吴恩达机器学习笔记(长期更新)
TensorFlow Implementation
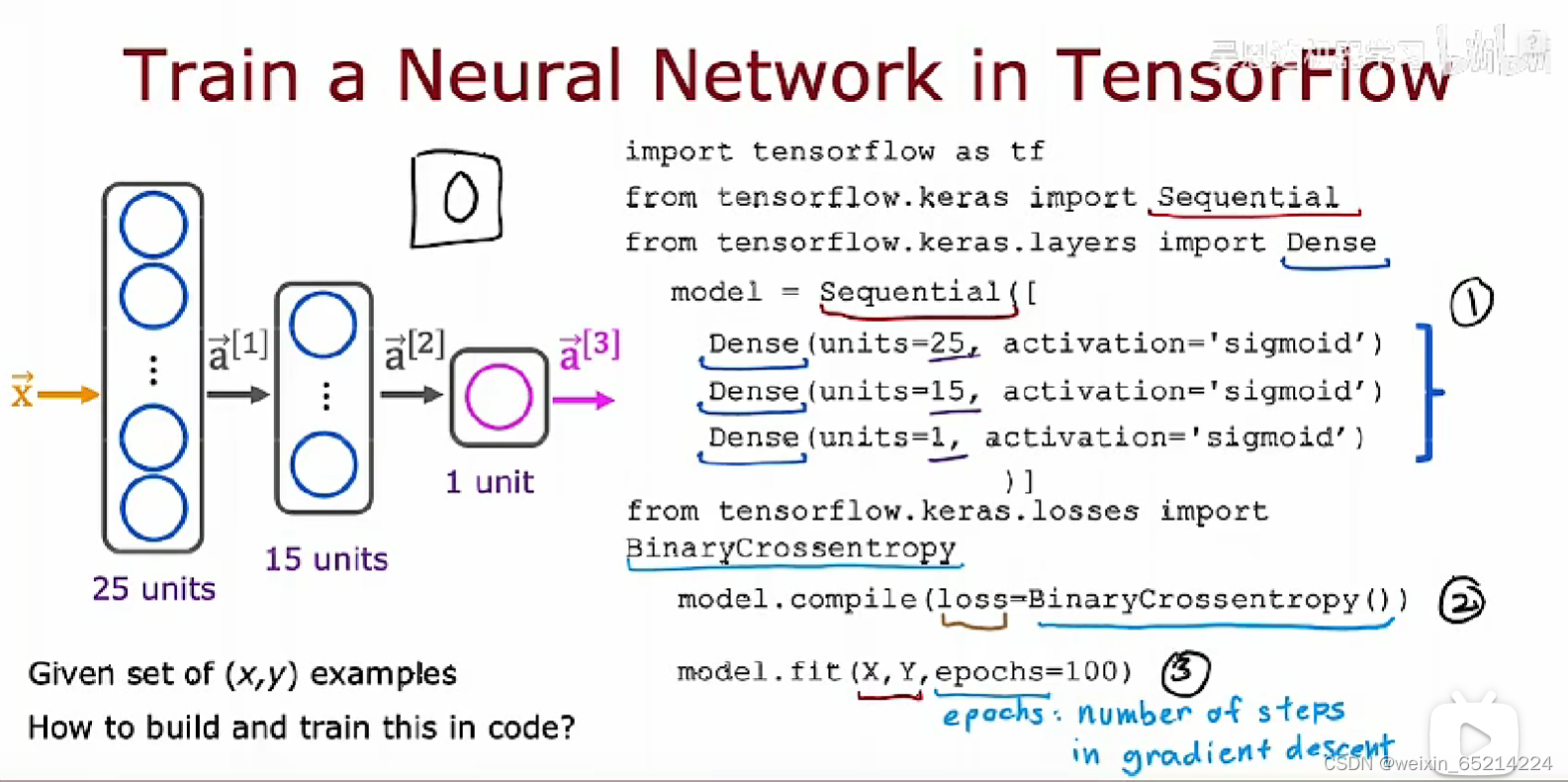
Training Details
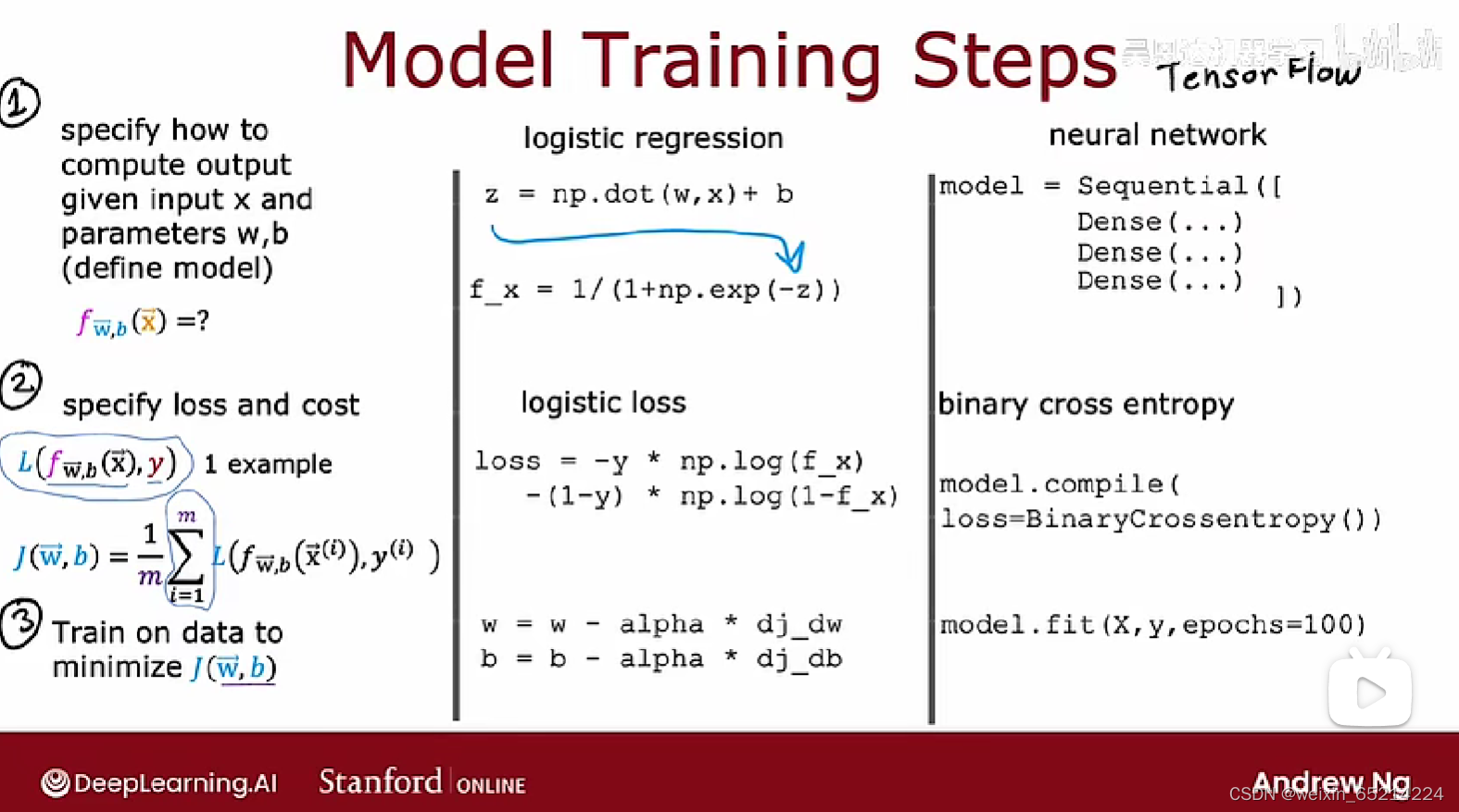
不同模型编译时使用的loss functions:
线性回归:model.compile( loss = MeanSquaredError())
逻辑回归: model.compile(loss = BinaryCrossentropy())
神经网络训练的标准:使用反向传播的算法(Tensorflow中通过fit一步自动实现)
更多的激活函数
ReLU函数:g(z) = max(0, z)
线性激活函数:g(z) = w * x + b
sigmoid
