本次编译环境为vs2022
文章目录
前言
在较为浅显的学完C语言后 就要开始我们数据结构的路了 本次顺序表需要的知识 有指针传地址 动态内存管理 结构体的使用这三大部分 其他的基础知识需要自备了
顺序表专题
一.了解顺序表
在写之前 我们需要了解顺序表其实有两种:
1.静态顺序表 里面的数据内容 是不会动态改变的 这就会造成有些人 创造的时候存在空间不够用 或者空间浪费的问题 没有最大程度的使用资源
2.动态顺序表 顾名思义就是可以动态改变内存 供我们更好的使用 让空间尽量减少浪费 有利于公司的最大收益率
二.静态顺序表的书写
首先是创造三个文件 如图所示
接下来书写我们的代码
typedef int SLDateType;
#define N 4
typedef struct Seqlist
{
SLDateType arr[N];
SLDateType size;
SLDateType capacity;
}SL;
这便是简单的静态顺序表 通过宏来给定顺序表中的数组大小 即空间
三.动态顺序表的书写及实现
1.书写动态顺序表
typedef int SLDateType;
typedef struct Seqlist
{
SLDateType *arr;
SLDateType size;//数据个数
SLDateType capacity;//空间大小
}SL;
这便是我们的动态顺序表 区别其实不大 主要是 删除宏的使用 改为用指针传递
让我们能用动态内存管理来实现扩容
后面我们将通过函数的一个个实现来完成动态顺序表的实现
2.顺序表的定义和销毁
定义即是给定结构体空间和大小 销毁则是要把开辟的动态空间还回去
所以这两步必不可少
1.定义
首先要在头文件中给到定义 后面到 11.19.c文件中去实现
给到实现代码
void SLInit(SL* ps)//定义
{
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
这里使用指针来接受 ps本质上是数组的地址传递 所以给到arr空指针 给到空间为0这是初始化想看到的结果
2.销毁
给到实现代码
void SLDestory(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->arr != NULL)
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
这里我们要看到 有个判断过程 就是要看 arr是否为空指针 不是的话 我们就要销毁释放 后给到初始化
3.顺序表的尾插头插 尾删头删
1.尾插 头插
尾插顾名思义就是 在顺序表的尾部插入 但在此之前我们需要给顺序表扩容 以免数据不够 所以一个扩容代码
扩容
SLstart(SL* ps)//扩容代码
{
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)
{
//这里给到Newcapacity目的则是 因为capacity初始化为0 若 * 下去 0*n=0没有必要
int Newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
//ps->arr = (SLDateType*)realloc(ps->arr, sizeof(SLDateType))//本质上是 ps->capacity * sizeof(SLDateType)* 2
//这里最好给到一个临时变量tmp来接收 后面赋值给 arr 以免 这步错了 arr直接爆炸
