一、NSInvocation的基本用法
在 iOS中可以直接调用某个对象的消息方式有两种:
一种是performSelector:withObject;
再一种就是NSInvocation。
第一种方式比较简单,能完成简单的调用。但是对于>2个的参数或者有返回值的处理,那performSelector:withObject就显得有点有心无力了,那么在这种情况下,我们就可以使用NSInvocation来进行这些相对复杂的操作
NSInvocation的基本使用
方法签名类
// 方法签名中保存了方法的名称/参数/返回值,协同NSInvocation来进行消息的转发
// 方法签名一般是用来设置参数和获取返回值的, 和方法的调用没有太大的关系
//1、根据方法来初始化NSMethodSignature
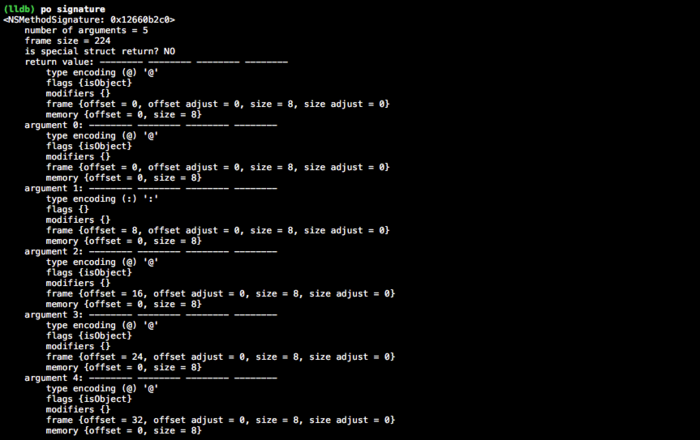
NSMethodSignature *signature = [ViewController instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:@selector(run:)];
根据方法签名来创建NSInvocation对象
// NSInvocation中保存了方法所属的对象/方法名称/参数/返回值
//其实NSInvocation就是将一个方法变成一个对象
//2、创建NSInvocation对象
NSInvocation *invocation = [NSInvocation invocationWithMethodSignature:signature];
//设置方法调用者
invocation.target = self;
//注意:这里的方法名一定要与方法签名类中的方法一致
invocation.selector = @selector(run:);
NSString *way = @"byCar";
//这里的Index要从2开始,以为0跟1已经被占据了,分别是self(target),selector(_cmd)
[invocation setArgument:&way atIndex:2];
//3、调用invoke方法
[invocation invoke];
//实现run:方法
- (void)run:(NSString *)method{
}
优化
但是上述方法有很多弊端,首先我们来一一解决
1、如果调用的方法不存在
//此时我们应该判断方法是否存在,如果不存在这抛出异常
if (signature == nil) {
//aSelector为传进来的方法
NSString *info = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@方法找不到", NSStringFromSelector(aSelector)];
[NSException raise:@"方法调用出现异常" format:info, nil];
}
2、方法的参数个数与外界传进来的参数数组元素个数不符
//此处不能通过遍历参数数组来设置参数,因为外界传进来的参数个数是不可控的
//因此通过numberOfArguments方法获取的参数个数,是包含self和_cmd的,然后比较方法需要的参数和外界传进来的参数个数,并且取它们之间的最小值
NSUInteger argsCount = signature.numberOfArguments - 2;
NSUInteger arrCount = objects.count;
NSUInteger count = MIN(argsCount, arrCount);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
id obj = objects[i];
// 判断需要设置的参数是否是NSNull, 如果是就设置为nil
if ([obj isKindOfClass:[NSNull class]]) {
obj = nil;
}
[invocation setArgument:&obj atIndex:i + 2];
}
```
#### 3、判断当前调用的方法是否有返回值
```objc
//方法一:
id res = nil;
if (signature.methodReturnLength != 0) {//有返回值
//将返回值赋值给res
[invocation getReturnValue:&res];
}
return res;
//方法二:
//可以通过signature.methodReturnType获得返回的类型编码,因此可以推断返回值的具体类型在消息转发中提到过NSInvocation这个类,这里说一下我所理解的NSInvocation。NSInvocation是命令模式的一种实现,它包含选择器、方法签名、相应的参数以及目标对象。所谓的方法签名,即方法所对应的返回值类型和参数类型。当NSInvocation被调用,它会在运行时通过目标对象去寻找对应的方法,从而确保唯一性,可以用[receiver message]来解释。实际开发过程中直接创建NSInvocation的情况不多见,这些事情通常交给系统来做。比如bang的JSPatch中arm64方法替换的实现就是利用runtime消息转发最后一步中的NSInvocation实现的。
正文
基于这种命令模式,可以利用NSInvocation调用任意SEL甚至block。
SEL
- (id)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector withArguments:(NSArray *)arguments {
