数据结构
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type; //函数指针
void *privdata;
/*ht属性是一个包含两个项的数组,数组中的每个项都是一个dictht哈希表,一般情况下, 字典只使用ht[0]哈希表,ht[1]哈希表只会在对ht[0]哈希表进行rehash时使用*/
dictht ht[2]; //hash表
/*它记录了rehash目前的进度,如果目前没有在进行rehash,那么它的值为-1*/
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 重新排列*/ //数据量特别大时一个数组槽位一个数组槽位的移动
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table; //哈希表,哈希冲突通过链表进行连接
unsigned long size; //哈希表大小
unsigned long sizemask; //哈希表大小掩码,用于计算索引值。总是等于size-1
unsigned long used; //该哈希表已有节点的数量
} dictht;
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key; //key值
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
typedef struct redisObject {//value结构体
unsigned type:4; // 数据类型
unsigned encoding:4; // 数据编码
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */ // LRU时钟
int refcount; //引用计数
void *ptr; // 指向数据的指针。当robj存储的数据可以使用long类型表示的时候,数据直接存储在ptr字段
//当使用OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR编码时,ptr指向sdshdr8的flags字段之后
} robj;
typedef char *sds;
/* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */ //用户已用的内存
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */ //申请的内存
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */ //标记SDS_TYPE_8
char buf[]; //字符串数据区域
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
请求数据解析argc,argv
void readQueryFromClient(connection *conn) {
...
nread = connRead(c->conn, c->querybuf+qblen, readlen);
printf("c->querybuf_peak=%ld,qblen=%ld,nread=%d,c->querybuf+qblen=%s",c->querybuf_peak,qblen,nread,c->querybuf+qblen);
...
}
调用命令
127.0.0.1:6379> set abcd aa
OK
打印结果如下:
c->querybuf_peak=0,qblen=0,nread=31,c->querybuf+qblen=*3
$3
set
$4
abcd
$2
aa
对c->querybuf中的数据解析出参数argc和argv
void processInputBuffer(client *c) {
...
if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK) { //redis-cli命令请求的协议类型
if (processMultibulkBuffer(c) != C_OK) break; //解析read出来的参数
}
...
}
int processMultibulkBuffer(client *c) {
...
serverAssertWithInfo(c,NULL,c->querybuf[c->qb_pos] == '*'); //*2表示后面有2个参数,*3表示后面有3个参数
ok = string2ll(c->querybuf+1+c->qb_pos,newline-(c->querybuf+1+c->qb_pos),&ll);
...
c->multibulklen = ll;//参数数量
/* Setup argv array on client structure */
if (c->argv) zfree(c->argv);
c->argv = zmalloc(sizeof(robj*)*c->multibulklen);
...
while(c->multibulklen) { //参数数量
...
if (c->querybuf[c->qb_pos] != '$') {
addReplyErrorFormat(c,
"Protocol error: expected '$', got '%c'",
c->querybuf[c->qb_pos]);
setProtocolError("expected $ but got something else",c);
return C_ERR;
}
ok = string2ll(c->querybuf+c->qb_pos+1,newline-(c->querybuf+c->qb_pos+1),&ll);
....
c->bulklen = ll; //参数长度 $5表示5个字节,$7表示7个字节
...
c->argv[c->argc++] =createStringObject(c->querybuf+c->qb_pos,c->bulklen); //加入到参数argv里面
...
}
}