以上几者构成神经网络中最常用的几种激活函数
hidden layers:建议选择ReLU函数作为默认激活函数。Do not use linear activations in hidden layers。
Multiclassification多分类问题

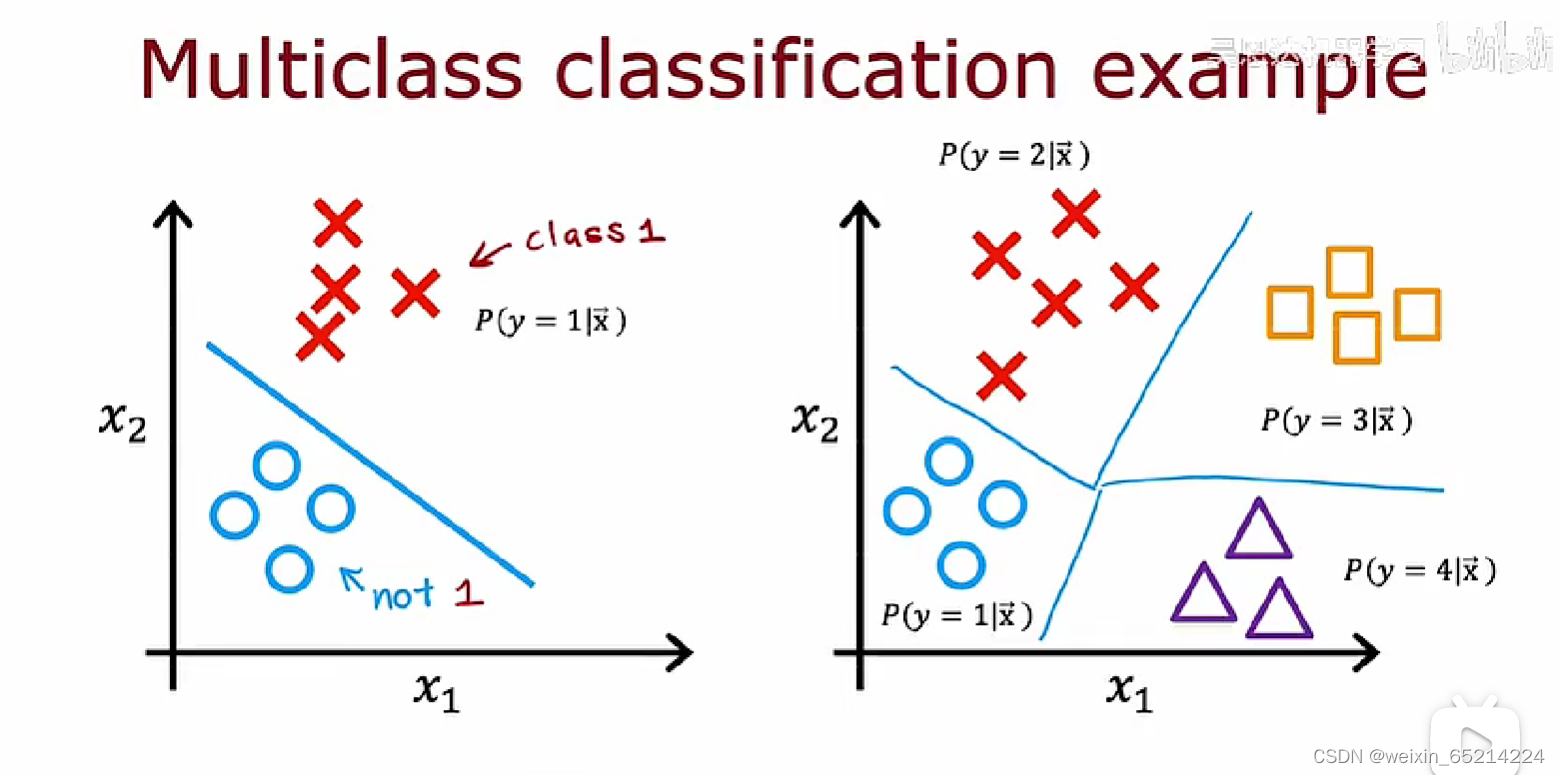
Softmax 函数
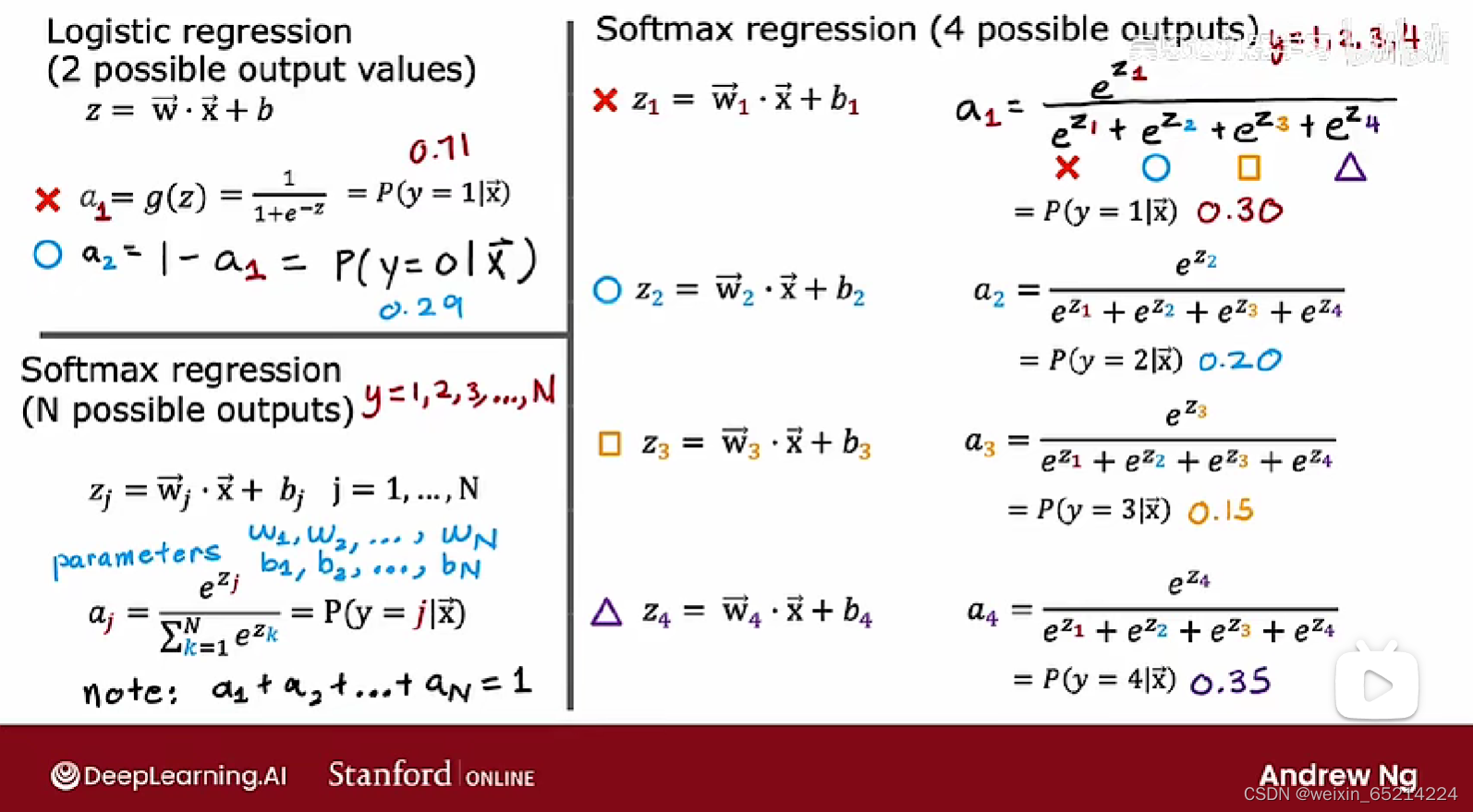
softmax函数(多分类)其实是sigmoid函数(二分类)的推广
Softmax output in neural network:
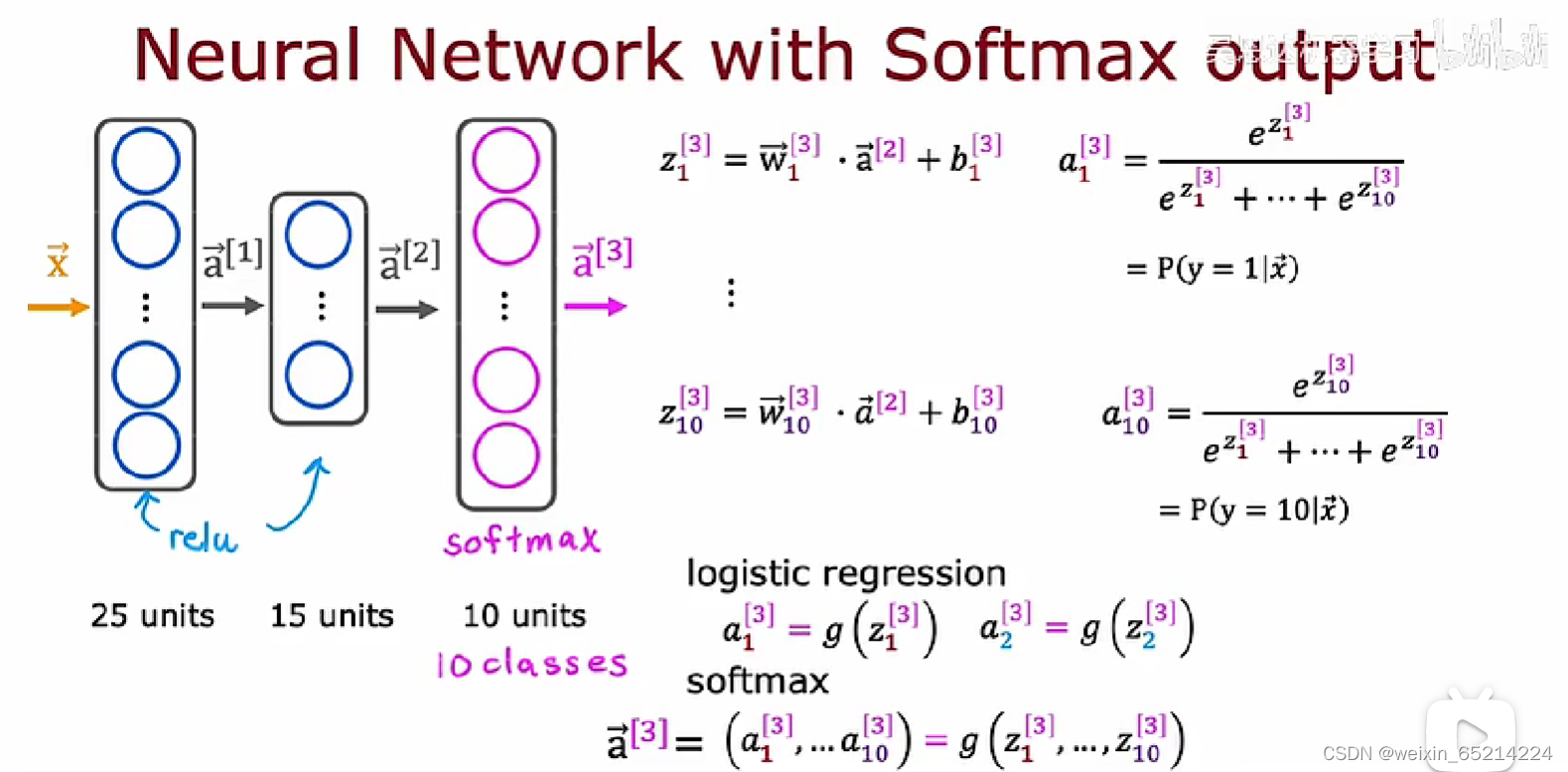
Softmax输出而言的独特属性: 每个输出值a_j都依赖于z_j从(j=1, 2, 3…10)的所有值
