文章目录
8.JSP
8.1.什么是jsp
Java Server Pages: Java服务器端页面, 也和servlet一样, 用于动态web技术
特点:
- 写jsp就像是在写HTML
- 区别:
- HTML只给用户提供静态的数据
- JSP页面中可以嵌入java代码, 为用户提供动态数据
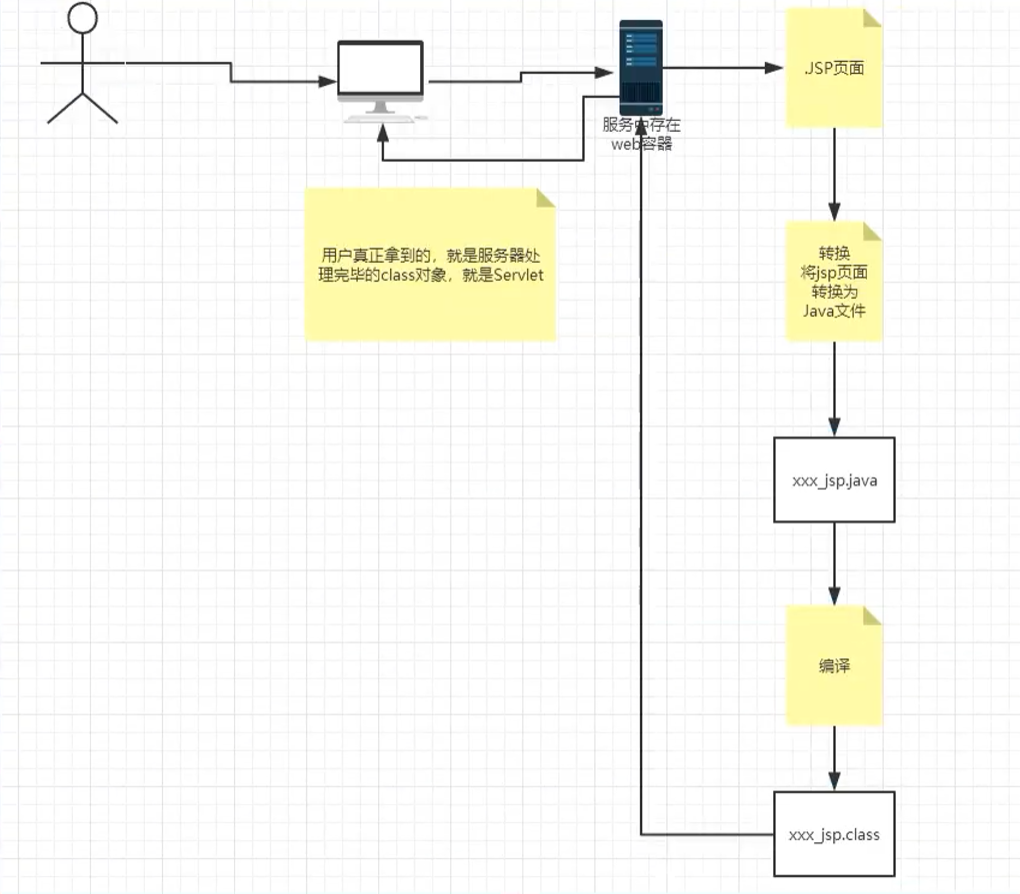
8.2.JSP原理
思路: JSP到底怎么执行的
- 代码层面没有任何问题
- 服务器内部工作
IDEA Tomcat的工作空间
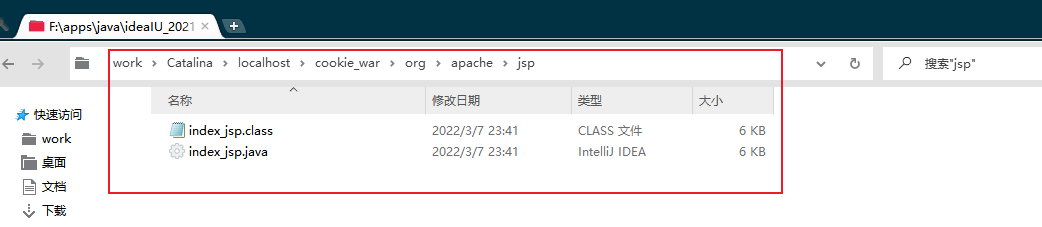
发现页面转成了java程序
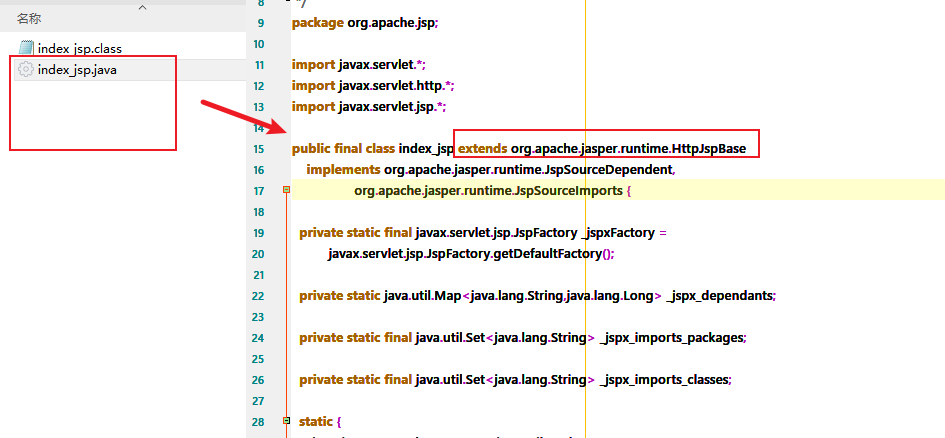
继承了HttpJspBase
HttpJspBase继承了HTTPServlet
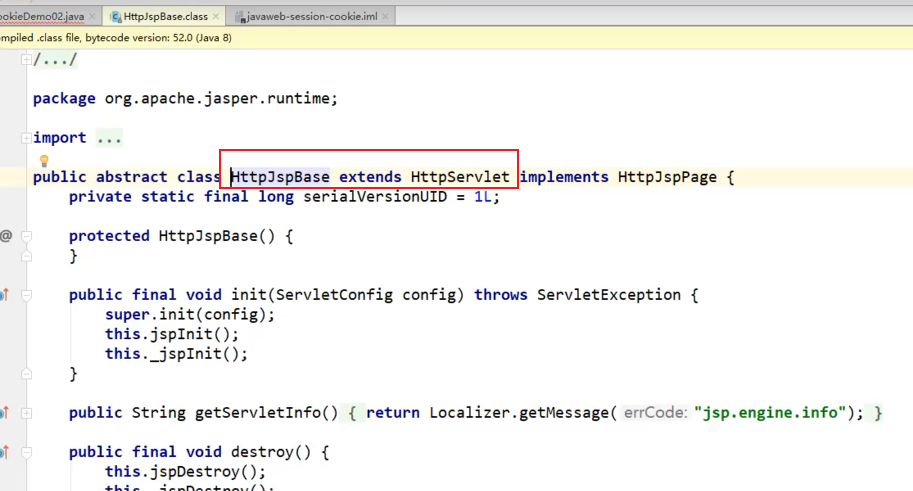
结论
- JSP最终也会被转换成为一个Java类
- JSP本质就是一个Servlet
//index_jsp.java
//初始化
public void _jspInit() {
}
//销毁
public void _jspDestroy() {
}
//jsp服务
