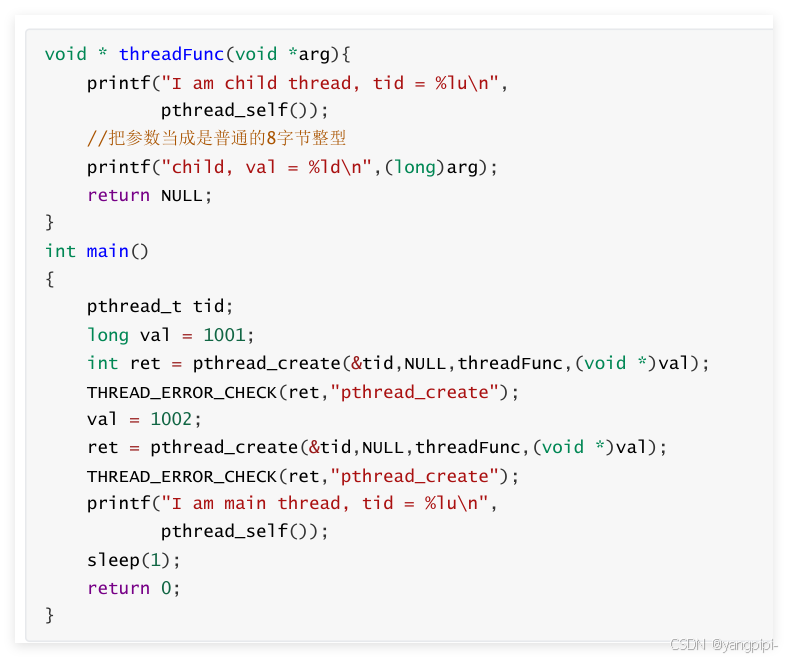
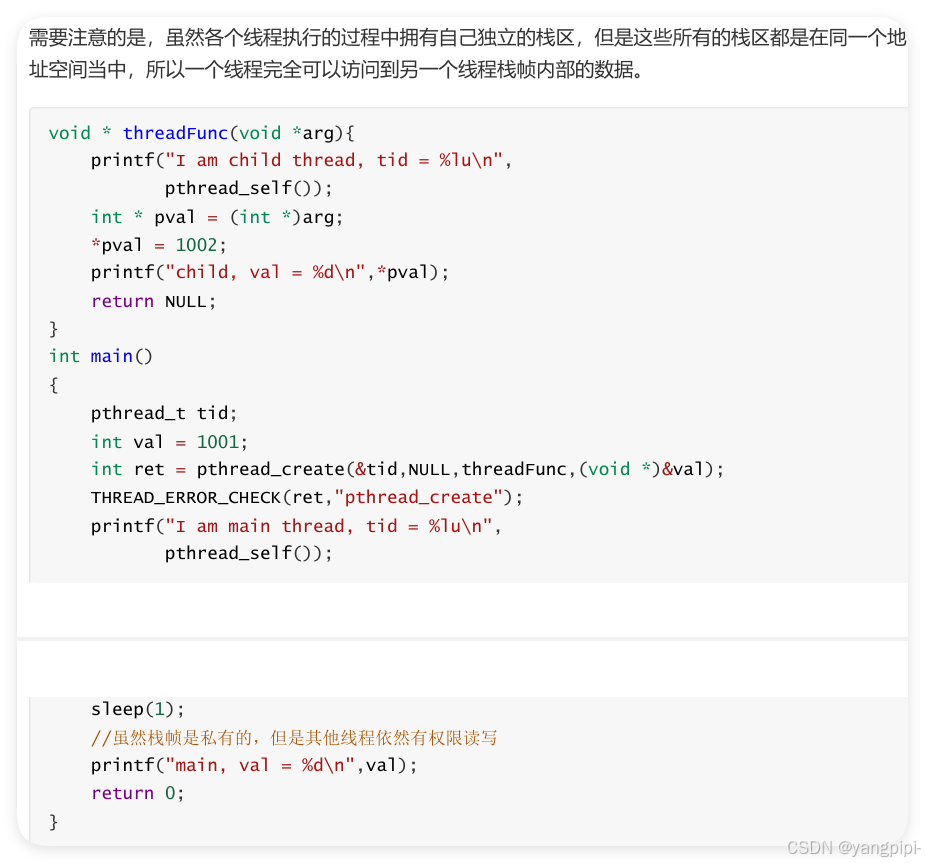

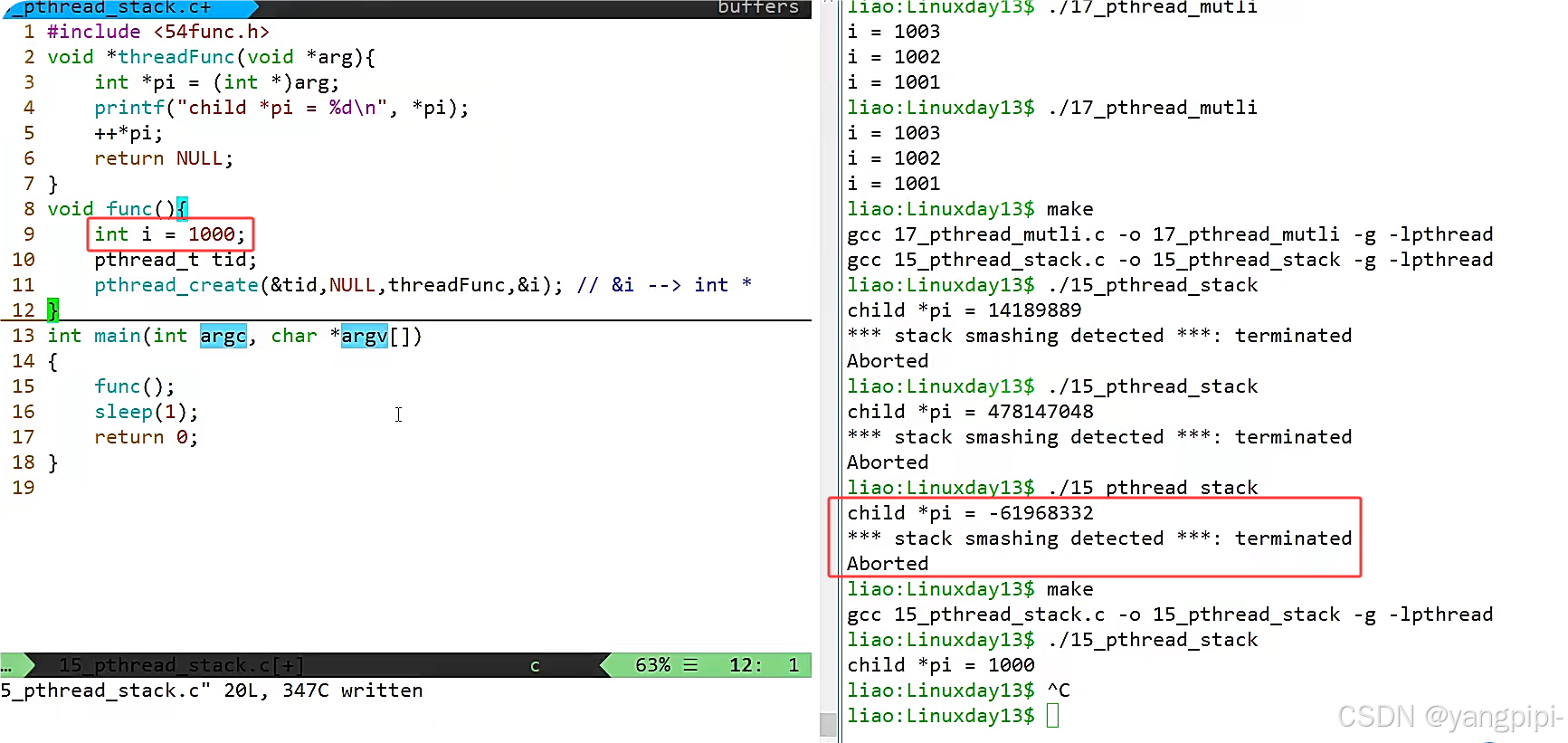
- 保证传递过去的变量不能是销毁的。
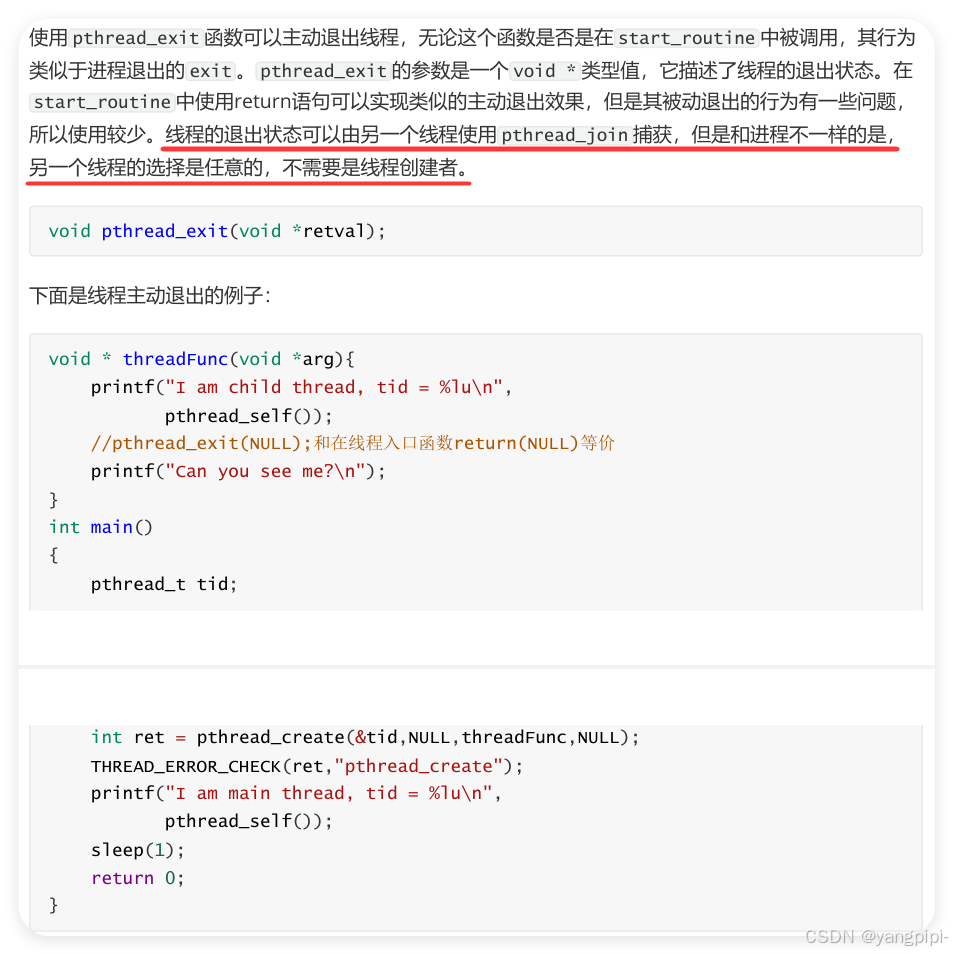
2.4 线程主动退出
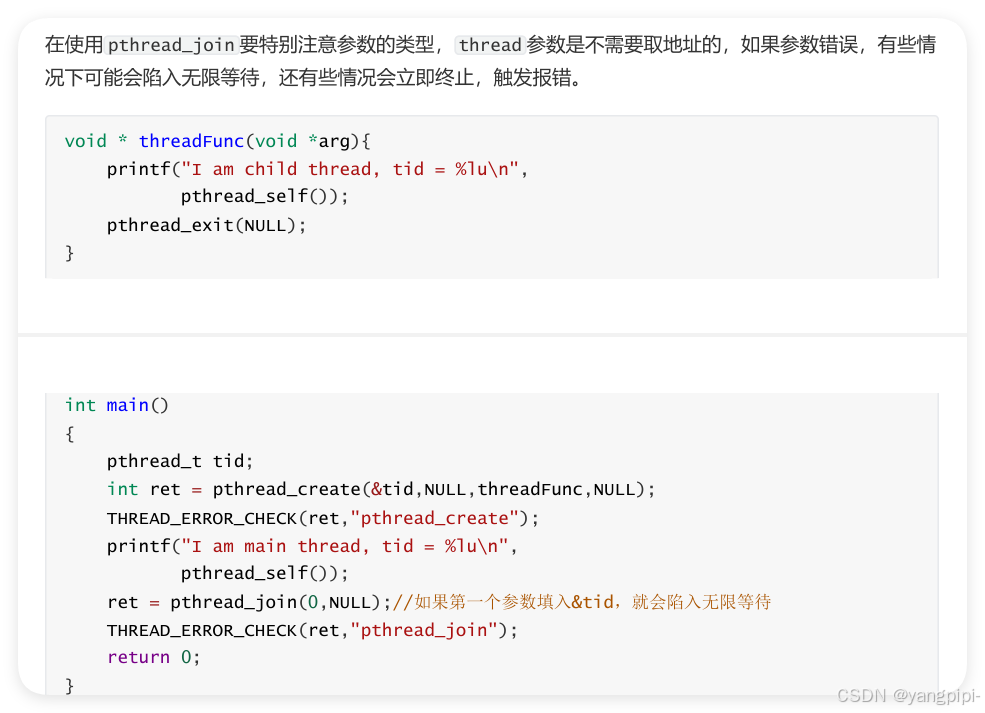
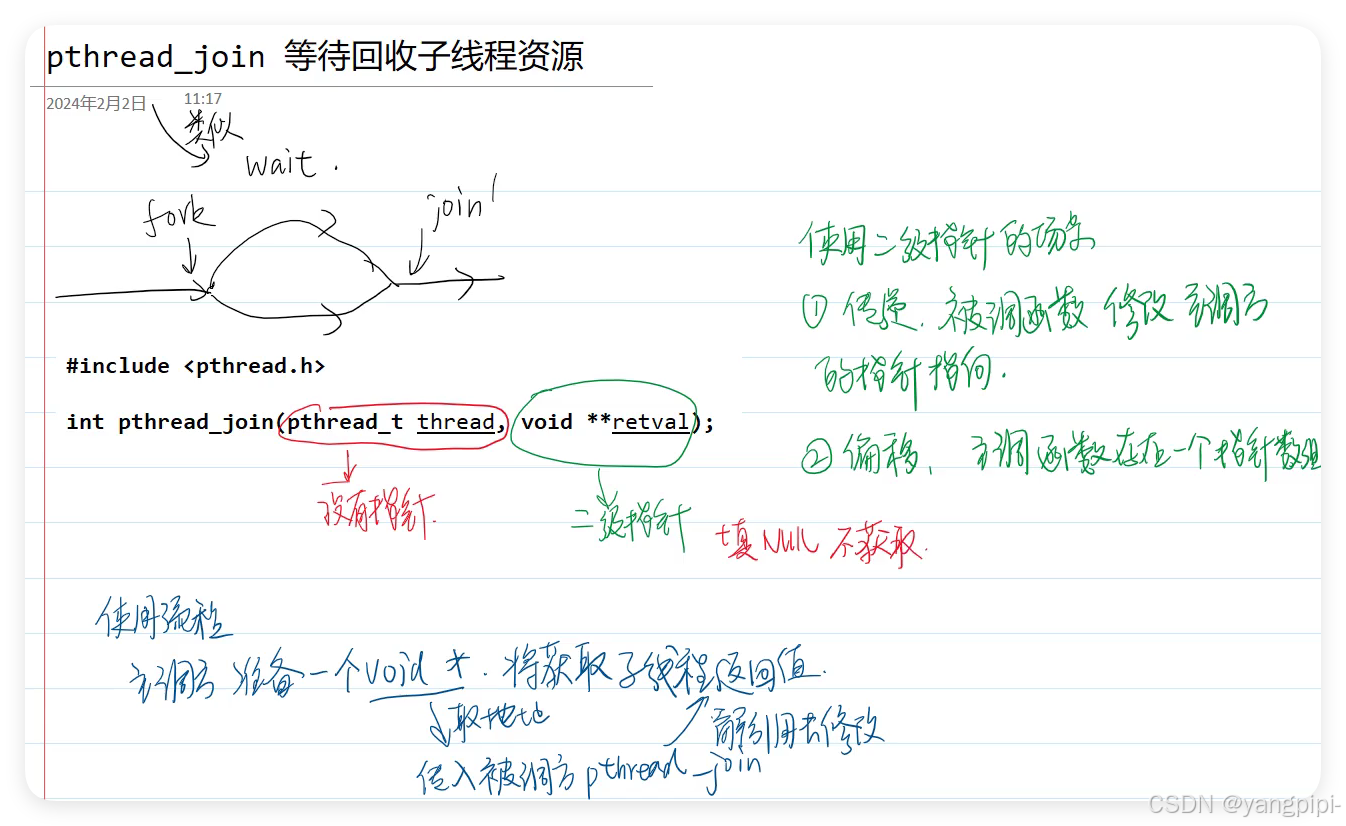
2.5 获取线程退出状态
- 查看所有线程
ps -elLF