Sparse Categorical Crossentropy: 稀疏范畴交叉熵函数,
稀疏范畴:指依然将y进行分类;
稀疏:输出值y只能从y_j(j = 1, 2, 3…10)中选一个

有何需要改进地方?见下一目录
Improved implementation of softmax
对于softmax等复杂函数的计算,通过先指定(赋值)中间变量再代入,从而给予Tensorflow更多的灵活性,可以更加accurate, 降低产生的误差。
如,在下图实现逻辑回归时:
不推荐:model.compile(loss = BinaryCrossEntropy())
推荐用:model.compile(loss = BinaryCrossEntropy(from_logits=True))
如此,TF将z作为中间值,通过重新排列带入更精确的参数计算,缩小numerical round off errrors
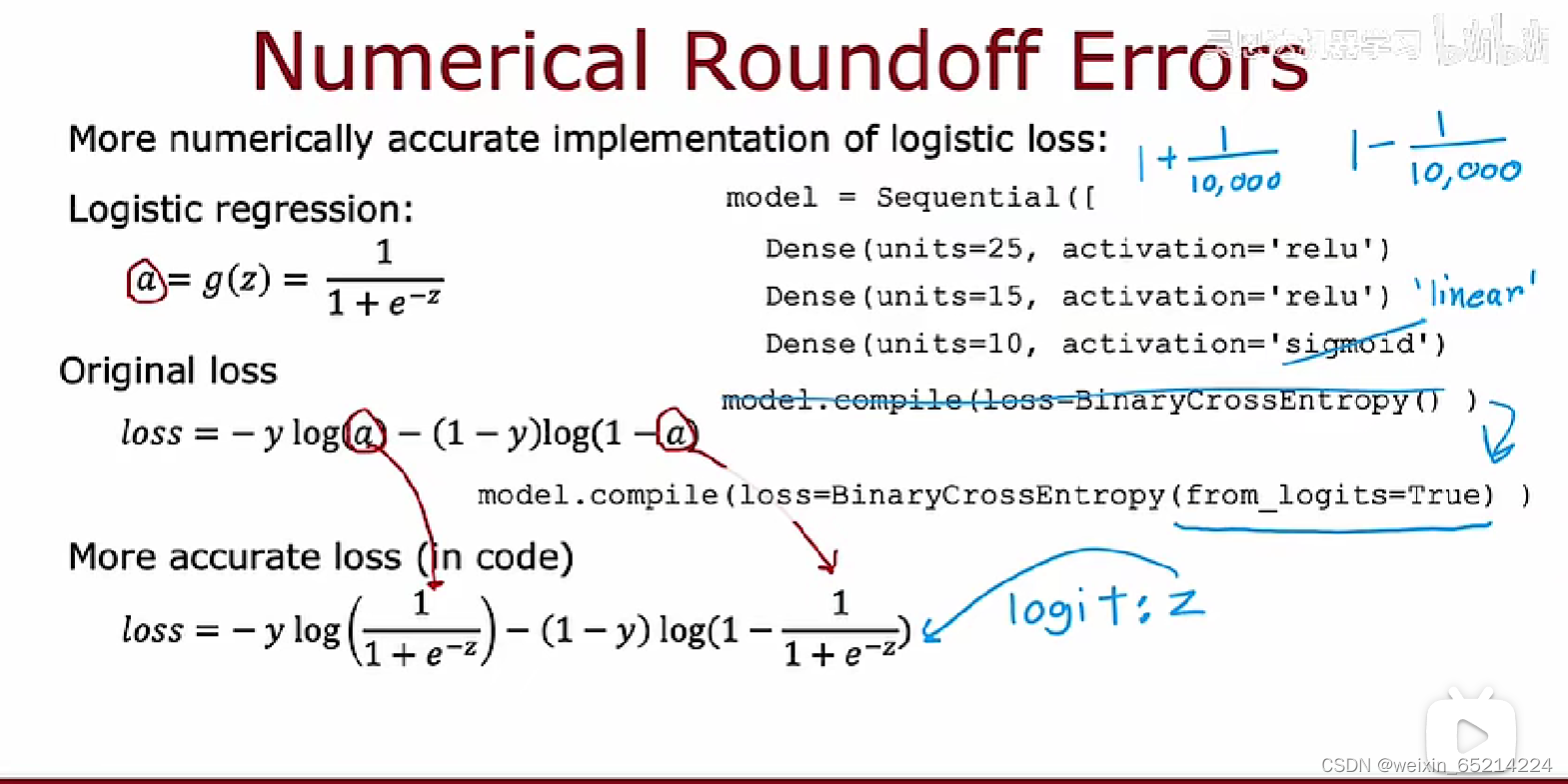
同理,计算sigmoid函数的loss function时
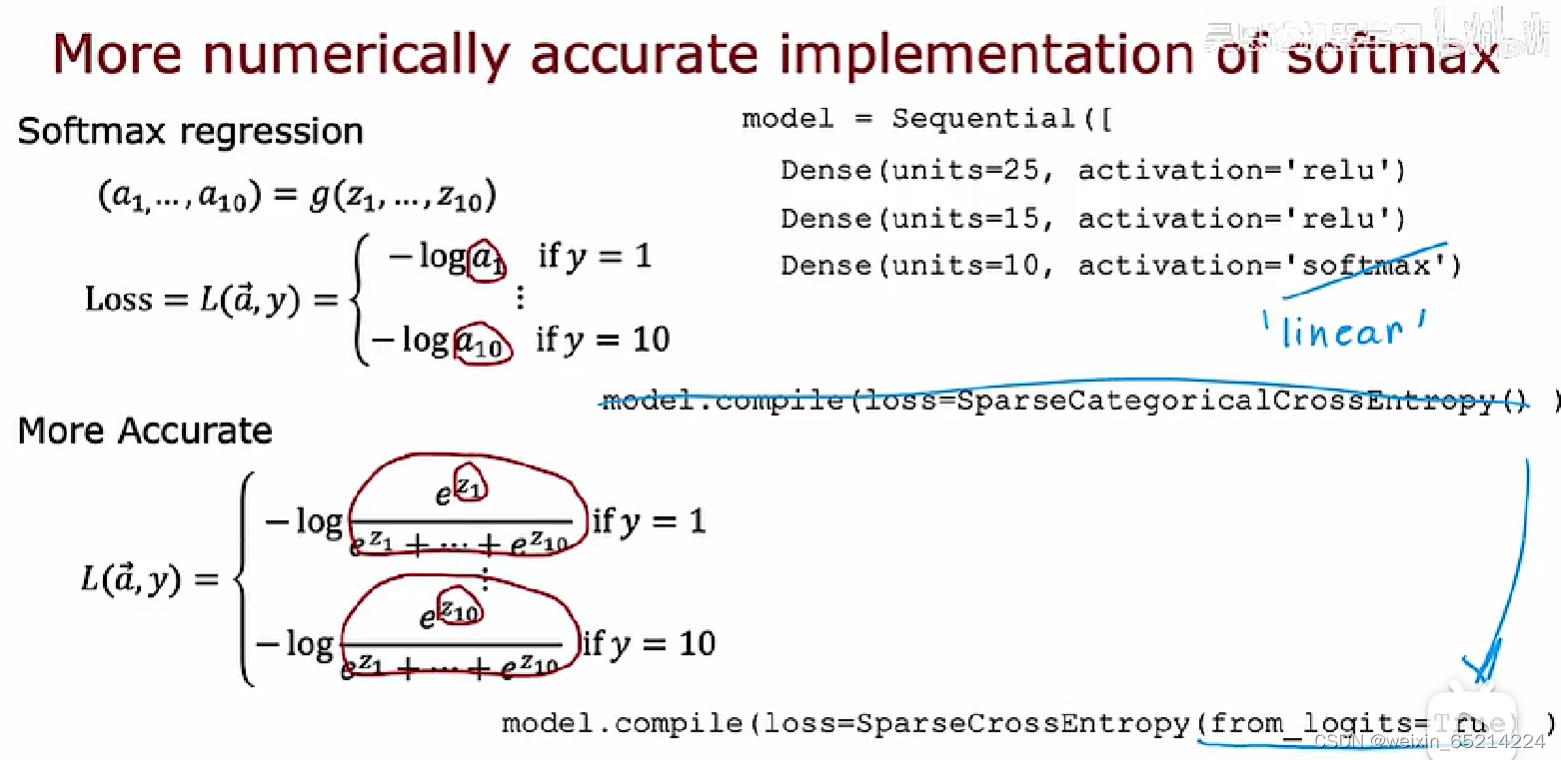
进行多分类问题时,最后输出层的激活函数应使用线性:For multiclass classification, the recommended way to implement softmax regression is to set from_logits=True in the loss function, and also to define the model’s output layer with a ‘linear’ activation.


