文章目录
1. 顺序表的概念
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
1)静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素。
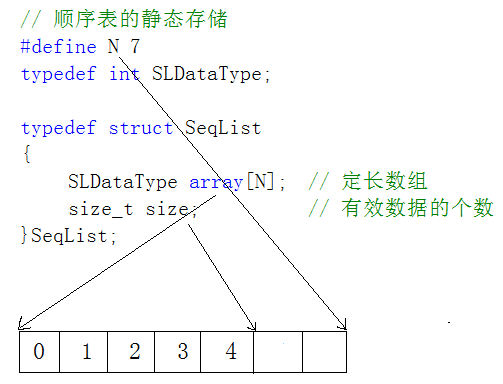
2)动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。
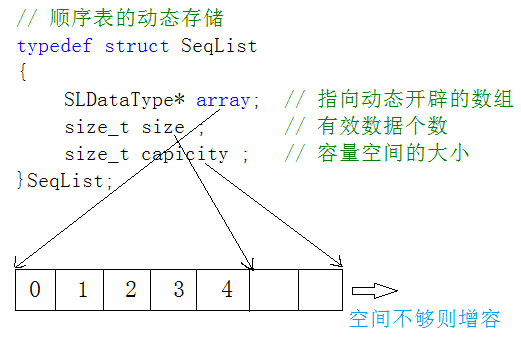
由于静态顺序表只适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景。静态顺序表的定长数组导致N定大了,空间开多了浪费,开少了不够用。所以现实中基本都是使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态的分配空间大小。
但在竞赛中,为了方便,可以采用静态顺序表,给一个较大的空间。
2. 动态顺序表的实现
下面将其分为3个模块进行实现SeqList.h,SeqList.c,test.c
2.1 接口设计(SeqList.h)
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int SLDataType; //方便改变类型
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a; //动态开辟的数组
// size是数据个数,看做下标的话,他是最后一个数据的下一个位置
int size; //有效空间
int capacity; //空间容量
}SL;
//初始化销毁
void SLInit(SL* psl);
void SLDestroy(SL* psl);
//打印及扩容操作
void SLPrint(SL* psl);
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl);
// 头尾插入删除
void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDataType x);
void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDataType x);
void SLPopBack(SL* psl);
void SLPopFront(SL* psl);
//任意位置插入删除
void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, SLDataType x);
void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos);
//查找,查找失败则返回-1
int SLSearch(SL* psl, SLDataType x);
2.2 接口实现(SeqList.c)
1)初始化销毁接口
assert的作用是为了符合设计的要求,传入的是一个结构体,而非结构体指针。
void SLInit(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
psl->a = NULL;
psl->size = 0;
psl->capacity = 0;
}
void SLDestroy(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
if (psl->a != NULL)
{
free(psl->a);
psl->a = NULL;
psl->size = 0;
psl->capacity = 0;
}
}
2)打印及扩容操作
void SLPrint(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", psl->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
注意:乘2并非是数据结构规定的,而是从开辟空间的成本上考虑的,2倍既考虑了开辟空间的效率,也能满足满足所需空间
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
if (psl->size == psl->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = psl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : psl->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->a, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail\n");
return;
}
psl->a = tmp;
psl->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
3)头尾插入删除
删除时之所以不赋值,是因为无法确定赋值哪个,而有效空间就可以直接限制住,因此删除时不进行赋值操作。
注意:对数组越界读操作时,一般不会报错,但写操作可能会报错,因此一定要检查有效空间是否符合要求
void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
SLCheckCapacity(psl);
psl->a[psl->size++] = x;
}
void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
SLCheckCapacity(psl);
//挪动数据
int end = psl->size - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end];
