Fluent API
除了惯例原则与属性数据注解外,FluentAPI是另一种支持实体类配置设置的方式。与属性数据注解相比,它提供了更广泛的功能与设置弹性。实体类若同时设置了数据注解,则采用的优先权是“Fluent API” > "数据注解" > "惯例"。一旦设置了Fluent API 无论数据注解还是惯例规则均会被覆盖。
DbContext类定义的OnModelCreating 方法是最常调用FLuent API的地方,如下图所示:
public class SchoolContext: DbContext
{
public KTStoreContext():base("name=KTStore")
{
}
public DbSet<Product> Products { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
//Write Fluent API configurations here
}
}
| 配置 | Fluent API方法 | 作用 |
| 架构相关配置 | HasDefaultSchema() | 数据库的默认架构 |
| ComplexType() | 把一个类配置为复杂类型 | |
| 实体相关配置 | HasIndex() | 实体的的索引 |
| HasKey() | 实体的主键(可其实现复合主键,[Key]在EF core中不能实现复合主键) | |
| HasMany() | 1对多的或者 多对多关系 | |
| HasOptional() | 一个可选的关系,这样配置会在数据库中生成一个可空的外键 | |
| HasRequired() | 一个必有的关系,这样配置会在数据库中生成一个不能为空的外键 | |
| Ignore() | 实体或者实体的属性不映射到数据库 | |
| Map() | 设置一些优先的配置 | |
| MapToStoredProcedures() | 实体的CUD操作使用存储过程 | |
| ToTable() | 为实体设置表名 | |
| 属性相关配置 | HasColumnAnnotation() | 给属性设置注释 |
| IsRequired() | 在调用SaveChanges()方法时,属性不能为空 | |
| IsOptional() | 可选的,在数据库生成可空的列 | |
| HasParameterName() | 配置用于该属性的存储过程的参数名 | |
| HasDatabaseGeneratedOption() | 配置数据库中对应列的值怎样生成的,如计算,自增等 | |
| HasColumnOrder() | 配置数据库中对应列的排列顺序 | |
| HasColumnType() | 配置数据库中对应列的数据类型 | |
| HasColumnName() | 配置数据库中对应列的列名 | |
| IsConcurrencyToken() | 配置数据库中对应列用于乐观并发检测 |
举一个简单例子, 新建一个FluentApiDemo的控制台应用程序,添加Product实体类和上下文类KTStoreModel,如下图所示:
namespace FluentApiDemo
{
public class Product
{
public int XPId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Price { get; set; }
public int SPrice { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
}
}
public class KTStoreModel : DbContext
{
public KTStoreModel()
: base("name=KTStoreModel")
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>().ToTable("tbProduct");
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>().HasKey(p => p.XPId);
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>().Property(p => p.Name).HasColumnName("ProductName");
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>().Property(p => p.Name).HasMaxLength(50);
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>().Property(p => p.Name).IsRequired();
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>().Property(p => p.Price).HasColumnName("ProductPrice");
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>().Ignore(p => p.SPrice);
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
public virtual DbSet<Product> Product { get; set; }
}
Main函数中的代码如下图所示:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using (KTStoreModel db = new KTStoreModel())
{
Console.Write("count:{0}",db.Product.Count());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
运行后在数据库生成的表结果如下图所示:
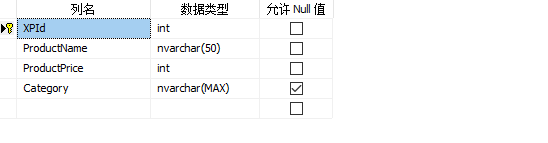
CodeFirst配置一对一,一对多,多对多关系
产品类Product和书本类Book是典型的一对一关系,产品中可能有书本这个属性,也可能没书本这个属性。但是书本必属于产品的一部分。
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set;}
public int CategoryId { get; set; }
public int Price { get; set; }
//导航属性
public virtual Book Book { get; set; }
}
public class Book
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public int Pages { get; set; }