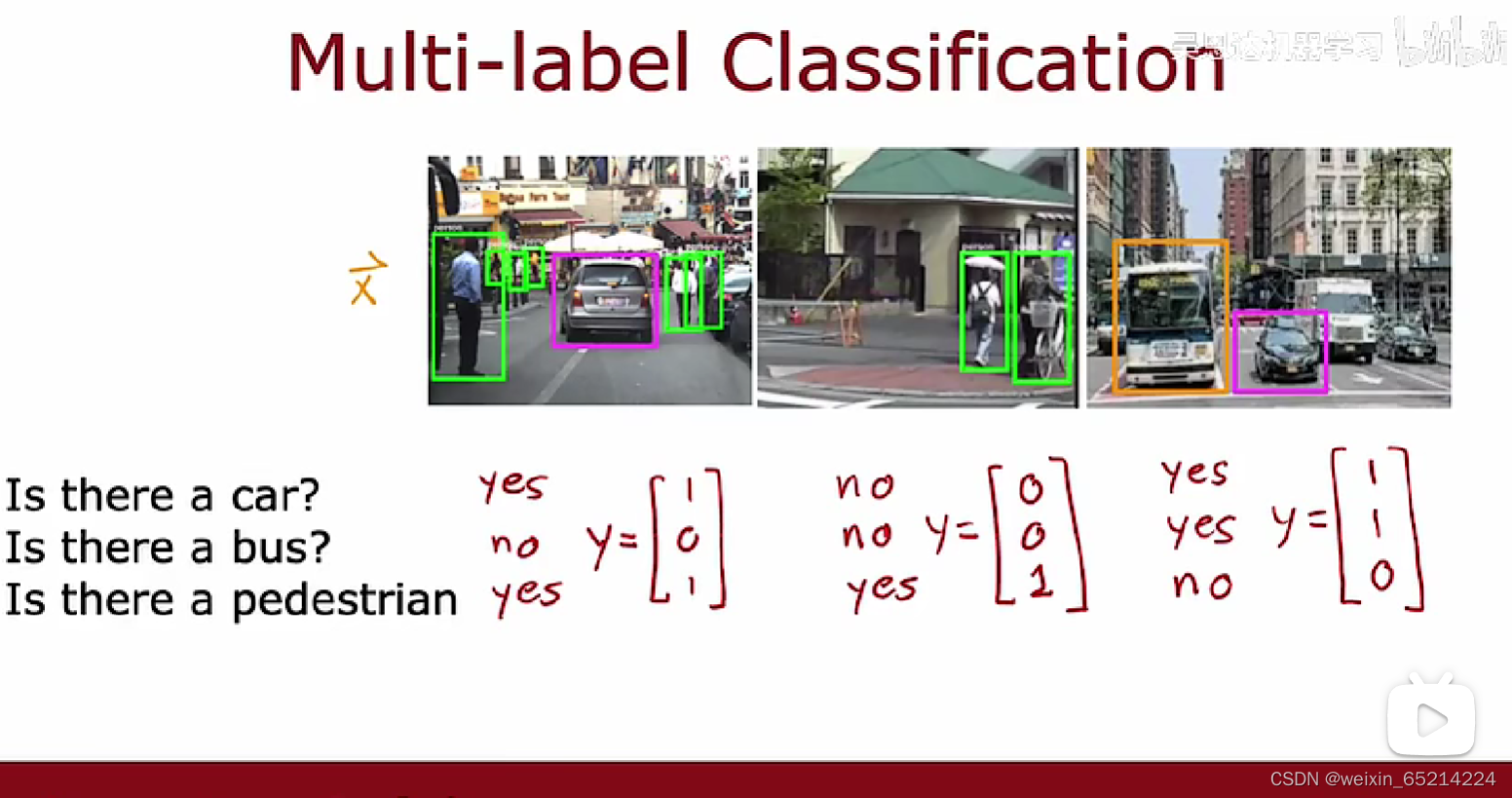
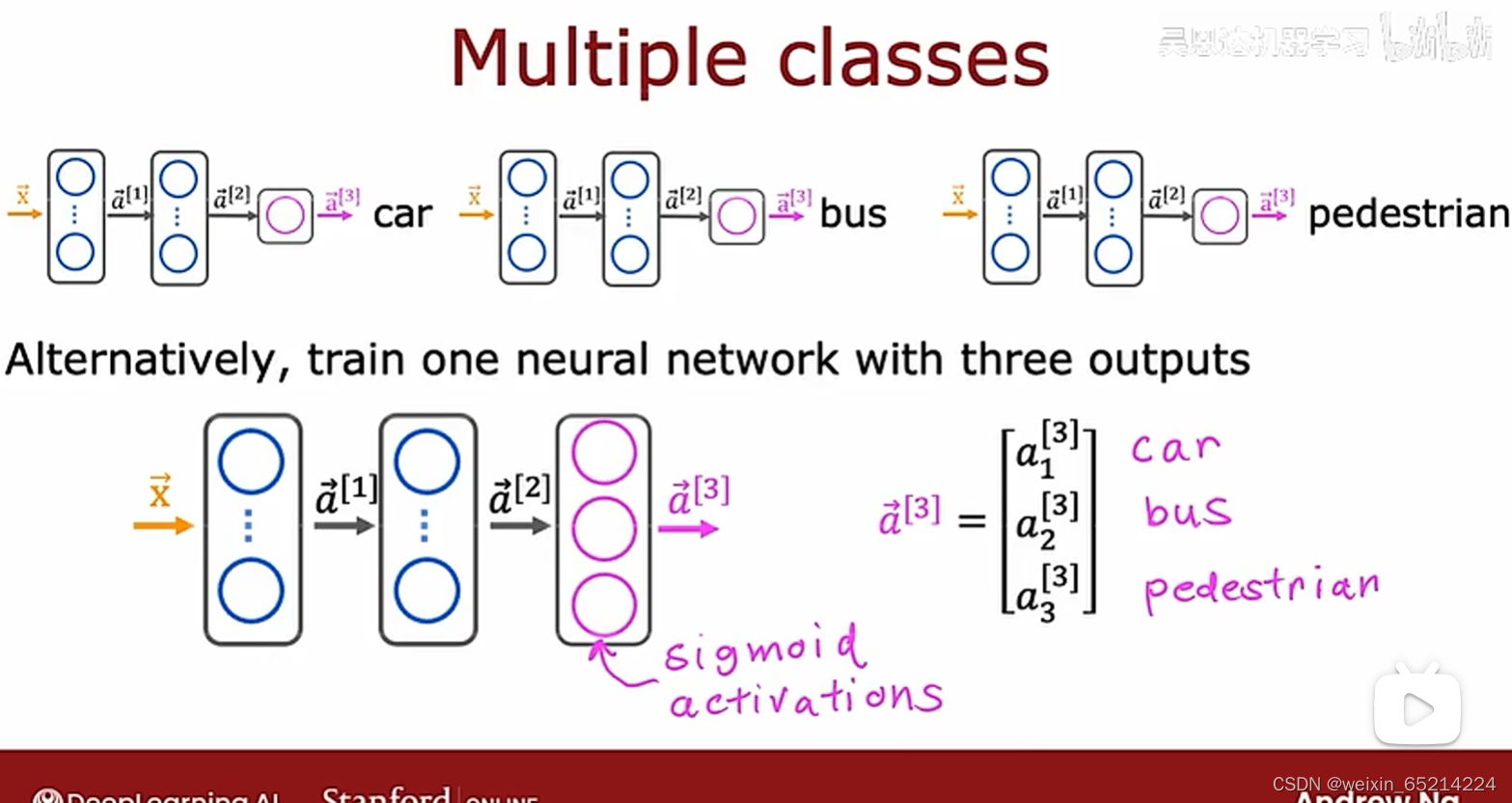
Classification with multiple outputs:
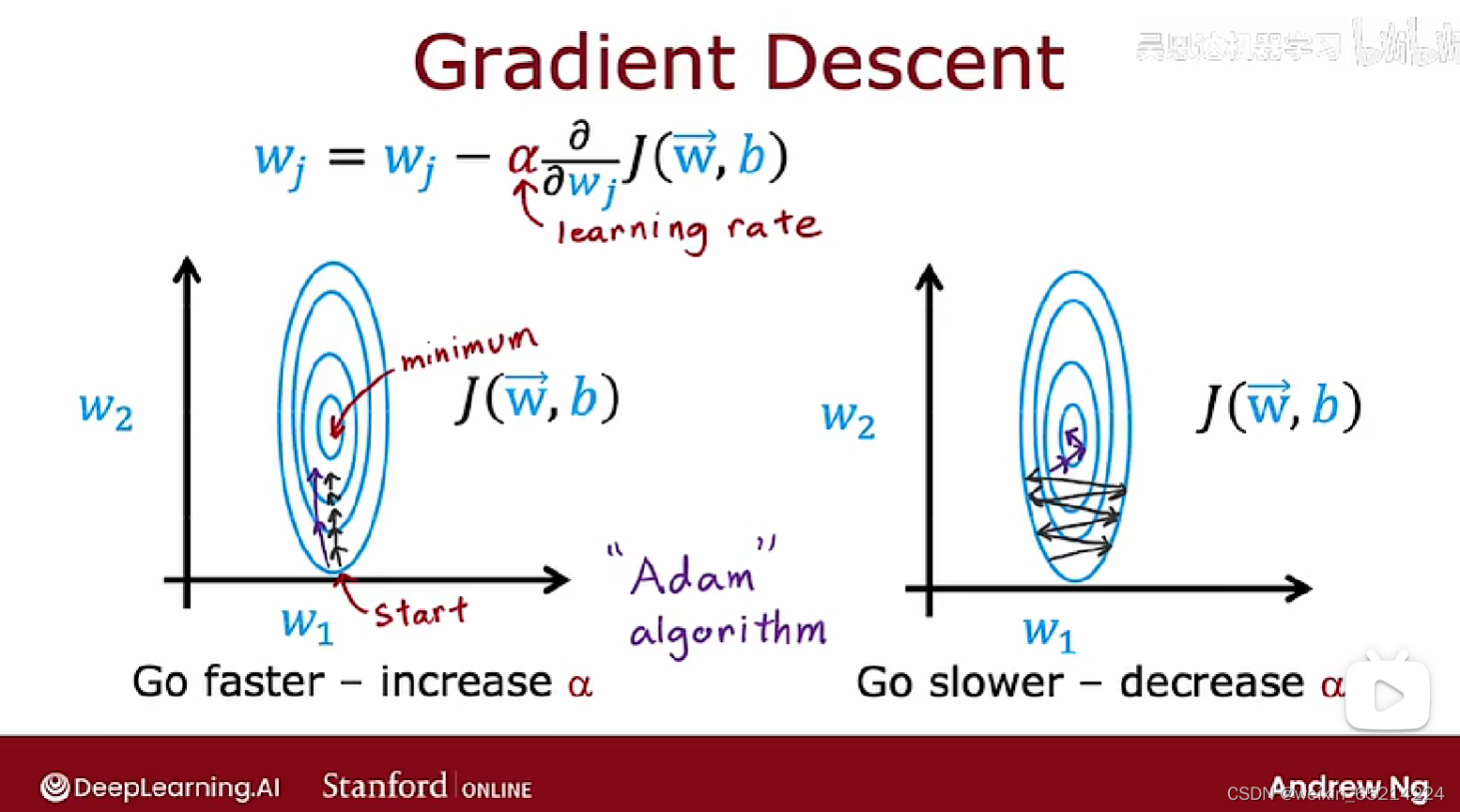
Advanced Optimization
梯度下降算法很好,然而有一些其他的算法在最小化cost function方面做得更好。
Adam 算法:自动调整学习速率。对模型的每个参数使用不同的学习速率。
