java Try/Catch的简单用法
public class TestTryCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
nullPointExcertion();
arithmeticException();
arrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
classCastException("6");
}
// 空指针异常
public static void nullPointExcertion() {
try {
String name = null;
System.out.println(name.getClass());
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("这个是空指针异常");
}
}
// 算数异常
public static void arithmeticException() {
try {
int i = 0;
int j = 10 / i;
System.out.println(j);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("这个是算数异常");
}
}
// 数组下标越界
public static void arrayIndexOutOfBoundsException() {
try {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
System.out.println(arr[5]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("这个是数组下标越界异常");
}
}
// 类型转换异常
public static void classCastException(Object str) {
try {
Integer i = (Integer)str;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
System.out.println("这个是类型转换异常");
}
}
}
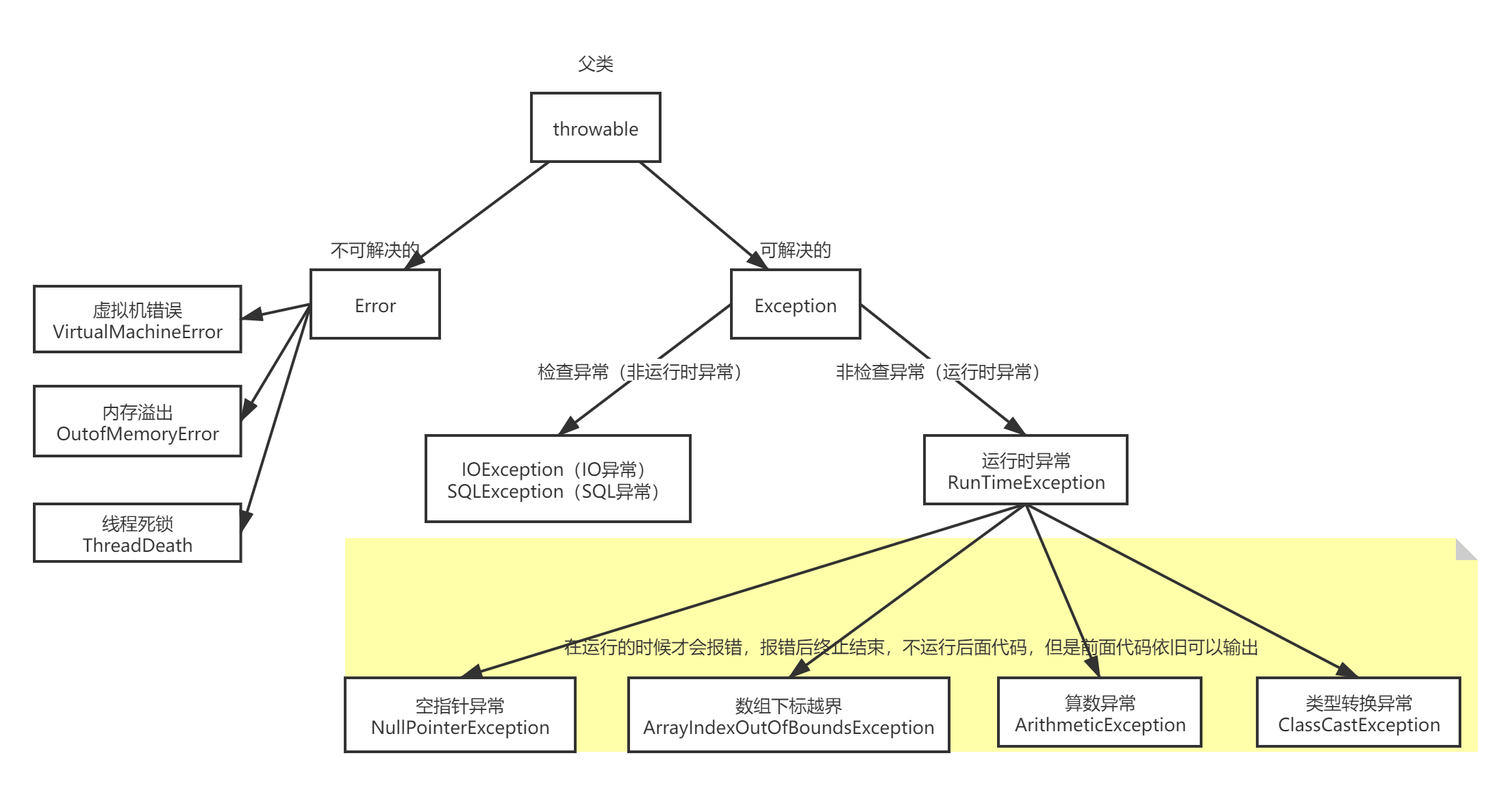





 本文深入探讨了Java中常见的异常处理机制,包括空指针异常、算数异常、数组下标越界异常及类型转换异常。通过具体代码示例,详细解释了如何使用try/catch语句来捕获和处理这些异常,为Java开发者提供了实用的异常处理指南。
本文深入探讨了Java中常见的异常处理机制,包括空指针异常、算数异常、数组下标越界异常及类型转换异常。通过具体代码示例,详细解释了如何使用try/catch语句来捕获和处理这些异常,为Java开发者提供了实用的异常处理指南。
















 337
337

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