int* tmp = (SLDateType*)realloc(ps->arr, Newcapacity*sizeof(SLDateType));
if (tmp == NULL)//判断临时变量 tmp是否可靠
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(1);
}
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity = Newcapacity;//新空间的扩容就完成了
}
}
这里扩容给到的就是个函数 后面会放到 头插尾插的代码中使用
一.尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLstart(ps);
ps->arr[ps->size++] = x;
}
这里给到assert断言 使用前记得先包含 #include <stdio.h>
用来判断是否为空指针
二.头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLstart(ps);
for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i-1];
}
ps->arr[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
头插与尾插最主要还是头插的 for循环 size++是为了 每次循环给前面开辟一个空间
2.尾删 头删
一.尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
ps->size--;//只需要size--来减少空间直接少个数
}
二.头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
这里头删 用for循环 慢慢的把后面的一个个放到前面去 然后通过 size–删除
本质逻辑哈哈。
3.在指定位置插入 删除 以及查找函数
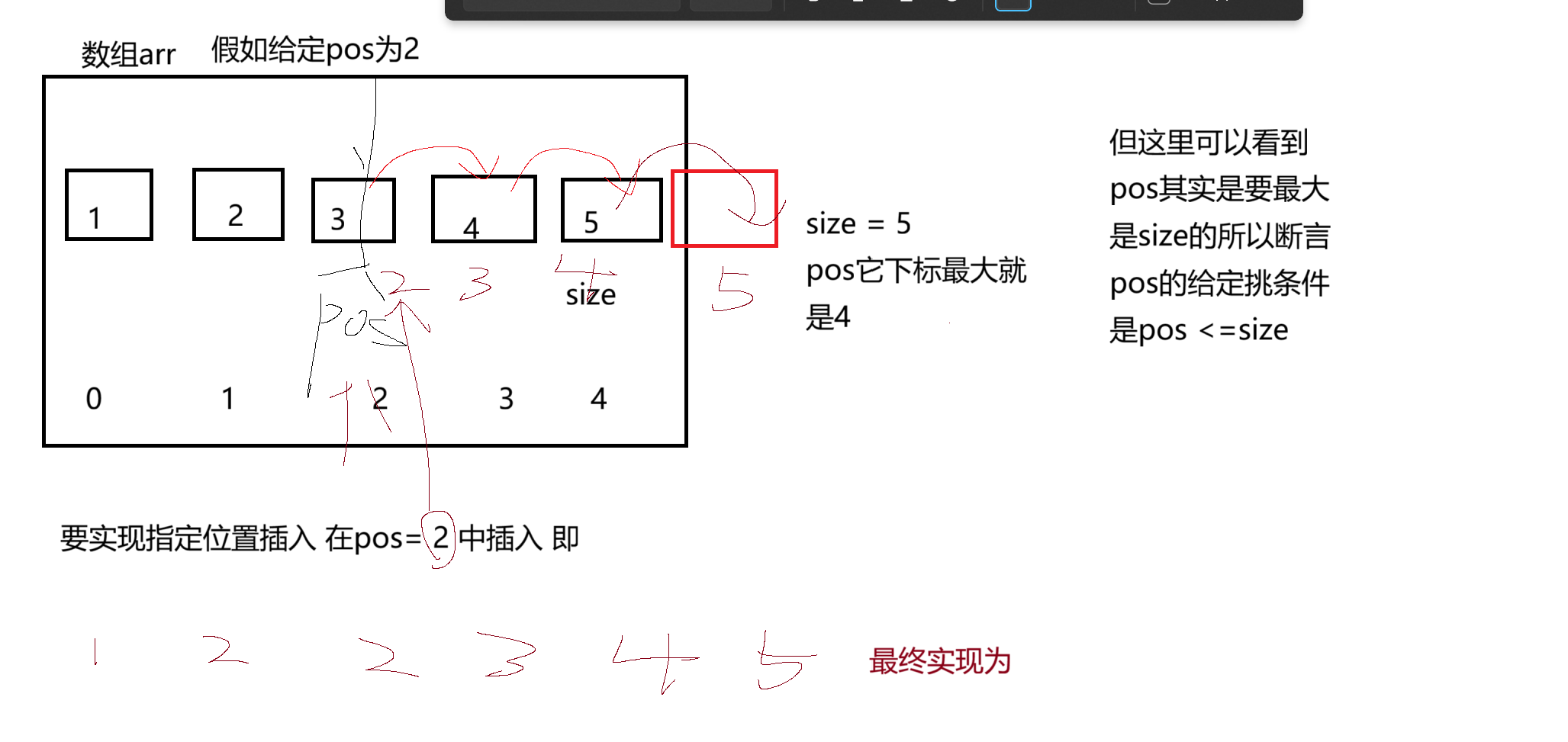
一.在指定位置插入
在指定位置插入相对于头插尾插 本质上是多一个 参数当作位置的下标来让我们插入
所以在定义函数时要多一个pos参数来当作位置
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLstart(ps);
//判断完空间够不够后 我们的目标是将pos下标的数组往后挪动给与位置给到x插入
for (int i = ps->size; i>pos; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
二.在指定位置删除
删除相对于插入是少一个结构体定义的整数的参数
其中内部循环也是大差不差 无非逻辑上有点差别 给各位以图片形式展示
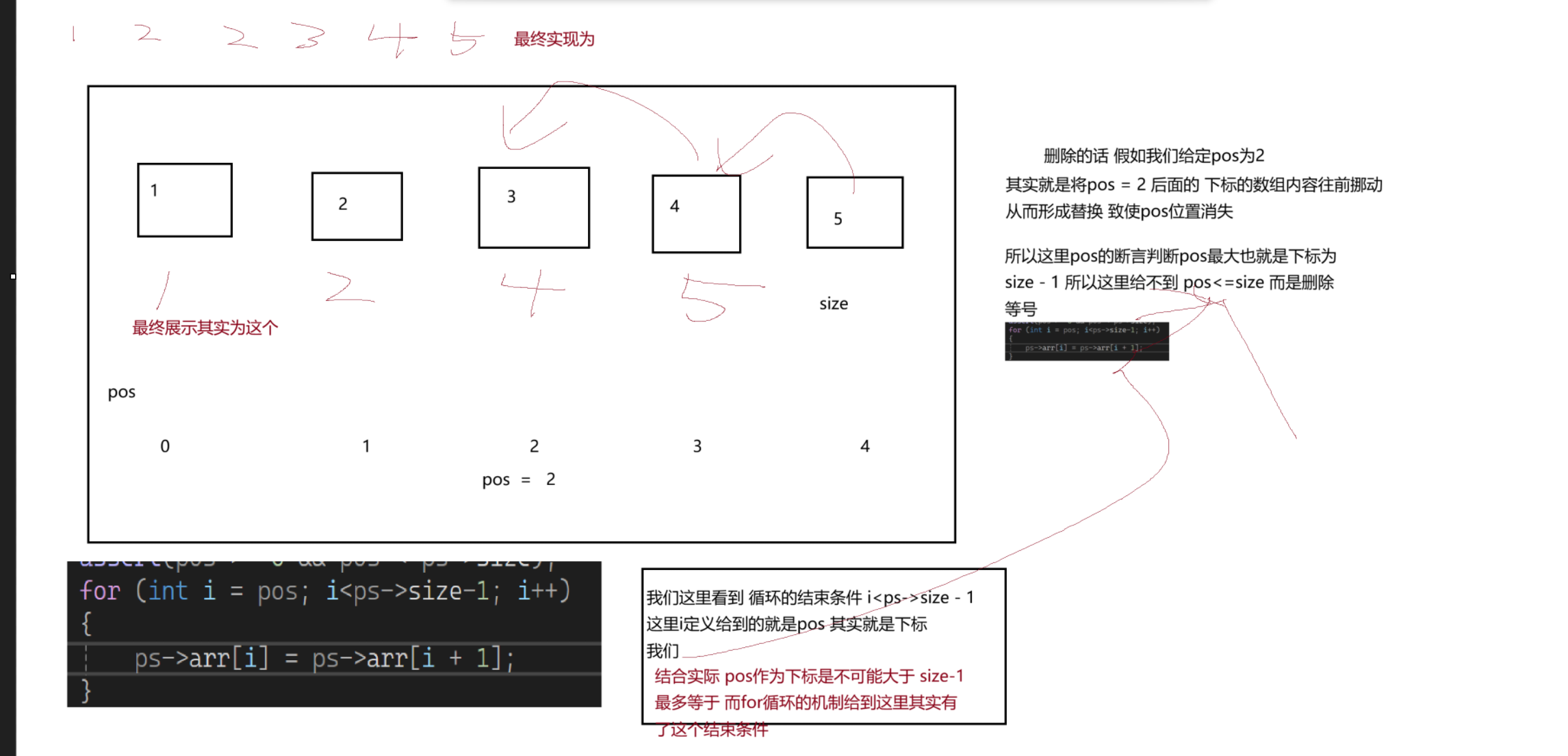
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
SLstart(ps);
for (int i = pos; i<ps->size-1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
三.查找
查找函数其实就是通过给个一个数来进行循环查找 找不到就跳出 找到了就返回该数组的下标
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
//找到了
return i;
}
}
//跳出循环就是没找到