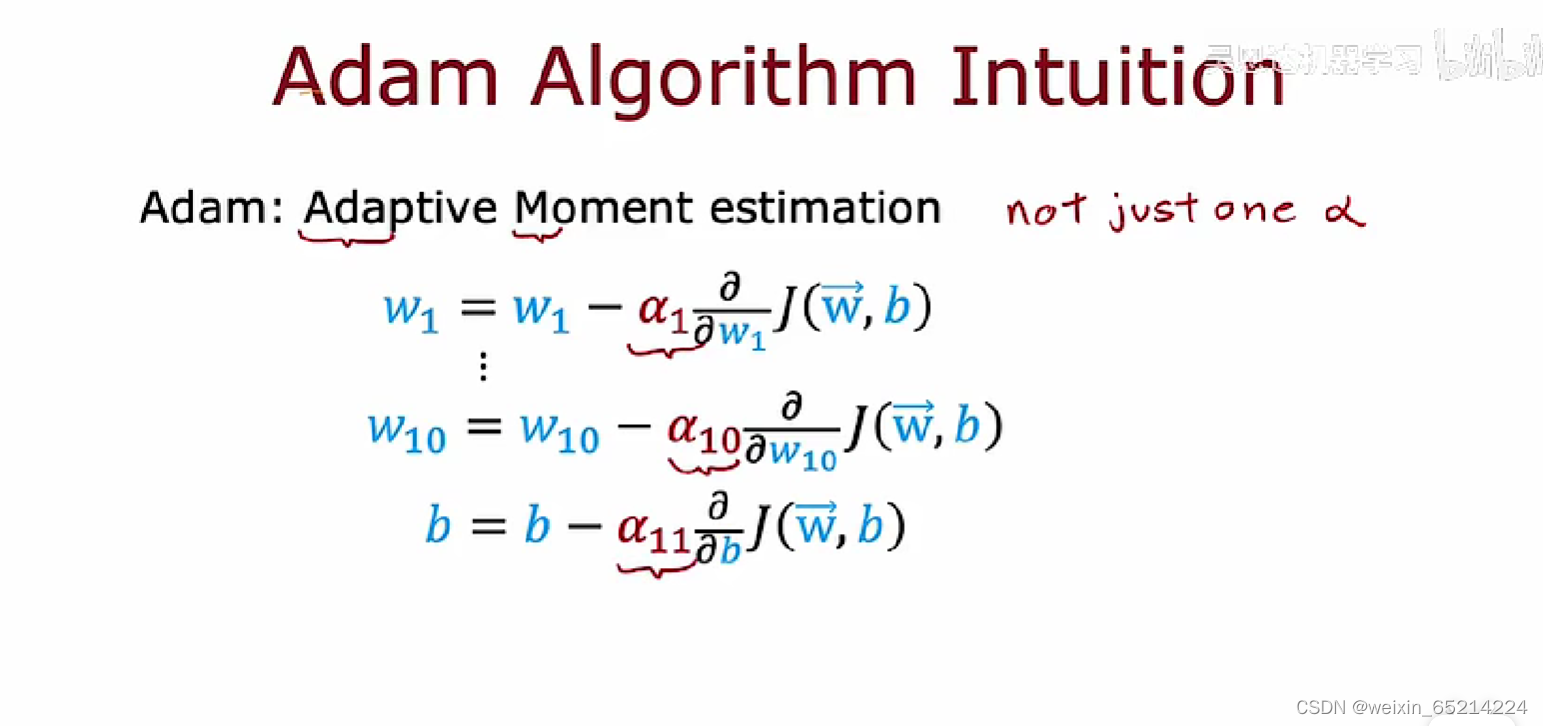
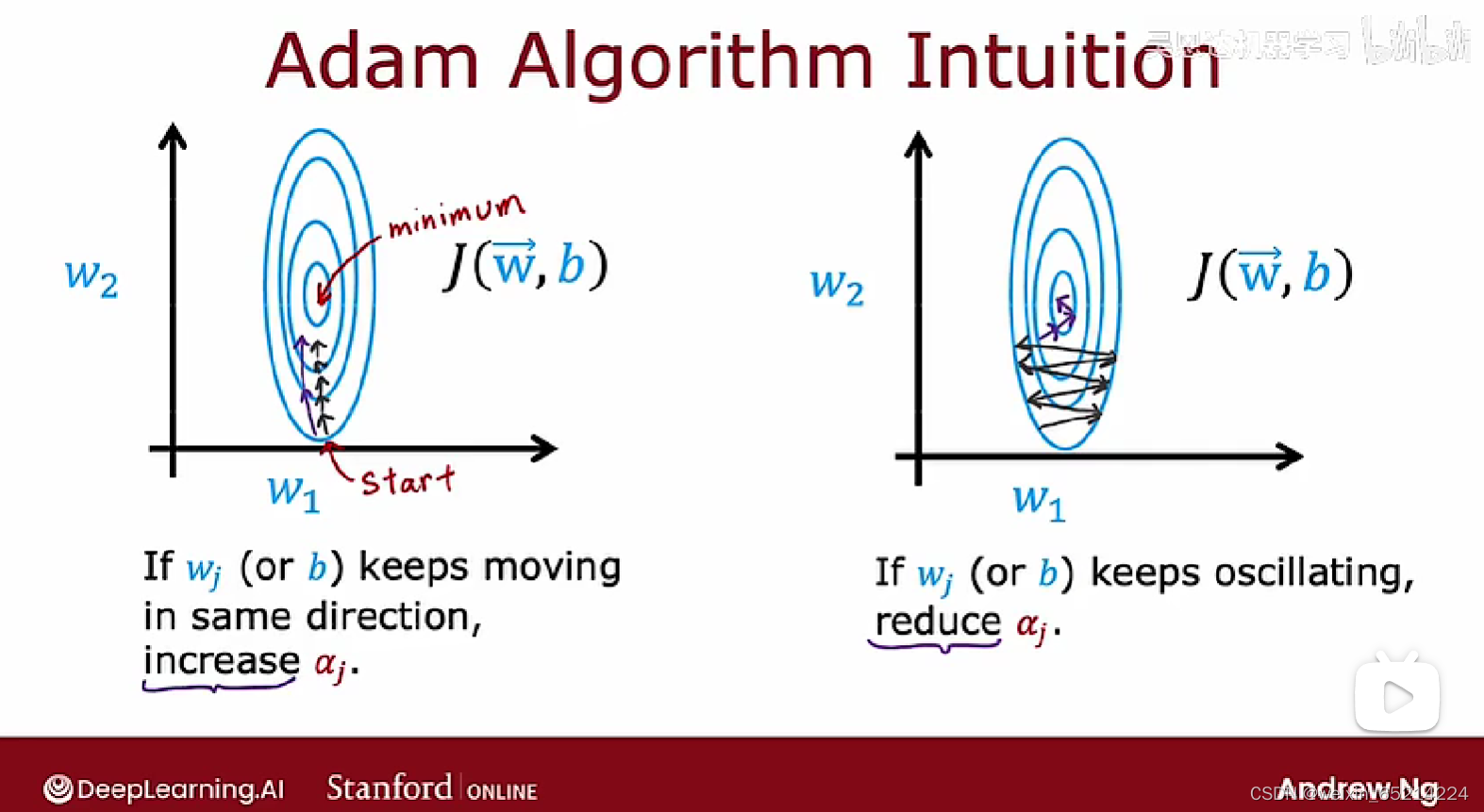
下图引入Adam算法的compile代码中,learning_rate代表初始学习率:

Additional Layer Types
迄今为止,本课程介绍的神经网络层都是密集型的(Dense Layer),即一层中的每个神经元输入来自于上一层的所有activations(输出)
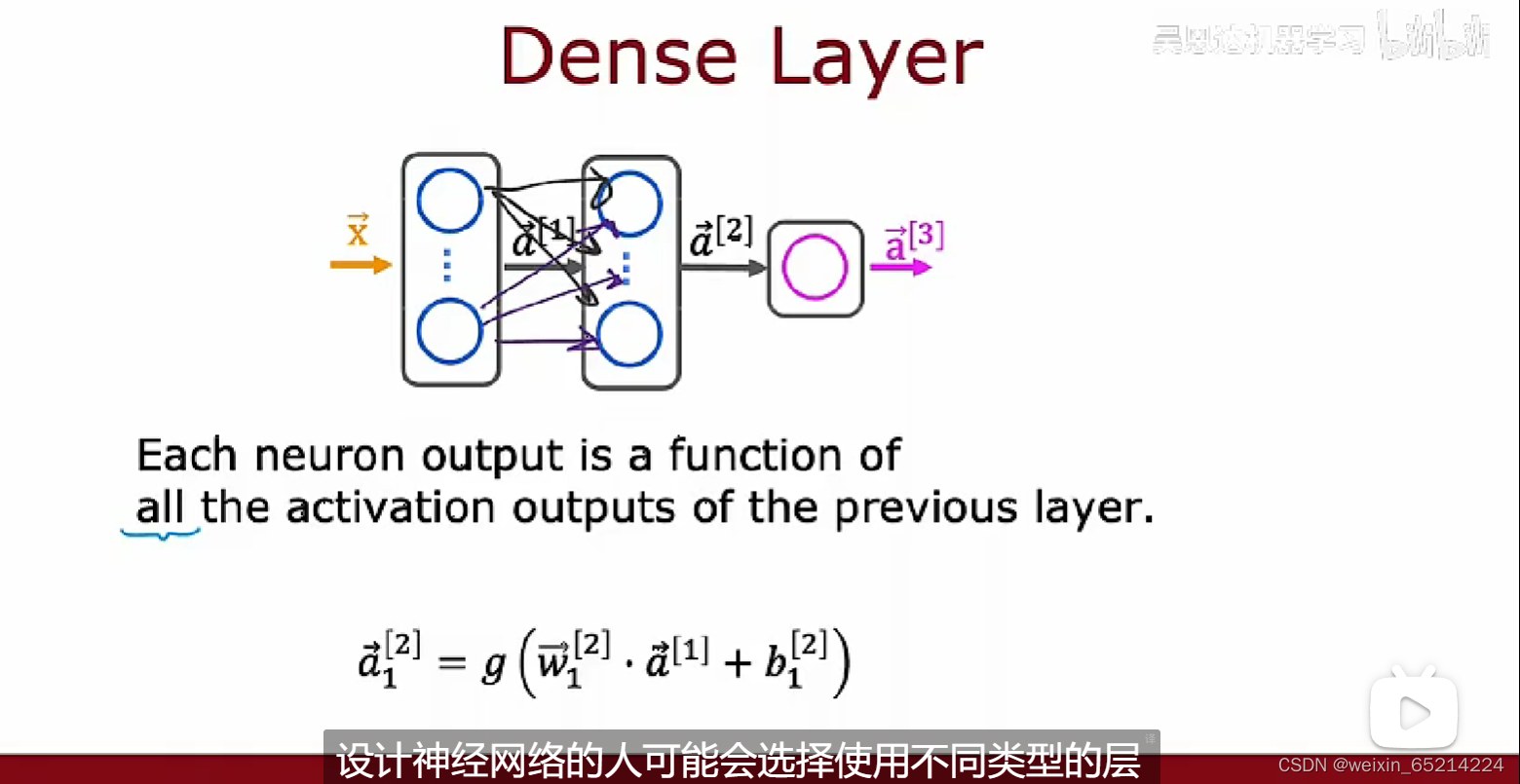
