如果对Django基本配置还是小白的话,请移步:
第一:在setting中配置模版文件夹
My_Django/setting.py
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
|
TEMPLATES = [ #模版
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')] # 模版文件夹
....
],
},
]
|
第二:编写一个模版html
templates/hello/index.html
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>{{ title }}</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
{% for item in list%}
<li>{{ item }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</body>
</html>
|
第三:使用视图函数返回模版
Django提供了一个函数render封装了以上代码 方法render包含3个参数
- 第一个参数为request对象
- 第二个参数为模板文件路径
- 第三个参数为字典,表示向模板中传递的上下文数据
hello/views.py:
[AppleScript] 纯文本查看 复制代码
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
|
from django.http import HttpResponse, request
from django.shortcuts import render
'''
定义了一个试图函数
requset : 请求的request
'''
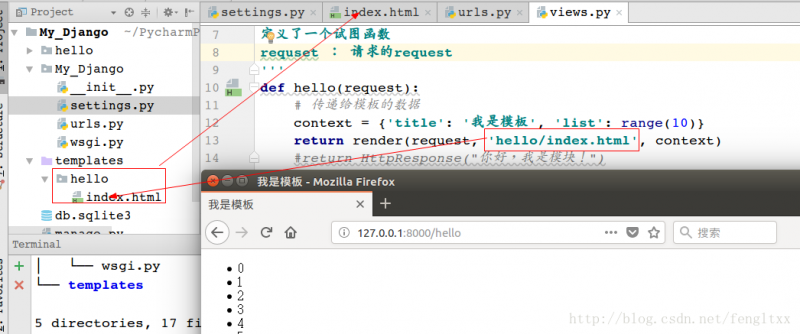
def hello(request):
# 传递给模板的数据
context = {'title': '我是模板', 'list': range(10)}
return render(request, 'hello/index.html', context)
#return HttpResponse("你好,我是模块!")
|
访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/hello 效果如下:




 本文详细介绍了Django框架中模板系统的配置与使用方法,包括设置模版文件夹、编写HTML模版以及通过视图函数返回模版。适合初学者快速上手。
本文详细介绍了Django框架中模板系统的配置与使用方法,包括设置模版文件夹、编写HTML模版以及通过视图函数返回模版。适合初学者快速上手。
















 393
393

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