public string ISBN { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
public string Publisher { get; set; }
//导航属性
public virtual Product Product { get; set; }
}
使用Fluent API配置如下:
public class kTStoreModel : DbContext
{
public kTStoreModel()
: base("name=kTStoreModel")
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>()
.HasOptional(e => e.Book)//给Product设置可空的Book属性
.WithRequired(e => e.Product);//给Book设置不能为空的Product属性,没有Book属性时不能保存
}
public virtual DbSet<Product> Product { get; set; }
public virtual DbSet<Book> Book { get; set; }
}
生成的数据表结构如下图所示:

书本类Book和作者类Author是典型的多对多关系,一本书可能有多个作者,一个作者可能写了多本书。
public class Book
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public int Pages { get; set; }
public string ISBN { get; set; }
public string Publisher { get; set; }
//导航属性
public virtual List<Author> Author { get; set; }
}
public class Author
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
//导航属性
public virtual List<Book> Book { get; set; }
}
使用Fluent API配置如下:
public class kTStoreModel : DbContext
{
public kTStoreModel()
: base("name=kTStoreModel")
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Author>()
.HasMany(e => e.Book)//配置一个作者有多本书
.WithMany(e => e.Author)//配置一本书有多个作者
.Map(m => m.ToTable("BookAuthor")//生成BookAuthor中间表
.MapLeftKey("AuthorId")//因为是通过Entity<Author>开始的,所以左表是Author
.MapRightKey("BookId"));//又表是BookId
}
public virtual DbSet<Book> Book { get; set; }
public virtual DbSet<Author> Author { get; set; }
}
生成的数据库表结构如下图所示:

多对多关联——附加数据字段
还有一种多对多关联的情况是,存储两个数据表关联信息的数据库表 本身具有其他有效的数据字段。这种情况下,实体数据模型必须为此数据表建立起专用的数据类型。
产品Product类和订单Order类是一个多对多的关系,OrderDetail存储两个数据表的关联信息,并且OrderDetail表中存在其他数据字段。
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set;}
public int Price { get; set; }
//导航属性
public virtual List<OrderDetail> OrderDetail { get; set; }
}
public class Order
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; }
//导航属性
public virtual List<OrderDetail> OrderDetail { get; set; }
}
public class OrderDetail
{
[Key]
[Column(Order = 0)]
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.None)]
public int OrderId { get; set; }
[Key]
[Column(Order = 1)]
[DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.None)]
public int ProductId { get; set; }
public int Quantity { get; set; }
public int Price { get; set; }
//导航属性
public virtual Product Product { get; set; }
public virtual Order Order { get; set; }
}
运行后建立的数据库表结构如下图所示:
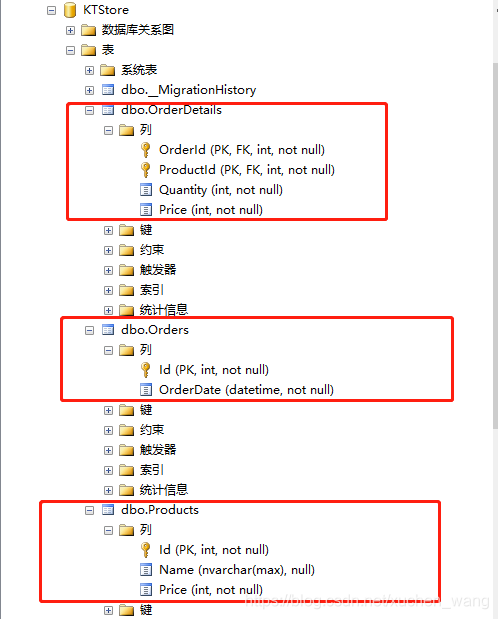
订单系统中,订单主表和明细表是典型的一对多关系。
public class Order
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; }
//导航属性
public virtual List<OrderDetail> OrderDetail { get; set; }
}
public class OrderDetail
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string ProductName { get; set; }
public int Quantity { get; set; }
public int Price { get; set; }
public int XOrderId { get; set; }
//导航属性
public virtual Order Order { get; set; }
}
使用Fluent API配置如下:
public class kTStoreModel : DbContext
{
public kTStoreModel()
: base("name=kTStoreModel")
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Conventions.Remove<PluralizingTableNameConvention>();//取消数据库表复数形式