3. 线程的取消和资源清理
3.1 线程的取消
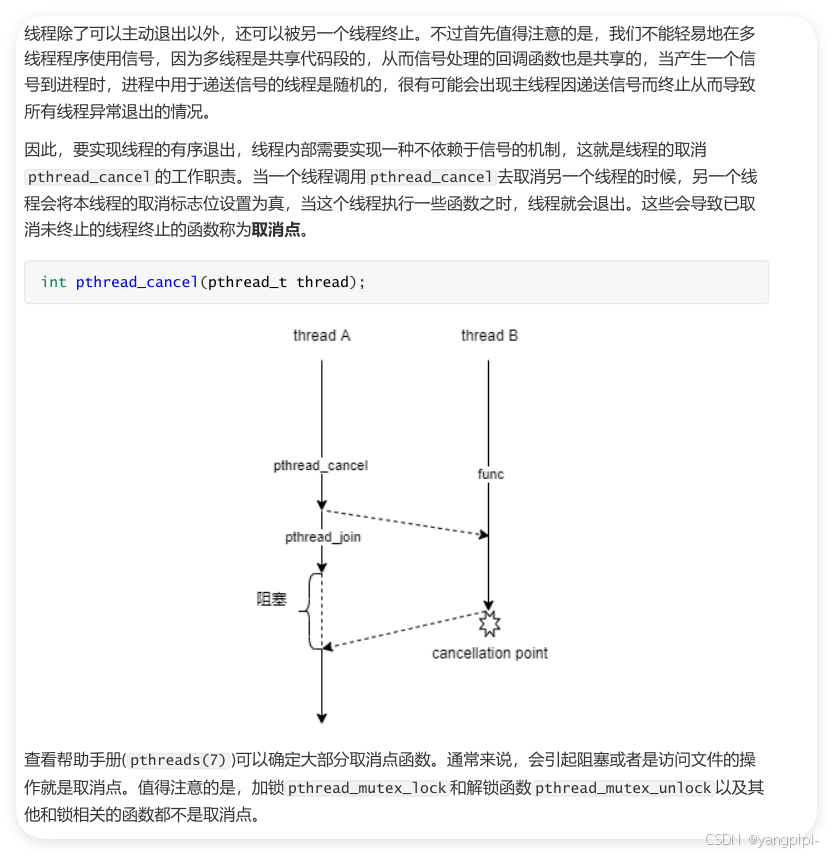
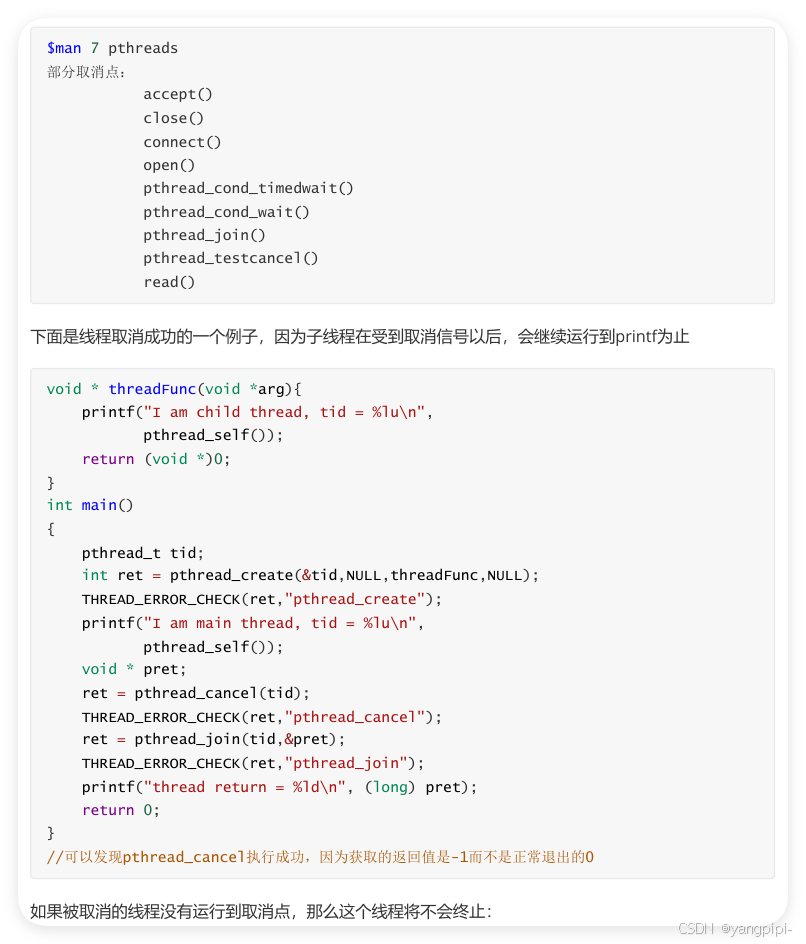

- 取消机制可能会导致资源泄漏
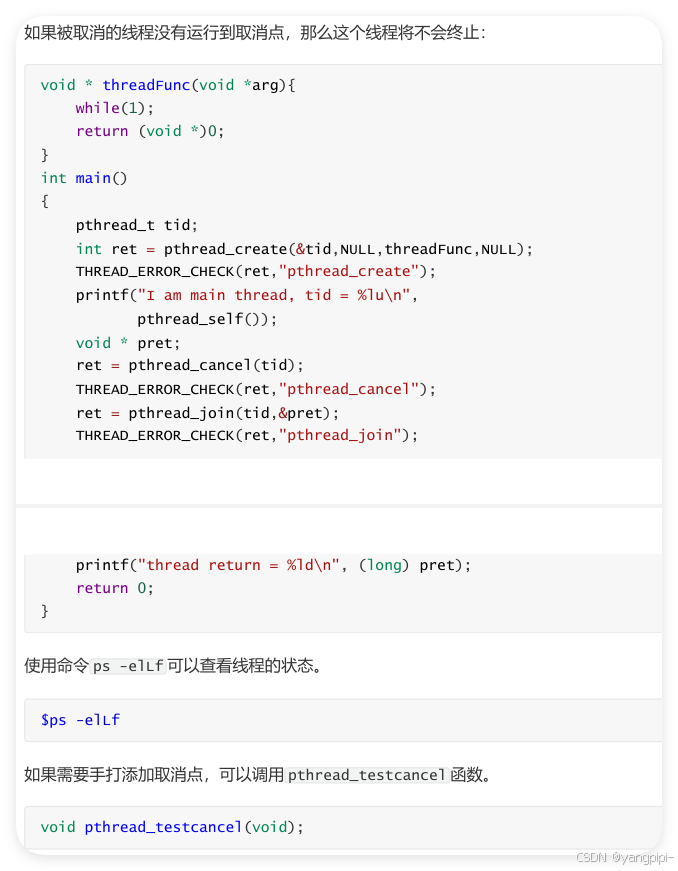

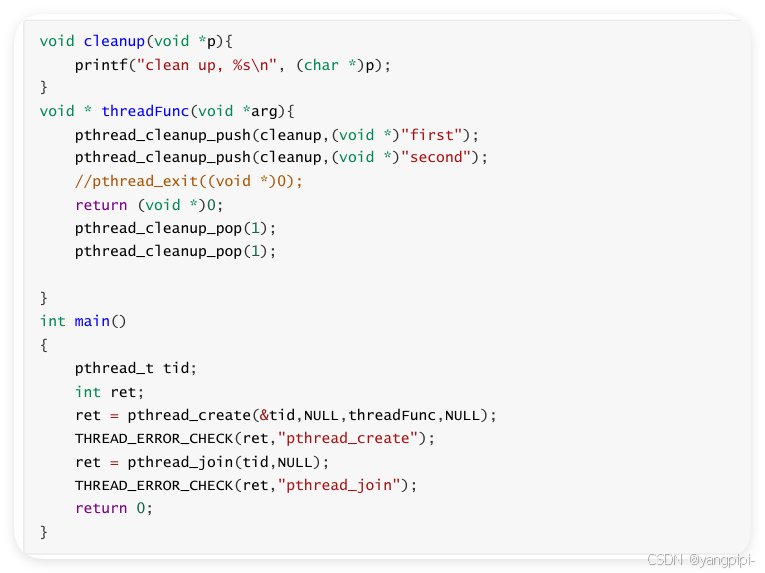
3.2 线程资源清理
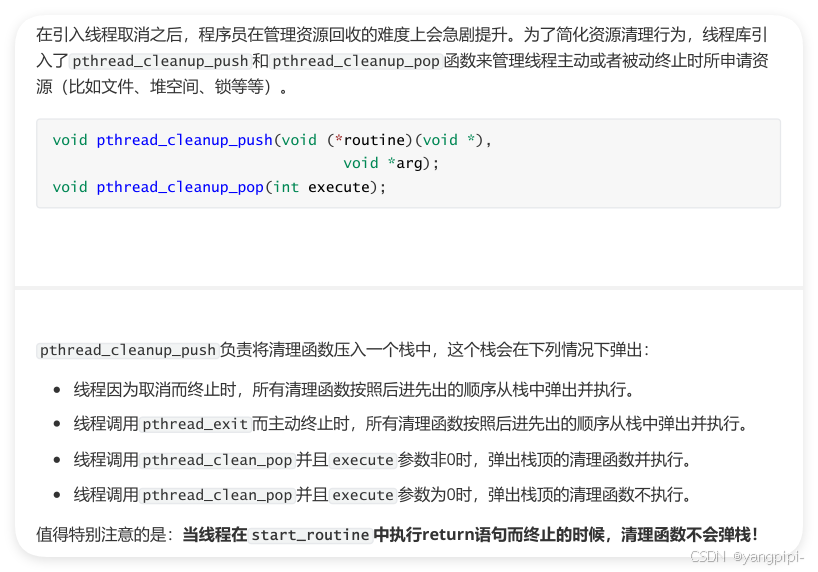

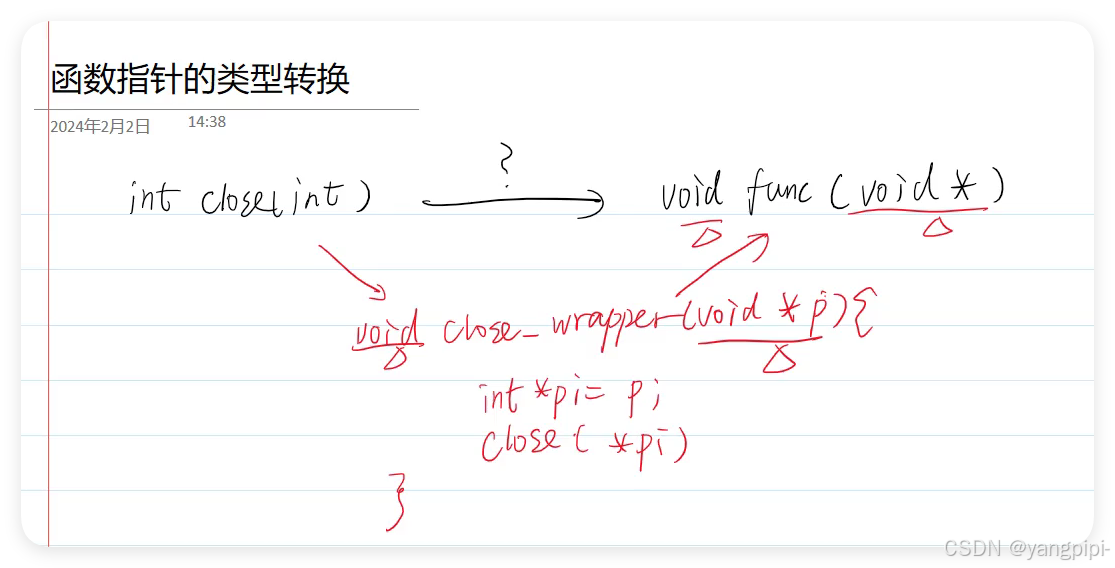



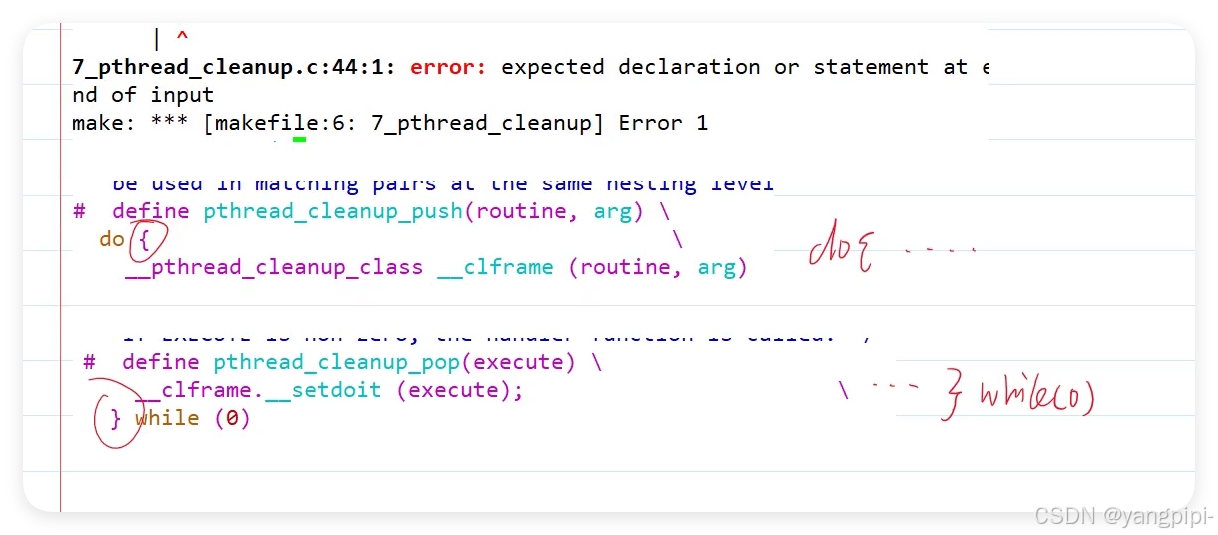
- 必须在同一个作用域中成对出现,否则会报编译错误。why
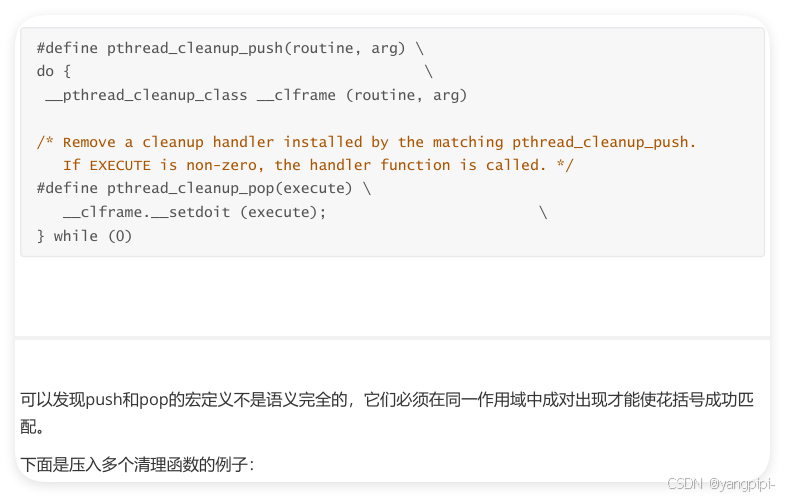
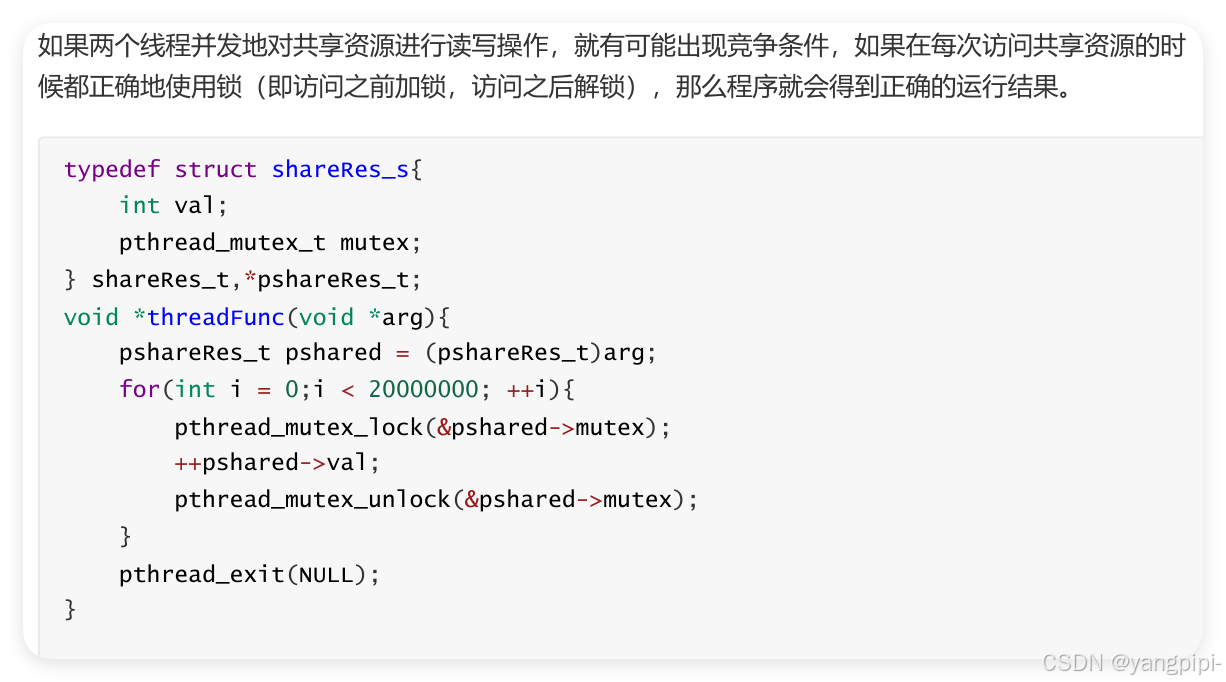
4. 线程的同步和互斥


