一、basedao + druid
数据库连接池
c3p0
druid:魔鬼,号称最好的java 连接池
为什么要用数据连接池?
1.避免重复创建链接,链接创建不关闭情况
数据库链接非常宝贵/资源有限
2.可以提高查选效率(以前频繁创建链接)
3.便于对链接的同一管理和监控,便于优化应用
线程池和数据库连接池统称为 池化技术
1、创建servelt工程
commons-beanutils-1.8.3.jar 将map 转化为对象工具类
commons-dbutils-1.7.jar queryRunner的封装用简化查询
commons-logging-1.1.3.jar 日志相关组件,commons-dbutils依赖commons-logging
druid-1.2.3.jar 数据连接池
mysql-connector-java-5.1.47.jar mysql 驱动
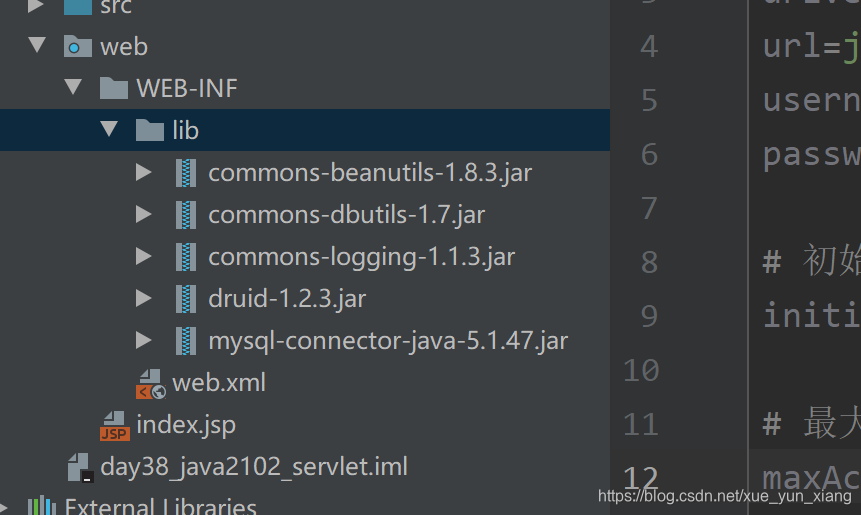
2、在src 引入配置文件druid.properties
# druid.properties文件
# 文件名 druid.properties 存储在src目录下
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2102?useSSL=false
username=root
password=123456
# 初始化数据库连接池容量 起始初始化 10个链接
initialSize=10
# 最大容量 当前应用最多 有30个 防止当前应用占据所有 mysql 的链接
maxActive=30
# TimeOut 等待超时时间
maxWait=2000
3、导入baseDao ,dbutils
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.*;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 对 queryRunner 进行封装
*/
public class BaseDao {
// queryRunner 数据源来源于 druid
public static QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(JDBCUtil.getDataSource());
/**
* 通用update更新方法,用于处理insert update delete SQL语句
*
* @param sql 当前需要指定的目标SQL语句
* @param parameters 当前SQL语句对应的参数,为Object类型不定长参数
* @return 当前SQL语句执行对于数据库的影响行数
* @throws SQLException SQL异常
*/
public int update(String sql, Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
return queryRunner.update(sql, parameters);
}
/**
* 查询一个符合JavaBean规范类对象
*
* @param sql 需要处理的SQL语句
* @param cls 目标数据类型Class对象
* @param parameters 对应当前SQL语句的参数
* @param <T> 泛型约束当前数据类型,需要通过参数传入
* @return 泛型约束数据类型
* @throws SQLException SQL异常
*
* 根据 id 查询 唯一 数据 返回一个对象
*/
public <T> T queryBean(String sql, Class<T> cls, Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
return queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanHandler<>(cls), parameters);
}
/**
* 通用query查询方法,用于处理select语句
*
* @param sql Select SQL 语句 DQL语句
* @param cls 当前查询目标的数据类型Class对象,
* @param parameters 对应SQL语句参数
* @param <T> 泛型约束当前数据类型,需要通过参数传入
* @return List集合包含有用户查询的目标数据,如果为找到任何数据,返回null
* @throws SQLException SQL异常
*/
public <T> List<T> queryBeanList(String sql, Class<T> cls, Object... parameters)
throws SQLException {
return queryRunner.query(sql, new BeanListHandler<>(cls), parameters);
}
public Map<String, Object> queryMap(String sql, Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
return queryRunner.query(sql, new MapHandler(), parameters);
}
public List<Map<String, Object>> queryMapList(String sql, Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
return queryRunner.query(sql, new MapListHandler(), parameters);
}
public Object[] queryArray(String sql, Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
