多线程 相关知识
文章目录
创建线程
继承java.lang.Thread类
定义MyThread类继承Thread类
重写run()方法,编写线程执行体
创建线程对象,调用start()方法启动线程
public class MyThread extends Thread{
//重写run()方法
public void run(){
for(int i=1;i<100;i++){ System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}}}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start(); //启动线程
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start(); //启动线程
}
编写简单,可直接操作线程。适用于单继承
实现java.lang.Runnable接口
定义MyRunnable类实现Runnable接口
实现run()方法,编写线程执行体
创建线程对象,调用start()方法启动线程
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for(int i=1;i<100;i++){ System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
}}}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();
Thread myThread = new Thread(myRunnable);
thread.start(); //启动线程}
避免单继承局限性,便于共享资源
线程状态
创建状态
就绪状态
运行状态
阻塞状态
死亡状态
常用方法
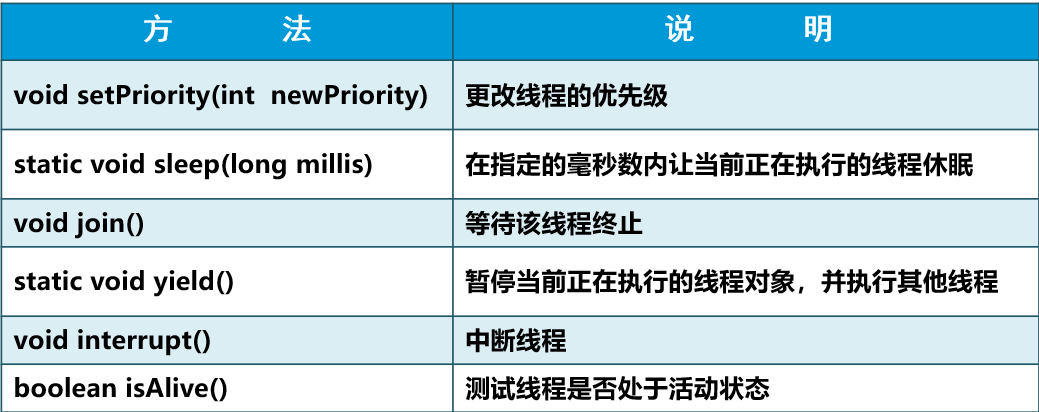
线程调度指按照特定机制为多个线程分配CPU的使用权
线程优先级
线程优先级由1~10表示,1最低,默认优先级为5
优先级高的线程获得CPU资源的概率较大
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new MyThread(),"线程A");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new MyThread(),"线程B");
t1.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t2.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
//省略代码……
}}
线程休眠
让线程暂时睡眠指定时长,线程进入阻塞状态
睡眠时间过后线程会再进入可运行状态
public class Wait {
public static void bySec(long s) {
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
System.out.println(i + 1 + "秒");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000); //线程休眠一秒 单位为毫秒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}}}
线程的强制运行
u强制执行当前线程,join写在哪个线程,就阻塞谁
public final void join()
public final void join(long mills)
public final void join(long mills,int nanos)
millis:以毫秒为单位的等待时长
nanos:要等待的附加纳秒时长
需处理InterruptedException异常
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread temp = new Thread(new MyThread());
temp.start();
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
if(i==5){
try {
temp.join();// 阻塞主线程,子线程强制执行
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"运行:"+i);
}
//省略代码…
}
线程的礼让
暂停当前线程,允许其他具有相同优先级的线程获得运行机会
该线程处于就绪状态,不转为阻塞状态
public class MyThread implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().
getName()+"正在运行:"+i);
if(i==3){
System.out.print("线程礼让:");
Thread.yield();
} } }}
Synchronized
同步方法
使用synchronized修饰的方法控制对类成员变量的访问
访问修饰符 synchronized 返回类型 方法名(参数列表){……}
synchronized 访问修饰符 返回类型 方法名(参数列表){……}
synchronized就是为当前的线程声明一把锁
同步代码块
使用synchronized关键字修饰的代码块
syncObject为需同步的对象,通常为this
效果与同步方法相同
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (this) { //同步代码块
// 省略修改数据的代码......
// 省略显示信息的代码......
}}}
同一时刻只能有一个线程进入synchronized(this)同步代码块
当一个线程访问一个synchronized(this)同步代码块时,其他synchronized(this)同步代码块同样被锁定
当一个线程访问一个synchronized(this)同步代码块时,其他线程可以访问该资源的非synchronized(this)同步代码
线程安全的类型

常见类型对比
Hashtable && HashMap
Hashtable
继承关系 实现了Map接口,Hashtable继承Dictionary类
线程安全,效率较低
键和值都不允许为null
HashMap
继承关系 实现了Map接口,继承AbstractMap类
非线程安全,效率较高
键和值都允许为null
StringBuffer && StringBuilder
Hashtable
继承关系 实现了Map接口,Hashtable继承Dictionary类
线程安全,效率较低
键和值都不允许为null
HashMap
继承关系 实现了Map接口,继承AbstractMap类
非线程安全,效率较高
键和值都允许为null
StringBuffer && StringBuilder
前者线程安全,后者非线程安全





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








