在分布式模式下,微服务的跨服务调用,需要在每个服务中实现controller层,比较麻烦,最好可以把service层的方法直接映射到controller。
有个叫leecho的大佬捣鼓出一个叫spring-cloud-feign-proxy的微服务动态代理框架,可惜3年多没更新了,目前的springboot版本已经没法用了,更何况最新的springboot3版本了。
下面分享一个我日常使用的方法,不受springcloud版本限制,比较灵活。
java版本:17
springboot版本:2.6.2
springcloud版本:2021.0.0
以一个小型分布式系统为例,看下代理模块的结构


先定义2个注解
/**
*
* @author 万剑魔君
* 定义需要提供服务的类
*/
@Documented
@Target(value = { ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface FeignProxy {
String value() default "";
//是否自动扫描类中的方法
boolean autoScan() default true;
}
/**
*
* @author 万剑魔君
* 定义方法上的请求路径
*/
@Documented
@Target(value = { ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ProxyPath {
String value() default "";
//开启自动扫描时,是否忽略该方法
boolean ignore() default false;
}
增加一个组件,用于获取spirng上下文
@Component
public class SpringContext implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
public Object getBean(String name) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(name);
}
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(clazz);
}
public <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> clazz) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(name, clazz);
}
}
由于是通过引入模块来装配,需要引入子模块配置文件
@Configuration
@PropertySource(factory = YamlPropertySourceFactory.class, value = "classpath:application-util-proxy.yaml")
public class UtilProxyConfig {
@Autowired
private ProxyFilter reqResFilter;
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean<ProxyFilter> reqResFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean<ProxyFilter> filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<ProxyFilter>();
filterRegistrationBean.setOrder(1);
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(reqResFilter);
filterRegistrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
}
forward-path: forward
添加一个核心过滤器(是不是觉得这个名字很熟悉)
初始化的时候先根据@FeignProxy注解从spirng上下文拿到注册的服务,再扫描注解属性,自动把实例化的服务、方法、映射路径添加到methodMap,当拦截到匹配的路径,进行转发
@Value("${forward-path}")
private String forwardPath;
@Autowired
private SpringContext springContext;
private String firstPath = Const.PROXY_URL.getValue();
private Map<String, ServiceDeclared> methodMap = new HashMap<String, ServiceDeclared>();
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
Map<String, Object> beans = springContext.getApplicationContext().getBeansWithAnnotation(FeignProxy.class);
beans.keySet().forEach(k -> {
Object service = beans.get(k);
Class<?>[] inters = service.getClass().getInterfaces();
Class<?> inter = null;
FeignProxy fp = null;
for (Class<?> i : inters) {
if (i.getAnnotation(FeignProxy.class) != null) {
inter = i;
fp = i.getAnnotation(FeignProxy.class);
break;
}
}
if (fp == null) {
inters = service.getClass().getSuperclass().getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> i : inters) {
if (i.getAnnotation(FeignProxy.class) != null) {
inter = i;
fp = i.getAnnotation(FeignProxy.class);
break;
}
}
}
String parentPath = fp.value();
if (parentPath.equals(Const.EMPTY_STRING.getValue()))
parentPath = Const.SPLIT_SLASH.getValue().concat(inter.getSimpleName());
Method[] ms = inter.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m : ms) {
ProxyPath pp = m.getDeclaredAnnotation(ProxyPath.class);
if (pp != null) {
String secondPath = pp.value();
if (secondPath.equals(Const.EMPTY_STRING.getValue())) {
secondPath = Const.SPLIT_SLASH.getValue().concat(m.getName());
}
if (!pp.ignore())
methodMap.put(parentPath.concat(secondPath), new ServiceDeclared(service, m));
} else if (fp.autoScan()) {
methodMap.put(parentPath.concat(Const.SPLIT_SLASH.getValue().concat(m.getName())),
new ServiceDeclared(service, m));
}
}
});
Filter.super.init(filterConfig);
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
if (request.getRequestURI().startsWith(firstPath) || !methodMap.containsKey(request.getRequestURI()))