return -1;
}
最后的打印函数就不写了 直接把原码放给大家
测试会单独出一片更加好的各位。
第一个头文件 .h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
//typedef int SLDateType;
//#define N 4
//typedef struct Seqlist
//{
// SLDateType arr[N];
// SLDateType size;
// SLDateType capacity;
//}SL;
typedef int SLDateType;
typedef struct Seqlist
{
SLDateType *arr;
SLDateType size;//数据个数
SLDateType capacity;//空间大小
}SL;
void SLPrint(ps);
void SLInit(SL* ps);//定义
void SLDestory(SL* ps);//销毁
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDateType x);//尾插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDateType x);//头插
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);//尾删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);//头删
void SLInsert(SL* ps,int pos,SLDateType x);//指定位置插入
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);//指定位置删除
int SLFind(SL* ps,SLDateType x);
第一个.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "11.19.h"
void SLInit(SL* ps)//定义
{
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
void SLDestory(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->arr != NULL)
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}
SLstart(SL* ps)//扩容代码
{
if (ps->capacity == ps->size)
{
//这里给到Newcapacity目的则是 因为capacity初始化为0 若 * 下去 0*n=0没有必要
int Newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
//ps->arr = (SLDateType*)realloc(ps->arr, sizeof(SLDateType))//本质上是 ps->capacity * sizeof(SLDateType)* 2
//这里最好给到一个临时变量tmp来接收 后面赋值给 arr 以免 这步错了 arr直接爆炸
int* tmp = (SLDateType*)realloc(ps->arr, Newcapacity*sizeof(SLDateType));
if (tmp == NULL)//判断临时变量 tmp是否可靠
