lvm的建立
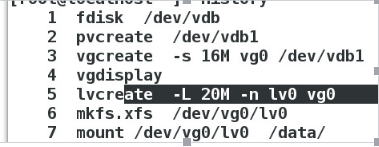
各命令解释:
1.物理存储介质为/dev/vdb
2.从设备上的分区创建物理卷/dev/vdb1
3.从物理卷创建卷组vg0
5.在卷组创建逻辑卷
6.格式化逻辑卷
7.挂载逻辑卷至/data
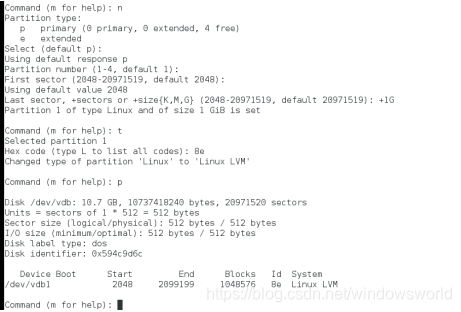
新增分区并修改其标签为LVM
Pvcreate /dev/vdb1创建物理卷/dev/vdb1
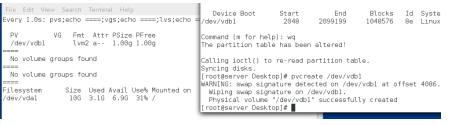
Vgcreate -s 16M vg0 /dev/vdb1在卷组/dev/vdb1创建卷组vg0

Lvcreate -L 20M -n lv0 vg0在vg0卷组中创建逻辑卷lv0
格式化创建的逻辑卷/dev/vg0/lv0
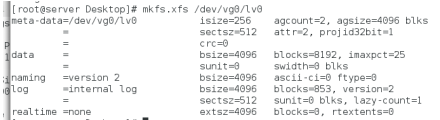
挂载逻辑卷该分区到/data
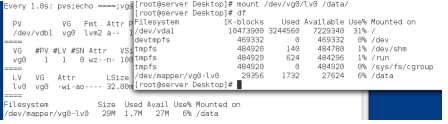
Lvm的拉伸
1.不超过卷组
不超过卷组大小时,直接拉伸即可
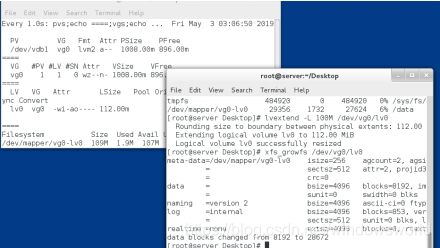
2.超过卷组
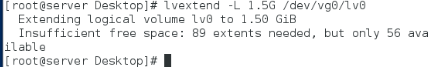
可以看到提示信息并不够1.5g大,所以我们需要添加新的卷组。
Partprobe
同步磁盘配区
新增第二块lvm分区
由于/dev/vdb1大小最大为1G,所以vg0wufa拉伸至1.5G,我们需要先添加新的分区。然后将该分区加至vg0,使vg0的大小够拉伸的大小,我们就可以进行拉伸了。
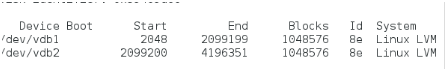
增加物理卷/dev/vdb2
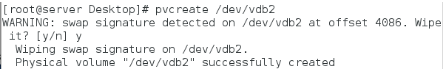
增加/dev/vdb2至vg0

重新拉伸vg0分区至1.5G
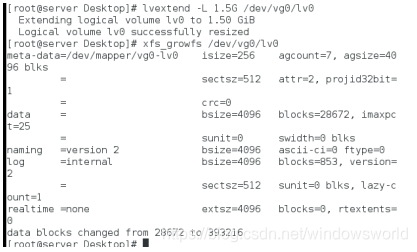
可以看到vg0的大小被拉伸至1.5G
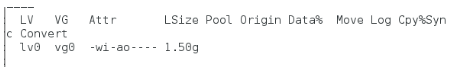
lvm缩减
取消挂载

格式化逻辑卷lv0
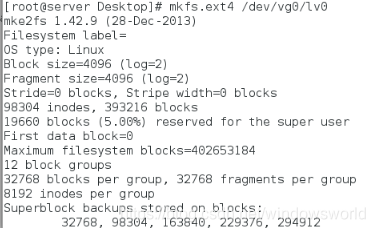
查看逻辑卷中的数据(防止数据被损坏)
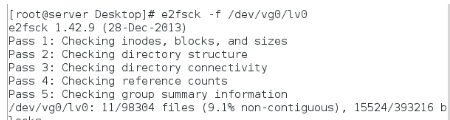
缩减分区至100M,
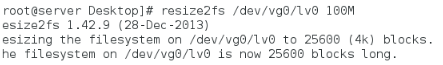
挂载后查看逻辑卷大小

缩减物理卷
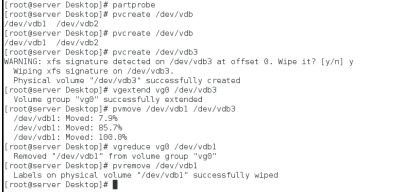
快照方式建立lvm
建立挂载
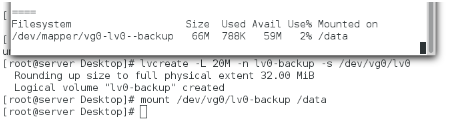
删除快照
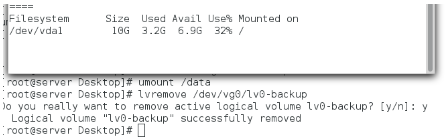
删除lvm分区
Umount /data
去除挂载
删除逻辑卷,卷组,物理卷

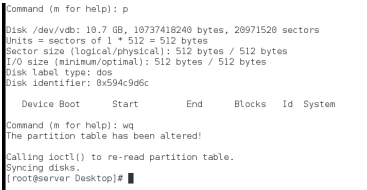
删除磁盘lvm的分区





















 1440
1440

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








