453. Minimum Moves to Equal Array Elements
Given a non-empty integer array of size n, find the minimum number of moves required to make all array elements equal, where a move is incrementing n - 1 elements by 1.
Example:
Input:
[1,2,3]
Output:
3
Explanation:
Only three moves are needed (remember each move increments two elements):
[1,2,3] => [2,3,3] => [3,4,3] => [4,4,4]
方法1: brute force
官方题解: https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-moves-to-equal-array-elements/solution/
思路:
每次为了赶上mx,我们将除了mx的所有n - 1个值+1。那么每次记录当前最大值和最小值,只要循环直到最大==最小,可以结束。
Complexity
Time complexity : O(n^2 k), where n is the length of the array and k is the difference between maximum element and minimum element.
Space complexity : O(1). No extra space required.
方法2:
discussion:https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-moves-to-equal-array-elements/discuss/93817/It-is-a-math-question
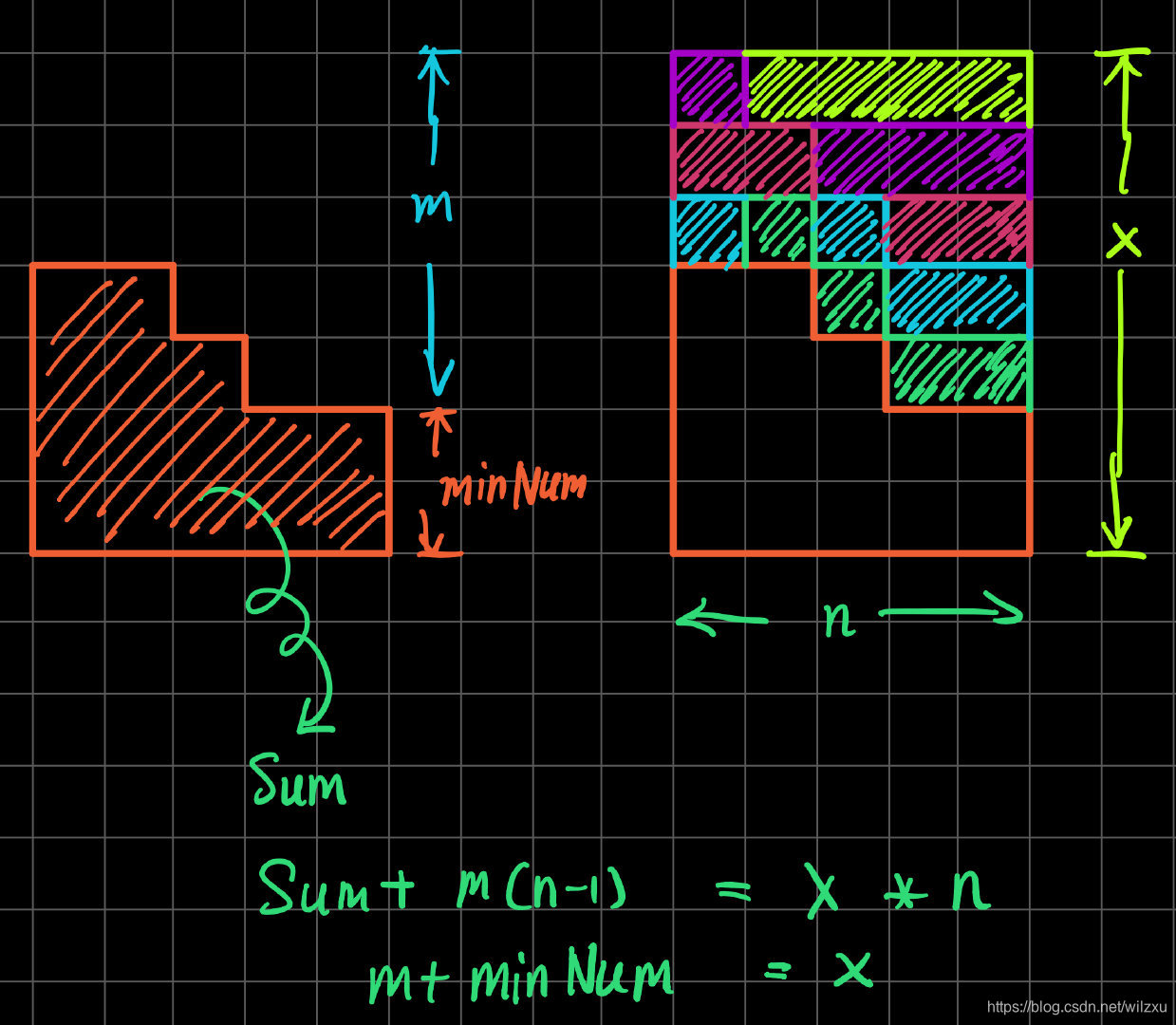
思路:
如图。
易错点
不用long会overflow
class Solution {
public:
int minMoves(vector<int>& nums) {
int mn = INT_MAX;
long sum = 0;
for (int num: nums){
mn = min(mn, num);
sum += num;
}
return sum - mn * nums.size();
}
};
Complexity
Time complexity : O(n). We traverse the complete array once.
Space complexity : O(1). No extra space required.
方法3: math
grandyang: http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/6053827.html
思路:
将n - 1个++相当于将最大值–。那么每一次move都相当于从最大值-1。一共需要减多少次才能全部相等?首先全部相等的时候一定全部等于最小值,因为没有必要更小。那么只要先求出最小,然后计算每个num和最小值之间的差值,累计下来就是moves。
class Solution {
public:
int minMoves(vector<int>& nums) {
int mn = *min_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int result = 0;
for (int num: nums){
result += (num - mn);
}
return result;
}
};




 本文探讨了LeetCode题目453“最少移动次数使数组元素相等”的三种解法,包括暴力破解法、数学法及讨论区提供的高效解法。通过分析不同方法的时间和空间复杂度,帮助读者理解最优解背后的数学原理。
本文探讨了LeetCode题目453“最少移动次数使数组元素相等”的三种解法,包括暴力破解法、数学法及讨论区提供的高效解法。通过分析不同方法的时间和空间复杂度,帮助读者理解最优解背后的数学原理。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