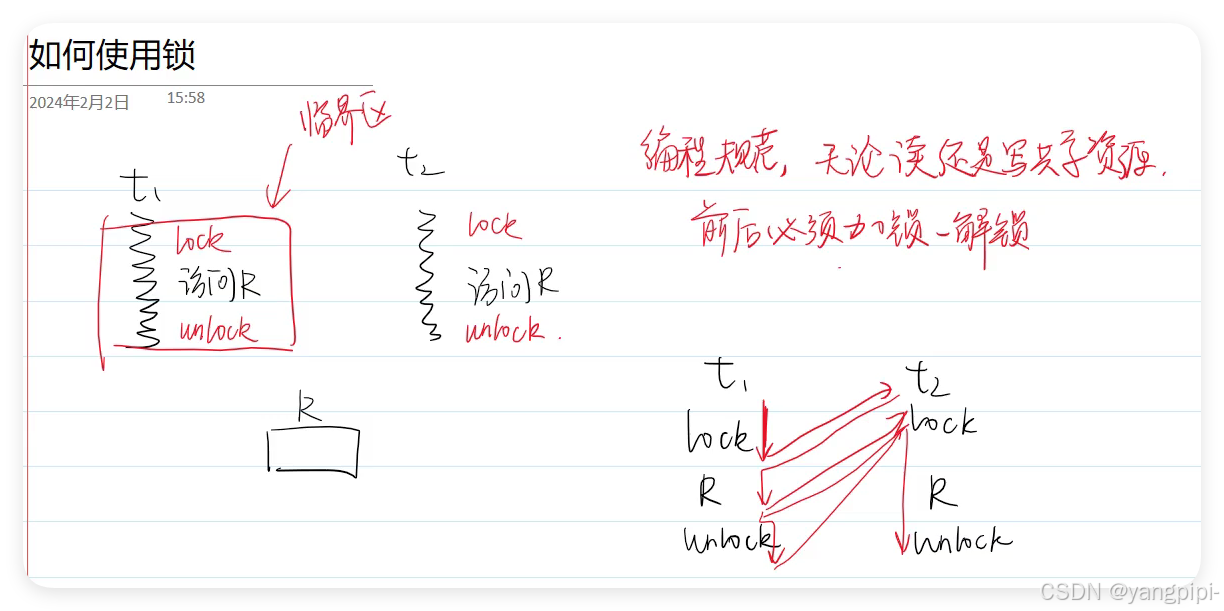
4.1 互斥锁的基本使用

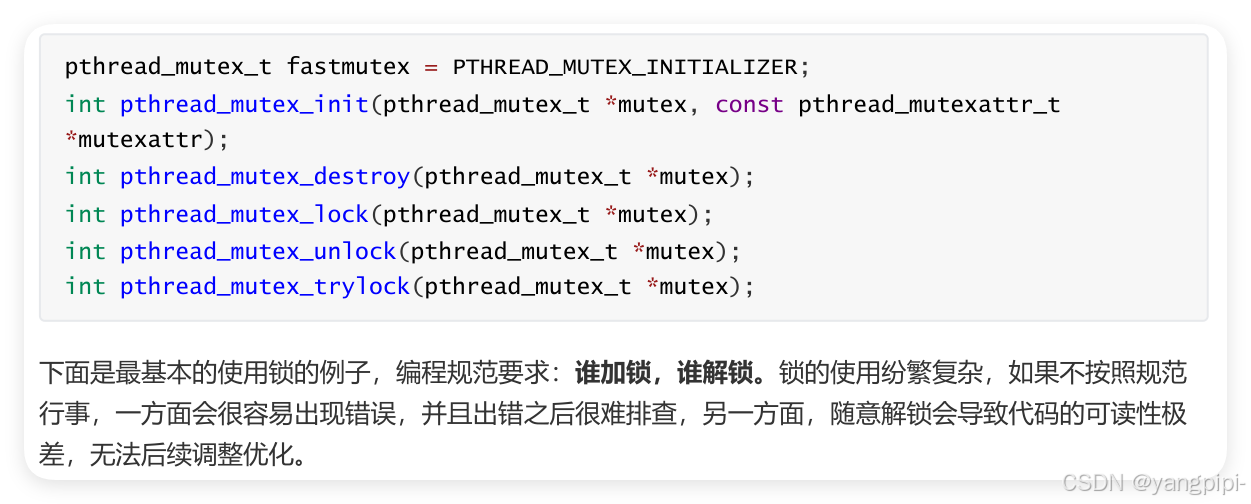
- 临界区越小越好,避免饥饿。
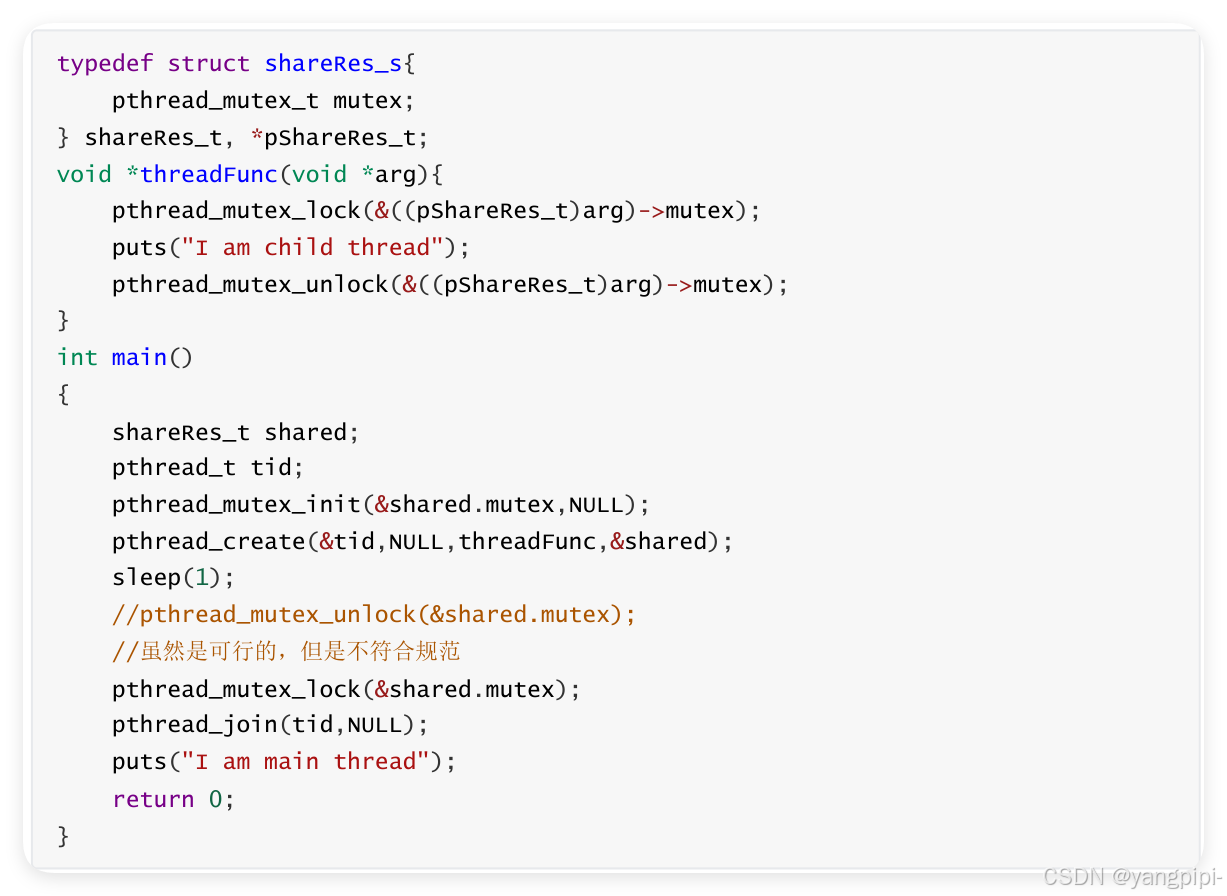
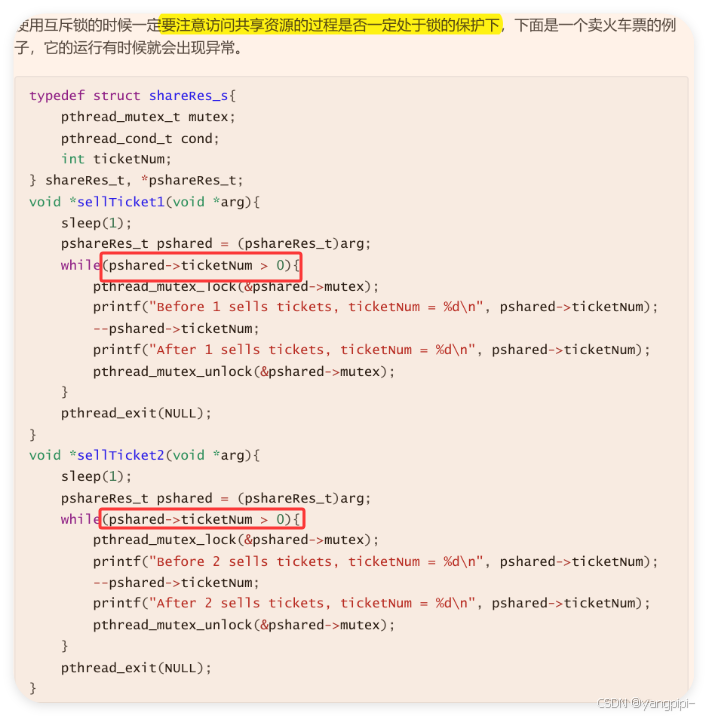
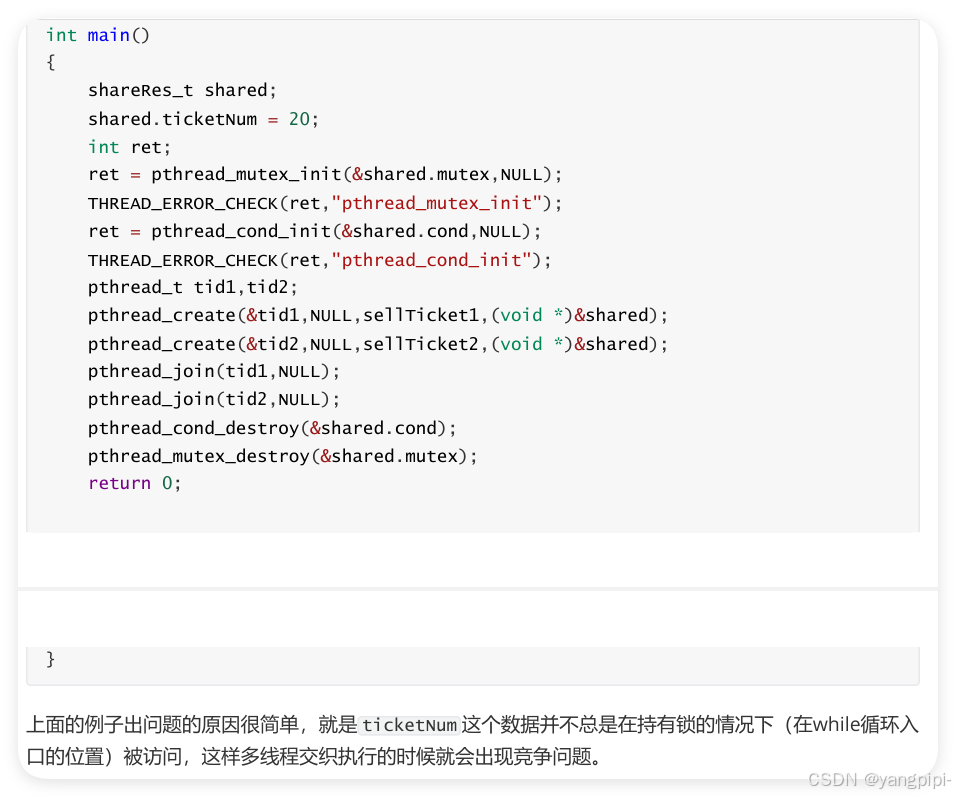
4.2 使用互斥锁访问共享资源