return queryRunner.query(sql, new ArrayHandler(), parameters);
}
public List<Object[]> queryArrayList(String sql, Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
return queryRunner.query(sql, new ArrayListHandler(), parameters);
}
}
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* 使用Druid数据库完备JDBC工具类
* 1. JDBC数据库连接所需的必要资源准备和驱动加载
* 2. 提供一个工具类方法,获取数据库连接对象 Connection getConnection
* 3. 关闭用户使用的数据库资源
*
* @author Anonymous
*/
public class JDBCUtil {
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
// 读取Properties配置文件
// JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties") 读取 druid.properties变为文件流
properties.load(JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties"));
// Druid数据库连接池工厂类创建一个数据库连接池
// 数据来源 druid
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 返回当前JDBCUtils创建的DataSource数据库连接池对象
*
* @return DataSource 数据库连接池对象
*/
public static DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
/**
* 获取数据库连接对象方法
*
* @return java.sql.Connection 对象。如果获取连接失败返回null
*/
public static Connection getConnection() {
Connection connection = null;
try {
// 获取数据库连接从 dataSource 数据库连接池对象中获取对应的数据库连接对象。
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return connection;
}
/**
* 数据库操作使用的资源都是AutoCloseable接口的实现类,可以使用
* 不定长参数直接完成关闭方法,传入的参数是AutoCloseable实现类
* 个数不限
*
* @param res AutoCloseable实现类对象,个数不限
*/
public static void close(AutoCloseable... res) {
try {
// 遍历当前AutoCloseable数组,使用增强for循环
for (AutoCloseable re : res) {
// 当前资源不为null,直接关闭
if (re != null) {
re.close();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4、创建emp 表
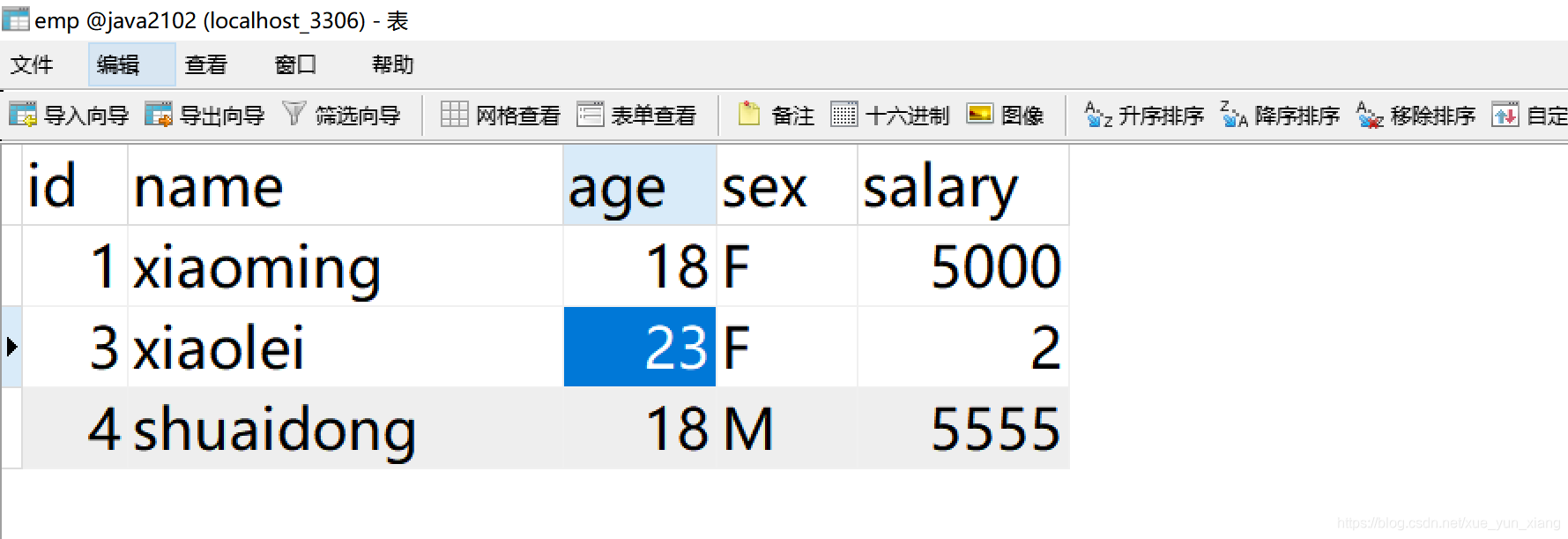
5、 创建emp 实体类
public class Emp implements Serializable {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
private float salary;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public float getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(float salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
", salary=" + salary +
'}';
}
}
6、创建emp dao
public interface EmpDao {
/**
* 查选所有 雇员
* @return
*/
List<Emp> findAllEmp() throws SQLException;
/**
* 根据id 查询雇员
* @param id
* @return
*/
Emp findEmpById(int id) throws SQLException;
/**
* 添加雇员
* @param emp
* @return
*/
int addEmp(Emp emp) throws SQLException;
/**
* 删除雇员
* @param id
* @return
*/
int deleteEmp(int id) throws SQLException;
/**
* 更新雇员
* @param emp
* @return
*/
int updateEmp(Emp emp) throws SQLException;
}
/**
* EmpDao empDao = new EmpDaoImpl();
* empDao 对应的对象 是 EmpDaoImpl
* 是 EmpDao
* 是 BaseDao
*/
public class EmpDaoImpl extends BaseDao implements EmpDao {
@Override
public List<Emp> findAllEmp() throws SQLException {
// 那个sql 性能好?