chain.doFilter(request, response);
else {
String path = firstPath.concat(forwardPath);
request.setAttribute(Const.SERVICE.getValue(), methodMap.get(request.getRequestURI()));
request.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(request, response);
}
}
添加一个转发控制器,所有请求都被转发到该控制器,控制器自动执行映射路径中注册的服务实例中的方法,然后返回
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@PostMapping(value = "/proxy/{forwardPath}", produces = "application/json;charset=utf-8")
public String forwardPost(@PathVariable String forwardPath, HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
StringBuffer body = new StringBuffer();
BufferedReader reader = request.getReader();
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null)
body.append(line);
Map<String, String> paramMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
request.getParameterNames().asIterator().forEachRemaining(name -> {
paramMap.put(name, request.getParameter(name));
});
ServiceDeclared sd = (ServiceDeclared) request.getAttribute(Const.SERVICE.getValue());
Method method = sd.getMethod();
Parameter[] params = method.getParameters();
Object[] objParams = new Object[params.length];
if (params.length == 1 && !isBasicData(params[0].getType())) {
objParams[0] = objectMapper.readValue(body.toString(), params[0].getType());
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
Parameter p = params[i];
if (paramMap.containsKey(p.getName())) {
String val = paramMap.get(p.getName());
if (p.getType() == String.class) {
objParams[i] = val;
} else if (p.getType() == Integer.class || p.getType() == int.class) {
objParams[i] = Integer.valueOf(val);
} else if (p.getType() == Long.class || p.getType() == long.class) {
objParams[i] = Long.valueOf(val);
} else if (p.getType() == Boolean.class || p.getType() == boolean.class) {
objParams[i] = Boolean.valueOf(val);
} else if (p.getType() == Float.class || p.getType() == float.class) {
objParams[i] = Float.valueOf(val);
} else if (p.getType() == Short.class || p.getType() == short.class) {
objParams[i] = Short.valueOf(val);
} else if (p.getType() == Byte.class || p.getType() == byte.class) {
objParams[i] = Byte.valueOf(val);
} else if (p.getType() == Character.class || p.getType() == char.class) {
objParams[i] = Byte.valueOf(val);
} else {
objParams[i] = null;
}
} else
objParams[i] = null;
}
}
Object res = method.invoke(sd.getService(), objParams);
if (method.getReturnType() == String.class)
return (String) res;
else
return objectMapper.writeValueAsString(res);
} catch (Exception e) {
return new ResponseData(1, Const.FAILURE.getValue(), e.getMessage(), null).toString();
}
}
private boolean isBasicData(Class<?> type) {
if (type.isPrimitive() || type == Integer.class || type == Long.class || type == Boolean.class
|| type == Float.class || type == Short.class || type == Byte.class || type == Character.class
|| type == String.class) {
return true;
} else
return false;
}
使用方法
直接在服务接口类中加上@FeignProxy注解
默认开启autoScan,方法上不需要加@ProxyPath
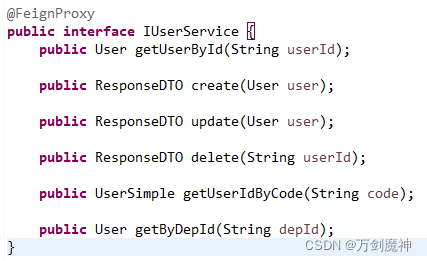
在不需要的方法上加上注解@proxyPath并设置属性ignore为true
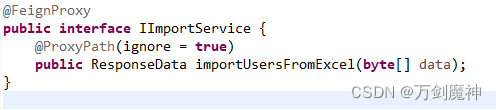
@FeignProxy中不写参数,路径默认为类名
@ProxyPath中不写参数,路径默认为方法名
不影响@Cacheable注解的使用
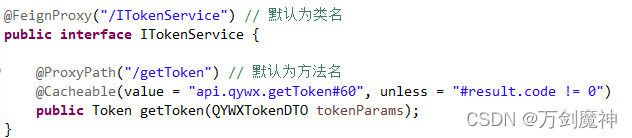
这样不需要写controller就比较方便




 本文介绍了如何在SpringCloud微服务环境中,通过自定义注解和过滤器实现服务自动转发,避免在每个服务中重复编写controller。文中详细讲解了实现过程,包括定义注解、获取Spring上下文、添加核心过滤器和转发控制器,并提供了具体的使用方法。此方法不受SpringCloud版本限制,适用于Java 17、SpringBoot 2.6.2和SpringCloud 2021.0.0。
本文介绍了如何在SpringCloud微服务环境中,通过自定义注解和过滤器实现服务自动转发,避免在每个服务中重复编写controller。文中详细讲解了实现过程,包括定义注解、获取Spring上下文、添加核心过滤器和转发控制器,并提供了具体的使用方法。此方法不受SpringCloud版本限制,适用于Java 17、SpringBoot 2.6.2和SpringCloud 2021.0.0。
















 1141
1141

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