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)
-
判断请求
-
内置一些对象
final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; //页面上下文 javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null; //Session final javax.servlet.ServletContext application; //applicationContext final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config; //config javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null; //out final java.lang.Object page = this; //page HttpServletRequest request //请求 HttpServletResponse response //响应 -
输出页面前增加的代码
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8"); //设置响应页面类型 pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response, null, true, 8192, true); _jspx_page_context = pageContext; application = pageContext.getServletContext(); config = pageContext.getServletConfig(); session = pageContext.getSession(); out = pageContext.getOut(); _jspx_out = out; -
以上的这些对象以后可以在JSP页面中直接使用
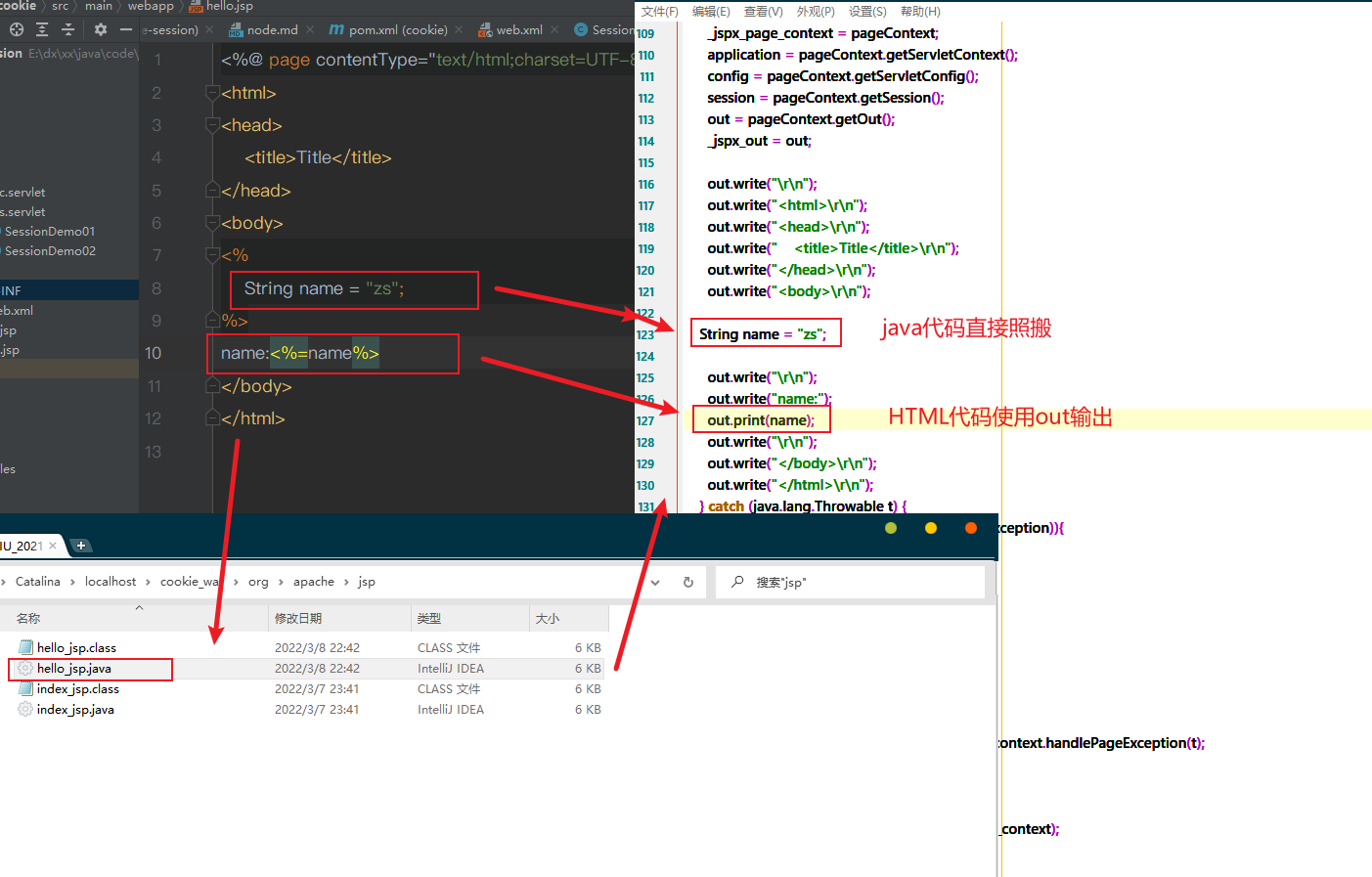
jsp里的java代码
只要是java代码就原封不懂的输出
如果是HTML代码就会被转换为:out.write("<html>\r\n");格式输出到前端
8.3.JSP基础语法
任何语言都有自己的语法,JAVA中有。JSP作为java技术的一种应用,它拥有一些自己扩充的语法(了解,知道
即可!),Java所有语法都支持!