robj结构体与sdshdr8、sdshdr16、sdshdr32结构体
robj *createStringObject(const char *ptr, size_t len) {
if (len <= OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT)
return createEmbeddedStringObject(ptr,len);
else
return createRawStringObject(ptr,len);
}
其中createEmbeddedStringObject为创建一整片内存,即robj结构体和ptr指针都在一片内存当中。createRawStringObject为创建两片内存,robj和ptr指向的内存为不同内存片。
robj *createEmbeddedStringObject(const char *ptr, size_t len) {
robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(robj)+sizeof(struct sdshdr8)+len+1);
struct sdshdr8 *sh = (void*)(o+1);
o->type = OBJ_STRING;
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR;
o->ptr = sh+1;
o->refcount = 1;
if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
o->lru = (LFUGetTimeInMinutes()<<8) | LFU_INIT_VAL;
} else {
o->lru = LRU_CLOCK();
}
sh->len = len;
sh->alloc = len;
sh->flags = SDS_TYPE_8;
if (ptr == SDS_NOINIT)
sh->buf[len] = '\0';
else if (ptr) {
memcpy(sh->buf,ptr,len);
sh->buf[len] = '\0';
} else {
memset(sh->buf,0,len+1);
}
return o;
}
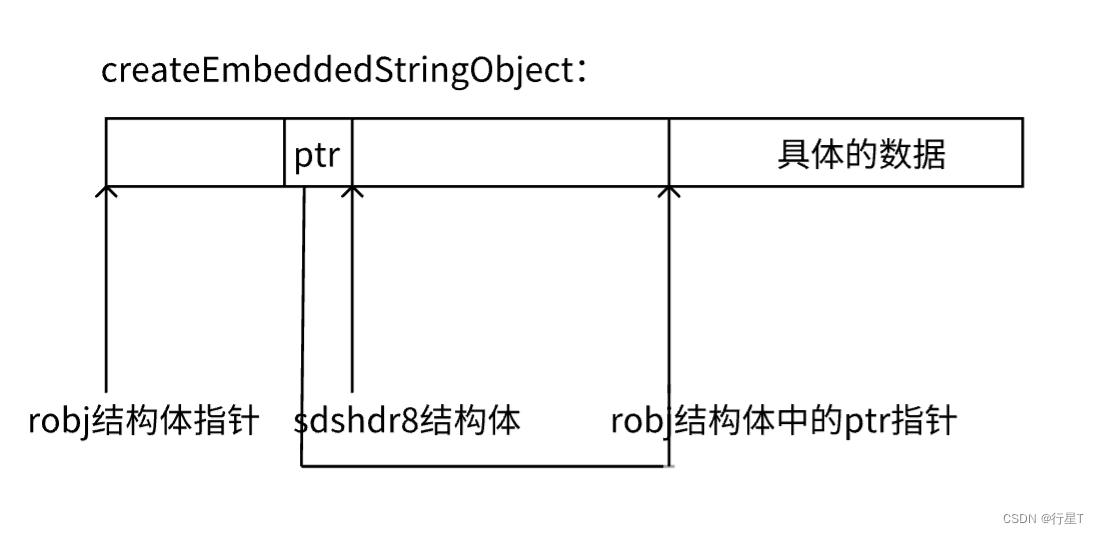
robj *createRawStringObject(const char *ptr, size_t len) {
return createObject(OBJ_STRING, sdsnewlen(ptr,len));
}
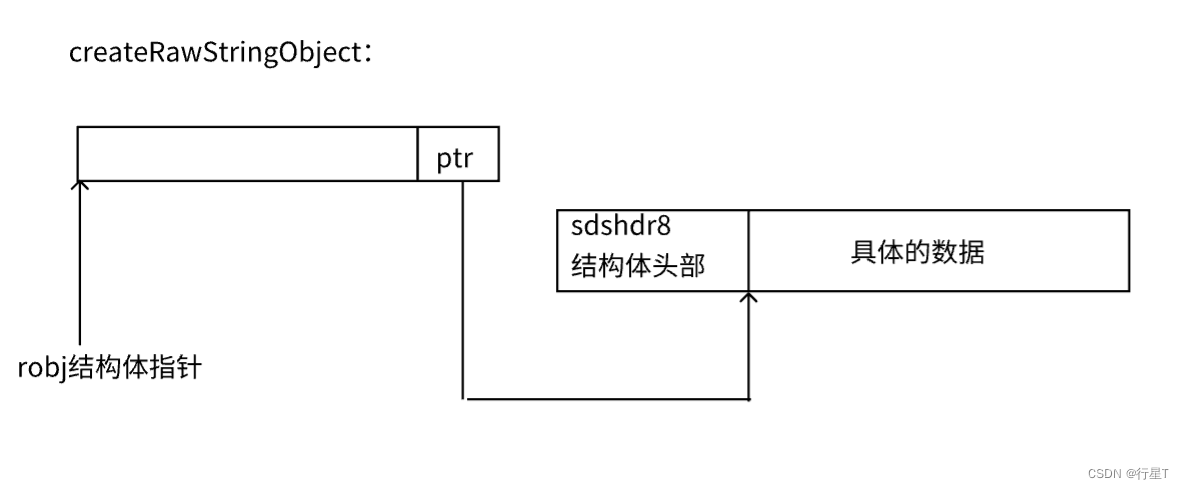
sds类型内存模型如下:
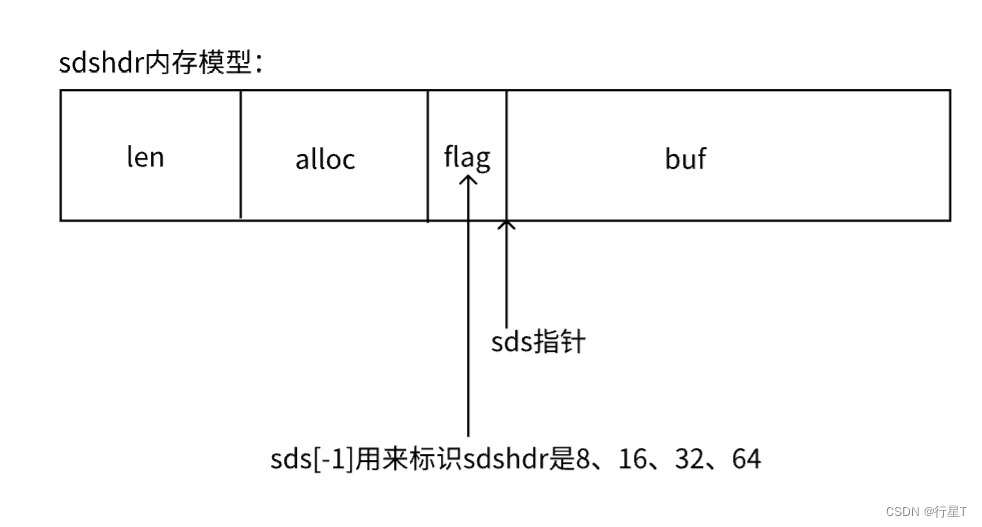
其中关键的宏定义和函数定义如下:
#define SDS_TYPE_5 0
#define SDS_TYPE_8 1
#define SDS_TYPE_16 2
#define SDS_TYPE_32 3
#define SDS_TYPE_64 4
#define SDS_TYPE_MASK 7
#define SDS_TYPE_BITS 3
#define SDS_HDR_VAR(T,s) struct sdshdr##T *sh = (void*)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr##T)));
#define SDS_HDR(T,s) ((struct sdshdr##T *)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr##T))))
#define SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(f) ((f)>>SDS_TYPE_BITS)
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) { //已使用的内存
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5:
return SDS_TYPE_5_LEN(flags);
case SDS_TYPE_8:
return SDS_HDR(8,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_16:
return SDS_HDR(16,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_32:
return SDS_HDR(32,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_64:
return SDS_HDR(64,s)->len;
}
return 0;
}
static inline size_t sdsavail(const sds s) { //剩余内存
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_5: {
return 0;
}
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
case SDS_TYPE_32: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(32,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
case SDS_TYPE_64: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(64,s);
return sh->alloc - sh->len;
}
}
return 0;
}
哈希表dict的扩容和缩容
int dictResize(dict *d) //哈希表缩容
{
unsigned long minimal;
if (!dict_can_resize || dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_ERR;