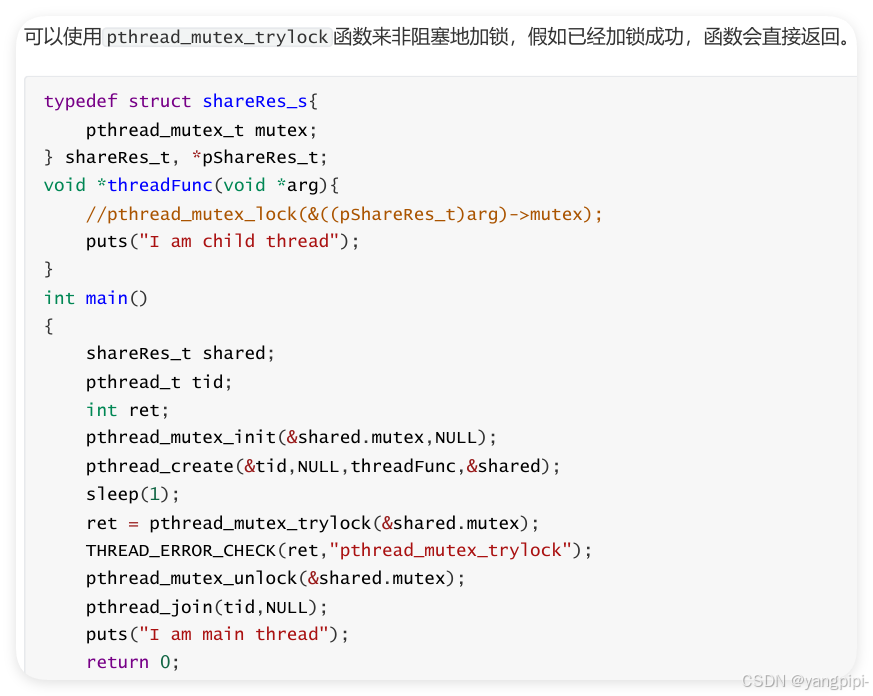
4.3 互斥锁出错的例子
- 尽量只使用一把锁。
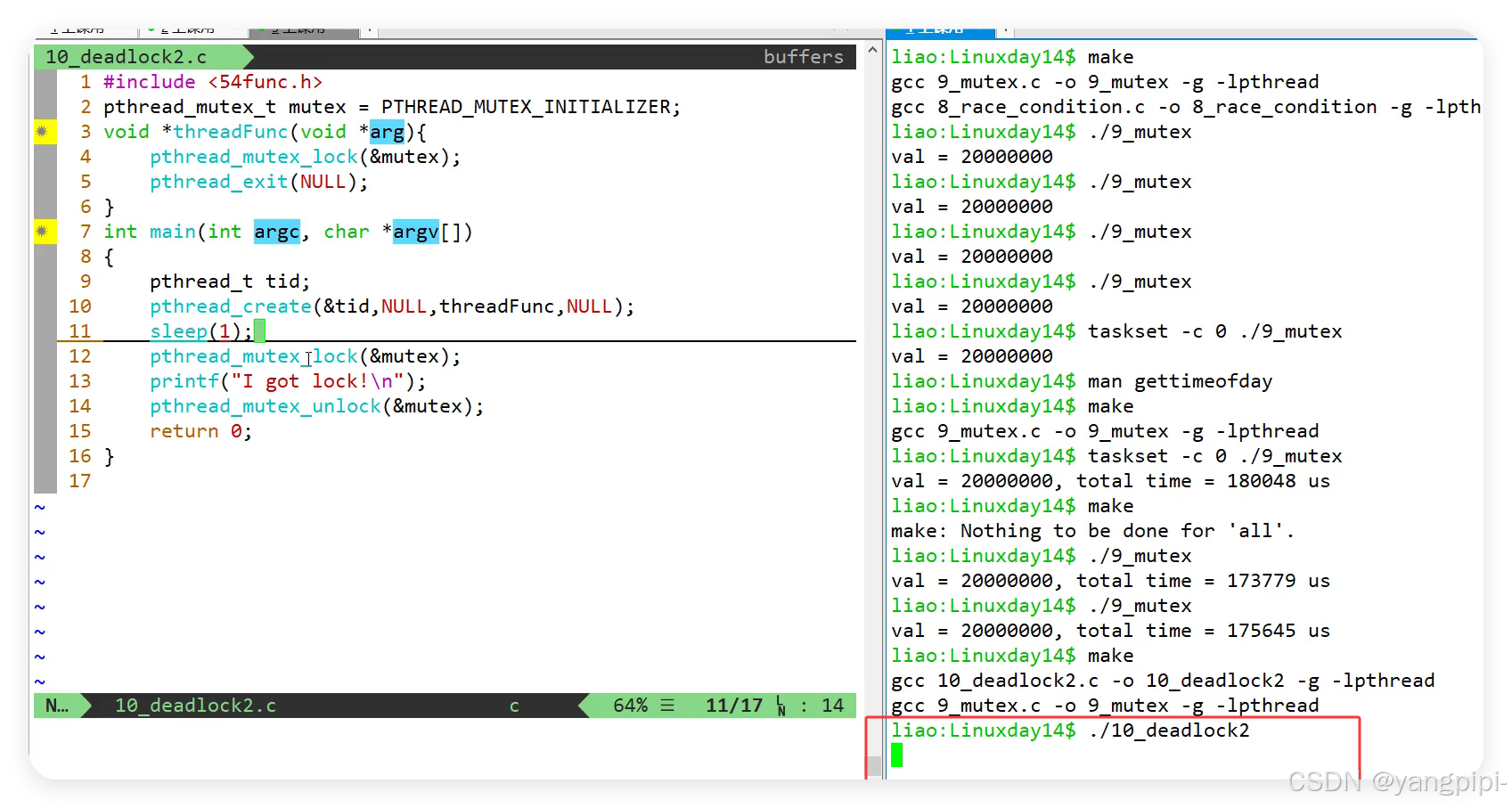
4.4 死锁
-
第一种死锁
- 因为加锁的顺序问题,两个线程想多个资源加锁,必须同时访问这两个资源
-
第二种死锁
- 一个线程在持有锁的情况下异常终止了。
-
第三种锁
- 一个线程对同一把锁,锁两次。
-
解锁
-
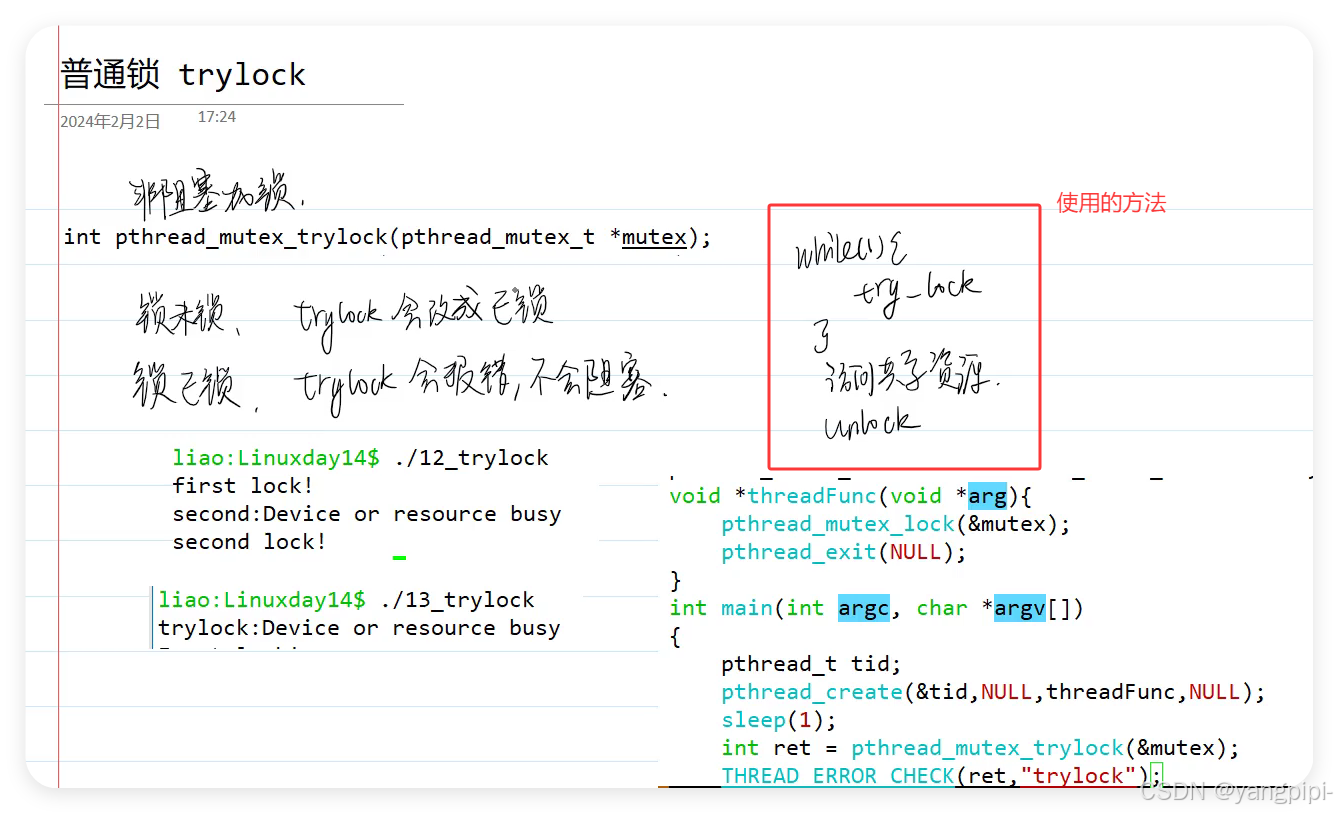
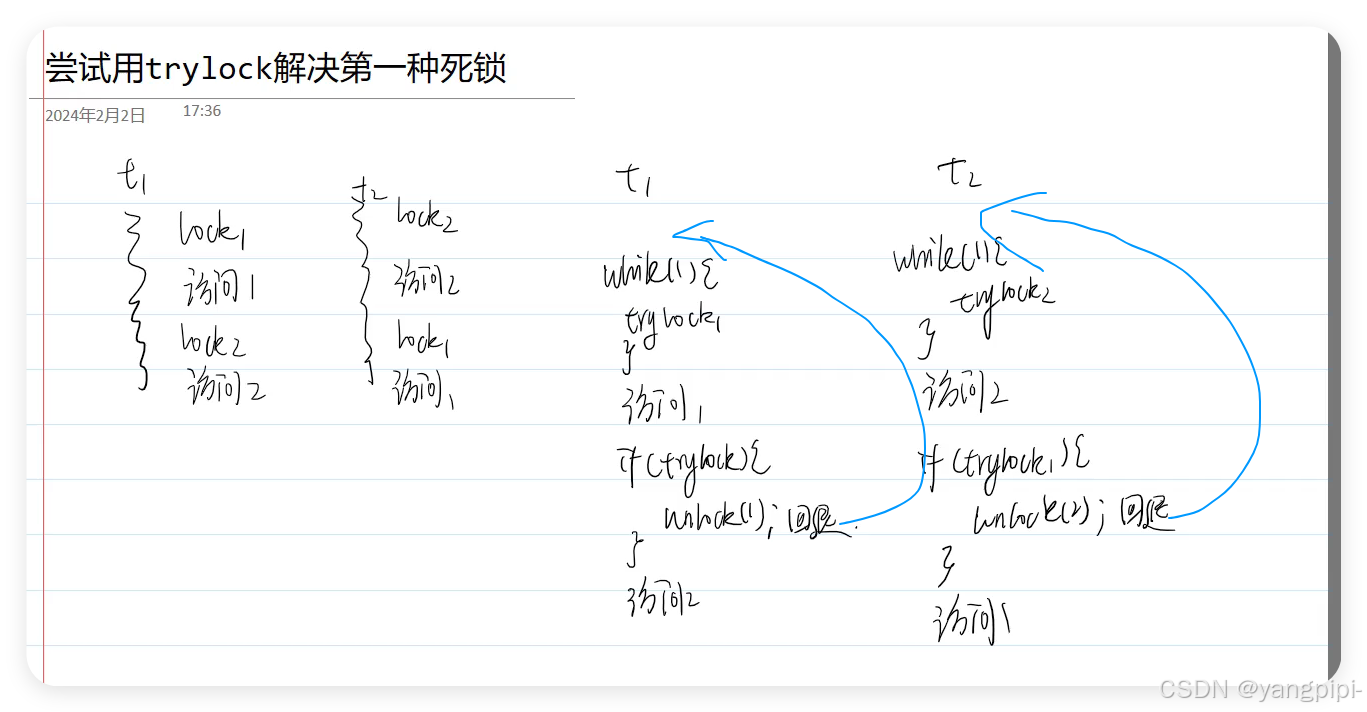
- trylock,自己线程加锁和别人加锁,又加锁,依然会报错。
-
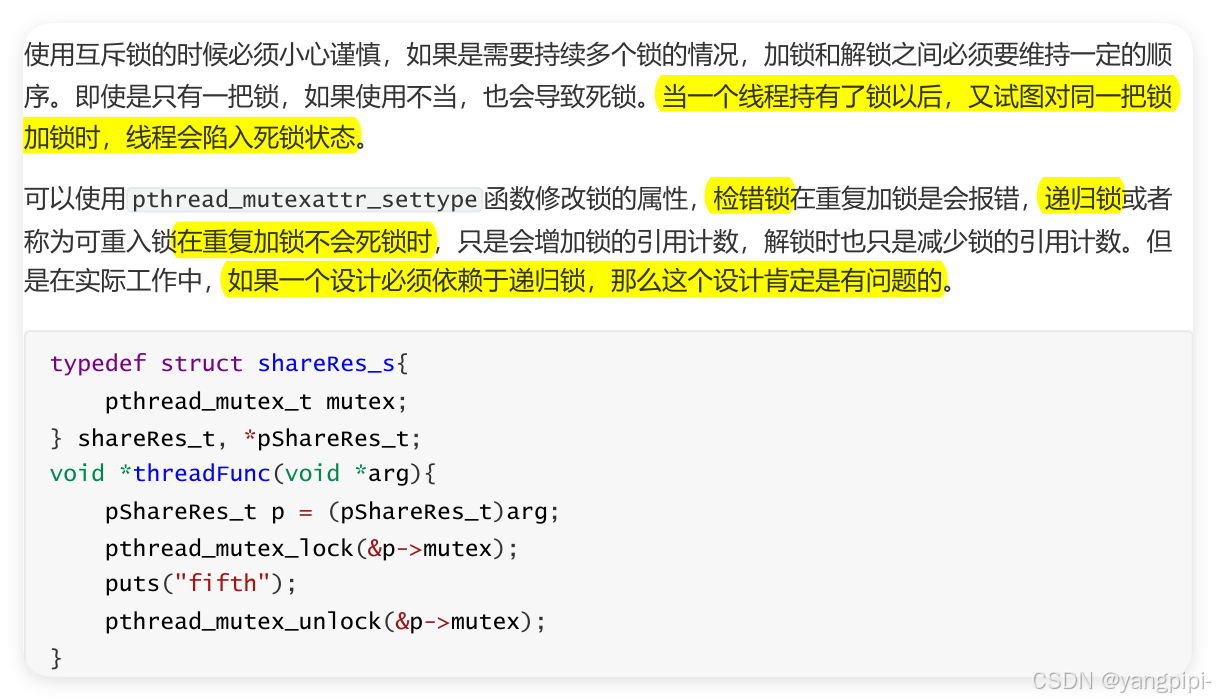
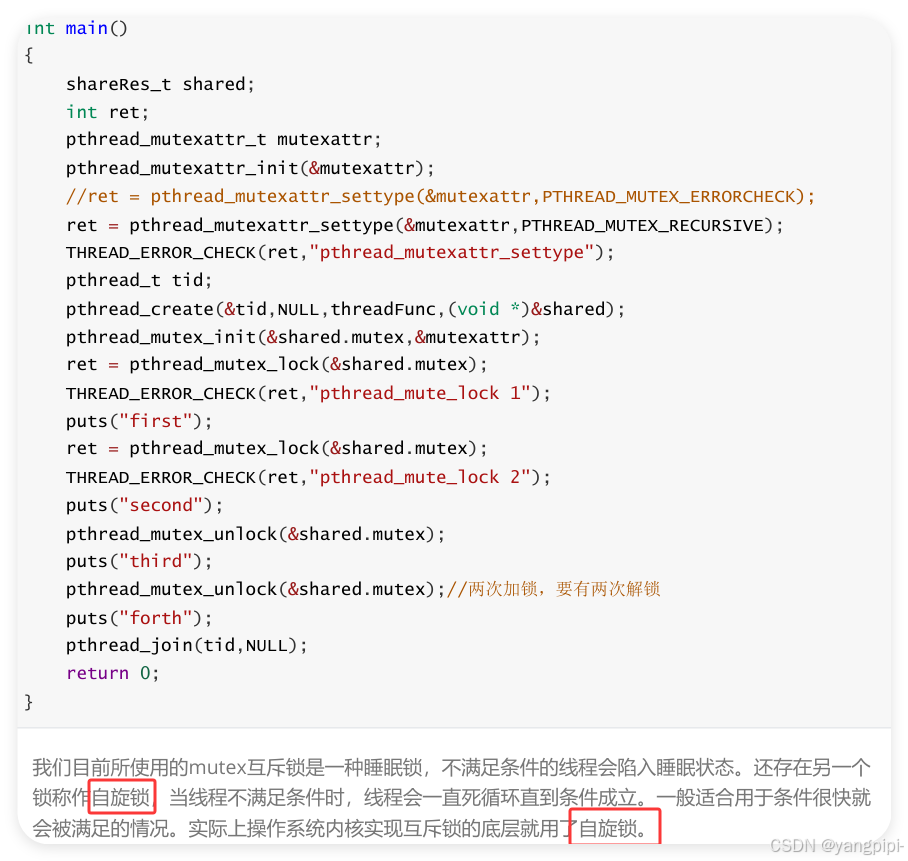
设置mutex(检错锁和递归锁)的属性来避免第三种死锁类型 。只有自己加锁,再加锁才会报错,别人加锁,我再加锁不会报错。
-
-
互斥锁的类型
- 互斥锁又称为阻塞锁,mutexlock,lock之后阻塞。
- 自旋锁,spinlock,lock之后一直占用cpu循环等待
- 读写锁

-
作业,A再B之前执行
#include<54func.h>
typedef struct shareRes_s
{
int flag;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
}shareRes_t;
void A()
{
printf("~~~A before\n");
sleep(3);
printf("~~~A After\n");
}
void B()
{
printf("~~~B before\n");
sleep(3);
printf("~~~B After\n");
}
void *thFun(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t* share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
// 注意只要访问共享资源就要加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
if(share->flag == 1)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
break;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
}
B();
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
shareRes_t share;
share.flag = 0; // 刚开始还没有准备好
pthread_mutex_init(&share.mutex,NULL);
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thFun,&share);
pthread_mutex_lock(&share.mutex);
share.flag = 1;
A();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share.mutex);
pthread_join(tid,NULL);
return 0;
}