JSP表达式
<%--JSP表达式
作用:用来将程序的输出,输出到客户端
<%=变量或者表达式%>
--%>
<%= new java.util. Date ()%>
jsp脚本片段
<%--jsp脚本片段--%>
<%
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <=100 ; i++) {
sum+=i;
}
out.println("<h1>sum="+sum+"</h1>");
%>
<%
int x = 10;
out.println(x);
%>
<p>这是一个JSP文档</p>
<%
int y = 2;
out. println(y);
%>
<hr>
<%--在代码族入HTML元素--%>
<%
for (int i = e; i < 5; i++) f
<h1>Hello, World <%=i%> </h1>
%>
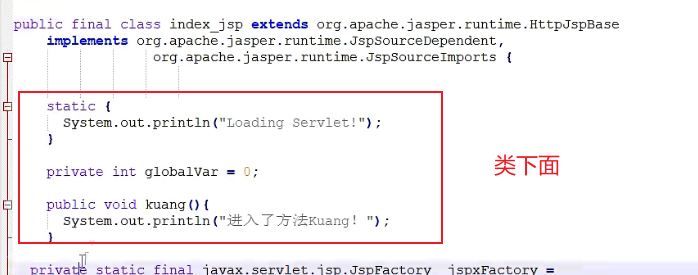
JSP声明
<%!
static {
System.out.println("Loading Servlet!");
}
private int globalVar = 9;
public void kuang(){
System.out.println("进入了方法Kuang! ");
}
%>
JSP声明: 会被编译到jspjava类中, 作用域高一些
其他: 会被生成到_JSPService方法中
8.4JSP指令
跳转错误页面 : jsp
<%@page errorPage="error/500.jsp" %>
web.xml
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/error/404. jsp</location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<error-code>500</error-code>
<location>/error/500.jsp</location>
</error-page>
include , 添加页面
<%--@incLude会将两个页面合二为---%>
<%@include file="common/header.jsp"%>
<h1>网页主体</h1>
<%@include file="common/footer.jsp"%>
<hr>
<%--jSP标签
jsp:include:拼接页面,本质还是三个
<jsp:include page="/common/header.jsp"/>
<h1>网页主体</h1>
<jsp:include page="/common/footer.jsp"/>
8.5.九大内置对象
- PageContext 存东西
- Request 存东西
- Response
- Session 存东西
- Application------ServletContext 存东西
- config -----ServletConfig
- out
- page
- exception
//保存的数据只在一个页面有效
pageContext.setAttribute("name1","zs1");
//只在一次请求中有效, 请求转发会携带此数据
request.setAttribute("name2","zs2");
//只在一次会话中有效, 打开浏览器到关闭浏览器
session.setAttribute("name3","zs3");
//只在服务器中有效, 从打开服务器到关闭服务器
application.setAttribute("name4","zs4");
- request:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完就没用了,如:新闻,用户看完没用的。
- session:客户端向服务器发送请求,产生的数据,用户看完一会还有用,如:购物车;
- application:客户端先服务器发送请求,产生的数据,一个用户用完了,其他用户还可以使用,如:聊天数据
<%-- 内置对象 --%>
<%-- 存储属性 --%>
<%
// 保存的数据只在一个页面有效
pageContext.setAttribute("name1", "狂神1号");