minimal = d->ht[0].used;
if (minimal < DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE)
minimal = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;
return dictExpand(d, minimal);
}
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size) //哈希表进行扩容
{
/* the size is invalid if it is smaller than the number of
* elements already inside the hash table */
if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size)
return DICT_ERR;
dictht n; /* the new hash table */
/*
1.如果执行的是扩展操作,那么ht[1]的大小为第一个大于等于ht[0].used*2的2^n。 例如ht[0].used为5,ht[0].used*2=10,第一个大于的2^n次方为2^4即16。
2.如果执行的是收缩操作,那么ht[1]的大小为第一个大于等于ht[0].used的2^n。 例如ht[0].used为5,ht[0].used=5,第一个大于的2^n次方为2^3即8。
*/
unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size);
/* Rehashing to the same table size is not useful. */
if (realsize == d->ht[0].size) return DICT_ERR;
/* Allocate the new hash table and initialize all pointers to NULL */
n.size = realsize;
n.sizemask = realsize-1;
n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
n.used = 0;
/* Is this the first initialization? If so it's not really a rehashing
* we just set the first hash table so that it can accept keys. */
if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) {
d->ht[0] = n;
return DICT_OK;
}
/* Prepare a second hash table for incremental rehashing */
d->ht[1] = n;
d->rehashidx = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
其中哈希表dict包含两个哈希表项在通过key进行查找时ht[0]和ht[1]都会进行查找匹配表项中的key值。在int dictRehash(dict *d, int n)函数中每次移动哈希表中的一个n个槽位,从从ht[0]哈希表上重新哈希到ht[1].table[h]位置。
当ht[0]中已使用节点数为0时,将ht[1]赋值给ht[0]即d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];随后ht[1]进行复位,为下次扩容缩容做好准备。
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) { //挪动数据,n表示几个槽位 扩容缩容时同时通过key进行find时哈希表1和哈希表2同时进行查找
int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. 最大访问空桶数*/
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;
while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;
}
de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
while(de) {
uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;
de->next = d->ht[1].table[h];
d->ht[1].table[h] = de; //de节点从ht[0]哈希表上重新哈希到ht[1].table[h]位置
d->ht[0].used--;
d->ht[1].used++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {
zfree(d->ht[0].table);
d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]); //哈希表1复位
d->rehashidx = -1;
return 0;
}
/* More to rehash... */
return 1;
}





 本文解析了Redis中哈希表dict的数据结构,包括ht属性、rehashing过程,并展示了如何从客户端输入解析argc和argv。同时介绍了robj结构体与SDS内存模型,以及哈希表的扩容与缩容策略。
本文解析了Redis中哈希表dict的数据结构,包括ht属性、rehashing过程,并展示了如何从客户端输入解析argc和argv。同时介绍了robj结构体与SDS内存模型,以及哈希表的扩容与缩容策略。
















 3299
3299

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