end--;
}
psl->a[0] = x;
psl->size++;
}
void SLPopBack(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
//暴力检查
assert(psl->size > 0);
////温柔检查
//if (psl->size == 0)
//{
// return;
//}
//不用初始化该位置的值,因为没办法初始化成一个数
//假设赋值为-1,那本身也是-1呢?因此直接将有效空间-1即可
psl->size--;
}
void SLPopFront(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
assert(psl->size > 0);
int begin = 0;
while (begin < psl->size)
{
psl->a[begin] = psl->a[begin + 1];
begin++;
}
psl->size--;
}
4)任意位置插入删除以及查找
注意:要注意传入的下标是否符合标准,要在有效范围之内,因此要进行检查
void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= psl->size);
SLCheckCapacity(psl);
//挪动数据
int end = psl->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end];
end--;
}
psl->a[pos] = x;
psl->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos)
{
assert(psl);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < psl->size);
int begin = pos;
while (begin < psl->size - 1)
{
psl->a[begin] = psl->a[begin + 1];
begin++;
}
psl->size--;
}
//查找,查找失败则返回-1
int SLSearch(SL* psl, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
int begin = 0;
while (begin < psl->size)
{
if (psl->a[begin] == x)
{
return begin;
}
begin++;
}
return -1;
}
3. 完整代码
SeqList.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;
// size是数据个数,看做下标的话,他是最后一个数据的下一个位置
int size; //有效空间
int capacity; //空间容量
}SL;
void SLInit(SL* psl);
void SLDestroy(SL* psl);
void SLPrint(SL* psl);
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl);
// 头尾插入删除
void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDataType x);
void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDataType x);
void SLPopBack(SL* psl);
void SLPopFront(SL* psl);
//任意位置插入删除
void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, SLDataType x);
void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos);
//查找,查找失败则返回-1
int SLSearch(SL* psl, SLDataType x);
SeqList.c
#include "SeqList.h"
void SLInit(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
psl->a = NULL;
psl->size = 0;
psl->capacity = 0;
}
void SLDestroy(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
if (psl->a != NULL)
{
free(psl->a);
psl->a = NULL;
psl->size = 0;
psl->capacity = 0;
}
}
void SLPrint(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
for (int i = 0; i < psl->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", psl->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
if (psl->size == psl->capacity)
{
// 乘2并非是数据结构规定的,而是从开辟空间的成本上考虑的
int newCapacity = psl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : psl->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(psl->a, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail\n");
