AIDL 简介
Android 接口定义语言,利用它定义客户端与服务均认可的编程接口,以便二者进行进程间通信 (IPC) 。AIDL 使用实质就是对 Binder 机制的封装,主要就是将远程服务端的 Binder 封装成一个代理对象 Proxy,从用户的角度看,就像是客户端直接调用了服务端的代码。
AIDL 用例
服务端和客户端都要添加下面相同的 AIDL 文件和 Parcelable 数据类型的文件。
// IMyAidlInterface.aidl
// 必须导包,在同一文件夹也需要导包
import com.example.demo.ParcelableData;
// 服务端接口
interface IMyAidlInterface {
// 参数是基础数据类型的方法
void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat,
double aDouble, String aString);
// 参数是 in 类型的方法
void transInData(in ParcelableData data);
// 参数是 out 类型的方法
// 注意含有 out 时 ParcelableData 类需要实现 readFromParcel() 方法
ParcelableData transOutData(out ParcelableData data);
// 参数是 inout 类型的方法
// 注意含有 out 时 ParcelableData 类需要实现 readFromParcel() 方法
ParcelableData transInOutData(inout ParcelableData data);
// 返回值为非基础数据类型的方法
List<ParcelableData> getList();
// 设置客户端接口,用于服务端与客户端通信
void setClientInterface(IClientInterface callback);
}
// ICallback.aidl
// 客户端接口
interface IClientInterface {
void onResult(in ParcelableData data);
}
// ParcelableData.aidl
parcelable ParcelableData;
// ParcelableData.java
public class ParcelableData implements Parcelable {
private String name;
private int age;
public ParcelableData() {}
protected ParcelableData(Parcel in) {
name = in.readString();
age = in.readInt();
}
public static final Creator<ParcelableData> CREATOR = new Creator<ParcelableData>() {
@Override
public ParcelableData createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new ParcelableData(in);
}
@Override
public ParcelableData[] newArray(int size) {
return new ParcelableData[size];
}
};
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(name);
dest.writeInt(age);
}
public void readFromParcel(Parcel reply) {
name = reply.readString();
age = reply.readInt();
}
}
服务端
// RemoteService.java
public class RemoteService extends Service {
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new MyStub();
}
static class MyStub extends IMyAidlInterface.Stub {
...
}
}
// AndroidManifest.xml
<service
android:name=".RemoteService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.demo.RemoteService"/>
</intent-filter>
</service>
// 启动服务
startService(new Intent(this, RemoteService.class))
客户端
// 绑定服务
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setPackage("com.example.demo");
intent.setAction("com.example.demo.RemoteService");
bindService(intent, new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
IMyAidlInterface iInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
// 设置客户端接口
try {
iInterface.setClientInterface(new IClientInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public void onResult(ParcelableData data) {}
});
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {}
}, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
定向标签 Directional Tag
| DirectionalTag | 定义 | 图示 |
|---|---|---|
| in | 传入类型参数,数据会从调用方传到被调方,被调方调用结束后不会把数据写回参数 |  |
| out | 传出类型参数,数据不会从调用方传到被调方,被调方调用结束后会把数据写回参数 | 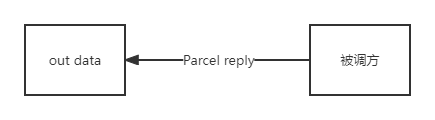 |
| inout | 传入传出类型参数,数据会从调用方传到被调方,被调方调用结束后会把数据写回参数 | 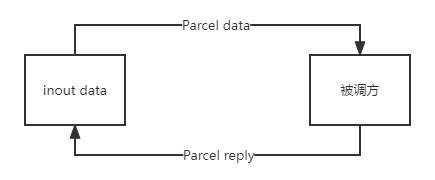 |
上面强调调用方和被调方是为了和客户端和服务端区分开,因为客户端和服务端是可以相互通信的,当客户端调用服务端的方法时,客户端时调用方;当服务端调用客户端的方法时,服务端是调用方。
为什么需要 Directional Tag?
