From Wiki, the definition of Levenshtein distance is a string metric for measuring the difference between two sequences. Informally, the Levenshtein distance between two words is equal to the number of single-character edits required to change one word into the other.
Mathematically, the Levenshtein distance between two strings  is given by
is given by 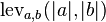 where
where
Note that the first element in the minimum corresponds to deletion(from  to
to  ), the second to insertion and the third to match or mismatch, depending on whether the respective symbols are the same.
), the second to insertion and the third to match or mismatch, depending on whether the respective symbols are the same.
Below is an implementation in java.
package test.LevenshteinDistance;
public class LevenshteinDistance {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String s = "kitten";
String t = "sitting";
LevenshteinDistance ld = new LevenshteinDistance();
//int recurlen = ld.recurLevenDistance(s, t);
int dynlen = ld.dynLevenDistance(s, t);
//System.out.println("The length is : " + recurlen);
System.out.println("The length is : " + dynlen);
System.out.println(s.length());
}
/*public int minimum(int a, int b, int c){
return Math.min(Math.min(a, b), c);
}*/
public int minimum(int a, int b, int c){
if(a < b && a < c) return a;
if(b < a && b < c) return b;
return c;
}
// compute the distance use recursive way
public int recurLevenDistance(String s, String t){
int slen = s.length();
int tlen = t.length();
int ins = 0; // for recording insert length
int del = 0; // for recording delete length
int sub = 0; // for substitution length
if(slen == 0 && tlen == 0) return 0;
if(slen == 0) return tlen;
if(tlen == 0) return slen;
/*if(s.charAt(slen - 1) == t.charAt(tlen - 1)){
sub = recurLevenDistance(s.substring(0, slen - 1), t.substring(0, tlen - 1));
}
else{
sub = recurLevenDistance(s.substring(0, slen - 1), t.substring(0, tlen - 1)) + 1;
}*/
sub = recurLevenDistance(s.substring(0, slen - 1), t.substring(0, tlen - 1))
+ ((s.charAt(slen - 1) == t.charAt(tlen - 1)) ? 0 : 1);
ins = recurLevenDistance(s.substring(0, slen - 1), t) + 1;
del = recurLevenDistance(s, t.substring(0, tlen - 1)) + 1;
return minimum(ins, del, sub);
}
// compute the distance use dynamic way
public int dynLevenDistance(String s, String t){
int[][] distance = new int[s.length() + 1][t.length() + 1];
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i <= s.length(); i++)
distance[i][0] = i;
for(j = 0; j <= t.length(); j++)
distance[0][j] = j;
for(i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++){
for(j = 1; j <= t.length(); j++){
distance[i][j] = minimum(distance[i - 1][j] + 1,
distance[i][j - 1] + 1,
distance[i - 1][j - 1] + ((s.charAt(i - 1) == t.charAt(j - 1)) ? 0 : 1));
}
}
return distance[s.length()][t.length()];
}
}







 本文介绍如何使用Java实现Levenshtein距离算法,包括递归和动态规划两种方式,详细解释了算法原理及代码实现。
本文介绍如何使用Java实现Levenshtein距离算法,包括递归和动态规划两种方式,详细解释了算法原理及代码实现。
![\qquad\operatorname{lev}_{a,b}(i,j) = \begin{cases}
0 &, i=j=0 \\
i &, j = 0 \text{ and } i > 0 \\
j &, i = 0 \text{ and } j > 0 \\
\min \begin{cases}
\operatorname{lev}_{a,b}(i-1,j) + 1 \\
\operatorname{lev}_{a,b}(i,j-1) + 1 \\
\operatorname{lev}_{a,b}(i-1,j-1) + [a_i \neq b_j]
\end{cases} &, \text{ else}
\end{cases}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/8/7/1/871cba439a7684b64d12d692e96d1e83.png)
















 1931
1931

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