// 作用域设置为sessiong
// pageContext.setAttribute("name1", "狂神1号",PageContext.SESSION_SCOPE);
// 保存的数据只在一次请求中有效,请求转发会携带这个数据
request.setAttribute("name2", "狂神2号");
// 保存的数据只在一次会话中有效,从打开浏览器到关闭浏览器
session.setAttribute("name3", "狂神3号");
// 保存的数据在服务器中有效,从打开服务器到关闭服务器
application.setAttribute("name4", "狂神4号");
%>
<%-- 通过pageContext取出保存的值,通过寻找的方式来
从底层到高层
--%>
<%
// request.getAttribute("");
String name1 = (String) pageContext.getAttribute("name1");
String name2 = (String) pageContext.getAttribute("name2");
String name3 = (String) pageContext.getAttribute("name3");
String name4 = (String) pageContext.getAttribute("name4");
String name5 = (String) pageContext.getAttribute("name5"); // 不存在
// 直接转发过来,request中的数据也会被转发过来,可以取到2号
pageContext.forward("pageContextDemo02.jsp");
%>
<%-- 使用EL表达式输出 ${} --%>
<h1>取出的值为: </h1>
<h3>${name1}</h3>
<h3>${name2}</h3>
<h3>${name3}</h3>
<h3>${name4}</h3>
<h3>${name5}</h3>
<%-- 会显示null --%>
<h3><%= name5%>
</h3>
<%--
scope 设置作用域
public void setAttribute(String name, Object attribute, int scope) {
switch(scope) {
case 1:
this.mPage.put(name, attribute);
break;
case 2:
this.mRequest.put(name, attribute);
break;
case 3:
this.mSession.put(name, attribute);
break;
case 4:
this.mApp.put(name, attribute);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bad scope " + scope);
}
}
--%>
8.6.JSP标签、JSTL标签、EL表达式
EL表达式:${}
- 获取数据
- 执行运算
- 获取web开发的常用对象
- 调用Java方法(一般不用)
JSP标签:<jsp:xxx>
-
include标签 -
forward转发标签
- 转发标签中可以使用
param参数标签携带参数 - 读取:
request.getParameter("key")
<%--jsp:include 包括标签--%> <jsp:include page="common/header.jsp"></jsp:include> <h3>body</h3> <%-- jsp:forward 转发标签 --%> <jsp:forward page="jsptag2.jsp"> <%-- param 可以携带参数 --%> <jsp:param name="name" value="Kuang"/> <jsp:param name="age" value="12"/> </jsp:forward> <%--取出参数--%> name: <%= request.getParameter("name")%> age: <%= request.getParameter("age")%> - 转发标签中可以使用