4.5 同步和条件变量


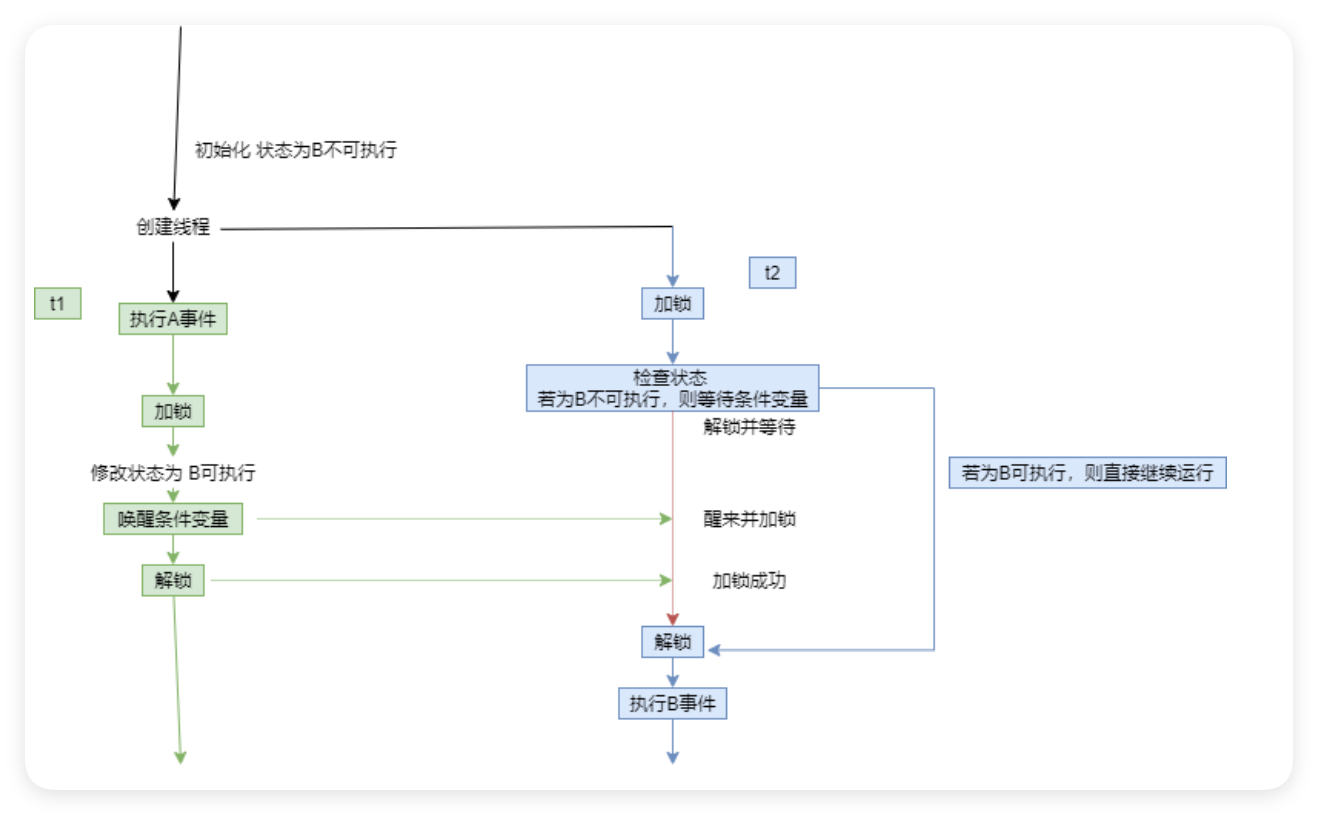

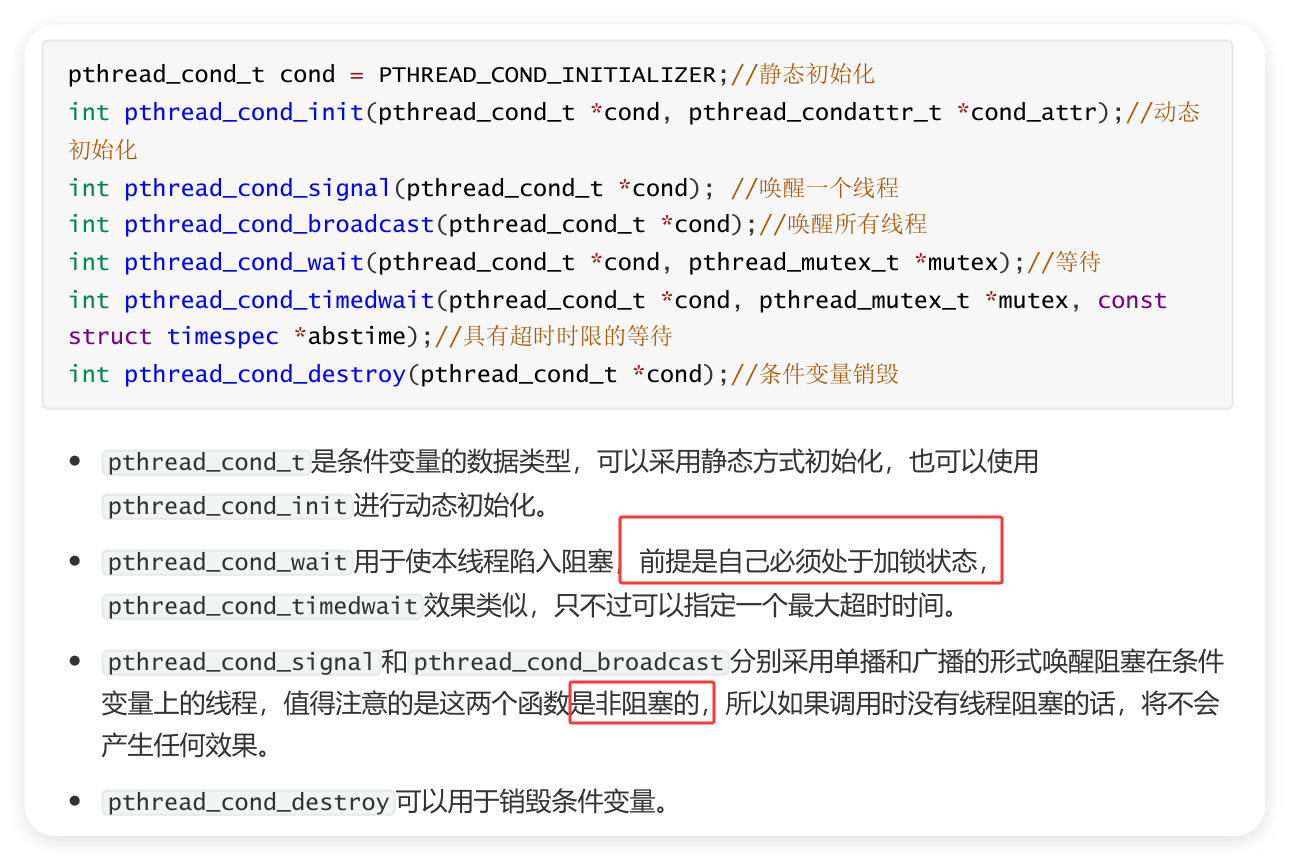

#include<54func.h>
typedef struct shareRes_s
{
int flag;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
}shareRes_t;
void A()
{
printf("~~~A before\n");
sleep(3);
printf("~~~A After\n");
}
void B()
{
printf("~~~B before\n");
sleep(3);
printf("~~~B After\n");
}
void *thFun(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t* share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
if(share->flag != 1)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&share->cond,&share->mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
B();
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
shareRes_t share;
share.flag = 0; // 刚开始还没有准备好
pthread_mutex_init(&share.mutex,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&share.cond,NULL);
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thFun,&share);
pthread_mutex_lock(&share.mutex);
share.flag = 1;
A();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share.mutex);
pthread_cond_signal(&share.cond);
pthread_join(tid,NULL);
return 0;
}
- pthread_cond_wait的实现


火车站买票

- 出现负值
#include<54func.h>
typedef struct shareRes_s
{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
int ticketsNum;
}shareRes_t;
// h 火车站买票:两个窗口卖票,当票的数量少于5张时,就开始加票
void * sellWin(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
//pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
//if(share->ticketsNum > 0 )
//{
// share->ticketsNum--;
//}
//pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
if(share->ticketsNum <= 0 )
{
pthread_cond_wait(&share->cond,&share->mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
share->ticketsNum--;
printf("sell %ld: 卖掉一张,剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),share->ticketsNum);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void * addWin(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
if(share->ticketsNum < 5 )
{
share->ticketsNum++;
printf("add %ld: 增加一张,剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),share->ticketsNum);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
pthread_cond_signal(&share->cond);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
shareRes_t share;
share.ticketsNum = 10; // 刚开始是10张票
pthread_cond_init(&share.cond,NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&share.mutex,NULL);
pthread_t sell1,sell2,addTick;
int ret = pthread_create(&sell1,NULL,sellWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sell1");
ret = pthread_create(&sell2,NULL,sellWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sell2");
ret = pthread_create(&addTick,NULL,addWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sadd");
pthread_cond_destroy(&share.cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&share.mutex);
pthread_join(sell1,NULL);
pthread_join(sell2,NULL);
pthread_join(addTick,NULL);
return 0;
}
- 现在没问题的
#include<54func.h>
typedef struct shareRes_s
{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
int ticketsNum;
}shareRes_t;
// h 火车站买票:两个窗口卖票,当票的数量少于5张时,就开始加票
void * sellWin(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
//pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
//if(share->ticketsNum > 0 )
//{
// share->ticketsNum--;
//}
//pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
if(share->ticketsNum <= 0 )
{
pthread_cond_wait(&share->cond,&share->mutex);
}
// 刚开始我没有这一个;:
if(share->ticketsNum > 0 )
{
share->ticketsNum--;
printf("sell %ld: 卖掉一张,剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),share->ticketsNum);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void * addWin(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
if(share->ticketsNum < 5 )
{
share->ticketsNum++;
printf("add %ld: 增加一张,剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),share->ticketsNum);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
pthread_cond_signal(&share->cond);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
shareRes_t share;
share.ticketsNum = 10; // 刚开始是10张票
pthread_cond_init(&share.cond,NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&share.mutex,NULL);
pthread_t sell1,sell2,addTick;
int ret = pthread_create(&sell1,NULL,sellWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sell1");
ret = pthread_create(&sell2,NULL,sellWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sell2");
ret = pthread_create(&addTick,NULL,addWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sadd");
pthread_cond_destroy(&share.cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&share.mutex);
pthread_join(sell1,NULL);
pthread_join(sell2,NULL);
pthread_join(addTick,NULL);
return 0;
}
在创建所有线程之后立即销毁了条件变量和互斥量,这是不正确的,因为这些资源在线程运行期间还需要被使用。你应该将pthread_cond_destroy(&share.cond);和pthread_mutex_destroy(&share.mutex);这两行移动到所有线程结束(即调用pthread_join之后)的位置。
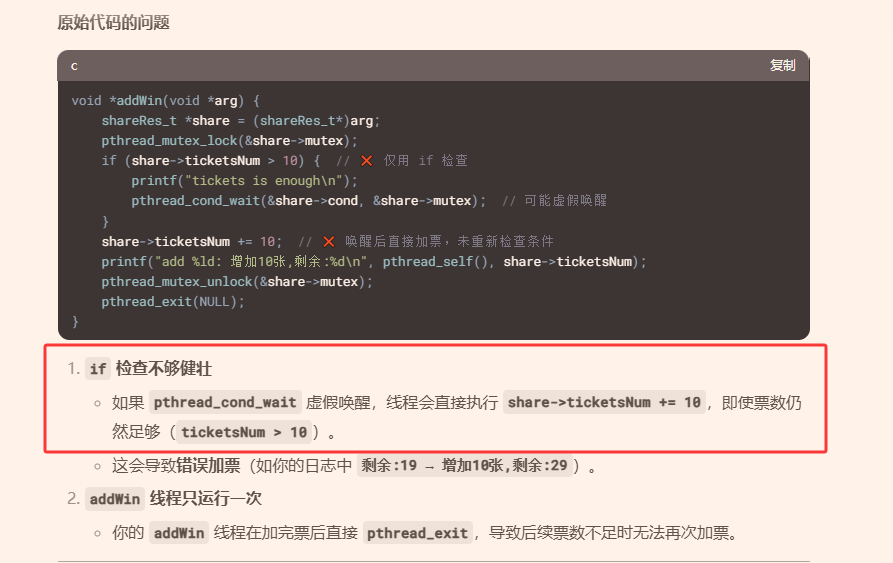
- 存在虚假唤醒
#include<54func.h>
typedef struct shareRes_s
{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
int ticketsNum;
}shareRes_t;
// h 火车站买票:两个窗口卖票,当票的数量少于5张时,就开始加票
void * sellWin(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
if(share->ticketsNum<=0)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
break;
}
printf("sell %ld: 卖掉一张,剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),share->ticketsNum);
share->ticketsNum--;
if(share->ticketsNum<=10)
{
pthread_cond_signal(&share->cond);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void * addWin(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
if(share->ticketsNum > 10)
{
printf("tickets is enough\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&share->cond,&share->mutex);
printf("______________________________\n");
printf("add %ld: 增加10张,剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),share->ticketsNum);
}
share->ticketsNum+=10;
printf("add %ld: 增加10张,剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),share->ticketsNum);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
shareRes_t share;
share.ticketsNum = 20; // 刚开始是10张票
pthread_cond_init(&share.cond,NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&share.mutex,NULL);
pthread_t sell1,sell2,addTick;
int ret = pthread_create(&sell1,NULL,sellWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sell1");
ret = pthread_create(&sell2,NULL,sellWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sell2");
ret = pthread_create(&addTick,NULL,addWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sadd");
pthread_cond_destroy(&share.cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&share.mutex);
pthread_join(sell1,NULL);
pthread_join(sell2,NULL);
pthread_join(addTick,NULL);
return 0;
}
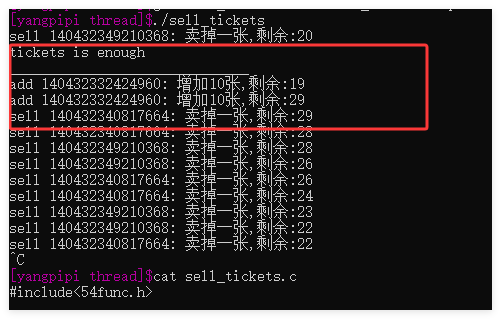
- 虚假唤醒的问题:注意pthread_cond_wait的条件判断使用while进行判断
#include<54func.h>
typedef struct shareRes_s
{
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
int ticketsNum;
}shareRes_t;
// h 火车站买票:两个窗口卖票,当票的数量少于5张时,就开始加票
void * sellWin(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
if(share->ticketsNum<=0)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
break;
}
printf("sell %ld: 卖掉一张,剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),share->ticketsNum);
share->ticketsNum--;
if(share->ticketsNum<=10 )
{
pthread_cond_signal(&share->cond);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void * addWin(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
while(share->ticketsNum > 10) // 注意需要while
{
pthread_cond_wait(&share->cond,&share->mutex);
}
share->ticketsNum+=10;
printf("add %ld: 增加10张,剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),share->ticketsNum);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
shareRes_t share;
share.ticketsNum = 20; // 刚开始是10张票
pthread_cond_init(&share.cond,NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&share.mutex,NULL);
pthread_t sell1,sell2,addTick;
int ret = pthread_create(&sell1,NULL,sellWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sell1");
ret = pthread_create(&sell2,NULL,sellWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sell2");
ret = pthread_create(&addTick,NULL,addWin,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread_create sadd");
pthread_cond_destroy(&share.cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&share.mutex);
pthread_join(sell1,NULL);
pthread_join(sell2,NULL);
pthread_join(addTick,NULL);
return 0;
}

- 根治虚假唤醒的问腿 if->while
- 生产者消费者问题
#include <54func.h>
typedef struct shareRes_S
{
int flag; // 0 没有 1 牛肉 2 酸菜
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
}shareRes_t;
// 吃牛肉
void * classmates1(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
while(share->flag!=1)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&share->cond,&share->mutex);
}
printf("同学1:我吃牛肉了\n");
share->flag = 0;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void * classmates2(void *arg)
{
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
while(share->flag!=2)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&share->cond,&share->mutex);
}
printf("同学2:我吃酸菜了\n");
share->flag = 0;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int min = 0;
int max = 10;
// 生成 [min, max] 范围内的随机数
void * product(void *arg)
{
int range = max - min + 1;
shareRes_t *share = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
int random_num = rand() % range + min;
pthread_mutex_lock(&share->mutex);
if(share->flag == 0 && random_num>5)
{
share->flag = 1;
printf("生产者:生产牛肉\n");
pthread_cond_broadcast(&share->cond);
}
if(share->flag == 0 && random_num<5)
{
share->flag =2;
printf("生产者:生成酸菜\n");
pthread_cond_broadcast(&share->cond);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&share->mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t stu1,stu2;
pthread_t pro;
shareRes_t share;
share.flag = 0;
pthread_mutex_init(&share.mutex,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&share.cond,NULL);
int ret = pthread_create(&stu1,NULL,classmates1,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread create stu1");
ret = pthread_create(&stu2,NULL,classmates2,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread create stu2");
ret = pthread_create(&pro,NULL,product,&share);
THREAD_ERROR_CHECK(ret,"pthread create pro");
pthread_join(stu1,NULL);
pthread_join(stu2,NULL);
pthread_join(pro,NULL);
pthread_cond_destroy(&share.cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&share.mutex);
return 0;
}