if (aSelector == nil) return nil;
NSMethodSignature *signature = [[self class] instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
NSInvocation *invocation = [NSInvocation invocationWithMethodSignature:signature];
invocation.target = self;
invocation.selector = aSelector;
// invocation 有2个隐藏参数,所以 argument 从2开始
if ([arguments isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]]) {
NSInteger count = MIN(arguments.count, signature.numberOfArguments - 2);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
const char *type = [signature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:2 + i];
// 需要做参数类型判断然后解析成对应类型,这里默认所有参数均为OC对象
if (strcmp(type, "@") == 0) {
id argument = arguments[i];
[invocation setArgument:&argument atIndex:2 + i];
}
}
}
[invocation invoke];
id returnVal;
if (strcmp(signature.methodReturnType, "@") == 0) {
[invocation getReturnValue:&returnVal];
}
// 需要做返回类型判断。比如返回值为常量需要包装成对象,这里仅以最简单的`@`为例
return returnVal;
}
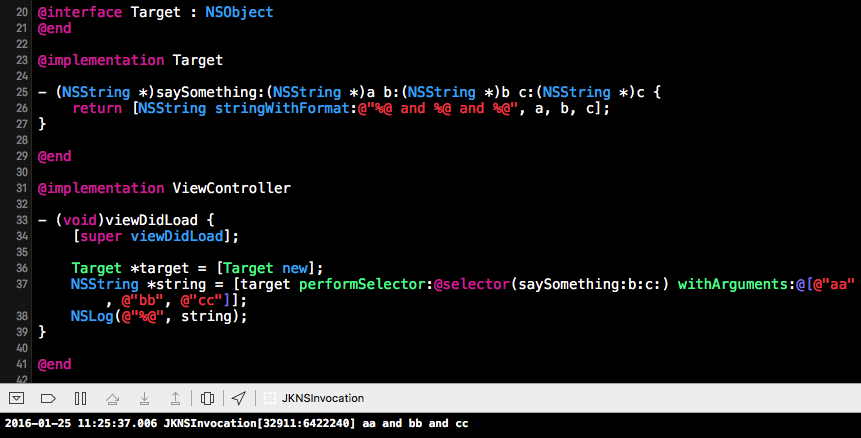
NSObject
中的
performSelector
相比,没有了参数个数限制。

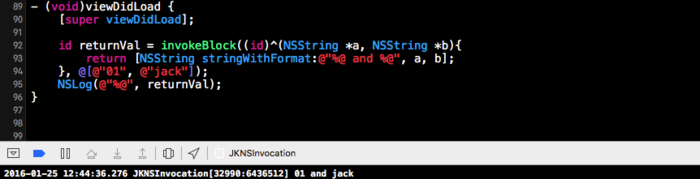
block
static id invokeBlock(id block ,NSArray *arguments) {
if (block == nil) return nil;
id target = [block copy];
const char *_Block_signature(void *);
const char *signature = _Block_signature((__bridge void *)target);
NSMethodSignature *methodSignature = [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:signature];
NSInvocation *invocation = [NSInvocation invocationWithMethodSignature:methodSignature];
invocation.target = target;
// invocation 有1个隐藏参数,所以 argument 从1开始
if ([arguments isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]]) {
NSInteger count = MIN(arguments.count, methodSignature.numberOfArguments - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
const char *type = [methodSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:1 + i];
NSString *typeStr = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:type];
if ([typeStr containsString:@"\""]) {
type = [typeStr substringToIndex:1].UTF8String;
}
// 需要做参数类型判断然后解析成对应类型,这里默认所有参数均为OC对象
if (strcmp(type, "@") == 0) {
id argument = arguments[i];
[invocation setArgument:&argument atIndex:1 + i];
}
}
}
[invocation invoke];
id returnVal;
const char *type = methodSignature.methodReturnType;
NSString *returnType = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:type];
if ([returnType containsString:@"\""]) {
type = [returnType substringToIndex:1].UTF8String;
}
