- 有时候我们会通过JavaScript来动态修改样式,这个时候我们有两个选择:
- 选择一:在CSS中编写好对应的样式,动态的添加class;
- 选择二:动态的修改style属性
- 开发中如何选择呢?
- 在大多数情况下,如果可以动态修改class完成某个功能,更推荐使用动态class
- 如果对于某些情况,无法通过动态修改class(比如精准修改某个css属性的值),那么就可以修改style属性
元素的className和classList
- 元素的class attribute,对应的property并非叫class,而是className:
- 这是因为JavaScript早期是不允许使用class这种关键字来作为对象的属性,所以DOM规范使用了className
- 虽然现在JavaScript已经没有这样的限制,但是并不推荐,并且依然在使用className这个名称
- 我们可以对className进行赋值,它会替换整个类中的字符串

- 如果我们需要添加或者移除单个的class,那么可以使用classList属性
- elem.classList 是一个特殊的对象:
- elem.classList.add (class) :添加一个类
- elem.classList.remove(class):添加/移除类
- elem.classList.toggle(class) :如果类不存在就添加类,存在就移除它
- elem.classList.contains(class):检查给定类,返回 true/false
- classList是可迭代对象,可以通过for of进行遍历
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>classList方法示例</title>
<style>
.active {
background-color: red;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">点击我</button>
<script>
// 获取按钮元素
var btn = document.getElementById('btn');
// 给按钮添加一个类名
btn.classList.add('btn-primary');
console.log(btn.classList); // 输出:DOMTokenList ["btn-primary"]
// 移除按钮的类名
btn.classList.remove('btn-primary');
console.log(btn.classList); // 输出:DOMTokenList []
// 切换按钮的类名
btn.classList.toggle('active');
console.log(btn.classList); // 输出:DOMTokenList ["active"]
// 检查按钮是否包含指定的类名
var hasClass = btn.classList.contains('active');
console.log(hasClass); // 输出:true
</script>
</body>
</html>
元素的style属性
-
如果需要单独修改某一个CSS属性,那么可以通过style来操作:
- 对于多词(multi-word)属性,使用驼峰式 camelCase
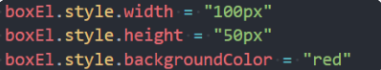
-
如果我们将值设置为空字符串,那么会使用CSS的默认样式:

多个样式的写法,我们需要使用cssText属性: -
不推荐这种用法,因为它会替换整个字符串;

元素style的读取 - getComputedStyle
getComputedStyle()是一个用于获取元素计算后样式的 API。它返回一个对象,其中包含了指定元素的所有计算后的样式属性及其对应的值。
getComputedStyle()接受两个参数,第一个参数是要获取样式的元素,第二个参数是伪元素(可选)。伪元素参数可以用来获取指定元素的伪元素计算后的样式,例如获取元素的::before或::after伪元素的样式。
getComputedStyle()方法返回的对象是一个只读对象,其中包含了指定元素的所有计算后的样式属性及其对应的值。这些样式属性包括字体、颜色、边框、内边距、外边距、宽度、高度等等。用得少,了解就行
- 如果我们需要读取样式:
- 对于内联样式,是可以通过style.*的方式读取到的;
- 对于style、css文件中的样式,是读取不到的
- 这个时候,我们可以通过getComputedStyle的全局函数来实现:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>getComputedStyle() 方法示例</title>
<style>
#example {
background-color: red;
color: white;
font-size: 20px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 5px;
border: 1px solid black;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="example">Hello, world!</div>
<script>
// 获取元素
var example = document.getElementById('example');
// 获取元素的计算后样式
var computedStyle = window.getComputedStyle(example);
// 获取元素的背景颜色
var backgroundColor = computedStyle.backgroundColor;
console.log('背景颜色:' + backgroundColor); // 输出:背景颜色:rgb(255, 0, 0)
// 获取元素的字体大小
var fontSize = computedStyle.fontSize;
console.log('字体大小:' + fontSize); // 输出:字体大小:20px
// 获取元素的边框宽度
var borderWidth = computedStyle.borderWidth;
console.log('边框宽度:' + borderWidth); // 输出:边框宽度:1px
</script>
</body>
</html>






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