// String sql = "select * from emp";
String sql = "select id,name,sex,age,salary from emp";
List<Emp> empList = queryBeanList(sql,Emp.class,null);
return empList;
}
@Override
public Emp findEmpById(int id) throws SQLException {
String sql = "select id,name,sex,age,salary from emp where id = ?";
Emp emp = queryBean(sql,Emp.class,id);
return emp;
}
@Override
public int addEmp(Emp emp) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into emp (name,age,sex,salary) values (?,?,?,?)";
int num = update(sql,emp.getName(),emp.getAge(),emp.getSex(),emp.getSalary());
return num;
}
@Override
public int deleteEmp(int id) throws SQLException {
String sql = "delete from emp where id = ?";
int num = update(sql,id);
return num;
}
@Override
public int updateEmp(Emp emp) throws SQLException {
String sql = "update emp set name = ?,age = ?,sex = ? ,salary = ? where id = ?";
int num = update(sql,emp.getName(),emp.getAge(),emp.getSex(),emp.getSalary(),emp.getId());
return num;
}
}
7、测试
public class EmpTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
EmpDao empDao = new EmpDaoImpl();
// 查选所有
List<Emp> empList = empDao.findAllEmp();
for (Emp emp:empList){
System.out.println("emp:"+emp);
}
// 根据id 查选
Emp emp = empDao.findEmpById(3);
System.out.println("根据id=3查询:"+emp);
// 插入emp
Emp empAdd = new Emp();
empAdd.setAge(18);
empAdd.setName("shuaidong");
empAdd.setSalary(5555);
empAdd.setSex("M");
int numAdd = empDao.addEmp(empAdd);
// 如果numAdd > 0 代表更新成功
System.out.println("numAdd:"+numAdd);
// 删除
int numDelete = empDao.deleteEmp(2);
System.out.println("numDelete:"+numDelete);
// 修改emp id=3 的年龄
emp.setAge(emp.getAge() + 1);
int numUpdate = empDao.updateEmp(emp);
System.out.println("numUpdate:"+numUpdate);
}
}
二、mvc 设计模式
mvc 设计模式,使用一种常见设计模式(一种套路/规范),所有前后端交互的软件都遵循mvc
m:model (模型) -----------》数据/实体类 从数据库中查询
v:view (视图)--------------》前端界面/jsp/html 接收数据/展示数据
c:controller (控制器)-------》后端servlet ,控制界面的跳转,返回响应的数据/model
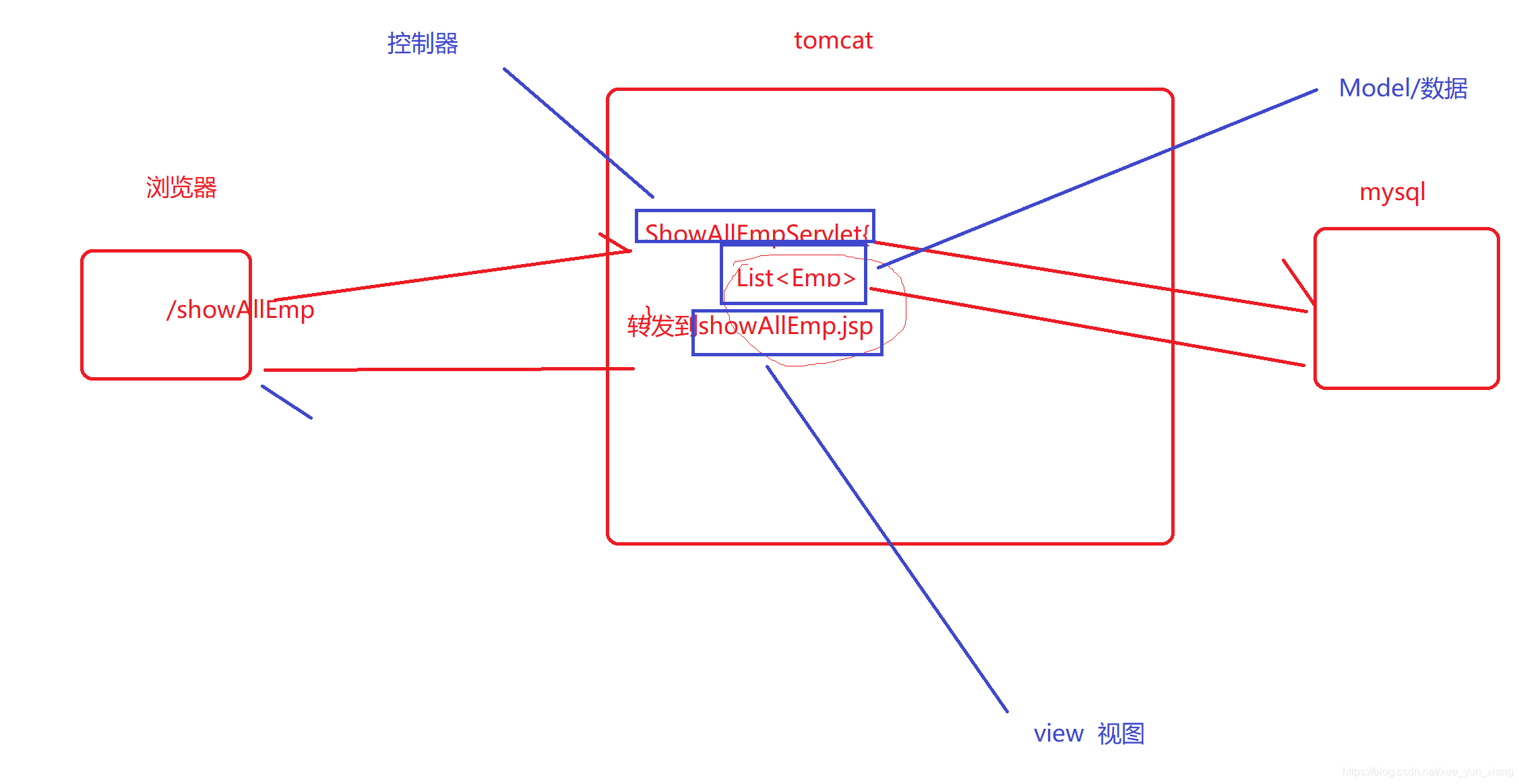
- 低耦合性:模块与模块之间的关联性不强,不与某一种具体实现产生密不可分的关联性
- 高维护性:基于低耦合性,可做到不同层级的功能模块灵活更换、插拔
- 高重用性:相同的数据库操作,可以服务于不同的业务处理。将数据作为独立模块,提高重用性
三层架构
三层架构 指的是 代码 不同业务的书写位置
View层(表示|界面层)、 html /jsp 前端 web
