代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Perceptron():
def __init__(self,epoch):
self.alpha = 0.0001
self.epochs=epoch
self.flag=0
self.X=np.vstack([np.random.randn(50, 2), (np.random.randn(50, 2) + 4)])
self.label=np.vstack([np.zeros((50, 1)), np.ones((50, 1))])
#预测函数
def predict(self,x):
predict=self.step_function(np.dot(self.w,x)+self.b)
return predict
#update
def update(self,x_train,Y):
update=self.alpha*(self.predict(x_train)-Y)
self.w =self.w-update*x_train
self.b =self.b-update
#激活函数
def step_function(self,X):
return np.where(X> 0, 1, 0)
#training
def fit(self):
self.n_samples,self.n_features=self.X.shape
self.w= np.zeros(self.n_features)
self.b = np.zeros(1)
for epoch_1 in range(self.epochs):
accuracy=0
for i in range(self.n_samples):
if (self.X[i]==self.predict(self.X[i])).all():
accuracy+=1
else:
self.update(self.X[i],self.label[i])
if accuracy == self.n_samples:
print("Training completed after {} epochs. Accuracy_num={}".format(epoch_1+1,accuracy))
self.flag=1
self.show()
break
if epoch_1 == self.epochs-1:
print("{} epochs reached. Training stopped. Accuracy_num={}".format(self.epochs,accuracy))
self.show()
print("Final weight:", self.w)
print("Final bias:", self.b)
return self.flag
# 图形显示结果
def show(self):
x1 = np.linspace(min(self.X[:, 0]), max(self.X[:, 0]), 100)
x2 = (- self.w[0] * x1-self.b ) / self.w[1]
plt.plot(x1, x2.reshape(-1))
# 画出数据集的散点图
plt.title("epoch:"+str(self.epochs))
colors = ['blue' if label == 1 else 'red' for label in self.label]
plt.scatter(self.X[:, 0], self.X[:, 1], c=colors)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
epochs=eval(input("请输入要迭代的次数:"))
classify=Perceptron(epochs)
flag=classify.fit()
print("flag=",flag)
结果:
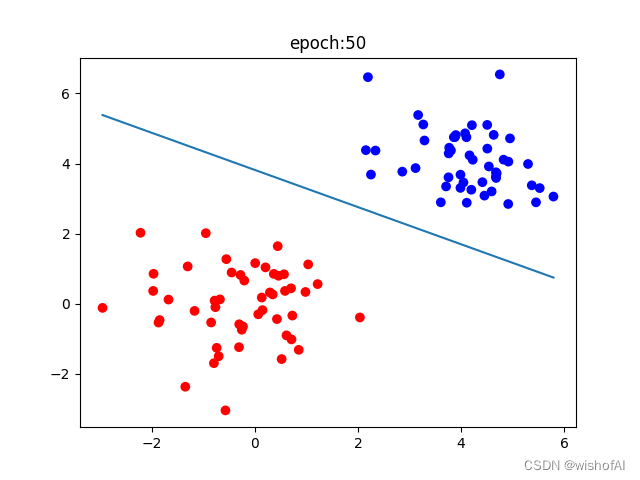
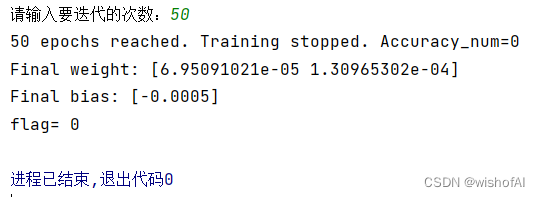





 该代码实现了一个简单的感知器类,用于训练数据。它包含了初始化、预测、更新权重、激活函数(阶跃函数)以及训练过程。在训练过程中,如果所有样本都被正确分类,则提前结束训练。最后,它会显示决策边界并输出最终的权重和偏置。
该代码实现了一个简单的感知器类,用于训练数据。它包含了初始化、预测、更新权重、激活函数(阶跃函数)以及训练过程。在训练过程中,如果所有样本都被正确分类,则提前结束训练。最后,它会显示决策边界并输出最终的权重和偏置。
















 810
810

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