- 自己实现的逻辑
#include <54func.h>
// 链表的结构
typedef struct node_s{
int data;
struct node_s *pNest;
}node_t;
//队列的结构:链式队列
typedef struct queue_s{
node_t * pFront;
node_t * pRear;
int queueSize;
}queue_t;
typedef struct shareRes_s{
queue_t queue;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
}shareRes_t;
// d入队
int enQueue(queue_t *pqueue,int data)
{
node_t * node = (node_t*)malloc(sizeof(node_t));
node->data = data;
node->pNest = NULL;
if(pqueue->queueSize == 0)
{
pqueue->pFront = pqueue->pRear = node;
}
else
{
pqueue->pRear->pNest = node;
pqueue->pRear = node;
}
pqueue->queueSize++;
}
int deQueue(queue_t *pQueue)
{
if(pQueue->queueSize == 0)
return 0;
int tmp = pQueue->pFront->data;
node_t* node = pQueue->pFront;
if(pQueue->queueSize == 1)
{
pQueue->pFront = pQueue->pRear = NULL;
}
else
{
pQueue->pFront = pQueue->pFront->pNest;
}
pQueue->queueSize--;
free(node);
node->pNest = NULL;
return tmp;
}
int visitQueue(queue_t *pQueue)
{
node_t * pCur = pQueue->pFront;
while(pCur)
{
printf("%d ",pCur->data);
pCur = pCur->pNest;
}
printf("\n");
}
// 初始商品为8个,最大商品数量为10个
// 生产者 3个 每3秒产生一个商品
// x消费者 2个 先睡眠 5秒 每个线程再每1秒消耗一个
void * pro_thread(void *arg)
{
shareRes_t * shareRes = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&shareRes->mutex);
while(shareRes->queue.queueSize>=10)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&shareRes->cond,&shareRes->mutex);
}
int data = rand()%1000;
enQueue(&shareRes->queue,data);
printf("%ld 生产 %d 剩余:%d \n",pthread_self(),data,shareRes->queue.queueSize);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&shareRes->cond); // 生产完一个商品就广播
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shareRes->mutex);
sleep(3);
}
}
void * cons_thread(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t * shareRes = (shareRes_t*)arg;
sleep(5);
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&shareRes->mutex);
while(shareRes->queue.queueSize<=0)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&shareRes->cond,&shareRes->mutex);
}
int data = deQueue(&shareRes->queue);
printf("%ld 消费 %d 剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),data,shareRes->queue.queueSize);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&shareRes->cond); // 消费完一个商品就广播
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shareRes->mutex);
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
shareRes_t shareRes;
memset(&shareRes.queue,0,sizeof(shareRes.queue));
pthread_cond_init(&shareRes.cond,NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&shareRes.mutex,NULL);
// 初始商品 8个
for(int i = 0;i<8;i++)
{
int data = rand()%1000;
enQueue(&shareRes.queue,data);
}
visitQueue(&shareRes.queue);
printf("____________________________________________________________\n");
pthread_t pro1,pro2,pro3;
pthread_t cons1,cons2;
pthread_create(&pro1,NULL,pro_thread,&shareRes);
pthread_create(&pro2,NULL,pro_thread,&shareRes);
pthread_create(&pro3,NULL,pro_thread,&shareRes);
pthread_create(&cons1,NULL,cons_thread,&shareRes);
pthread_create(&cons2,NULL,cons_thread,&shareRes);
pthread_join(pro1,NULL);
pthread_join(pro2,NULL);
pthread_join(pro3,NULL);
pthread_join(cons1,NULL);
pthread_join(cons2,NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&shareRes.mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&shareRes.cond);
return 0;
}
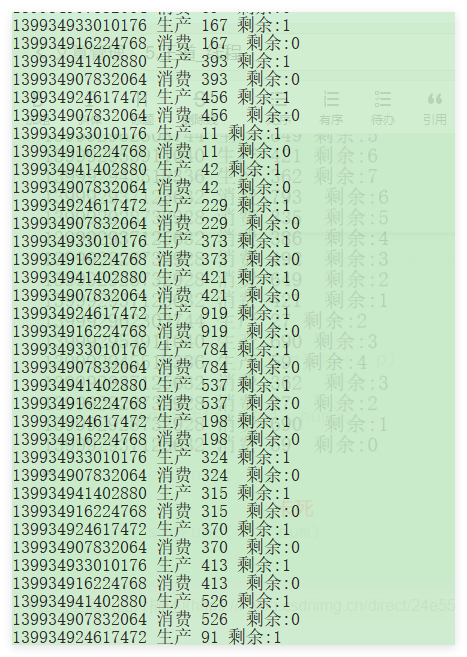
- 修改之后
#include <54func.h>
// 链表的结构
typedef struct node_s{
int data;
struct node_s *pNest;
}node_t;
//队列的结构:链式队列
typedef struct queue_s{
node_t * pFront;
node_t * pRear;
int queueSize;
}queue_t;
typedef struct shareRes_s{
queue_t queue;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
}shareRes_t;
// d入队
int enQueue(queue_t *pqueue,int data)
{
node_t * node = (node_t*)malloc(sizeof(node_t));
node->data = data;
node->pNest = NULL;
if(pqueue->queueSize == 0)
{
pqueue->pFront = pqueue->pRear = node;
}
else
{
pqueue->pRear->pNest = node;
pqueue->pRear = node;
}
pqueue->queueSize++;
}
int deQueue(queue_t *pQueue)
{
if(pQueue->queueSize == 0)
return 0;
int tmp = pQueue->pFront->data;
node_t* node = pQueue->pFront;
if(pQueue->queueSize == 1)
{
pQueue->pFront = pQueue->pRear = NULL;
}
else
{
pQueue->pFront = pQueue->pFront->pNest;
}
pQueue->queueSize--;
free(node);
node->pNest = NULL;
return tmp;
}
int visitQueue(queue_t *pQueue)
{
node_t * pCur = pQueue->pFront;
while(pCur)
{
printf("%d ",pCur->data);
pCur = pCur->pNest;
}
printf("\n");
}
// 初始商品为8个,最大商品数量为10个
// 生产者 3个 每3秒产生一个商品
// x消费者 2个 先睡眠 5秒 每个线程再每1秒消耗一个
void * pro_thread(void *arg)
{
shareRes_t * shareRes = (shareRes_t*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&shareRes->mutex);
while(shareRes->queue.queueSize>=10)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&shareRes->cond,&shareRes->mutex);
}
int data = rand()%1000;
enQueue(&shareRes->queue,data);
printf("%ld 生产 %d 剩余:%d \n",pthread_self(),data,shareRes->queue.queueSize);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&shareRes->cond); // 生产完一个商品就广播
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shareRes->mutex);
sleep(3);
}
}
void * cons_thread(void * arg)
{
shareRes_t * shareRes = (shareRes_t*)arg;
sleep(5);
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&shareRes->mutex);
while(shareRes->queue.queueSize<=0)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&shareRes->cond,&shareRes->mutex);
}
int data = deQueue(&shareRes->queue);
printf("%ld 消费 %d 剩余:%d\n",pthread_self(),data,shareRes->queue.queueSize);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&shareRes->cond); // 消费完一个商品就广播
pthread_mutex_unlock(&shareRes->mutex);
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
shareRes_t shareRes;
memset(&shareRes.queue,0,sizeof(shareRes.queue));
pthread_cond_init(&shareRes.cond,NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&shareRes.mutex,NULL);
// 初始商品 8个
for(int i = 0;i<8;i++)
{
int data = rand()%1000;
enQueue(&shareRes.queue,data);
}
visitQueue(&shareRes.queue);
printf("____________________________________________________________\n");
pthread_t pro1,pro2,pro3;
pthread_t cons1,cons2;
pthread_create(&pro1,NULL,pro_thread,&shareRes);
pthread_create(&pro2,NULL,pro_thread,&shareRes);
pthread_create(&pro3,NULL,pro_thread,&shareRes);
pthread_create(&cons1,NULL,cons_thread,&shareRes);
pthread_create(&cons2,NULL,cons_thread,&shareRes);
pthread_join(pro1,NULL);
pthread_join(pro2,NULL);
pthread_join(pro3,NULL);
pthread_join(cons1,NULL);
pthread_join(cons2,NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&shareRes.mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&shareRes.cond);
return 0;
}
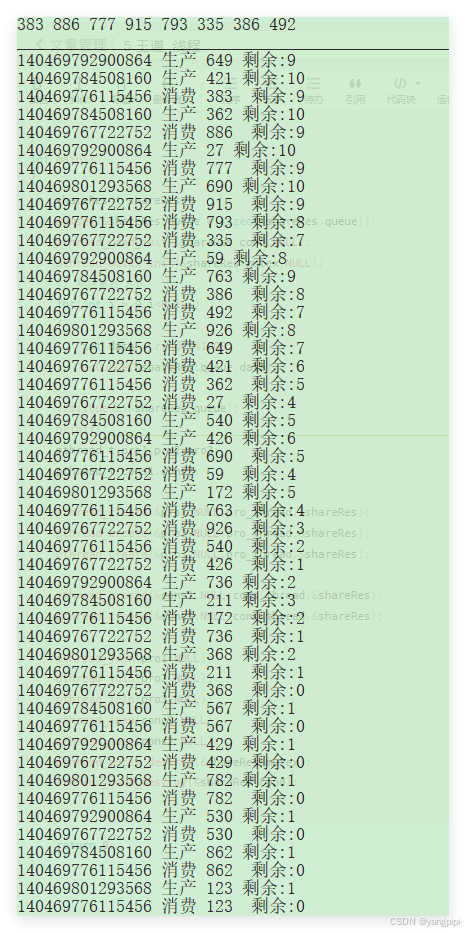
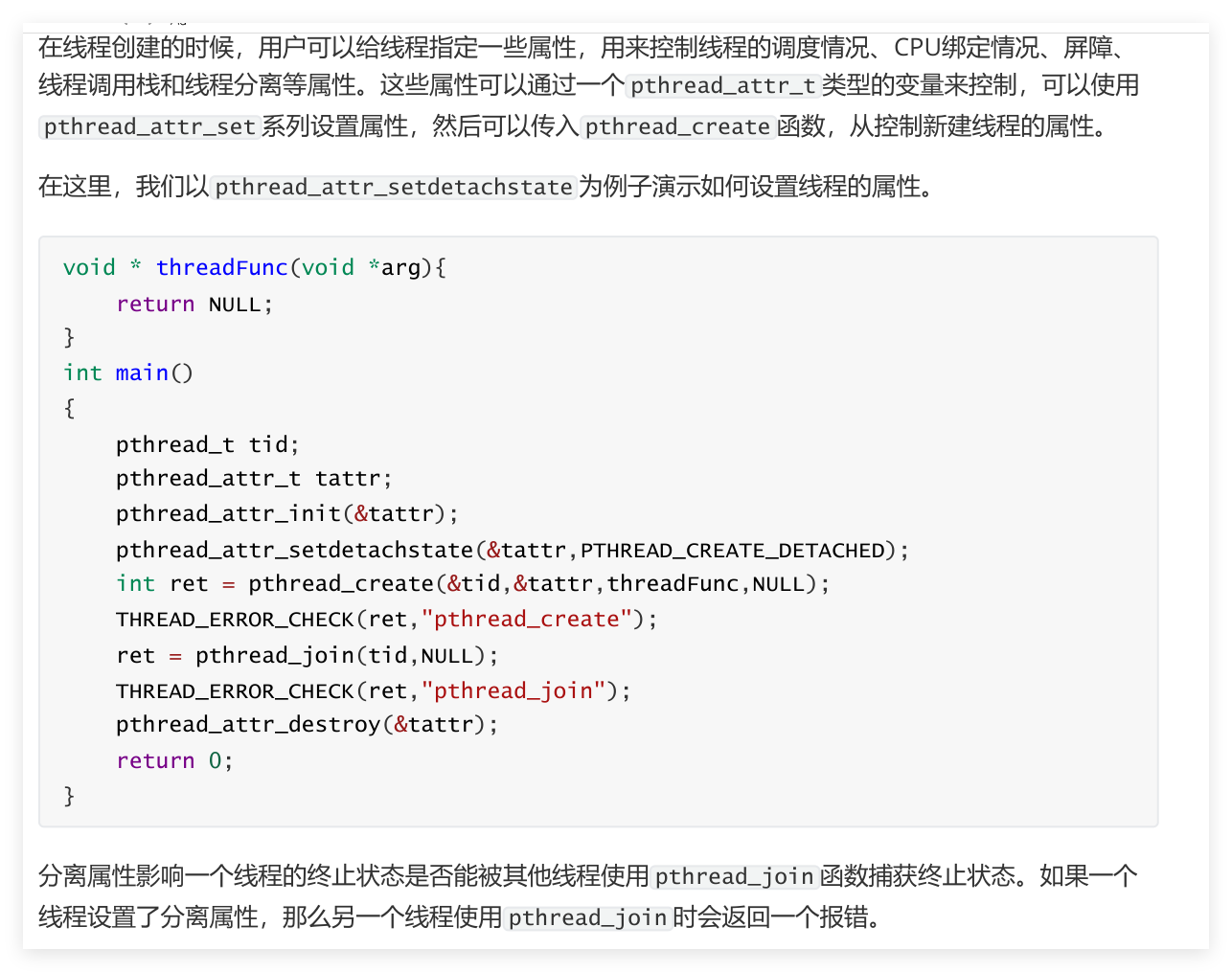
5. 线程的属性
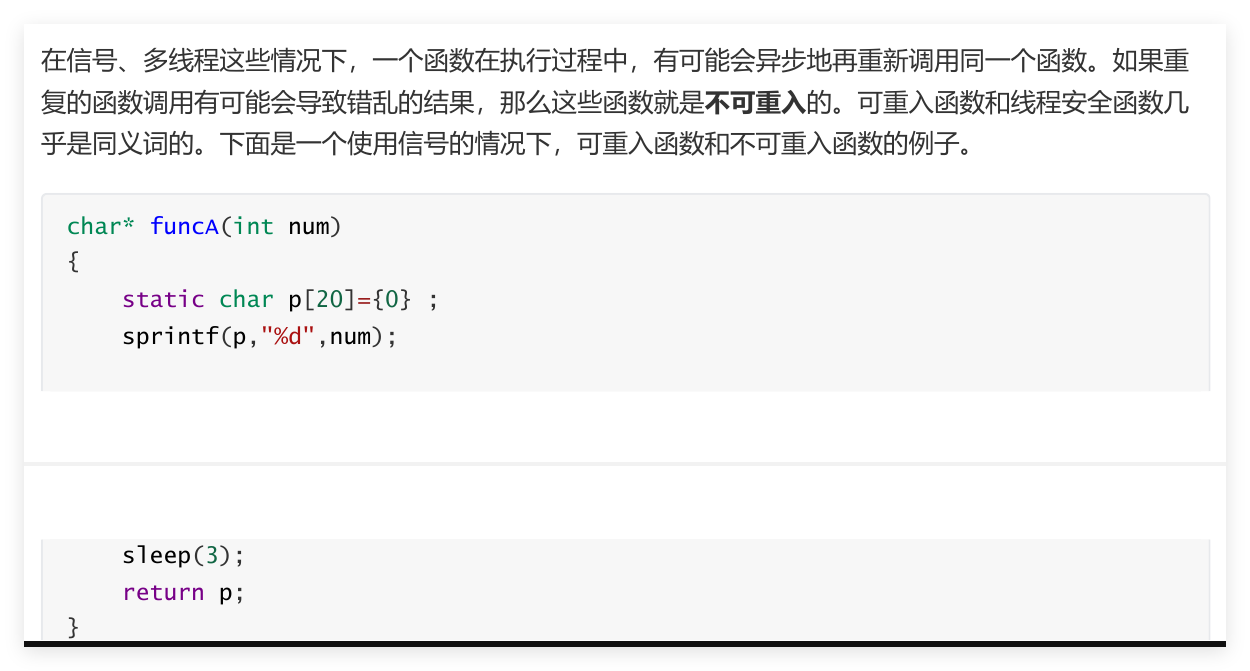
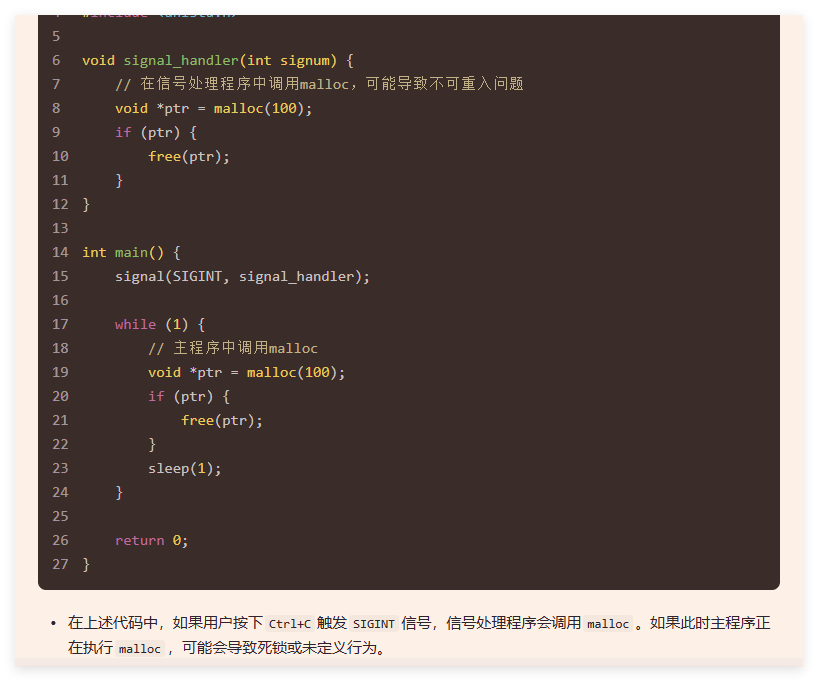
6. 线程安全与可重入性
6.1 线程安全