if (strcmp(type, "@") == 0) {
[invocation getReturnValue:&returnVal];
}
// 需要做返回类型判断。比如返回值为常量需要包装成对象,这里仅以最简单的`@`为例
return returnVal;
}

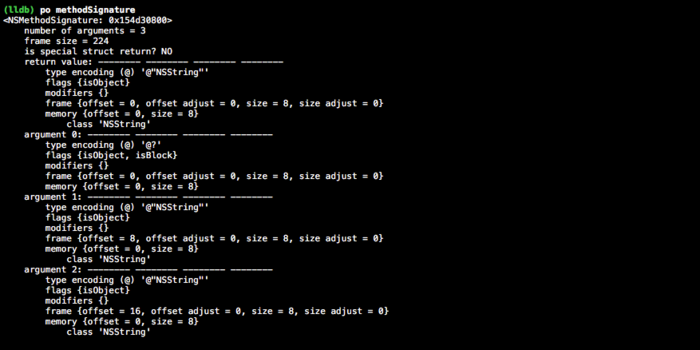
SEL与block比较
- invocation
SEL既有target也有selector,block只有target - signature
SEL有两个隐藏参数,类型均为类型为@@和:,分别对应target和selector。block有一个隐藏参数,类型为@?,对应target且block的target为他本身 - type
以OC对象为例:SEL的type为@,block的type会跟上具体类型,如@"NSString"
再谈block
在block的invocation中有这样的代码
const char *_Block_signature(void *);
const char *signature = _Block_signature((__bridge void *)target);
_Block_signature其实是JavaScriptCore/ObjcRuntimeExtras.h中的私有API(这个头文件并没有公开可以戳这里查看)
既然苹果把API封了,那就自己实现咯,万能的github早有答案CTObjectiveCRuntimeAdditions
把CTBlockDescription.h和CTBlockDescription.m拖到项目中,代码这样写
static id invokeBlock(id block ,NSArray *arguments) {
if (block == nil) return nil;
id target = [block copy];
CTBlockDescription *ct = [[CTBlockDescription alloc] initWithBlock:target];
NSMethodSignature *methodSignature = ct.blockSignature;
NSInvocation *invocation = [NSInvocation invocationWithMethodSignature:methodSignature];
invocation.target = target;
// invocation 有1个隐藏参数,所以 argument 从1开始
if ([arguments isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]]) {
NSInteger count = MIN(arguments.count, methodSignature.numberOfArguments - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
const char *type = [methodSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:1 + i];
NSString *typeStr = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:type];
if ([typeStr containsString:@"\""]) {
type = [typeStr substringToIndex:1].UTF8String;
}
// 需要做参数类型判断然后解析成对应类型,这里默认所有参数均为OC对象
if (strcmp(type, "@") == 0) {
id argument = arguments[i];
[invocation setArgument:&argument atIndex:1 + i];
}
}
}
[invocation invoke];
id returnVal;
const char *type = methodSignature.methodReturnType;
NSString *returnType = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:type];
if ([returnType containsString:@"\""]) {
type = [returnType substringToIndex:1].UTF8String;
}
if (strcmp(type, "@") == 0) {
[invocation getReturnValue:&returnVal];
}
// 需要做返回类型判断。比如返回值为常量需要包装成对象,这里仅以最简单的`@`为例
return returnVal;
}
运行结果
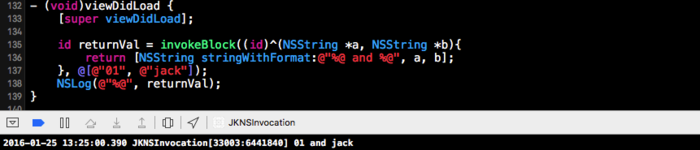





 本文详细介绍了iOS中NSInvocation的使用,包括基本用法、方法签名类、创建NSInvocation对象,以及针对方法不存在和参数不符问题的优化。文中还探讨了SEL与block的区别,并提供了使用block的invocation实现方式。
本文详细介绍了iOS中NSInvocation的使用,包括基本用法、方法签名类、创建NSInvocation对象,以及针对方法不存在和参数不符问题的优化。文中还探讨了SEL与block的区别,并提供了使用block的invocation实现方式。
















 5731
5731