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(1);
}
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity = Newcapacity;//新空间的扩容就完成了
}
}
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLstart(ps);
ps->arr[ps->size++] = x;
}
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLstart(ps);
for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i-1];
}
ps->arr[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
ps->size--;//只需要size--来减少空间直接少个数
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLstart(ps);
//判断完空间够不够后 我们的目标是将pos下标的数组往后挪动给与位置给到x插入
for (int i = ps->size; i>pos; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
SLstart(ps);
for (int i = pos; i<ps->size-1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void SLPrint(SL ps)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps.size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps.arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
测试代码各位可以慢慢增添删改来进行调试
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "cs.h"
void SLTest01()
{
SL sl;
SLInit(&sl);
SLPushBack(&sl, 1);
SLPushBack(&sl, 5);
SLPushBack(&sl, 4);
SLPushBack(&sl, 3);
SLPrint(sl);
//SLPushFront(&sl, 8);
//SLPushFront(&sl, 0);
SLPrint(sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
/*SLPopfront(&sl);
SLPopfront(&sl);
SLPopfront(&sl);*/
SLPrint(sl);
SLDestory(&sl);
}
int main()
{
SLTest01();
return 0;
}
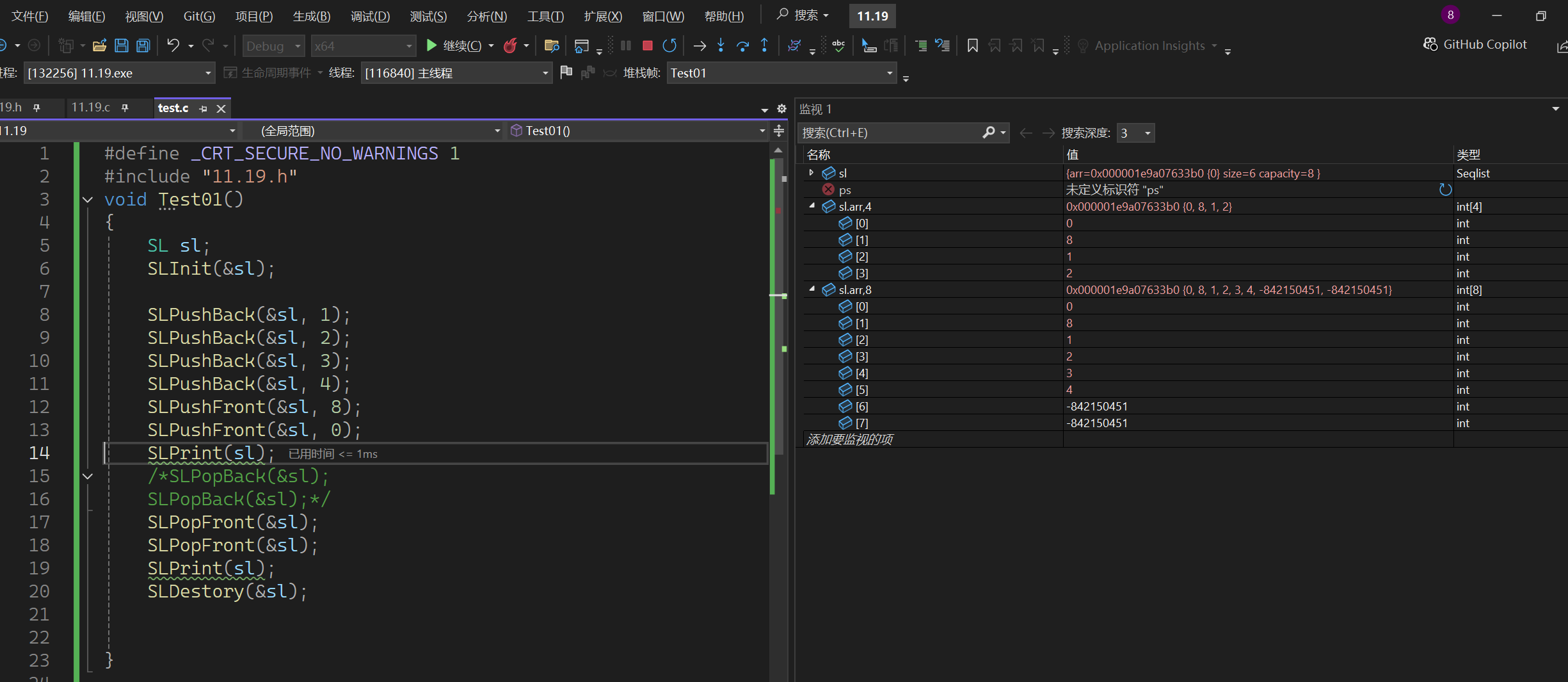
这是我调试用的监视可能有人不一定能打出来
谢谢各位!!彦祖亦菲点个赞





















 963
963

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