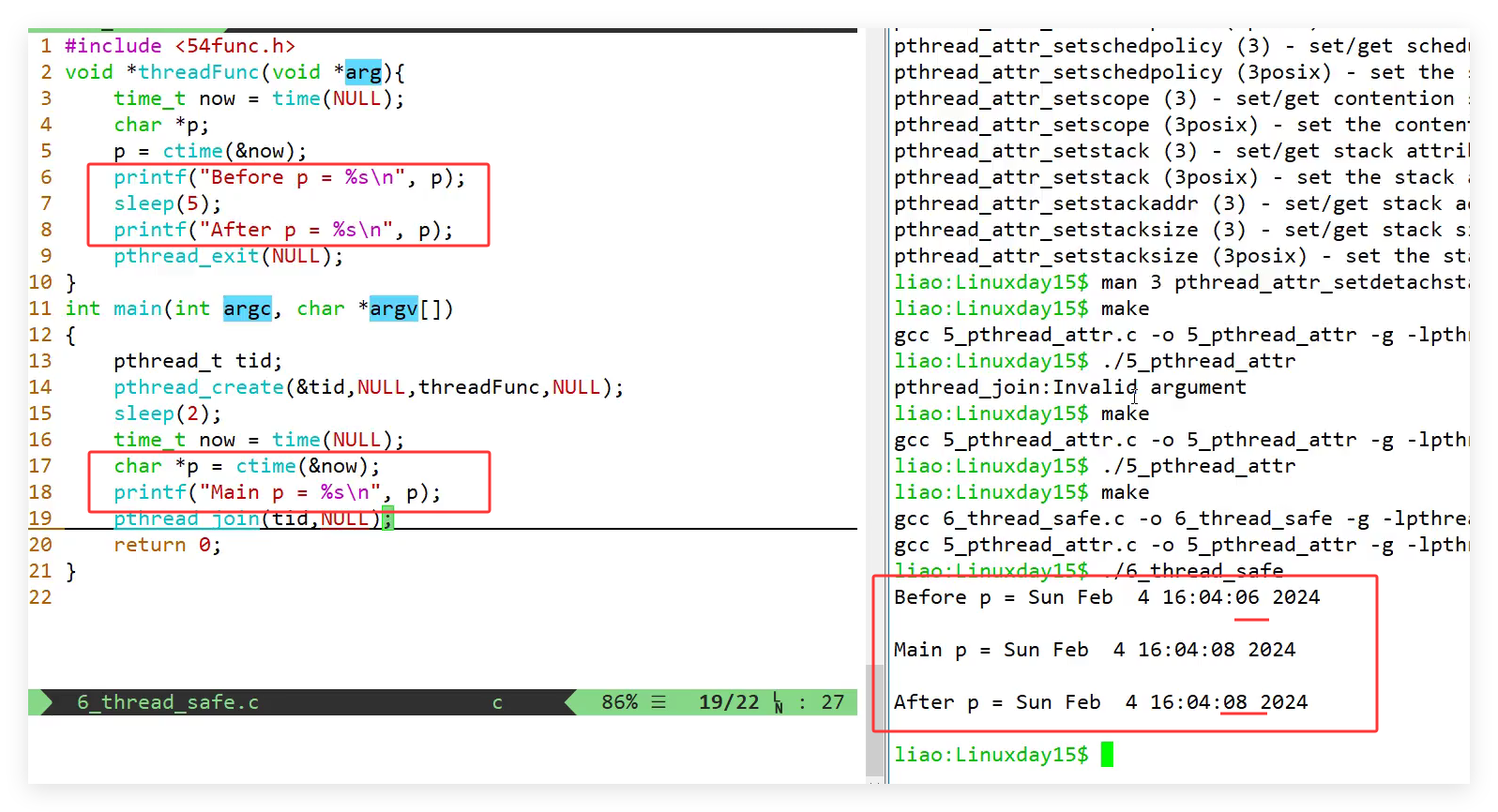
- 静态局部变量,分配在数据段
- 一般返回值为指针类型的是线程不安全的。

- 先事件就调用signal,后事件:加锁,判断,wait
6.2 可重入性




C++封装线程
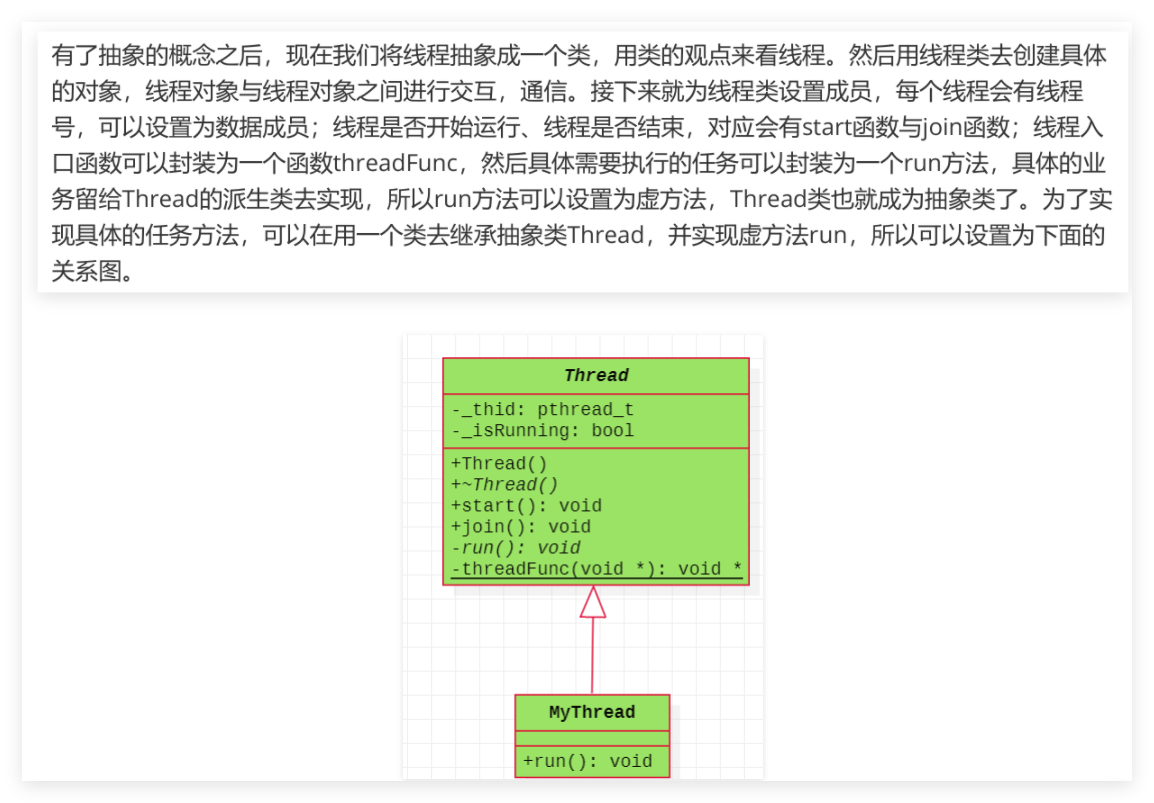
面向对象的线程的封装
-
Thread.h
-
#ifndef __THREAD_H__ #define __THREAD_H__ #include<pthread.h> class Thread { public: Thread(); virtual ~Thread(); void start(); void join(); private: // 线程入口函数 static void *threadFunc(void *arg); // 要求实现的任务 virtual void run() = 0; /// 子类实现这个函数即可 private: pthread_t _thid; bool _isRuning; }; #endif
-
-
Thread.cc
-
#include<iostream> #include<pthread.h> #include "Thread.h" Thread::Thread() :_thid(0), _isRuning(false){} Thread::~Thread() { if(_isRuning) { pthread_detach(_thid); } } void Thread::start() { // threadFunc应设置为静态成员函数,因为成员函数的第一个参数为this,第三个参数需要传入一个函数 // 由于threadFunc设置为静态成员函数导致在其内部没有this,不能调用run函数 int ret = pthread_create(&_thid,nullptr,threadFunc,this); if(ret) { perror("pthread_create"); return; } _isRuning = true; } void Thread::join() { if(_isRuning) { pthread_join(_thid,nullptr); _isRuning = false; } } void * Thread::threadFunc(void *arg) { // 得到this指针 Thread *pthread_this = static_cast<Thread*>(arg); if(pthread_this) { pthread_this->run(); //实现任务 } pthread_exit(nullptr); //return nullptr; }
-
#include <iostream>
#include<unistd.h> // sleep.h
#include<memory>
#include"Thread.h"
using namespace std;
class MyThread:public Thread
{
public:
void run()override
{
while(1)
{
cout<<"The thread id is running"<<endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
};
// main就是主线程
int main()
{
//Thread *pthread(new MyThread());
unique_ptr<Thread> pthread(new MyThread());
pthread->start();
pthread->join(); // 让主线程等待子线程的执行
std::cout << "Hello world" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
子类只需继承Thread类,并且自己覆盖run方法即可。
设计的逻辑:子线程的业务代码写在run方法中,在pthread_create注册线程的入口函数为thfun,然后在thfun中运行子线程的业务代码fun方法。
难点:1, 注册的thfun也要写在类中,但是其第一个参数默认为this,所以设计成static。2. 由于static中不能调用成员函数,所以需要传递在pthread_create通过子线程的入口函数参数传递this。
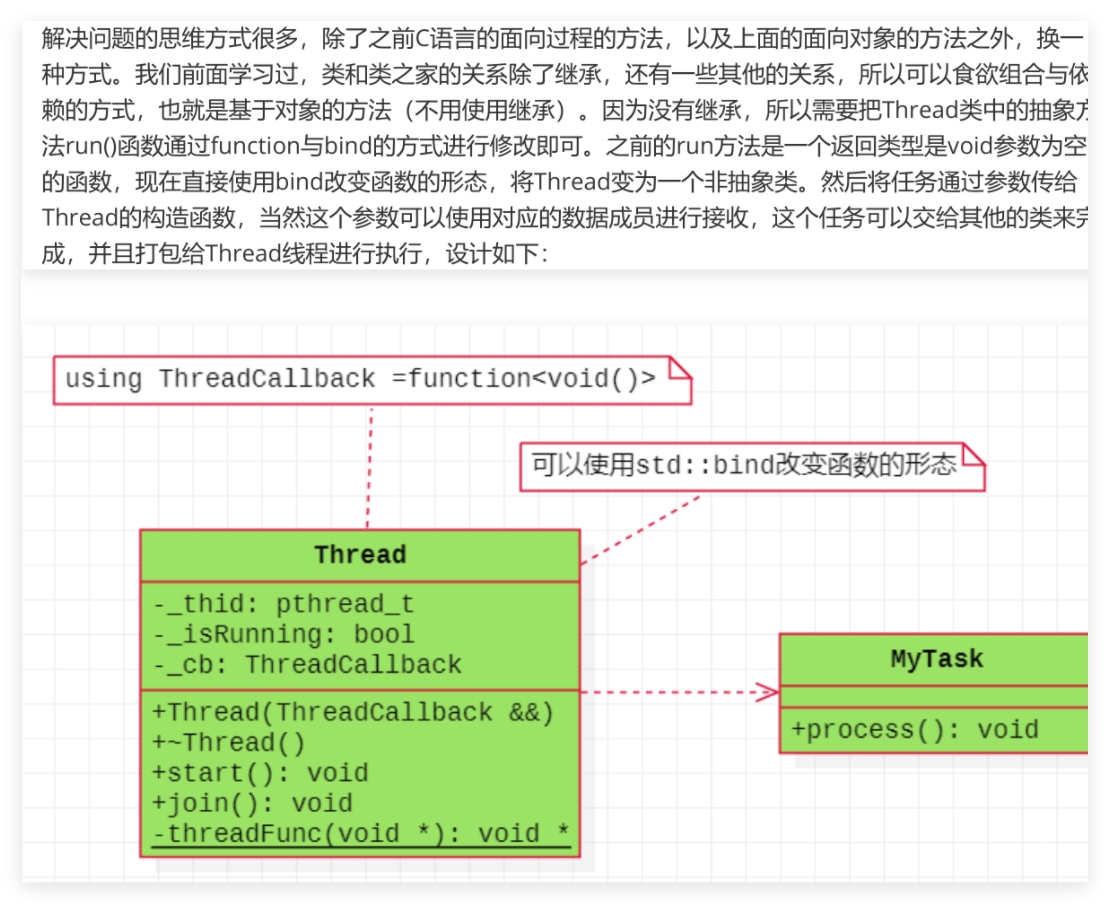
基于对象的线程封装
-
Thread.h
-
#ifndef __THREAD_H__ #define __THREAD_H__ #include<pthread.h> #include<functional> using ThreadCallback = function<void()>; class Thread { public: Thread(ThreadCallback &&cb); ~Thread(); void start(); void join(); private: // 线程入口函数 static void *threadFunc(void *arg); // 要求实现的任务 virtual void run() = 0; private: pthread_t _thid; bool _isRuning; // 要去实现的任务 ThreadCallback _cb; }; #endif
-
-
Thread.cc
-
#include<iostream> #include<pthread.h> #include "Thread.h" Thread::Thread(ThreadCallback &&cb) :_thid(0), _isRuning(false), _cb(std::move(cb)) {} Thread::~Thread() { if(_isRuning) { pthread_detach(_thid); } } void Thread::start() { // threadFunc应设置为静态成员函数,因为成员函数的第一个参数为this,第三个参数需要传入一个函数 // 由于threadFunc设置为静态成员函数导致在其内部没有this,不能调用run函数 int ret = pthread_create(&_thid,nullptr,threadFunc,this); if(ret) { perror("pthread_create"); return; } _isRuning = true; } void Thread::join() { if(_isRuning) { pthread_join(_thid,nullptr); _isRuning = false; } } void * Thread::threadFunc(void *arg) { Thread *pth = static_cast<Thread*>(arg); if(pth) { pth->cb();// 回调函数的形式 } pthread_exit(nullptr); //return nullptr; }
-
-
main.cc
#include <iostream>
#include<unistd.h> // sleep.h
#include<memory>
#include"Thread.h"
using namespace std;
class MyThread:
{
public:
void process()
{
while(1)
{
cout<<"The thread id is running"<<endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
};
// main就是主线程
int main()
{
MyThread myThread;
Thread th(bind(&MyThread::process,&myThread));
th.start();
th.join();
std::cout << "Hello world" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
生产者消费者问题
面向对象的封装
-
utexLock.h
-
#ifndef __MUTEXLOCK_H #define __MUTEXLOCK_H #include<pthread.h> class MutexLock { public: MutexLock() ; ~MutexLock() ; void lock(); void unlock(); pthread_mutex_t *getMutexLockPtr() { return &_mutex; } private: pthread_mutex_t _mutex; }; #endif
-
-
MutexLock.cc
-
#include <iostream> #include"MutexLock.h" MutexLock::MutexLock() { int ret = pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex,nullptr); if(ret) { perror("pthread_mutex_init"); } } MutexLock::~MutexLock() { int ret = pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex); if(ret) { perror("pthread_mutex_destory"); } } void MutexLock::lock() { int ret = pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex); if(ret) { perror("pthread_mutex_lock"); } } void MutexLock::unlock() { int ret = pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex); if(ret) { perror("pthread_mutex_unlock"); } }
-
-
Condition.h
-
#ifndef __CONDITION_H__ #define __CONDITION_H__ #include<pthread.h> class MutexLock; // 前向声明,直接使用头文件包含可能会出错 class Condition { public: Condition(MutexLock &mutex) ; ~Condition() ; void wait(); void notify(); void notifyAll(); private: pthread_cond_t _cond; MutexLock &_mutex; }; #endif
-
-
Condition.cc
-
#include"Condition.h" #include"MutexLock.h" // 这里就需要包含头文件了,而不能只是前向声明,因为后面需要访问其成员 Condition::Condition(MutexLock &mutex) :_mutex(mutex) { pthread_cond_init(&_cond,nullptr); } Condition::~Condition() { pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond); } void Condition::wait() { pthread_cond_wait(&_cond,_mutex.getMutexLockPtr()); } void Condition:: notify() { pthread_cond_signal(&_cond); } void Condition::notifyAll() { pthread_cond_broadcast(&_cond); }