JSTL:JSP标准标签库
为了弥补HTML标签的不足,自定义很多标签,标签功能和Java代码一样。
使用:引入对应的taglib,然后即可使用对应标签。 <%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
注意引入时要把对应的jstl和standard的jar包复制到tomcat的lib中,不然会报错。
-
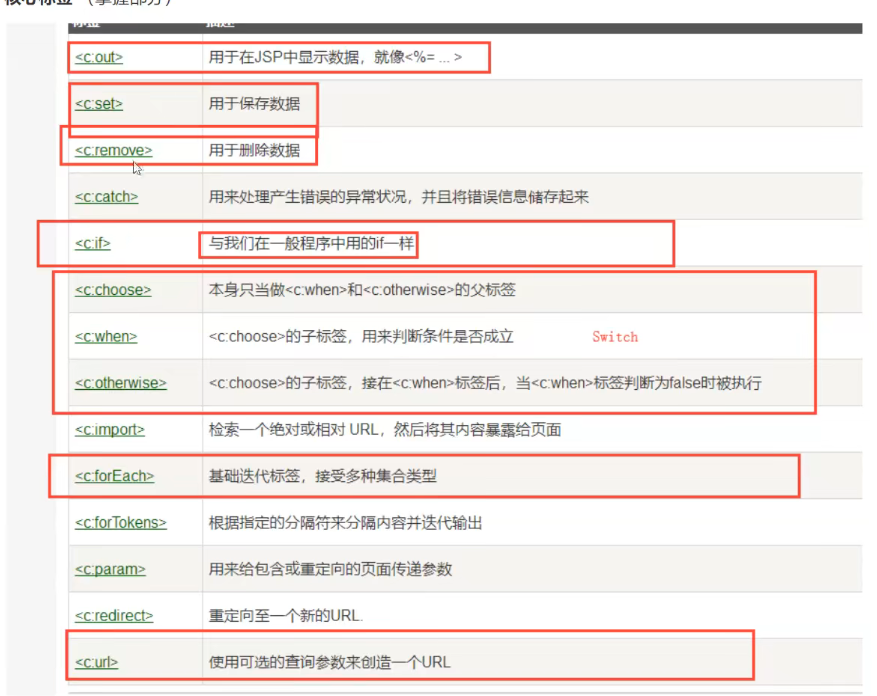
核心标签(掌握部分)
-
<c:out>在JSP中显示数据,就像<%= ... > -
<c:set>保存数据 -
<c:remove>删除数据 -
<c:if>程序中if一样 -
<c:chooose>作为
<c:when>和
<c:otherwise>的父标签
<c:when>判断条件是否成立<c:otherwise>when标签判断false时执行
-
<c:forEach>基础迭代标签,接受多种集合类型 -
<c:url>使用可选的查询参数创造一个URL
<form action="coreif.jsp" method="get"> <%--EL表达式获取表单中的数据 ${param.参数名} --%> <input type="text" name="username" value="${param.username}"> <input type="submit" value="登录"> </form> <%--判断提交的用户名--%> <%-- <%--%> <%-- if (request.getParameter("username").equals("admin")) {--%> <%-- out.println("登陆成功");--%> <%-- }--%> <%-- %>--%> <c:if test="${param.username=='admin'}" var="isAdmin"> <c:out value="登录成功"/> </c:if> <c:out value="${isAdmin}"/> <% ArrayList<String> peoples = new ArrayList<>(); peoples.add(0, "p0"); peoples.add(1, "p1"); peoples.add(2, "p2"); peoples.add(3, "p3"); peoples.add(4, "p4"); request.setAttribute("list", peoples); %> <%-- var, 每次遍历出来的变量 items:要便利的对象 --%> <c:forEach var="peoples" items="${list}" begin="1" end="3" step="1"> <c:out value="${peoples}"/><br/> </c:forEach> -
-
格式化标签
-
SQL标签
-
XML标签
核心标签





 本文详细介绍了JSP的概念、工作原理,包括JSP如何转化为Servlet执行。深入讲解了JSP的基础语法,如表达式、脚本片段和声明,并探讨了JSP指令如errorPage和include的应用。此外,还讨论了JSP的九大内置对象,如PageContext、Request、Session等,以及如何使用它们来存储和检索数据。最后,文章提到了EL表达式、JSP标签和JSTL的核心标签,如<c:out>、<c:set>等,展示了它们在数据展示和操作中的重要作用。
本文详细介绍了JSP的概念、工作原理,包括JSP如何转化为Servlet执行。深入讲解了JSP的基础语法,如表达式、脚本片段和声明,并探讨了JSP指令如errorPage和include的应用。此外,还讨论了JSP的九大内置对象,如PageContext、Request、Session等,以及如何使用它们来存储和检索数据。最后,文章提到了EL表达式、JSP标签和JSTL的核心标签,如<c:out>、<c:set>等,展示了它们在数据展示和操作中的重要作用。
















 7692
7692

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