return;
}
psl->a = tmp;
psl->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
// 头尾插入删除
void SLPushBack(SL* psl, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
SLCheckCapacity(psl);
psl->a[psl->size++] = x;
}
void SLPushFront(SL* psl, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
SLCheckCapacity(psl);
//挪动数据
int end = psl->size - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end];
end--;
}
psl->a[0] = x;
psl->size++;
}
void SLPopBack(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
//暴力检查
assert(psl->size > 0);
////温柔检查
//if (psl->size == 0)
//{
// return;
//}
//不用初始化该位置的值,因为没办法初始化成一个数
//假设赋值为-1,那本身也是-1呢?因此直接将有效空间-1即可
psl->size--;
}
void SLPopFront(SL* psl)
{
assert(psl);
assert(psl->size > 0);
int begin = 0;
while (begin < psl->size)
{
psl->a[begin] = psl->a[begin + 1];
begin++;
}
psl->size--;
}
//任意位置插入删除
//pos是下标
void SLInsert(SL* psl, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= psl->size);
SLCheckCapacity(psl);
//挪动数据
int end = psl->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
psl->a[end + 1] = psl->a[end];
end--;
}
psl->a[pos] = x;
psl->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* psl, int pos)
{
assert(psl);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < psl->size);
int begin = pos;
while (begin < psl->size - 1)
{
psl->a[begin] = psl->a[begin + 1];
begin++;
}
psl->size--;
}
//查找,查找失败则返回-1
int SLSearch(SL* psl, SLDataType x)
{
assert(psl);
int begin = 0;
while (begin < psl->size)
{
if (psl->a[begin] == x)
{
return begin;
}
begin++;
}
return -1;
}
test.c
#include "SeqList.h"
void SLTest()
{
SL sl;
SLInit(&sl);
SLPushBack(&sl, 1);
SLPushBack(&sl, 2);
SLPushBack(&sl, 3);
SLPushFront(&sl, 4);
SLPushFront(&sl, 5);
SLPushFront(&sl, 6);
SLPushFront(&sl, 7);
SLPushFront(&sl, 8);
SLPushFront(&sl, 9);
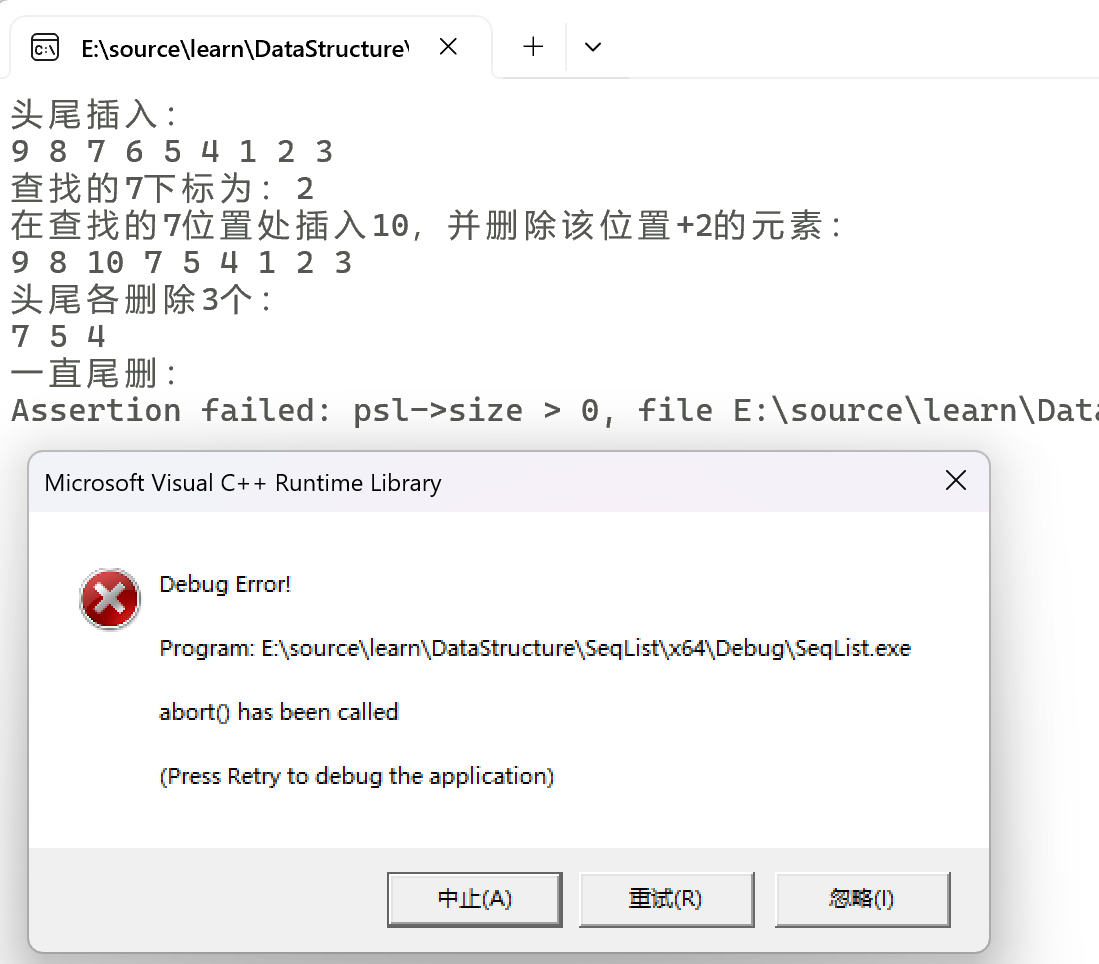
printf("头尾插入:\n");
SLPrint(&sl);
int pos = SLSearch(&sl, 7);
printf("查找的7下标为:%d\n", pos);
if (pos != -1)
{
SLInsert(&sl, pos, 10);
}
SLErase(&sl, pos + 2);
printf("在查找的7位置处插入10,并删除该位置+2的元素:\n");
SLPrint(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPopFront(&sl);
SLPopFront(&sl);
SLPopFront(&sl);
printf("头尾各删除3个:\n");
SLPrint(&SL);
printf("一直尾删:\n");
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLDestroy(&sl);
}
int main()
{
SLTest();
return 0;
}
运行效果
4. 问题反思
1)中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)
2)增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
3)增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
这些问题的解决就是另一种数据结构:链表!