-
-
TaskQueue.h
-
#ifndef __TASKQUEUE_H__ #define __TASKQUEUE_H__ #include<queue> #include"MutexLock.h" #include"Condition.h" using std::queue; class TaskQueue { public: TaskQueue(size_t queSize); ~TaskQueue(); bool empty()const; bool full()const; void push(const int &value); int pop(); private: size_t _queSize; queue<int> _que; MutexLock _mutex; Condition _notEmpty; Condition _notFull; }; #endif
-
-
TaskQueue.cc
-
#include"TaskQueue.h" TaskQueue::TaskQueue(size_t queSize) :_queSize(queSize), _que(), _mutex(), _notFull(_mutex), _notEmpty(_mutex) { } TaskQueue::~TaskQueue() {} bool TaskQueue::empty()const { return _que.size() == 0; } bool TaskQueue::full()const { return _que.size() == _queSize; } void TaskQueue::push(const int &value) { _mutex.lock(); if(full()) { _notFull.wait(); } _que.push(value); _notEmpty.notify(); _mutex.unlock(); } int TaskQueue::pop() { _mutex.lock(); if(empty()) { _notEmpty.wait(); } int tmp = _que.front(); _que.pop(); _notFull.notify(); _mutex.unlock(); return tmp; }
-
-
Produces.h
-
#ifndef __PRODUCER_H__ #define __PRODUCER_H__ #include<stdlib.h> // 使用随机数i #include <unistd.h> //sleer #include<iostream> #include"Thread.h" #include"TaskQueue.h" class Producer : public Thread { public: Producer(TaskQueue &taskQue) :_taskQue(taskQue) {} ~Producer() {} void run() override { int cnt = 20; ::srand(clock()); while(cnt-->0) { // 一般为了表明此函数是c中的函数,使用::,你们空间 int num = ::rand()%100; _taskQue.push(num); std::cout<<">> produce number = "<<num<<std::endl; sleep(1); } } private: TaskQueue & _taskQue; }; #endif
-
-
Consumers.h
-
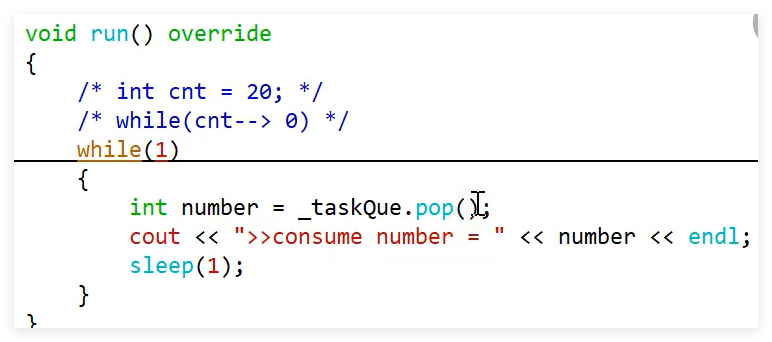
#ifndef __CONSUMER_H__ #define __CONSUMER_H__ #include<stdlib.h> // 使用随机数i #include <unistd.h> //sleer #include<iostream> #include"Thread.h" #include"TaskQueue.h" class Consumer : public Thread { public: Consumer(TaskQueue &taskQue) :_taskQue(taskQue) {} ~Consumer() {} void run() override { int cnt = 20; while(cnt-->0) { // 一般为了表明此函数是c中的函数,使用::,你们空间 int num = _taskQue.pop(); std::cout<<">> consume number = "<<num<<std::endl; sleep(1); } } private: TaskQueue & _taskQue; }; #endif
-
-
Thread.h
-
#ifndef __THREAD_H__ #define __THREAD_H__ #include<pthread.h> class Thread { public: Thread(); virtual ~Thread(); void start(); void join(); private: // 线程入口函数 static void *threadFunc(void *arg); // 要求实现的任务 virtual void run() = 0; private: pthread_t _thid; bool _isRuning; }; #endif
-
-
Thread.cc
-
#include<iostream> #include<pthread.h> #include "Thread.h" Thread::Thread() :_thid(0), _isRuning(false){} Thread::~Thread() { if(_isRuning) { pthread_detach(_thid); } } void Thread::start() { // threadFunc应设置为静态成员函数,因为成员函数的第一个参数为this,第三个参数需要传入一个函数 // 由于threadFunc设置为静态成员函数导致在其内部没有this,不能调用run函数 int ret = pthread_create(&_thid,nullptr,threadFunc,this); if(ret) { perror("pthread_create"); return; } _isRuning = true; } void Thread::join() { if(_isRuning) { pthread_join(_thid,nullptr); _isRuning = false; } } void * Thread::threadFunc(void *arg) { // 得到this指针 Thread *pthread_this = static_cast<Thread*>(arg); if(pthread_this) { pthread_this->run(); //实现任务 } pthread_exit(nullptr); //return nullptr; }
-
-
Test.cc
-
#include <iostream> #include<memory> #include"Producer.h" #include"Consumer.h" using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::unique_ptr; void test() { TaskQueue taskQue(10); unique_ptr<Thread> produce(new Producer(taskQue)); unique_ptr<Thread> consume(new Consumer(taskQue)); produce->start(); consume->start(); produce->join(); produce->join(); } int main() { test(); std::cout << "Hello world" << std::endl; return 0; }
-
-
问题1
当消费者改为while(1)最后会卡在消费者的pop处
由于生产者已经生产完毕,没有会唤醒消费者
-
使用RAII技术管理互斥锁的解锁和释放
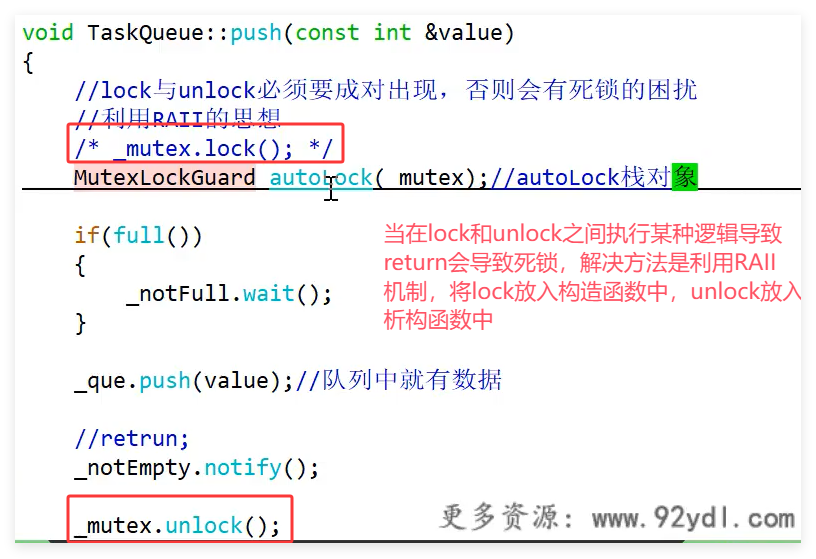
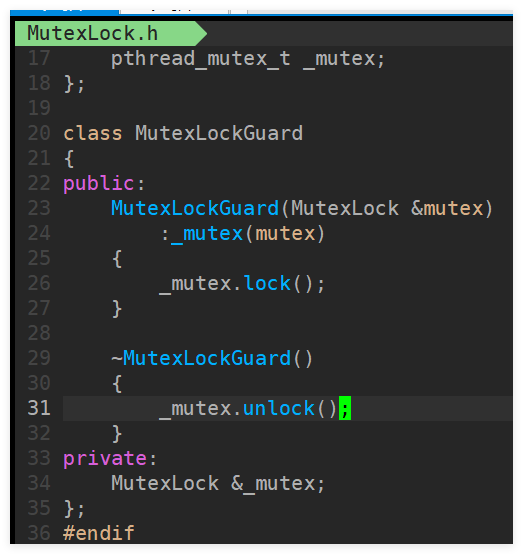
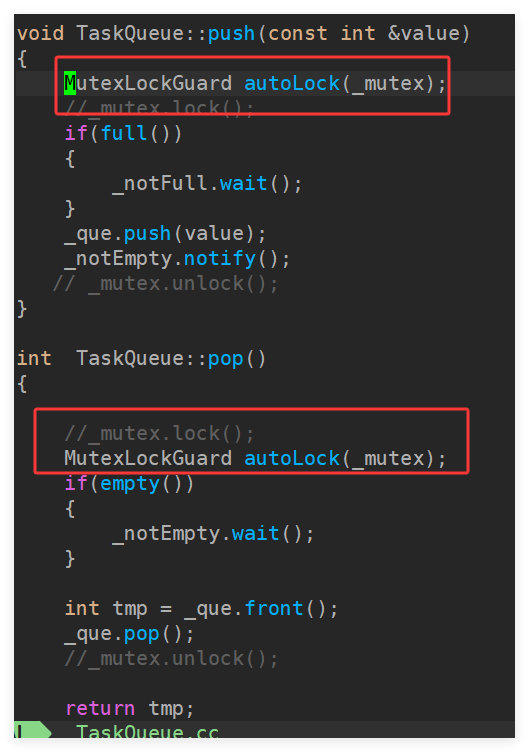
-
虚假唤醒
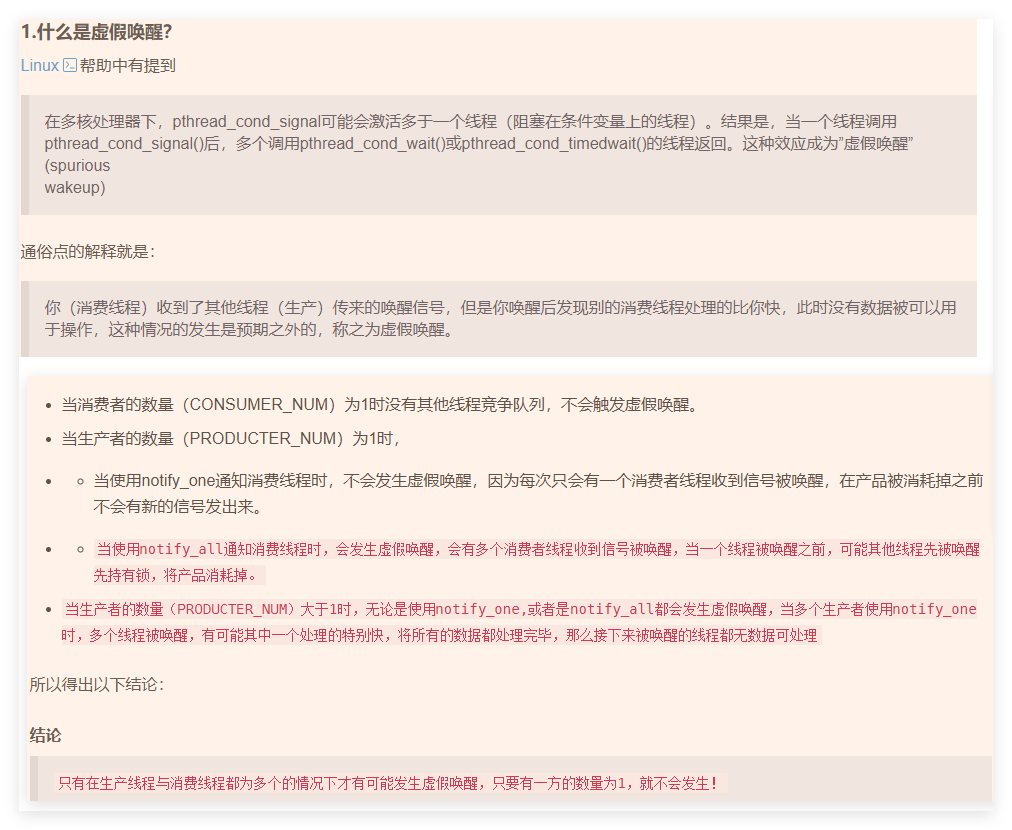
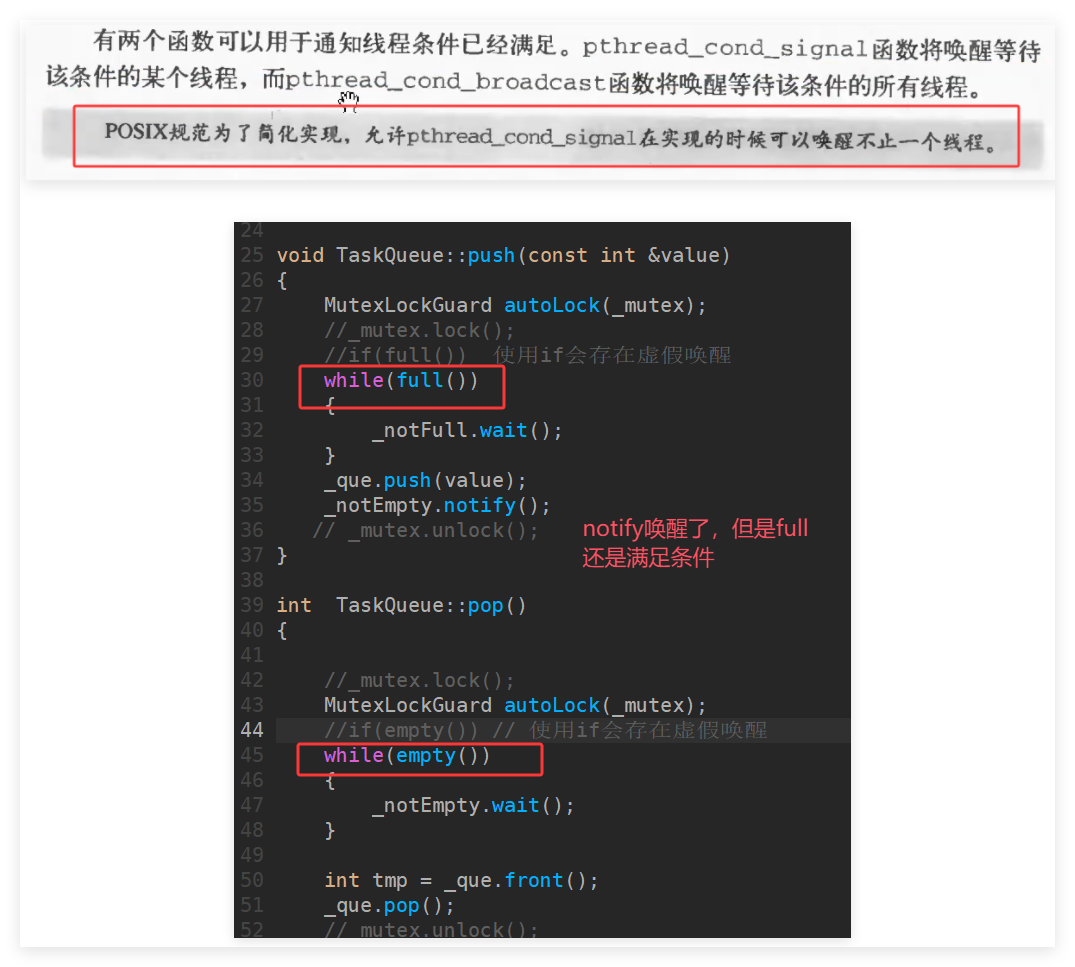
-
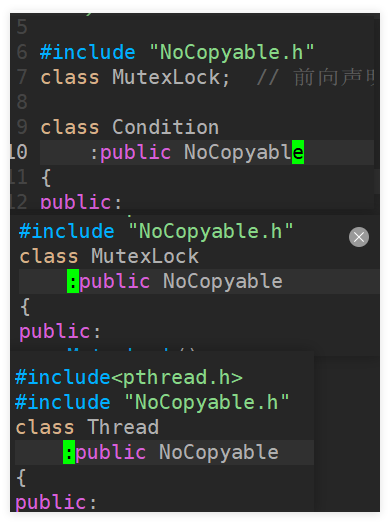
MutexLock应该禁止复制
-
MutexLock应该具有对象语义:禁止复制
-
对象语义:不能进行复制和赋值
-
值语义:可以进行复制和赋值
-
NoCopyable.h
-
#ifndef __NOCOPYABLE_H__ #define __NOCOPYABLE_H__ class NoCopyable { public: NoCopyable() {} ~NoCopyable() {} NoCopyable(const NoCopyable &rhs) = delete ; NoCopyable &operator=(const NoCopyable &rhs)=delete ; private: }; #endif -
为了让Nocopyable不能创建对象但是可以被继承
-
#ifndef __NOCOPYABLE_H__ #define __NOCOPYABLE_H__ class NoCopyable { protected: NoCopyable() {} ~NoCopyable() {} NoCopyable(const NoCopyable &rhs) = delete ; NoCopyable &operator=(const NoCopyable &rhs)=delete ; private: }; #endif
-
-
-
Example.h
-
#ifndef __EXAMPLE_H__ #define __EXAMPLE_H__ #include"NoCopyable.h" class Example :NoCopyable { public: Example() {} ~Example() {} private: }; #endif
-
-
test.c
-
#include <iostream> #include "Example.h" int main() { Example ex1; Example ex2 = ex1; // error std::cout << "Hello world" << std::endl; return 0; }
-
-

























 1043
1043

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