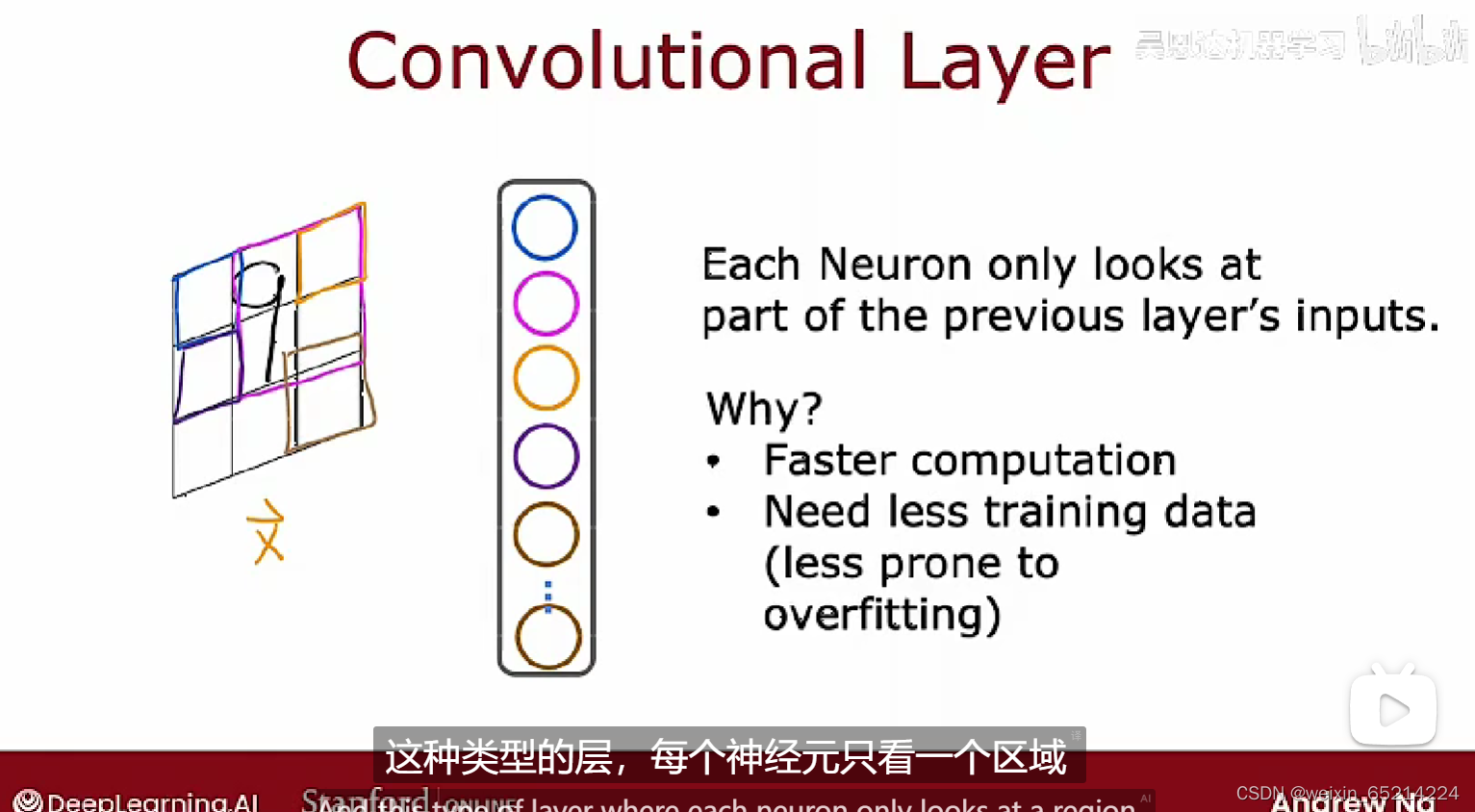
对比:卷积层(Convolutional Layer): 每个神经元只负责(接受处理)前一层中输出的部分数据
优点:方便快速计算,需要的训练数据更少;更不容易达到过拟合;
使用卷积层构建卷积神经网络:
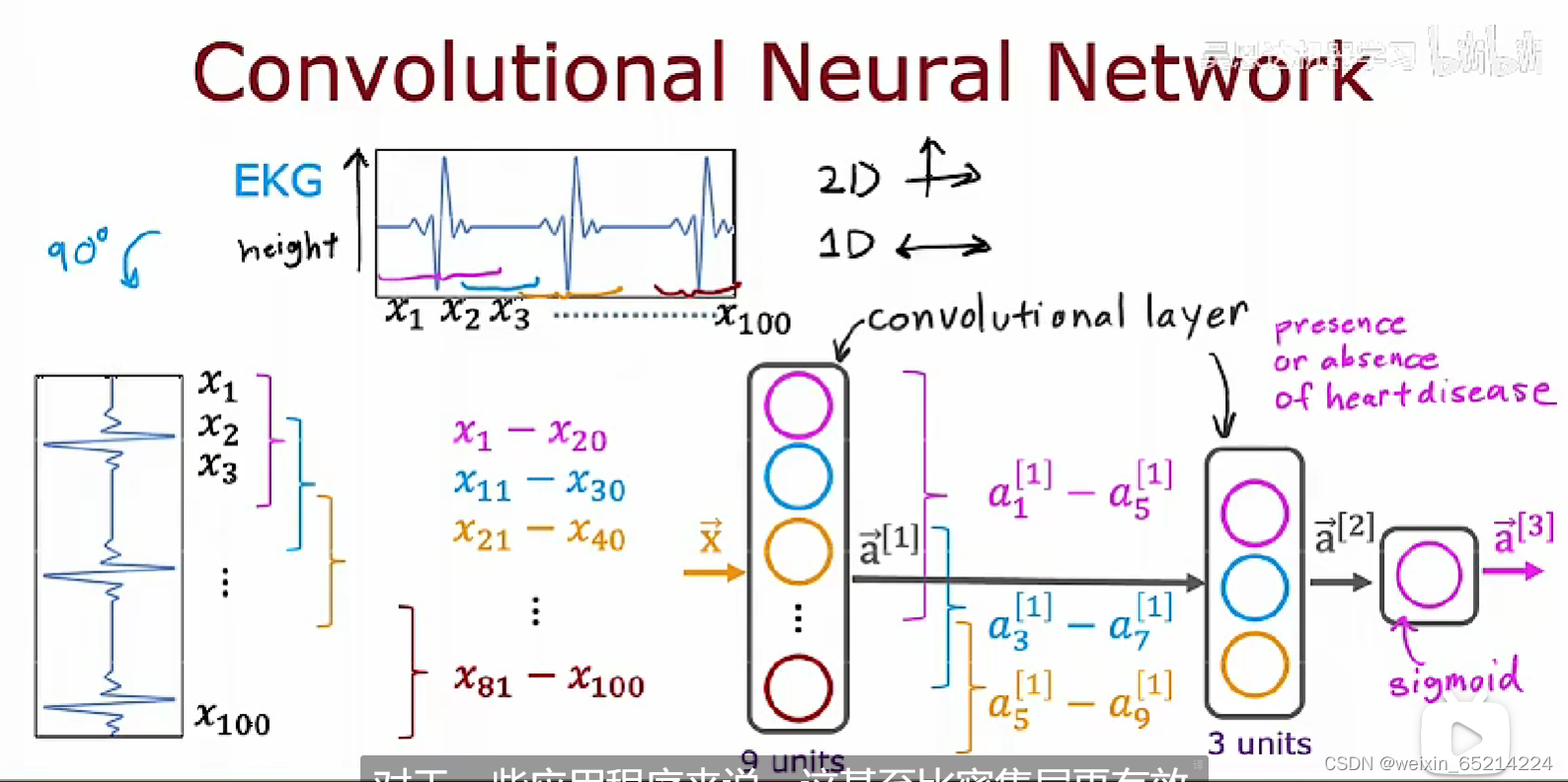
使用卷积层,可选择不同的体系结构:每个神经元负责的输入窗口大小,每层神经元的个数,etc.








 本文详细介绍了吴恩达机器学习笔记中关于TensorFlow的实现,包括训练细节、常用激活函数(如ReLU和Softmax)、多分类问题的处理、优化方法(如Adam算法)以及额外的层类型(如卷积层)。
本文详细介绍了吴恩达机器学习笔记中关于TensorFlow的实现,包括训练细节、常用激活函数(如ReLU和Softmax)、多分类问题的处理、优化方法(如Adam算法)以及额外的层类型(如卷积层)。
















 2043
2043

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