Service层(业务逻辑层)、处理器前端请求对应的业务数据----》service
DAO层(数据访问层) 专门用来做数据的增删该查-------->dao
controller(控制层) 负责界面跳转,返回响应数据--------->servlet/controller
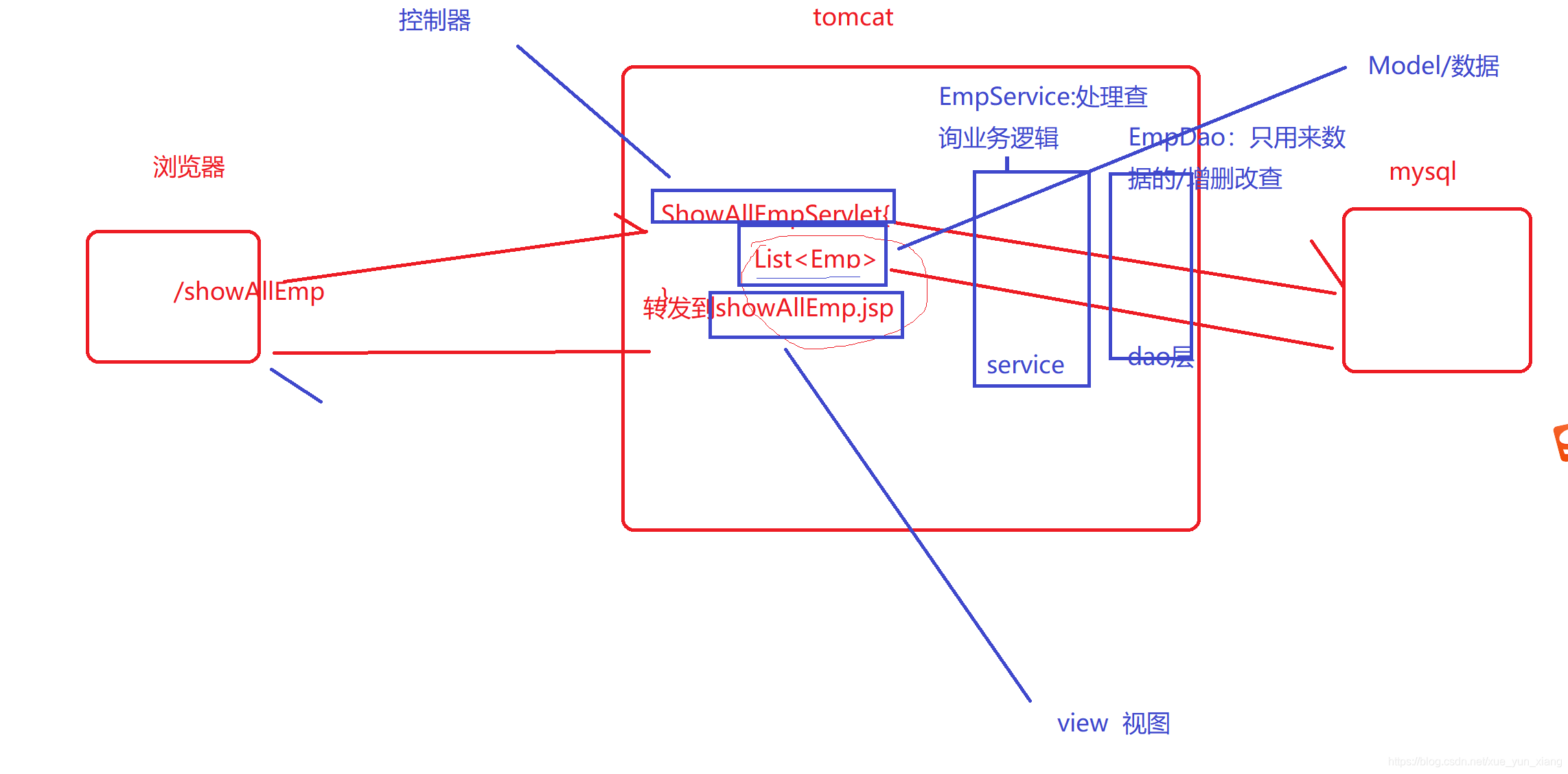
三、完成数据库中 数据列表展示
显示emp表中所有的数据,以表格的形式展示
四、分页
分页是Web应用程序非常重要的一个技术。数据库中的数据可能是成千上万的,不可能把这么多的数据一次显示在浏览器上面。一般根据每行数据在页面上所占的空间设置每页显示若干行,比如一般20行是一个比较理想的显示状态。
好处:
1.提高用户体验(提高响应速度,便于查看)
2.降低msyql服务压力
分页
select * from emp limit startIndex, size
参数:
pageIndex (那一页,从1开始)
pageSize(每页大小)
每页 5 pageSize=5
第一页 pageIndex =1
select * from emp limit 0, 5 (1-1)*5,5
第二页 pageIndex =2
select * from emp limit 5, 5 (2-1)*5,5
第三页 pageIndex =3
select * from emp limit 10, 5 (3-1)*5,5
分页公式:
select * from emp limit (pageIndex-1)*pageSize, pageSize
分页计算
/**
* 计算分页
*/
public class PageCountTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int countLine = 9;
int pageSize = 5;
int pageCount = 0;
if (countLine%pageSize == 0){
pageCount = countLine/pageSize;
}else {
pageCount = countLine/pageSize + 1;
}
System.out.println("pageCount:"+pageCount);
}
}





















 3733
3733

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