因为跨进程中的数据不能同步的修改,这个设计是为了减少数据传递的次数,因为这个数据的传递是比较消耗性能的。
基本数据类型及String不能是 out 类型,只能是 in 类型,所以可以省略。这个也很好理解,基本类型的数据是直接把数据赋值到参数,所以在方法内更改参数值不会影响到外面的数据,所以无法写回传参,只能作为传入类型参数。
源码分析
先来了解下 AIDL 文件编译后生成的两个重要的类:
| class | desc |
|---|---|
| Stub | 接收端返回的实现 AIDL 接口的 Binder。简单理解为被调方。 |
| Proxy | 远程 Stub 的代理类,通过Binder机制调用到远程相应的方法。简单理解为调用方。 |
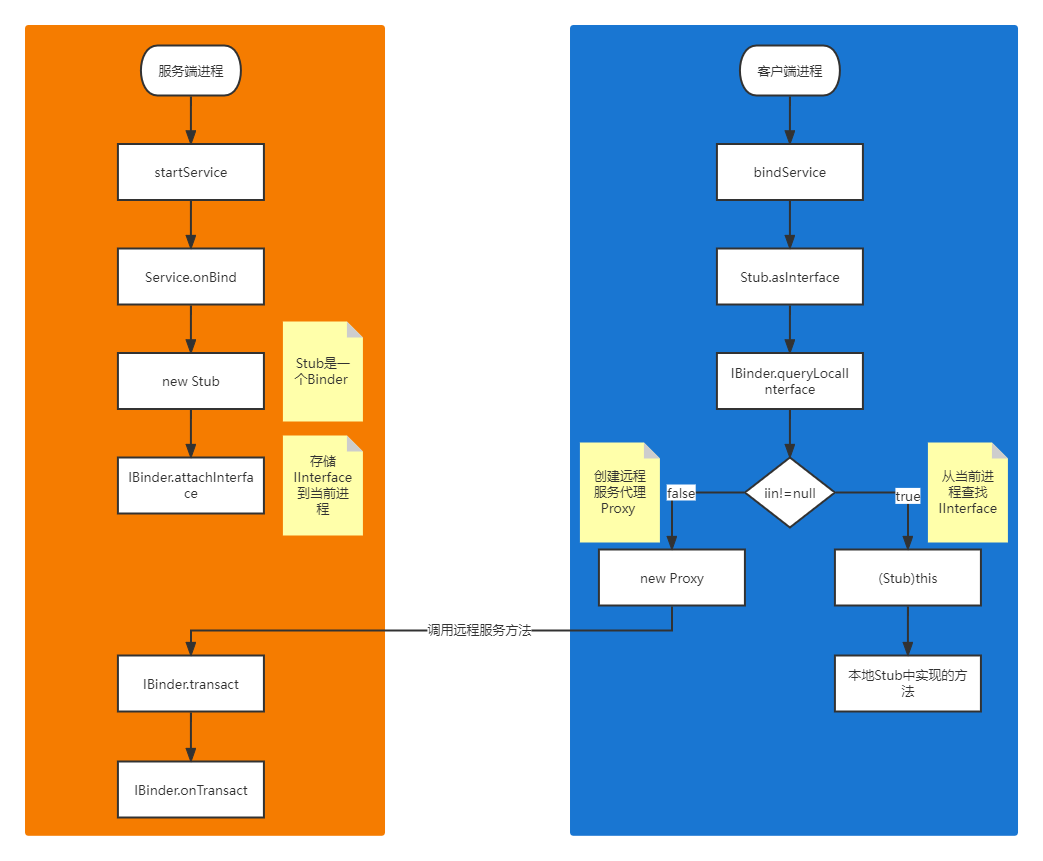
首先是服务端在 onBind() 方法中创建了一个 MyStub 继承自 Stub,看一下 Stub 的构造函数。
// IMyAidlInterface.java
public interface IMyAidlInterface extends android.os.IInterface {
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.example.demo.IMyAidlInterface {
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.example.demo.IMyAidlInterface";
/** Construct the stub at attach it to the interface. */
public Stub()
{
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
}
}
Stub 是一个 Binder 并实现了 IMyAidlInterface,IMyAidlInterface 继承了 IInterface。Stub 初始化时将 IInterface (MyStub) 保存到Binder。
然后是客户端绑定 service,获取到 service 传过来的 IBinder,然后调用 Stub.asInterface() 方法 。
//IMyAidlInterface.Stub.java
public static com.example.demo.IMyAidlInterface asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.example.demo.IMyAidlInterface))) {
return ((com.example.demo.IMyAidlInterface) iin);
}
return new com.example.demo.IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
该方法调用 IBinder 的 queryLocalInterface() 方法查找有没有 IInterface,如果能获取到,说明是本地进程,直接将 IBinder 中保存的 IInterface (MyStub) 返回,调用方法时将直接调用本地 MyStub 中实现的方法;如果获取不到,说明是远端进程,需要创建一个 Proxy 返回。下面看一下 Proxy 的源码。
// IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy.java
private static class Proxy implements com.example.demo.IMyAidlInterface {
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
// 参数是基础数据类型的方法
@Override
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, java.lang.String aString) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(anInt);
_data.writeLong(aLong);
_data.writeInt(((aBoolean) ? (1) : (0)));
_data.writeFloat(aFloat);
_data.writeDouble(aDouble);
_data.writeString(aString);
boolean _status = mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_basicTypes, _data, _reply, 0);
if (!_status && getDefaultImpl() != null) {
getDefaultImpl().basicTypes(anInt, aLong, aBoolean, aFloat, aDouble, aString);
return;
}
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
}
Proxy 是远程服务的代理类,继承 IMyAidlInterface 接口,方法实现是通过调用远程 IBinder 的 transact() 方法,参数及返回值以Parcel的形式传入,并传入调用远程方法的 type。可以看出 AIDL 其实是对 IBinder 的一层封装,底层是用了 IBinder 和 Parcel 的跨进程通信的能力。
IBinder 的 transact() 方法会调用 onTransact () 方法。
// IMyAidlInterface.Stub.java
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
java.lang.String descriptor = DESCRIPTOR;
switch (code) {
case TRANSACTION_basicTypes: {
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
int _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readInt();
long _arg1;
_arg1 = data.readLong();
boolean _arg2;
_arg2 = (0 != data.readInt());
float _arg3;
_arg3 = data.readFloat();
double _arg4;
_arg4 = data.readDouble();
java.lang.String _arg5;
_arg5 = data.readString();
this.basicTypes(_arg0, _arg1, _arg2, _arg3, _arg4, _arg5);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
default: {
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
}
}
该方法根据方法类型,获取参数并执行相应的方法,返回值通过reply参数返回,这样就实现了调用远端 MyStub 中实现的方法。
整个 AIDL 进程通信调用流程如下图所示:
in 定向参数源码
// IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy.java
@Override
public void transInData(com.example.demo.ParcelableData data) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
if ((data != null)) {
_data.writeInt(1);