modelBuilder.Entity<OrderDetail>()
.HasRequired(od => od.Order)//OrderDetail有必须要的导航属性Order
.WithMany(o => o.OrderDetail)//OrderDetail有集体导航属性OrderDetail
.HasForeignKey(x => x.XOrderId);//设置外键
}
public virtual DbSet<Order> Order { get; set; }
public virtual DbSet<OrderDetail> OrderDetail { get; set; }
}
也可以使用Fluent API 反向关联,代码如下:
modelBuilder.Entity<Order>()
.HasMany(o => o.OrderDetail)
.WithRequired(od => od.Order)
.HasForeignKey(od => od.XOrderId);
运行后建立的数据库表结构如下图所示:
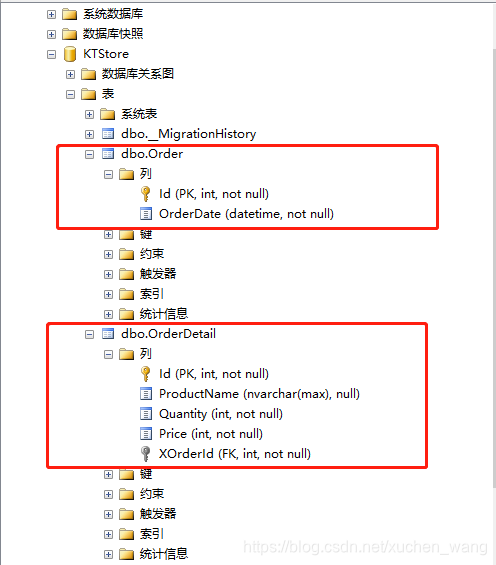
级联删除
级联删除是指父级记录删除时会自动删除子级记录。比如订单主表删除后自动删除订单从表。
在EF中,默认是打开级联删除的。
一对多:如订单主表删除时,订单从表从中外键OrderId变成null。
一对一:如删除Product时,对应的Book也会删除。
多对多:如删除一种book信息时,在中间表中对应的作者信息也会删除。
代码如下图所示:
modelBuilder.Entity<OrderDetail>()
.HasRequired(od => od.Order)
.WithMany(o => o.OrderDetail)
.HasForeignKey(x => x.XOrderId)
.WillCascadeOnDelete();//开启级联删除
modelBuilder.Entity<Order>()
.HasMany(o => o.OrderDetail)
.WithRequired(od => od.Order)
.HasForeignKey(od => od.XOrderId)
.WillCascadeOnDelete(false);//关闭级联删除
配置单个实体
我们已经知道了在OnModelCreating()方法中可以通过FluentApi对所有的实体类进行配置,然而当实体类很多时,我们把所有的配置都放在OnModelCreating()方法中很难维护。EF6允许我们给每一个实体添加一个单独的配置类,通过这个配置类来对相应的实体进行配置。
以配置Student实体类为例,我们在OnModelCreating()方法中配置Student实体,代码如下:
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>().ToTable("StudentInfo");
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>().HasKey<int>(s => s.StudentKey);
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>()
.Property(p => p.DateOfBirth)
.HasColumnName("Birthday")
.HasColumnOrder(3)
.HasColumnType("datetime2");
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>()
.Property(p => p.StudentName)
.HasMaxLength(50);
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>()
.Property(p => p.StudentName)
.IsConcurrencyToken();
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>()
.HasMany<Course>(s => s.Courses)
.WithMany(c => c.Students)
.Map(cs =>
{
cs.MapLeftKey("StudentId");
cs.MapRightKey("CourseId");
cs.ToTable("StudentCourse");
});
}
}
我们可以将每个实体类的配置放在一个对应的的配置类,(如Studnet的实体配置在StudentEntityConfiguratinos配置类中),如果程序中有很多实体类,采用单独配置的方式可以很好的提高配置的可维护性和可读性。
StudentEntityConfiguratinos类需要继承EntityTypeConfiguration<TEntity>:
public class StudentEntityConfiguration: EntityTypeConfiguration<Student>
{
public StudentEntityConfiguration()
{
this.ToTable("StudentInfo");
this.HasKey<int>(s => s.StudentKey);
this.Property(p => p.DateOfBirth)
.HasColumnName("DoB")
.HasColumnOrder(3)
.HasColumnType("datetime2");
this.Property(p => p.StudentName)
.HasMaxLength(50);
this.Property(p => p.StudentName)
.IsConcurrencyToken();
this.HasMany<Course>(s => s.Courses)
.WithMany(c => c.Students)
.Map(cs =>
{
cs.MapLeftKey("StudentId");
cs.MapRightKey("CourseId");
cs.ToTable("StudentCourse");
});
}
}
在OnModelCreating()方法中使用上边的配置类:
public class SchoolDBContext: DbContext
{
public SchoolDBContext(): base()
{
}
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
// 添加Student实体的配置
modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(new StudentEntityConfiguration());
}
}





















 967
967

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








