原文链接:https://www.tutorialspoint.com/sap_ui5/sap_ui5_mvc_concept.htm
Model-View-Controller (MVC) concept is used in SAP UI5 development to keep the application data separate from the user interactions. This allows you to develop the web applications and make changes to the applications independently.
Model-View-Controller plays a different role in UI development −
-
The Model is responsible for managing the application data in the database/backend.
-
The View is responsible for defining the user interface to users. When a user sends a requests from his device, the view is responsible for data view as per the request submitted.
-
The Controller is used to control the data and view events as per user interaction by updating the view and model.
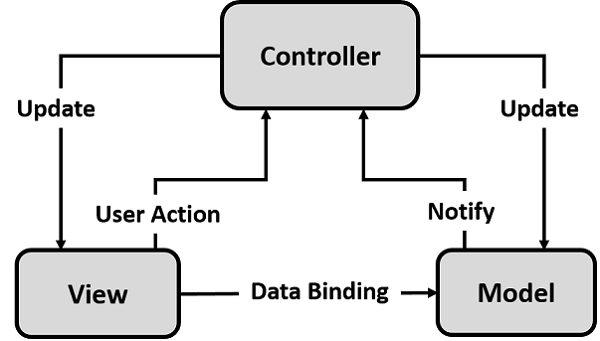
You can define Model-View-Controller concept in SAPUI5 with the following features −
Model
- Model acts as a bridge between the view and the application data.
- Model is used to get the request from the view and respond as per the user’s input.
- Model doesn’t depend on classes.
View
- View is responsible to manage information display to the users.
- Views are based on Model.
Controller
-
Controller is responsible for taking the input given by devices and communicates to model/view and to trigger correct action.
-
Controllers are based on model.
SAP UI5 offers Views and Controllers in the form of single files −
- sap.ui.core.mvc.XMLView
- sap.ui.core.mvc.JSView
- sap.ui.core.mvc.Controller
- sap.ui.core.mvc.JSONView
JSON Model
- JSON model is a client-side model and is used for small data sets.
- JSON model supports two-way binding. Data binding concept is mentioned in the latter half of this tutorial.
- JSON model can be used to bind controls to JavaScript object data.
XML Model
- XML model can be used to bind controls to XML data.
- XML is also a client side model and hence is used only for small data sets.
- XML model doesn’t provide any mechanism for server-based paging or loading of deltas.
- XML model also supports two-way data binding.





 本文介绍了 SAP UI5 开发中使用的 Model-View-Controller (MVC) 架构,解释了模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)在 UI 开发中的作用。模型负责管理应用数据,视图定义用户界面并响应用户请求,而控制器则处理用户交互,更新视图和模型。
本文介绍了 SAP UI5 开发中使用的 Model-View-Controller (MVC) 架构,解释了模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)在 UI 开发中的作用。模型负责管理应用数据,视图定义用户界面并响应用户请求,而控制器则处理用户交互,更新视图和模型。
















 465
465

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