data.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
} else {
_data.writeInt(0);
}
boolean _status = mRemote.transact(IMyAidlInterface.Stub.TRANSACTION_transInData, _data, _reply, 0);
if (!_status && getDefaultImpl() != null) {
getDefaultImpl().transInData(data);
return;
}
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
传入的参数 data 的数据会写入到远程方法中。
// IMyAidlInterface.Stub.java
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case TRANSACTION_transInData: {
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
com.example.demo.ParcelableData _arg0;
if ((0 != data.readInt())) {
_arg0 = com.example.demo.ParcelableData.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
} else {
_arg0 = null;
}
this.transInData(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
}
}
远程服务接收传入的 data 数据,被调用方法执行时传入该参数。
out 定向参数源码
// IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy.java
@Override
public void transOutData(com.example.demo.ParcelableData data) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
boolean _status = mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_transOutData, _data, _reply, 0);
if (!_status && getDefaultImpl() != null) {
getDefaultImpl().transOutData(data);
return;
}
_reply.readException();
if ((0 != _reply.readInt())) {
data.readFromParcel(_reply);
}
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
传入的参数 data 调用远程方法时没有传入,调用完远程方法后,将 reply 重新写入 data。
// IMyAidlInterface.Stub.java
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case TRANSACTION_transOutData: {
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
com.example.demo.ParcelableData _arg0;
_arg0 = new com.example.demo.ParcelableData();
this.transOutData(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
if ((_arg0 != null)) {
reply.writeInt(1);
_arg0.writeToParcel(reply, android.os.Parcelable.PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE);
} else {
reply.writeInt(0);
}
return true;
}
}
}
远程服务创建了一个新的 ParcelableData 传入被调用方法,方法执行结束后,将 ParcelableData 写入 reply。
inout 定向参数源码
// IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy.java
@Override
public void transInOutData(com.example.demo.ParcelableData data) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
if ((data != null)) {
_data.writeInt(1);
data.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
} else {
_data.writeInt(0);
}
boolean _status = mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_transInOutData, _data, _reply, 0);
if (!_status && getDefaultImpl() != null) {
getDefaultImpl().transInOutData(data);
return;
}
_reply.readException();
if ((0 != _reply.readInt())) {
data.readFromParcel(_reply);
}
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
传入的参数 data 的数据会写入到远程方法中,远程方法执行完后,如果 reply 不为空,会将 reply 重新写入 data。
// IMyAidlInterface.Stub.java
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case TRANSACTION_transInOutData: {
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
com.example.demo.ParcelableData _arg0;
if ((0 != data.readInt())) {
_arg0 = com.example.demo.ParcelableData.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
} else {
_arg0 = null;
}
this.transInOutData(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
if ((_arg0 != null)) {
reply.writeInt(1);
_arg0.writeToParcel(reply, android.os.Parcelable.PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE);
} else {
reply.writeInt(0);
}
return true;
}
}
}
远程服务接收传入的 data 数据,执行完被调用的方法后,将改变后的 data 数据写入 reply。






















 1632
1632

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








